Time-division multiple access method of optical fiber network media and traffic control mode applied to same
A technology of optical fiber network and access method, which is applied to the selection device of multiplexing system, data exchange network, digital transmission system, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to divide, unfair distribution of access rights, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
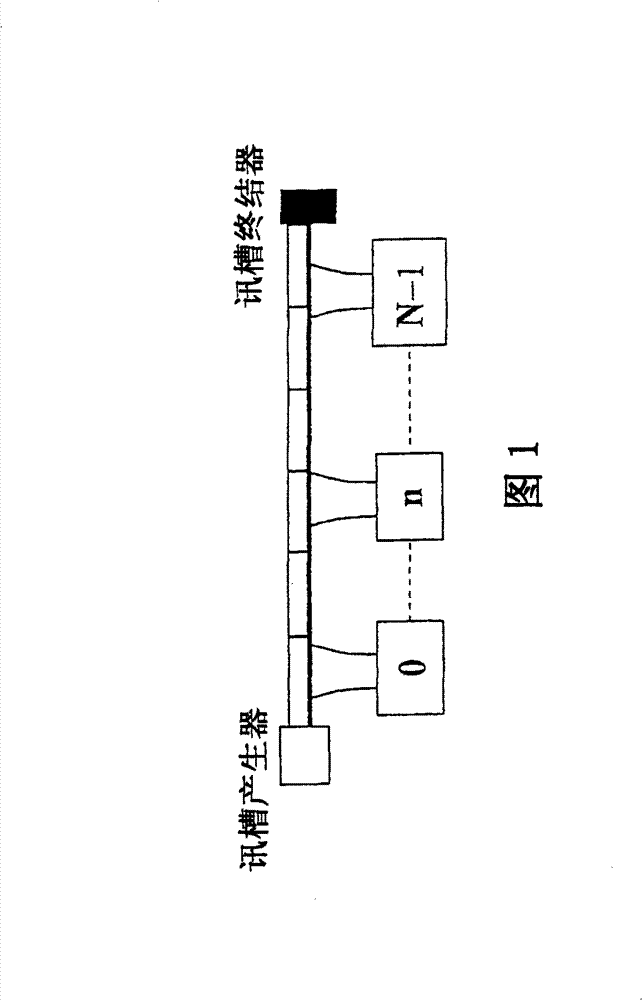
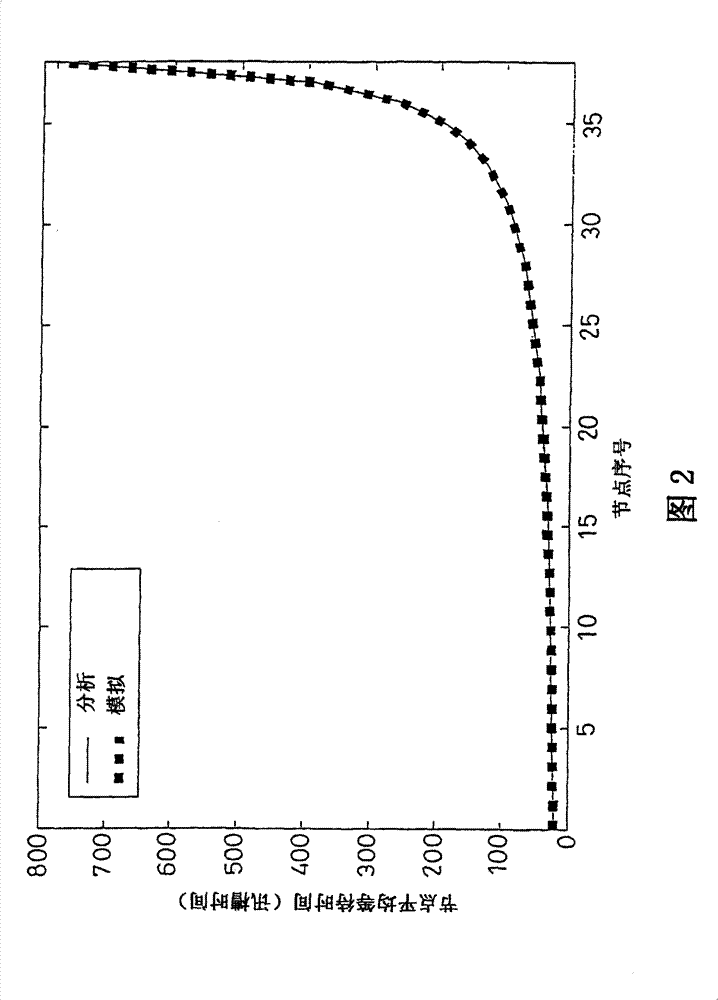
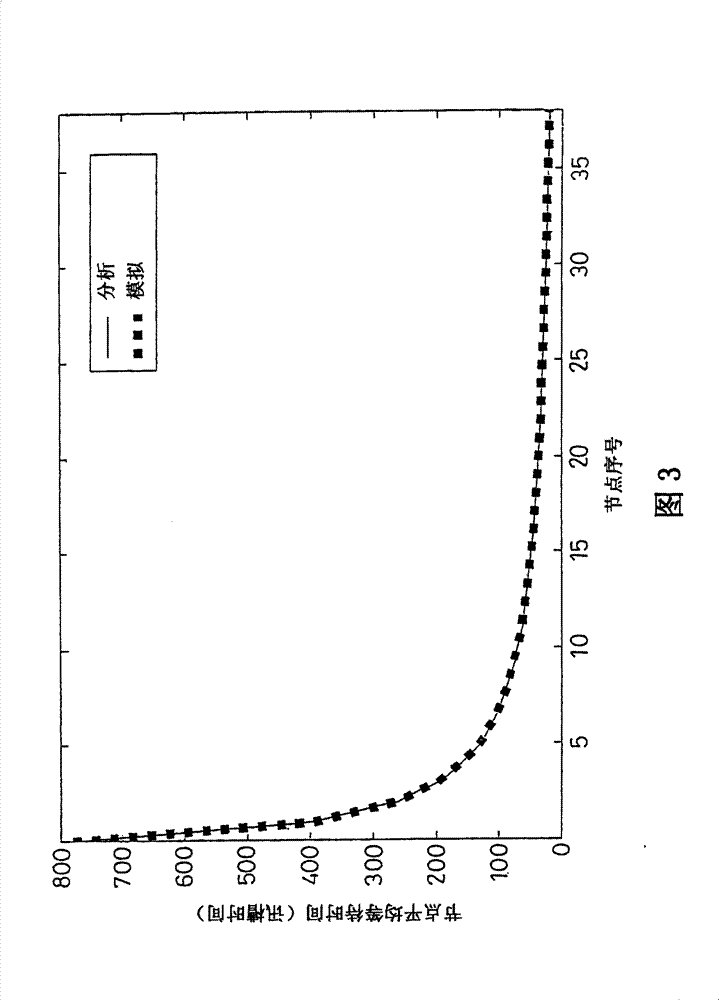
[0024] For a TDMA network, a node that wants to transmit information must first send a "transmission request" to notify the entire network to reserve a free slot. The number of reserved free slots corresponds to the number of sent "transmission requests". When the number of reserved idle slots increases, the average waiting time of nodes will decrease accordingly. Therefore, if a node has higher traffic, its average waiting time will be smaller. If the average waiting time of a TDMA node is used as a criterion for evaluating the slot access rights it has, then the nodes that generate a larger amount of traffic will have more access rights. In other words, TDMA nodes compete with each other according to the amount of traffic they generate, so as to gain access to the media. The relationship between the average waiting time of a TDMA node and its node traffic can be derived as follows.
[0025] The derivation of the average waiting time of TDMA nodes is based on three network...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com