Historical voice frequency noise detection and elimination method
A technology of audio noise and history, applied in speech analysis, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as high complexity, dependence on the accuracy of model coefficients, and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
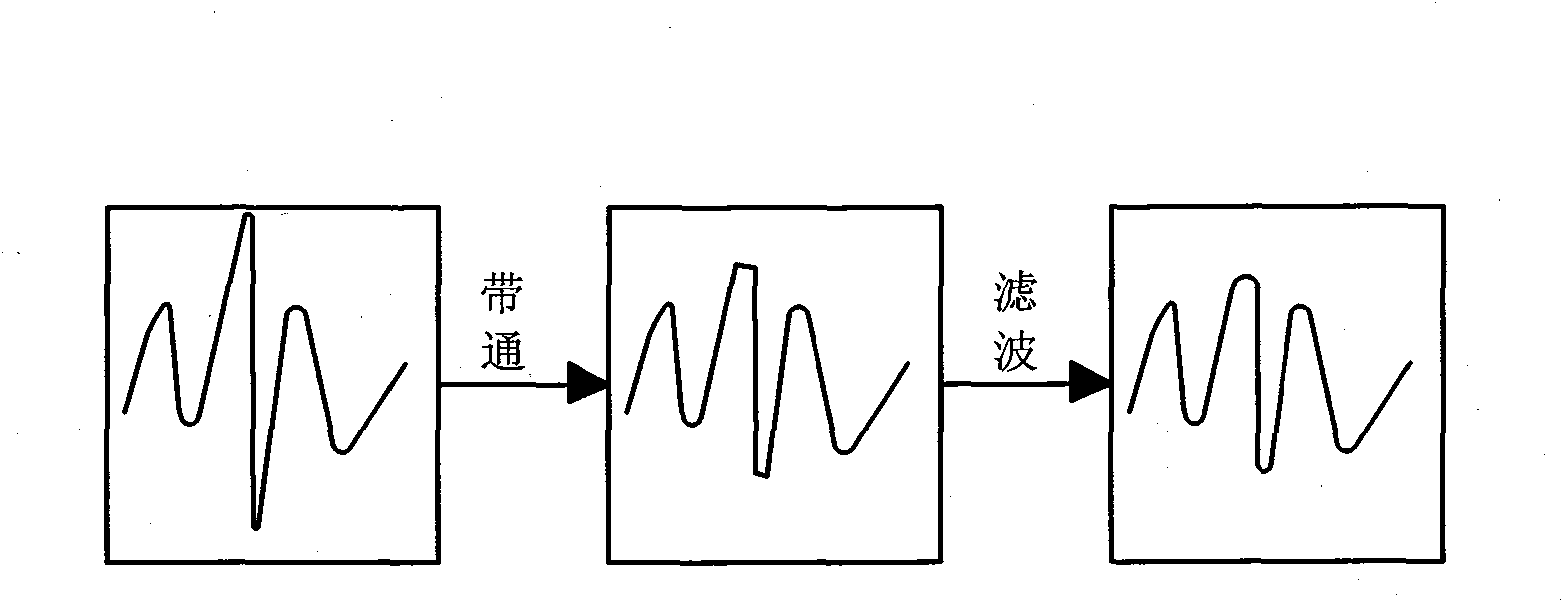
[0032] A method for detecting and eliminating historical audio noise, the method comprising the steps of:
[0033] (1) Sound modeling: Sound signals can be described by the following methods:
[0034] y(k)=x(k)+j(k)*d(k) (1)
