Transform circuit adopting symmetrical cross-linked structure
A technology for converting circuits and cross-linked structures, which is applied in the field of converting circuits, can solve problems such as increased losses, current-voltage stress conflicts of power devices, and reduced conversion performance, so as to achieve small internal resistance and loss, increase power density, and reduce voltage stress. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The following will further describe in detail with reference to the drawings and the embodiments of the present invention.
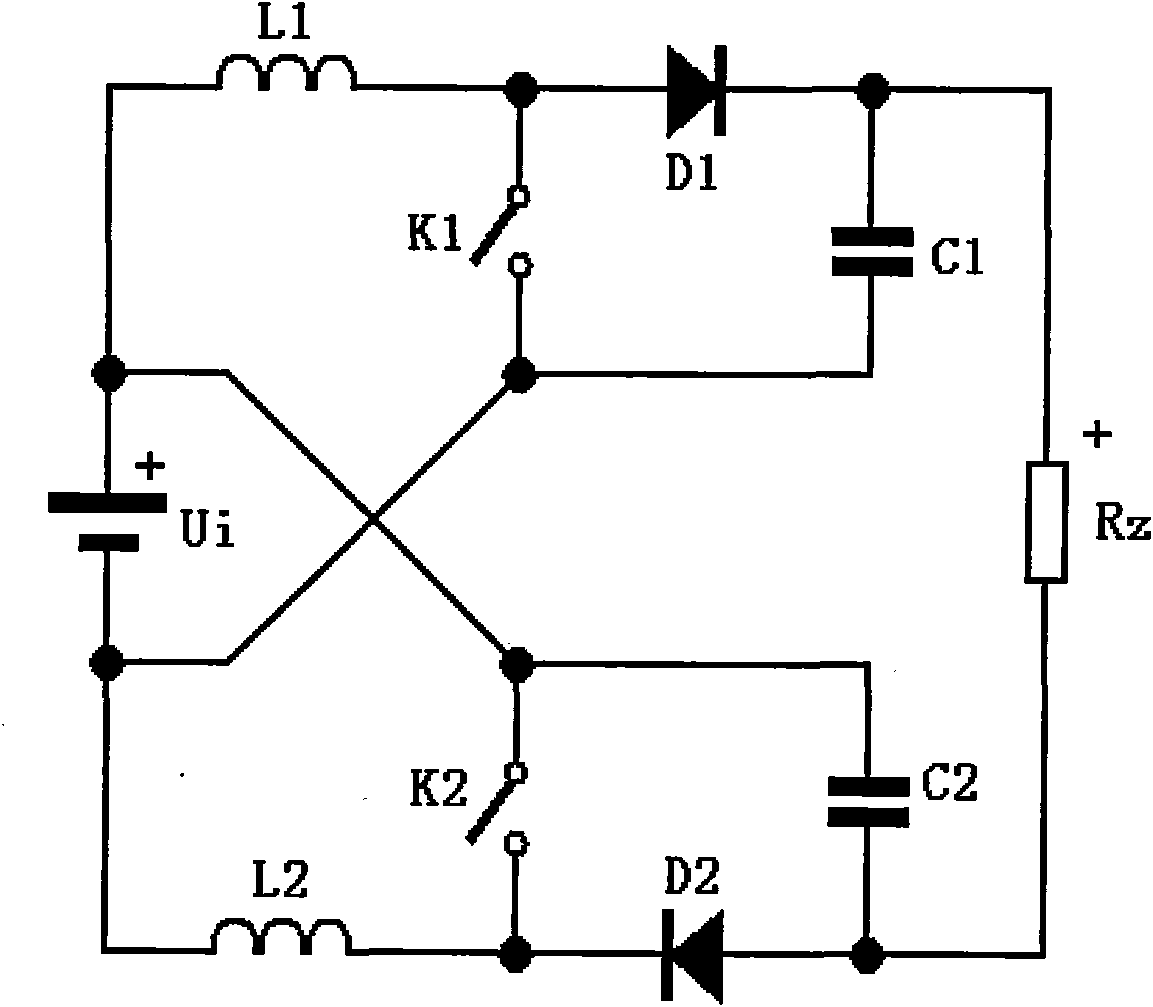
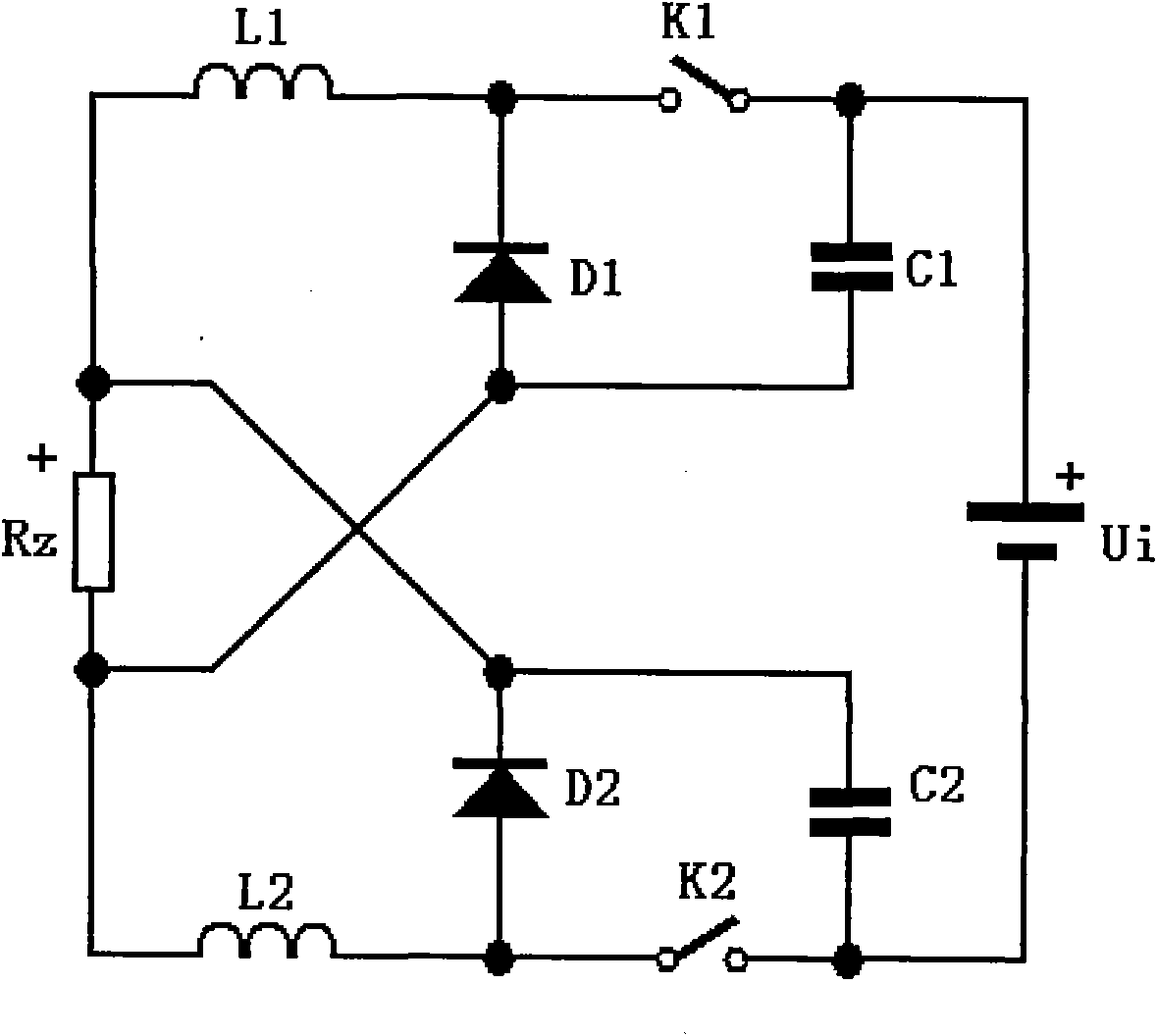
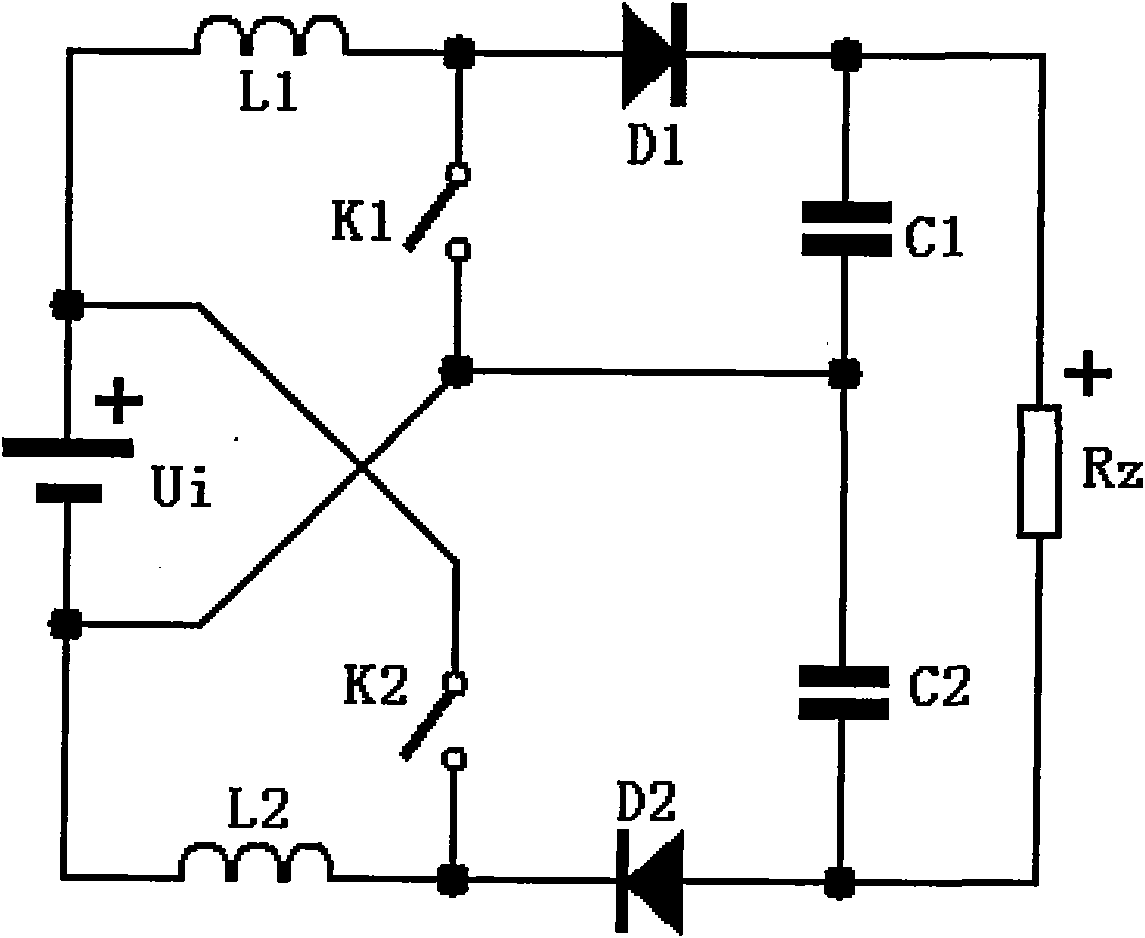
[0028] See figure 1 , Is a schematic diagram of the circuit structure of the first embodiment of a conversion circuit adopting a symmetrical cross-linked structure of the present invention, that is, a symmetrical cross-linked Boost conversion circuit. The conversion circuit includes a power supply Ui, a first inductor L1, a second inductor L2, a first diode D1, a second diode D2, a first capacitor C1, a second capacitor C2, a first switch K1, and a second switch K2 And load Rz. The positive pole of the power supply is connected to the negative pole of the power supply via the first inductor, the positive pole and negative pole of the first diode, the positive pole and negative pole of the load, the positive pole and negative pole of the second diode, and the second inductor to the negative pole of the power supply in turn. The terminal is connected ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com