Method for purifying plasmid DNA
A plasmid and drug technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid purification, can solve the problems of insufficient separation, time-consuming and cost-consuming, and difficulties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
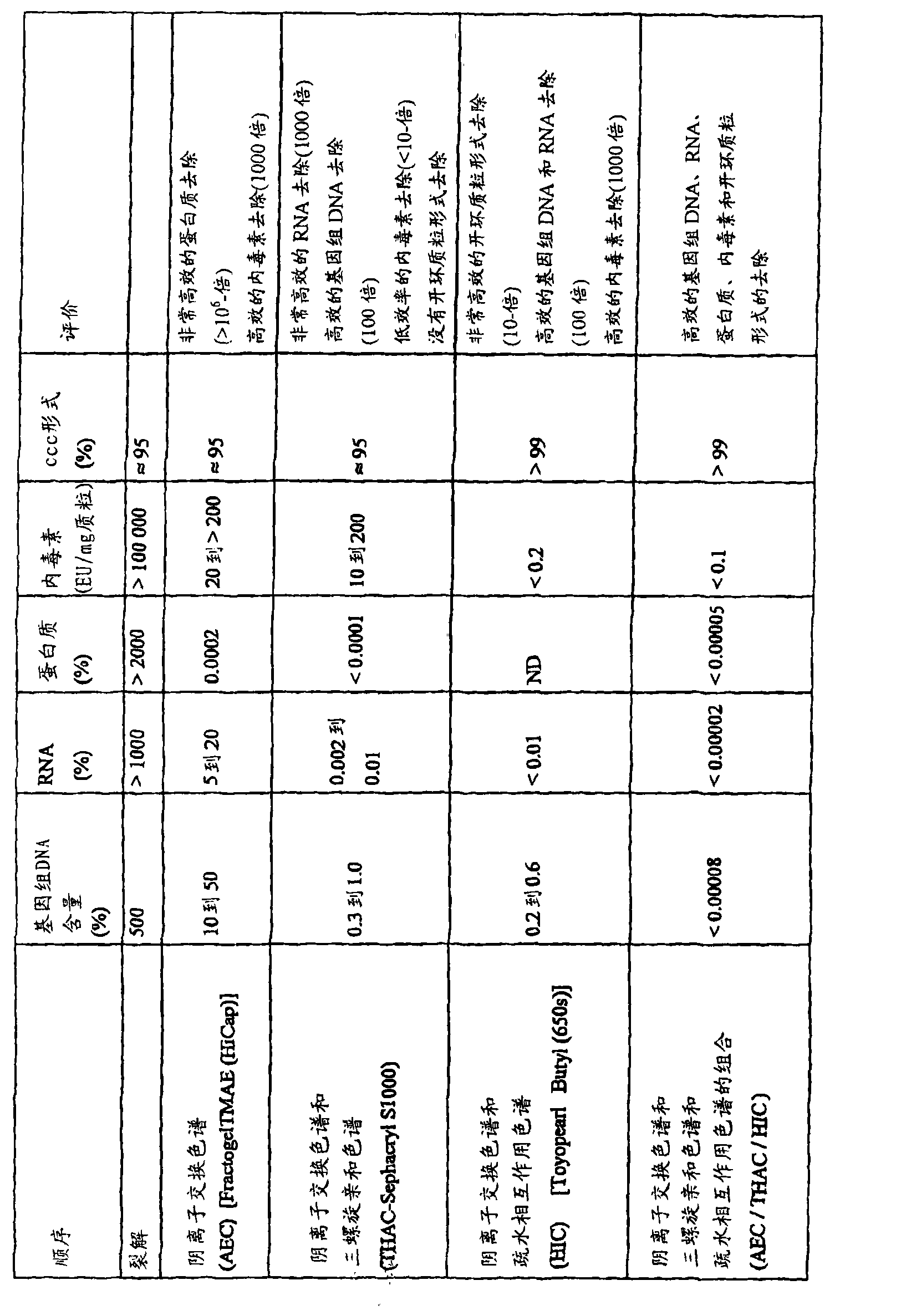
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0216] The diameter was adjusted for the flow rate used based on the calculation of the Reynolds number (Reynolds) in the coils of the continuous lysis system. Since the following analysis assumes Newtonian behavior of the fluid, the numbers reported below are fully valid only in Bla and to some extent in B2.
[0217] From the value of the Reynolds number, one skilled in the art can determine the type of behavior encountered. Here, we are only concerned with fluids flowing in pipes (hydraulic engineering).