[0035] Among them, y(k) is the polluted noisy signal, x(k) is the pure signal, j(k)*d(k) is the noise part, and j(k) is the flag bit, indicating whether there is a pulse here Noise, d(k) represents the amplitude value of impulse noise;
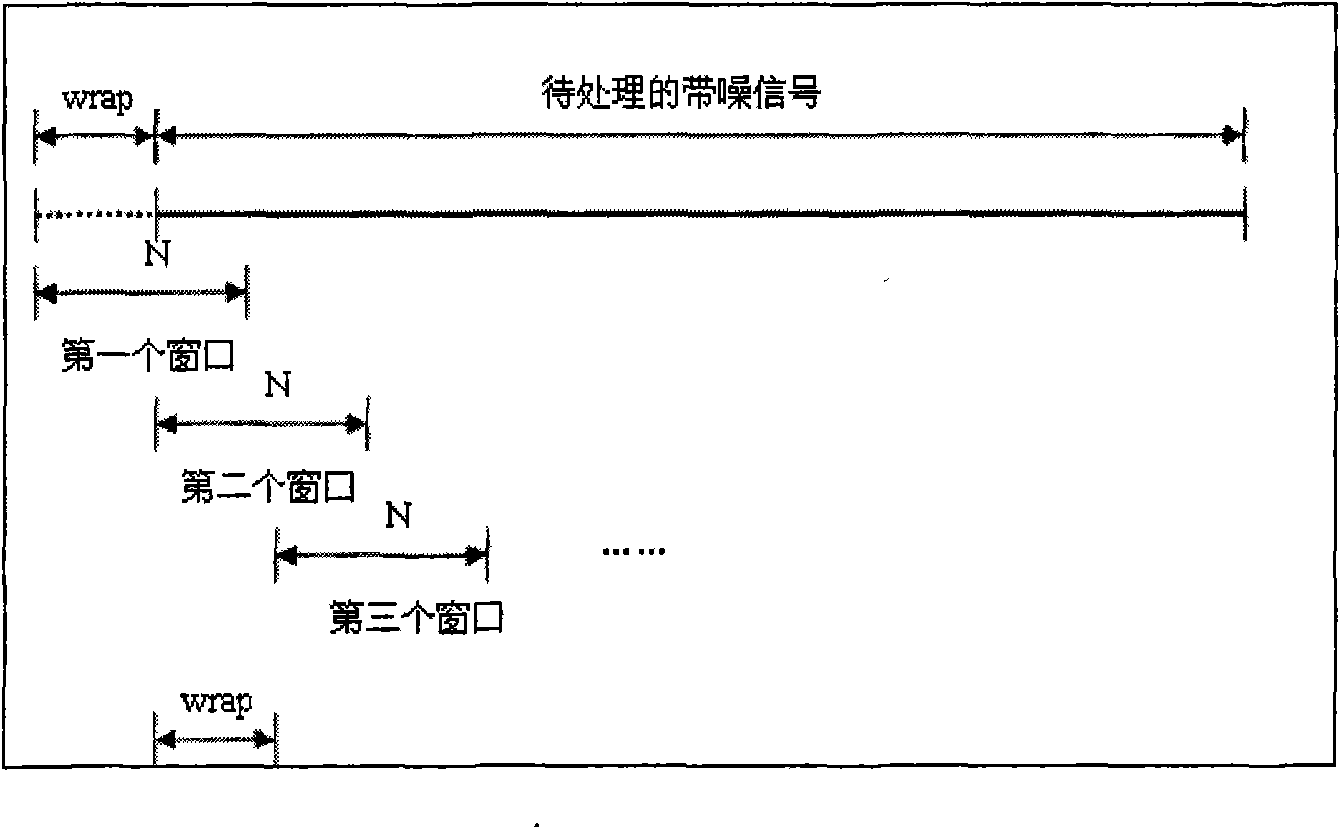
[0036](2) Short-time Fourier transform and spectrogram: Use a time-sliding analysis window to window and truncate the non-stationary signal to decompose the non-stationary signal into a series of approximately stable short-term signals, and then use Fourier transform to analyze each short-time stationary signal The spectrum of the signal; its definition is as follows:
[0037] STFT ( t , ω ) = ∫ - ...
