Method for recycling mother solid in PTA-refining wastewater
A recovery method and a technology for refining wastewater, which are applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as membrane devices cannot operate stably, and achieve easy clogging and avoid Waste of resources and high resource recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
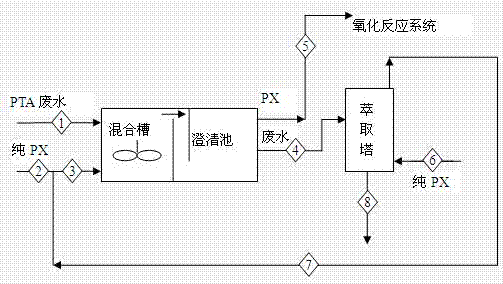
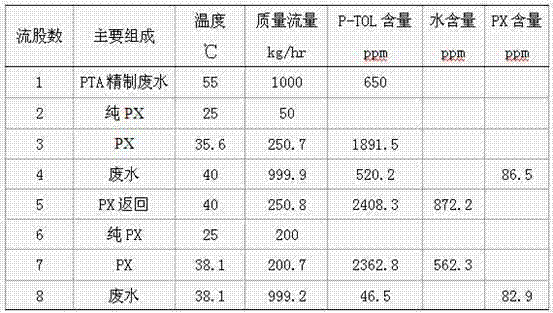
[0023] Stream 1 PTA (PTA refined wastewater) and stream 2 (pure PX) respectively enter the mixing tank through the flow regulating valve for mixing cooling and primary extraction. The mass ratio of stream 1 to stream 3 in the mixing tank is 1:4. Control the flow of cooling water in the mixing tank coil so that the outlet temperature of the mixing tank is 40°C. After the mixed solution enters the clarifier, there will be TA solid precipitated and precipitated in the clarifier, and at the same time, the P-TOL and PTA in the PX extraction wastewater form an oil phase and water layer, which flows out from the upper layer of the clarifier (stream 5), and returns to Oxidation reaction system. The PTA wastewater (stream 4) from the clarification tank enters from the upper part of the extraction tower, while pure PX (stream 6) enters from the bottom of the extraction tower through a regulating valve, and the mass ratio of stream 6 to stream 4 is 1 :5. In the extraction tower, after...
Embodiment 2
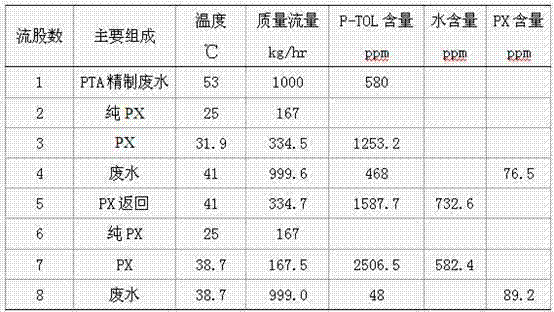
[0027] Stream 1 PTA (PTA refined wastewater) and stream 2 (including pure PX and the extraction phase discharged from the top of the extraction tower in Example 1) respectively enter the mixing tank through the flow regulating valve for mixing cooling and primary extraction. The mass ratio of stream 1 to stream 3 in the mixing tank is 1:3. Control the flow of cooling water in the mixing tank coil so that the outlet temperature of the mixing tank is 41°C. After the mixed solution enters the clarifier, there will be TA solid precipitated and precipitated in the clarifier, and at the same time, the P-TOL and PTA in the PX extraction wastewater form an oil phase and water layer, which flows out from the upper layer of the clarifier (stream 5), and returns to Oxidation reaction system. The PTA wastewater (stream 4) from the clarification tank enters from the upper part of the extraction tower, while pure PX (stream 6) enters from the bottom of the extraction tower through a regula...
Embodiment 3
[0031]Stream 1 PTA (PTA refined wastewater) and stream 2 (pure PX) respectively enter the mixing tank through the flow regulating valve for mixing cooling and primary extraction. The mass ratio of stream 1 to stream 3 in the mixing tank is 1:2. Control the flow of cooling water in the mixing tank coil so that the outlet temperature of the mixing tank is 40.5°C. After the mixed solution enters the clarifier, there will be TA solid precipitated and precipitated in the clarifier, and at the same time, the P-TOL and PTA in the PX extraction wastewater form an oil phase and water layer, which flows out from the upper layer of the clarifier (stream 5), and returns to Oxidation reaction system. The PTA wastewater (stream 4) from the clarification tank enters from the upper part of the extraction tower, while pure PX (stream 6) enters from the bottom of the extraction tower through a regulating valve, and the mass ratio of stream 6 to stream 4 is 1 :8. In the extraction tower, afte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com