Gene DvCRP1 with Cd<2+> and Cu<2+> resistance as well as coding protein and application thereof
A gene encoding and gene technology, applied to the gene DvCRP1 with anti-Cd2+ and anti-Cu2+ functions, its encoded protein and its application field, can solve the problems of inability to study and lack of transformation system in salina
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1: Cloning and analysis of the full-length coding region of DvCRP1
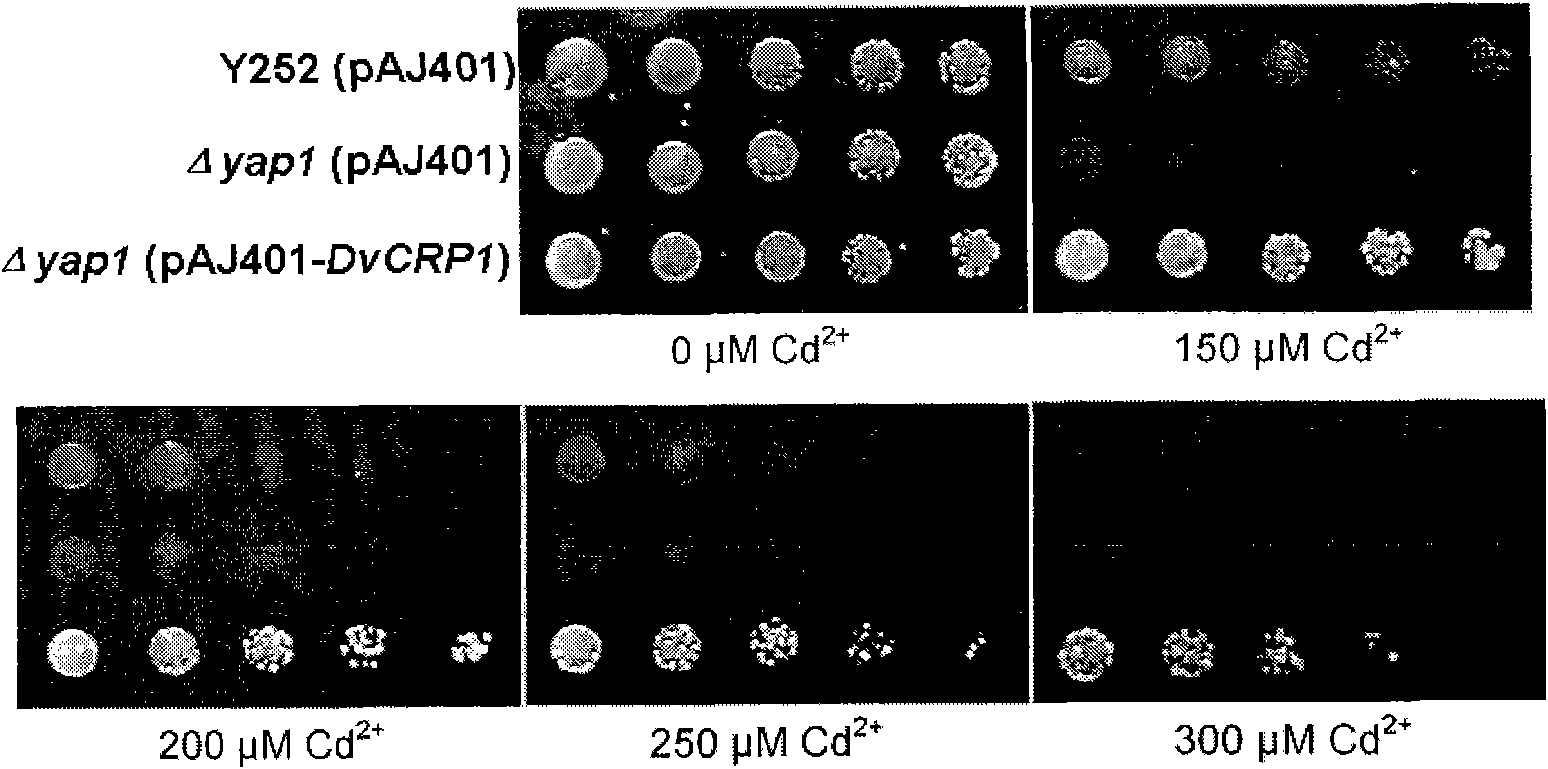
[0041] The yeast expression library was transformed into the yeast mutant Δyap1 by LiAc heat shock method, in the presence of 150 μM Cd 2+The yeast transformants with mutant phenotype recovery were screened under the screening pressure to obtain candidate clones. In order to exclude false positives caused by spontaneous mutations in the yeast genome, the expression vectors carried by the candidate clones were isolated from yeast cells, transformed into Escherichia coli for amplification, and the amplified vectors were reverted to the yeast mutant Δyap1 and incubated in 150 μM Cd 2+ The clones that can still grow stably under the treatment are the true positive clones. The insert fragment in the expression vector carried by the positive clone was sequenced to obtain the partial cDNA sequence of DvCRP1.