Embodiment 2
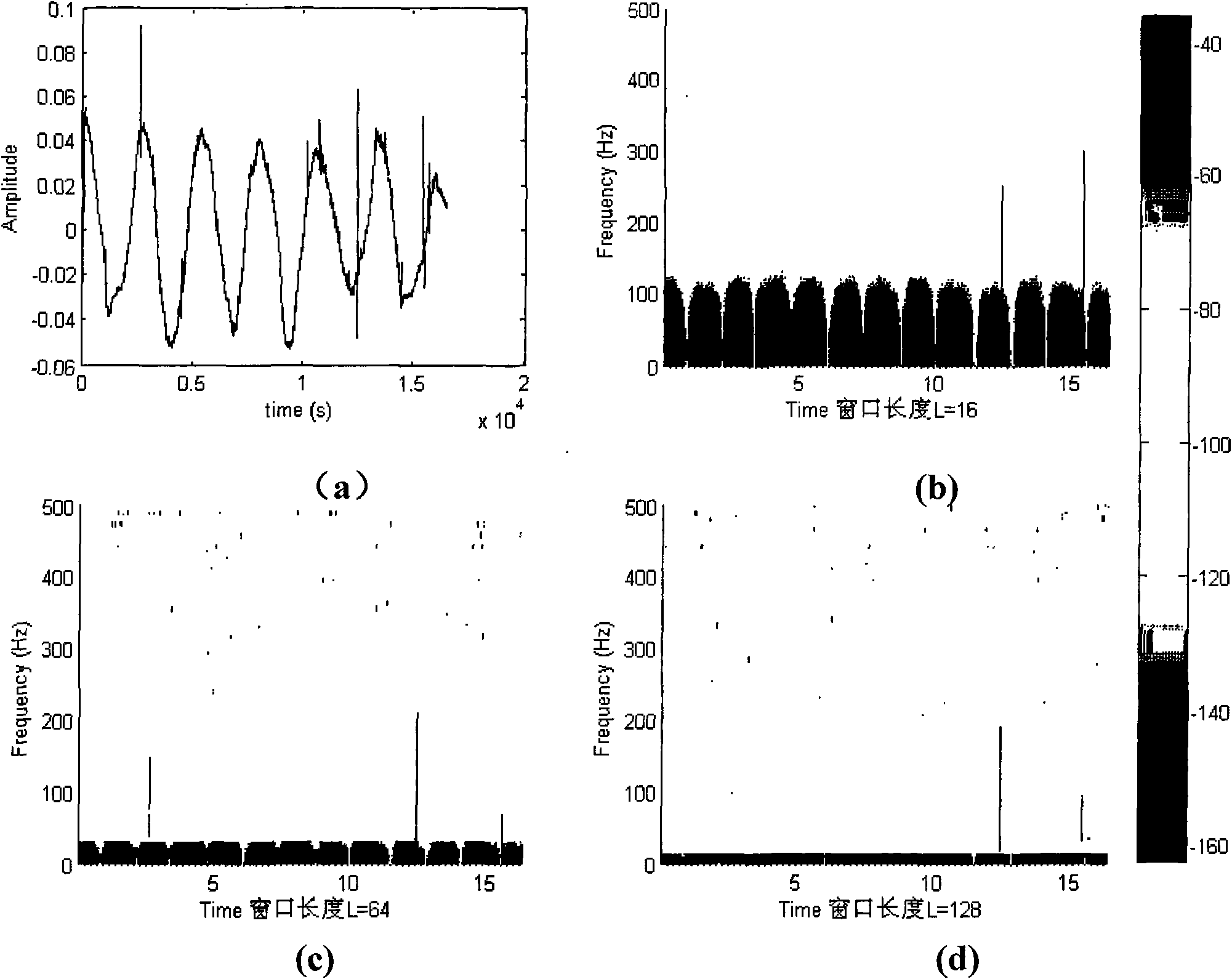
[0047] According to the historical audio noise detection and elimination method described in Embodiment 1, the detection of the impulsive noise includes: (1) carrying out short-time Fourier transform to the noisy signal, (2) applying selection criteria in the frequency domain to detect the noise containing The window of the impulse noise, (3) returns the position of the signal in the time domain according to the joint time-frequency domain (n, ω).
[0048] When performing STFT on the source signal, the window type and window size have a great influence on the spectrogram. Compared with rectangular windows, Hamming window and Hanning window have better analysis performance; if the window is too large, it will cause inaccurate detection position and reduce the effective detection rate (see Section 2.4); if the window is too small , it will greatly increase the amount of computation, and at the same time lose part of the information in the window.
[0049] In order to save the e...
Embodiment 3
[0053] According to the historical audio noise detection and elimination method described in embodiment 1, the described impulse noise detection performance analysis includes using effective detection rate (Efficient Detection Percentage, abbreviated as EDP) and detection success rate (Right Detection Percentage, abbreviated as RDP), as a performance evaluation index for the impulse noise detection process. The calculation formulas of the two are as follows:
[0054] EDP = (number of detected impulse noise / total number of detected signals)*100% (4)
[0055] RDP = (Number of Impulse Noise Detected / Total Impulse Noise in Signal)*100% (5)
[0056] Among them, EDP represents the accuracy of detection; RDP reflects the accuracy of detection, and obtaining the maximum RDP is the primary goal of the algorithm. The larger the EDP, the smaller the redundancy, the larger the RDP, the more accurate the detection, the better the detection performance, and the more beneficial it is for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com