Multiband reflection spectrum noninvasive blood component measuring device and method
A reflectance spectrum and blood component technology, which is applied in the field of multi-band reflectance spectrum non-invasive blood component measurement devices, can solve problems such as large prediction errors, loss of useful information, and inability to cover all situations, so as to increase the amount of information, improve the analysis accuracy, The effect of less interference from the external environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
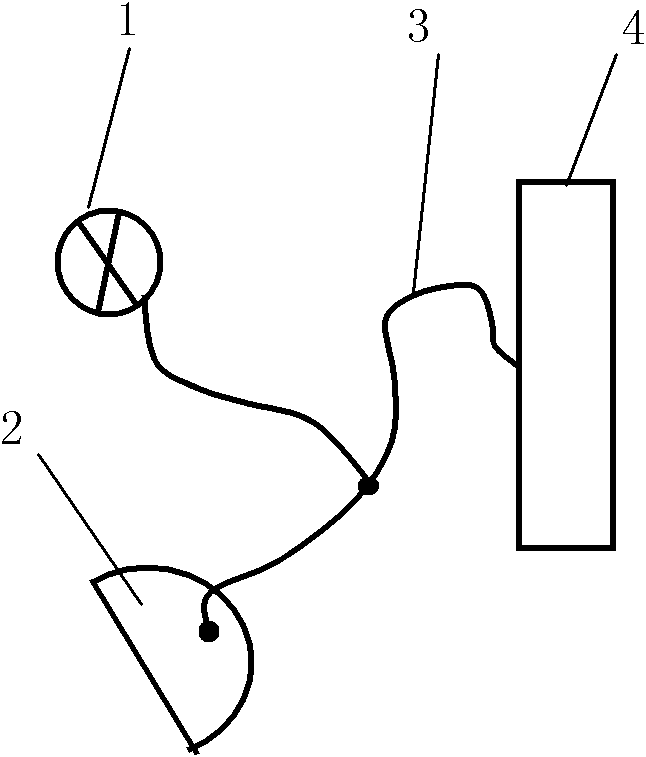
[0037] like figure 1 As shown, the broadband light source 1 emits a light beam in the ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared wavelength bands or a combined beam of several wavelength bands is introduced through the movable optical fiber 3, and the outgoing light is directly irradiated to a certain point of the tongue body 2, which reflects the light It is sent to the spectrometer 4 for acceptance. During the measurement, the fiber probe scans from the start position to the end position, and stops moving after moving to a set position to obtain the reflection spectrum at this position, and then the fiber probe moves to the next position again to collect the outgoing spectrum, and so on. , until the entire tongue surface reflectance spectral distribution measurement is completed. Spectrometer 4 applies the normalized calculation formula to the measured reflectance spectrum: R g =R / max(R)(1) for normalization, using principal component analysis (PCA, principle component analysi...
Embodiment 2
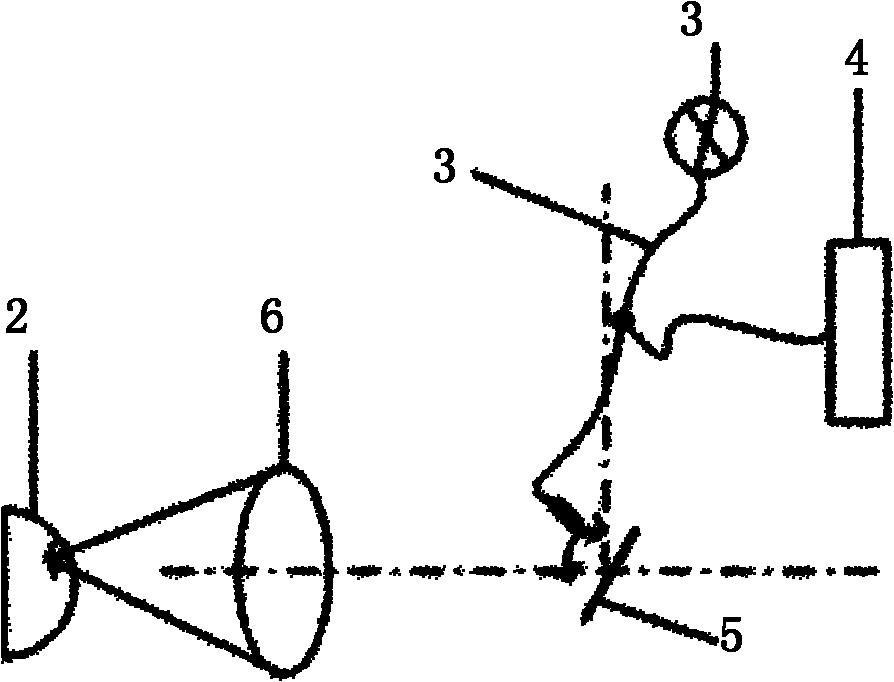
