Motor with strong weak air-gap field in alternative distribution
An air-gap magnetic field, strong and weak technology, used in motors, electric vehicles, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc., can solve problems such as out-of-step, locked rotor, large torque ripple, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
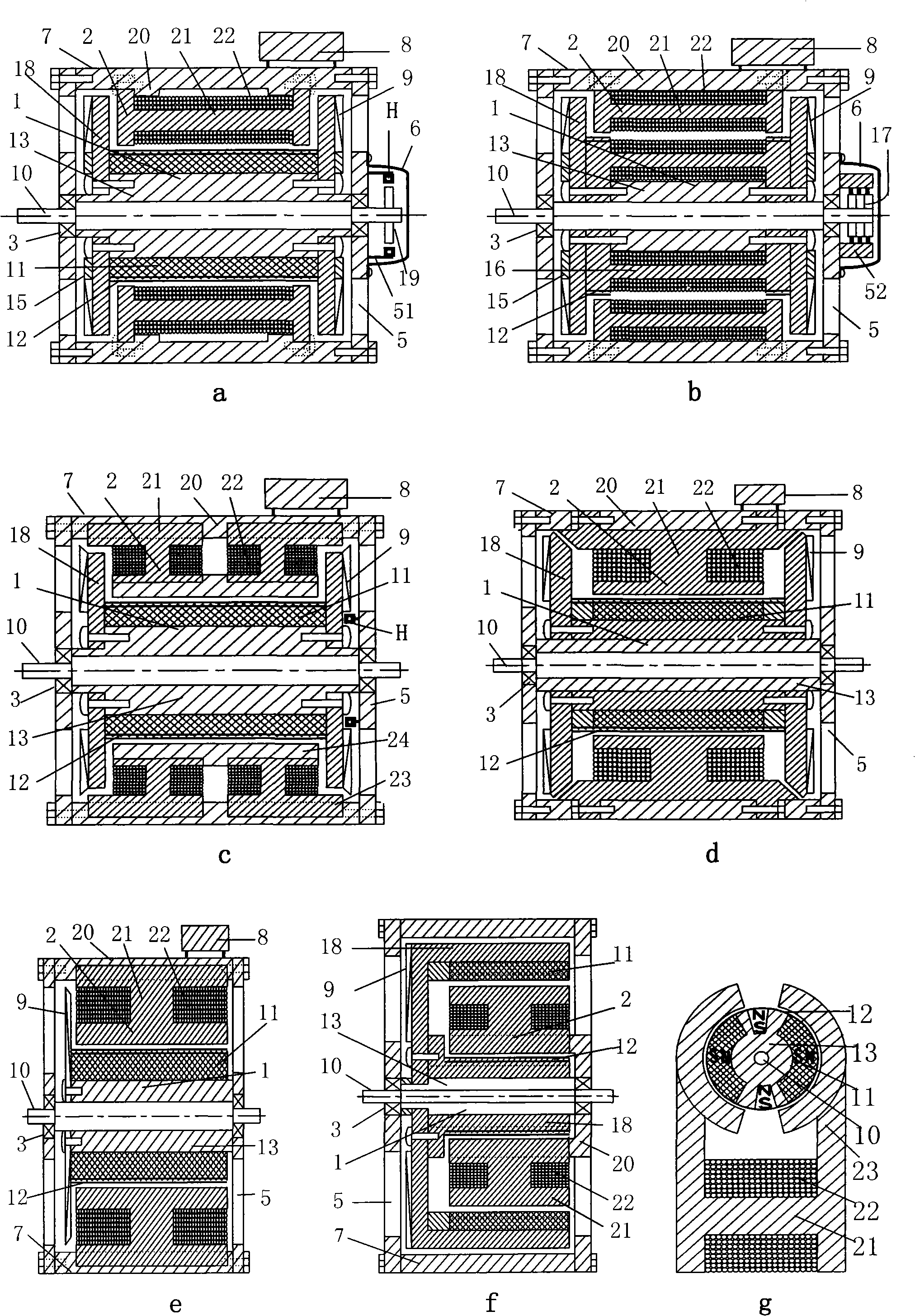
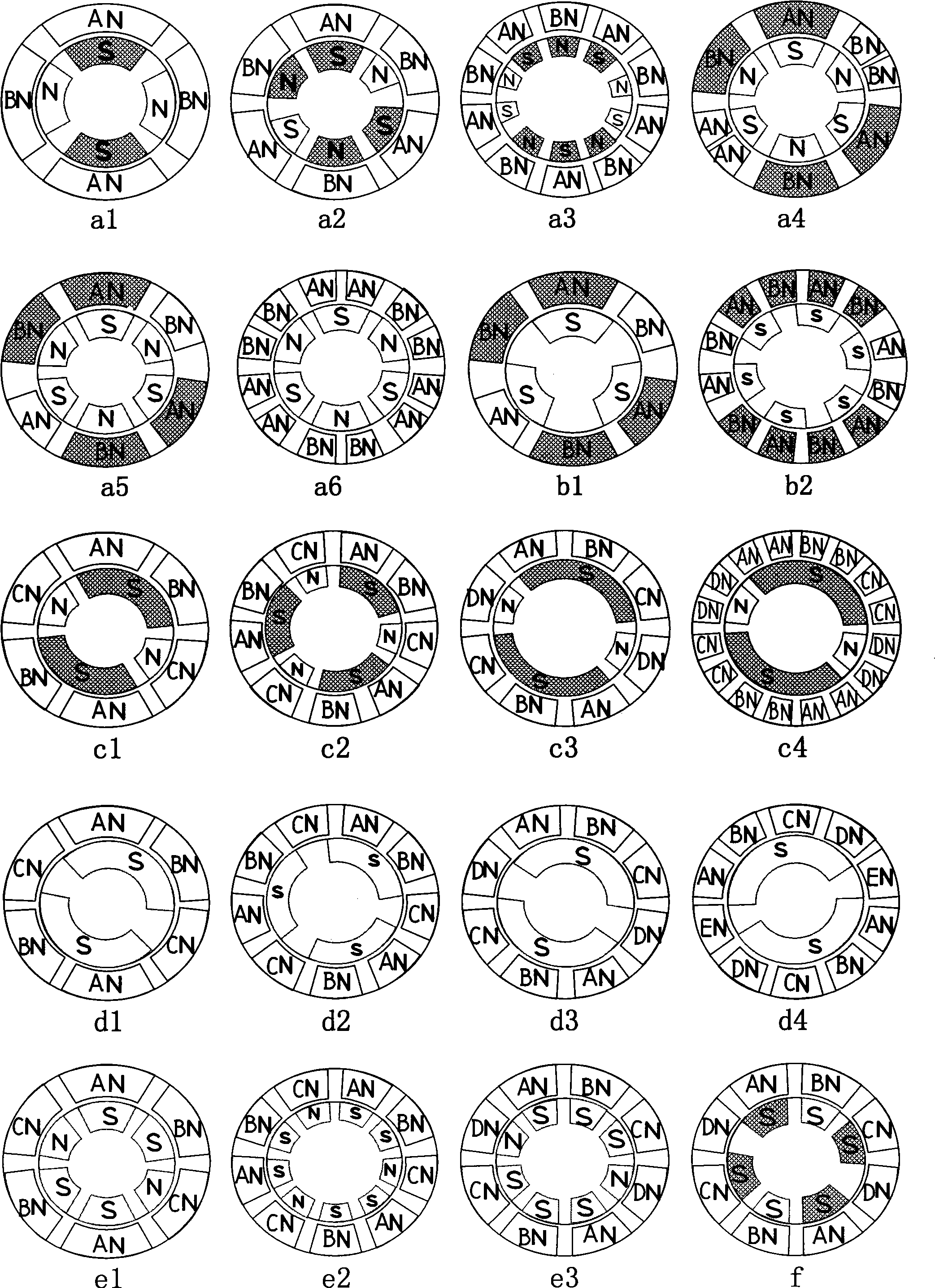
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
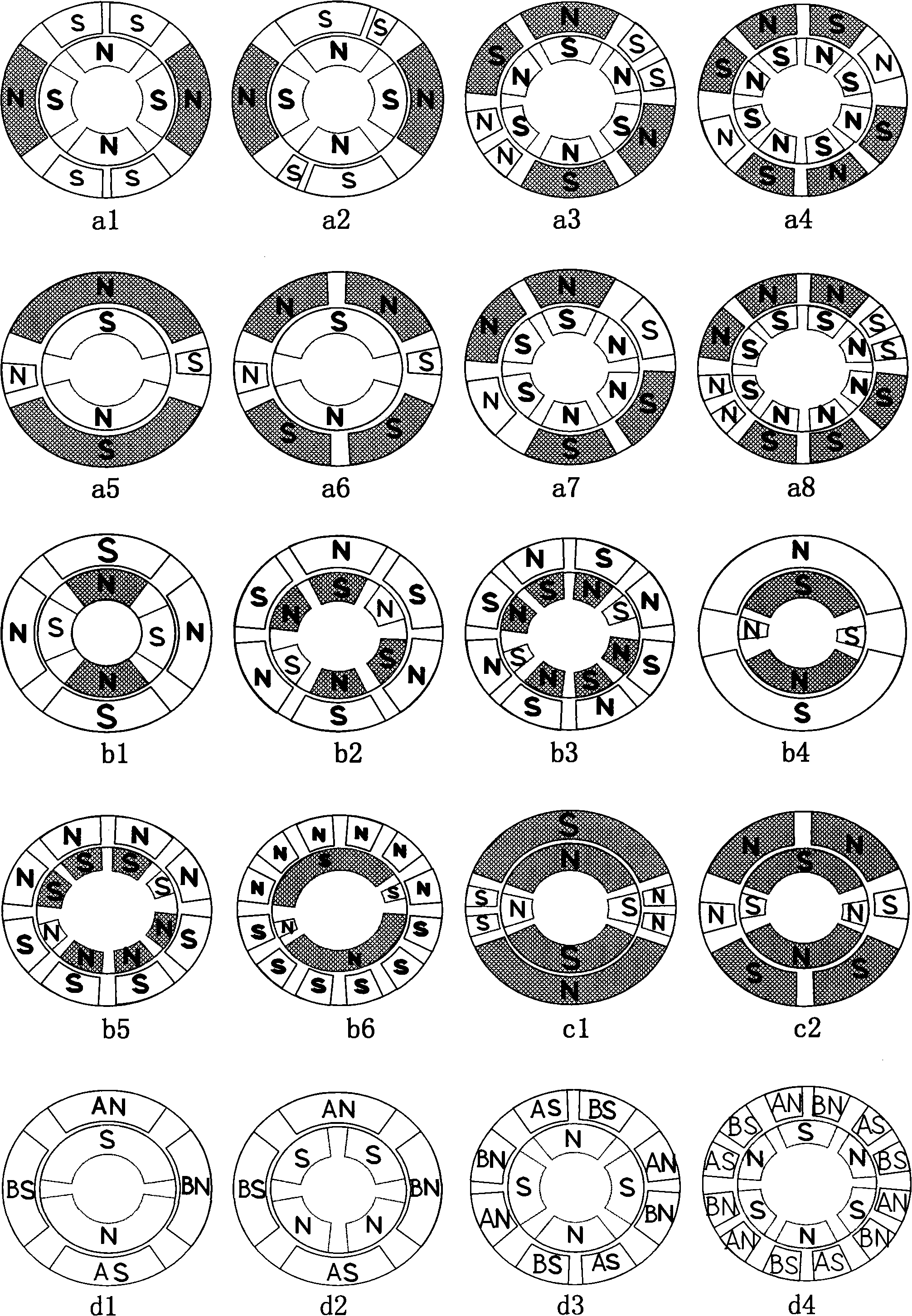
[0092]Embodiment 1: As shown in Figure 10a1, it is a four-pole permanent magnet stable pole magnet rotor equipped with a four-phase eight-pole pole-changing magnet stator with a position sensor DC commutation motor. The motor has four sensors H1-H4 to detect the rotor position The signal controls the four NPN triode switches of VT1-VT4 respectively, and the triode switches are respectively connected to the four-phase windings of A, B, C and D. As shown in the figure, H1 senses the rotor pole N, there is no signal output, VT1 is cut off, the A-phase winding is powered off, and loses its attraction to the rotor pole S; H4 senses the rotor pole S, outputs a positive signal, VT4 conducts, D