[0042] In order to obtain the cDNA sequence of the full-length coding region, the present ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Sequence analysis of DvCRP1
[0044] The full-length cDNA sequence of the DvCRP1 gene was searched for homology in the corresponding database of NCBI using Blastx, tBlastx and Blastn programs successively ( http: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov ), did not obtain effective Blast search results, indicating that the Salina DvCRP1 gene and its homologous genes have not been cloned and studied at present, and are discovered for the first time with anti-Cd 2+ Functional new genes.
Embodiment 3
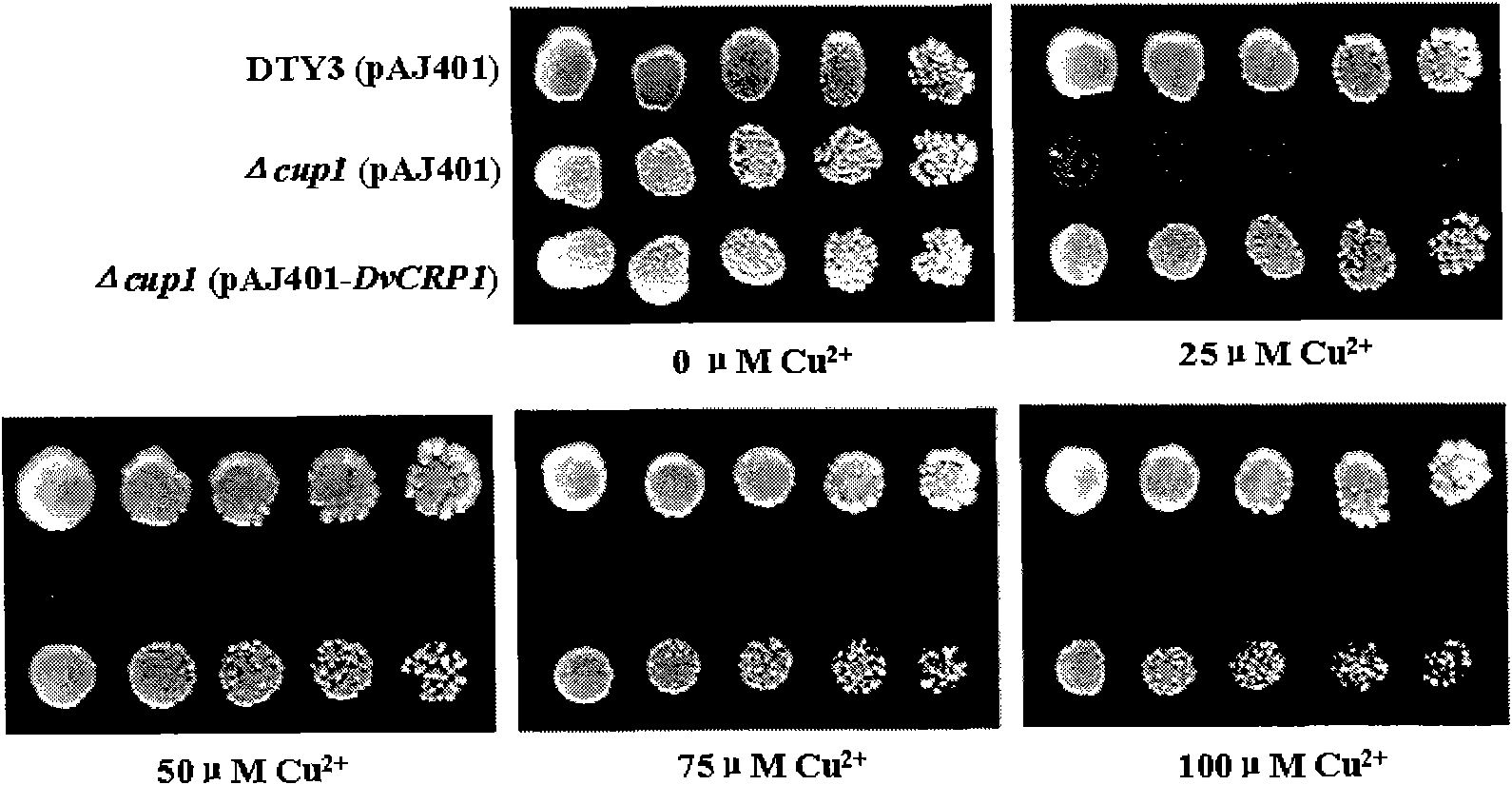
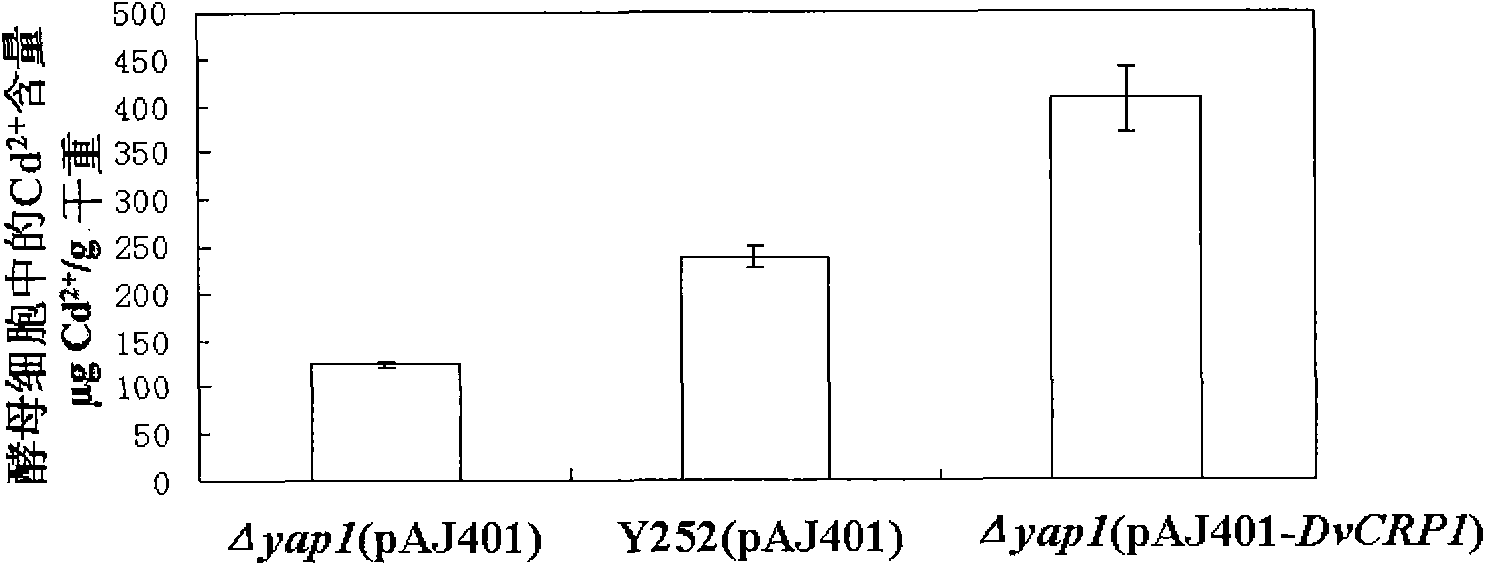
[0046] Example 3 Functional Analysis of DvCRP1 in Yeast
[0047] (1) Construction of yeast expression vector
[0048] The full-length ORF fragment of DvCRP1 was amplified by using the cDNA clone of DvCRP1 as a template by PCR method. In order to construct the clone, with the help of primer introduction method, an EcoRI restriction site is added to the 5' end of the target sequence, and an XhoI restriction site is added to its 3' end. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0049] DvCRP1+: 5'-attgaattcatgaacggagacgagtgtagg-3'
[0050] DvCRP1-:5'-attctcgagtcagcatctgcacagatcac-3'
[0051] The product amplified by PCR was directional cloned into the vector pAJ401 using the enzyme sites EcoRI and XhoI, and transformed into Escherichia coli Top10. The positive clone pAJ401-DvCRP1 was identified by enzyme digestion and sequencing.
[0052] (2) Transform yeast
[0053] Using the LiAc heat shock transformation method: the empty vector pAJ401 and the expression vector pAJ401-DvCRP1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com