[0039] like figure 2 As shown, the broadband light source 1 emits a light beam in the ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared wavebands or a combined beam of several wavebands is introduced into the galvanometer 5 through the optical fiber 3, and the light reflected by the galvanometer is converged by the field mirror 6, and the converged light spot When the light is irradiated to a certain position of the tongue body 2, when the condensed light moves to a position of the measured part, the reflected light at this point of the measured part enters the spectrometer and receives it. At this point, the measurement of this position ends, and the motor controls the galvanometer to swing. Thereby, the movement of the light spot is driven, and the detection of the reflection spectrum of the whole tongue is realized. After scanning, the reflection spectrum is normalized by formula (1), using principal component analysis (PCA, principle component analysis), artificial neural network (A...
Embodiment 3
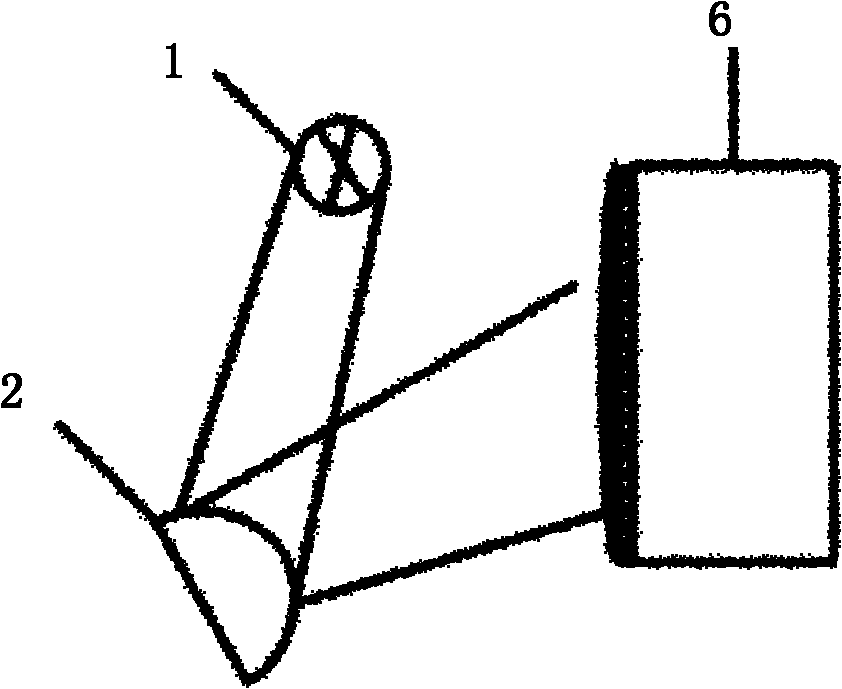
[0041] like image 3 As shown, the continuous monochromatic light emitted by the supercontinuum laser 1 directly illuminates the surface of the tongue body 2, and the reflected light of the tongue body is received by the spectral imager. The reflection spectrum is then normalized by formula (1), using principal component analysis (PCA, principle component analysis), artificial neural network (ANN, artificial neural network), partial least squares regression (PLSR, particle least squares calibration analysis) ), support vector machines (SVM, support vector machines) and other signal analysis and statistical methods to establish mathematical models. The newly collected unknown samples are normalized by the normalization method of the above formula (1), and then the normalized spectral data is used as an independent variable, and the established mathematical model is used for calculation to obtain the content of blood components.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com