The phase winding is energized, so that the stator magnetic pole DN generates a repulsive force to the rotor magnetic pole N (and part of the magnetic force line of DN passes through AN to make AN have S polarity, which generates a repulsive force to the rotor magnetic pole S, and the following ...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Embodiment 2: As shown in Figure 10a2, it is a position sensorless DC commutation motor with a four-pole permanent magnet stable pole magnet rotor and a four-phase eight-pole variable pole magnet stator. Its working principle is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the electronic The control signal of the switch is generated by the rotor position sensor instead by four circuits with the same frequency timing pulse generation circuit. As shown in the figure, the four channels of the same frequency sequential pulse generator circuit output four channels of pulse signals with the same frequency and the same duty cycle in turn at equal intervals, and turn on and off the four NPN transistor switches of VT1-VT4 in turn. , and then turns on and off the A, B, C, D four-phase stator windings in turn to form a stator rotating magnetic field, so that the rotor continues to rotate. At the same time, the motor is equipped with a mechanical forward switch. When the...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Embodiment 3: As shown in Figure 10a3, it is a sensorless AC commutation motor with an eight-pole permanent magnet stable pole magnet rotor and a two-phase eight-pole pole-changing magnet stator. Two diodes connect the two-phase stator windings to the unidirectional AC power supply respectively. As shown in the figure, when the power supply is in the positive half cycle, the current is given by Flow through VD1, A winding, VD4 Make the stator magnetic pole AN and the rotor magnetic pole S attract each other; when the power supply is in the negative half cycle, the current is from Flow through VD2, B winding, VD3 Make the stator magnetic pole BN and the rotor magnetic pole N repel each other, because the rotor magnet corresponding to the small magnet of the stator is on the clockwise side, the rotor rotates clockwise, and then the stator magnetic pole BN and the rotor magnetic pole S attract each other until the center of the magnetic pole is aligned; when the powe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com