[0218] 1) Non-Newtonian fluid
[0219] The two most commonly encountered non-Newtonian fluids in industry are Bingham fluids and Ostwald de Waele fluids.
[0220] Here, the Reynolds number (Re) is calculated as follows:
[0221] Re N is the generalized Reynolds number
[0222] Re N =(1 / (2 n-3 ))x(n / 3n+1) n x((ρx D n w 2-n ) / m) (1)
[0223] D: Inner diameter of cross section (m)
[0224] ρ: volumetric mass of the fluid (kg / m 3 )
[0225] w: spatial velocity o...
Embodiment 2
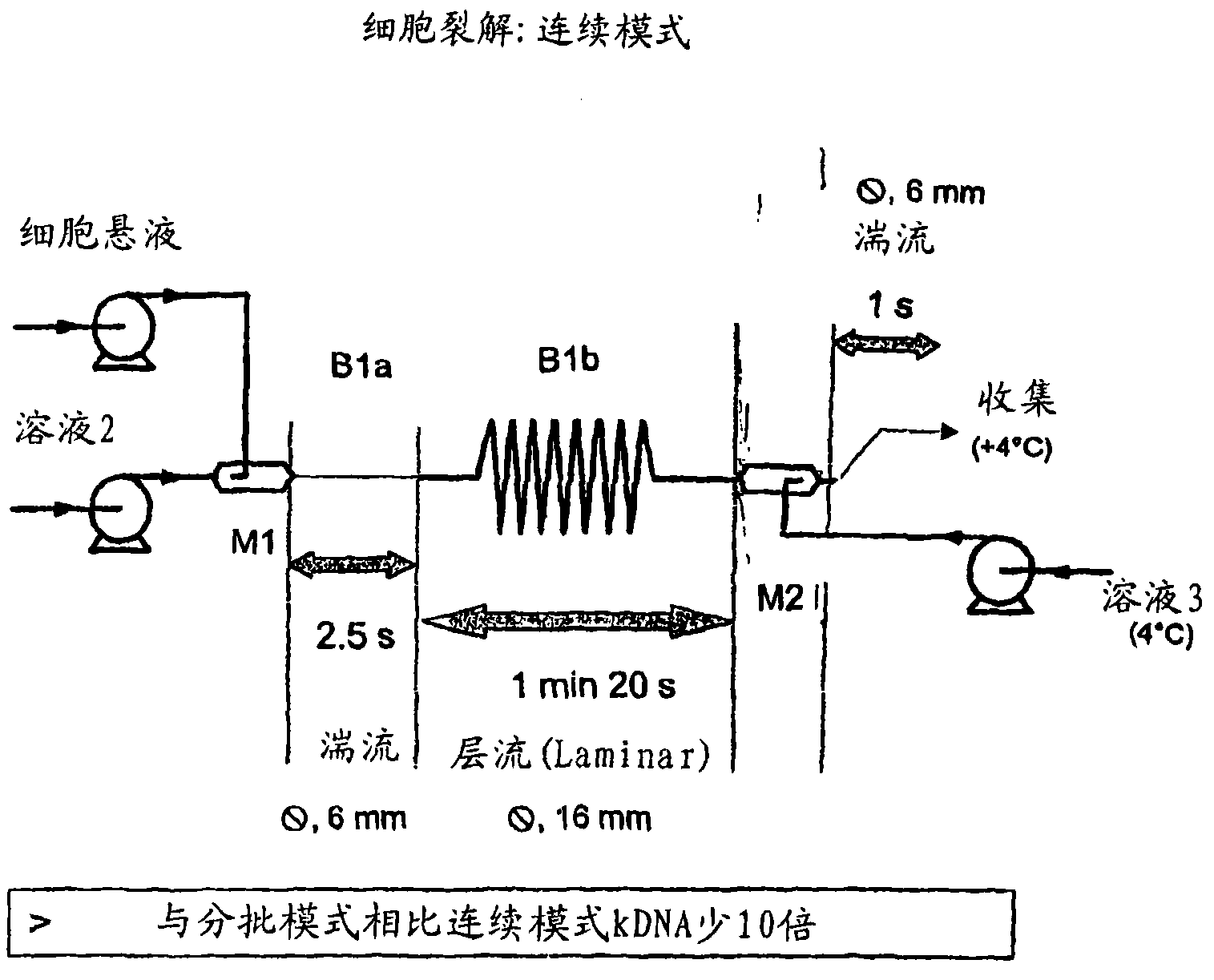
[0270] We can split the CL system into 5 steps. In a specific implementation, the configuration is as follows:
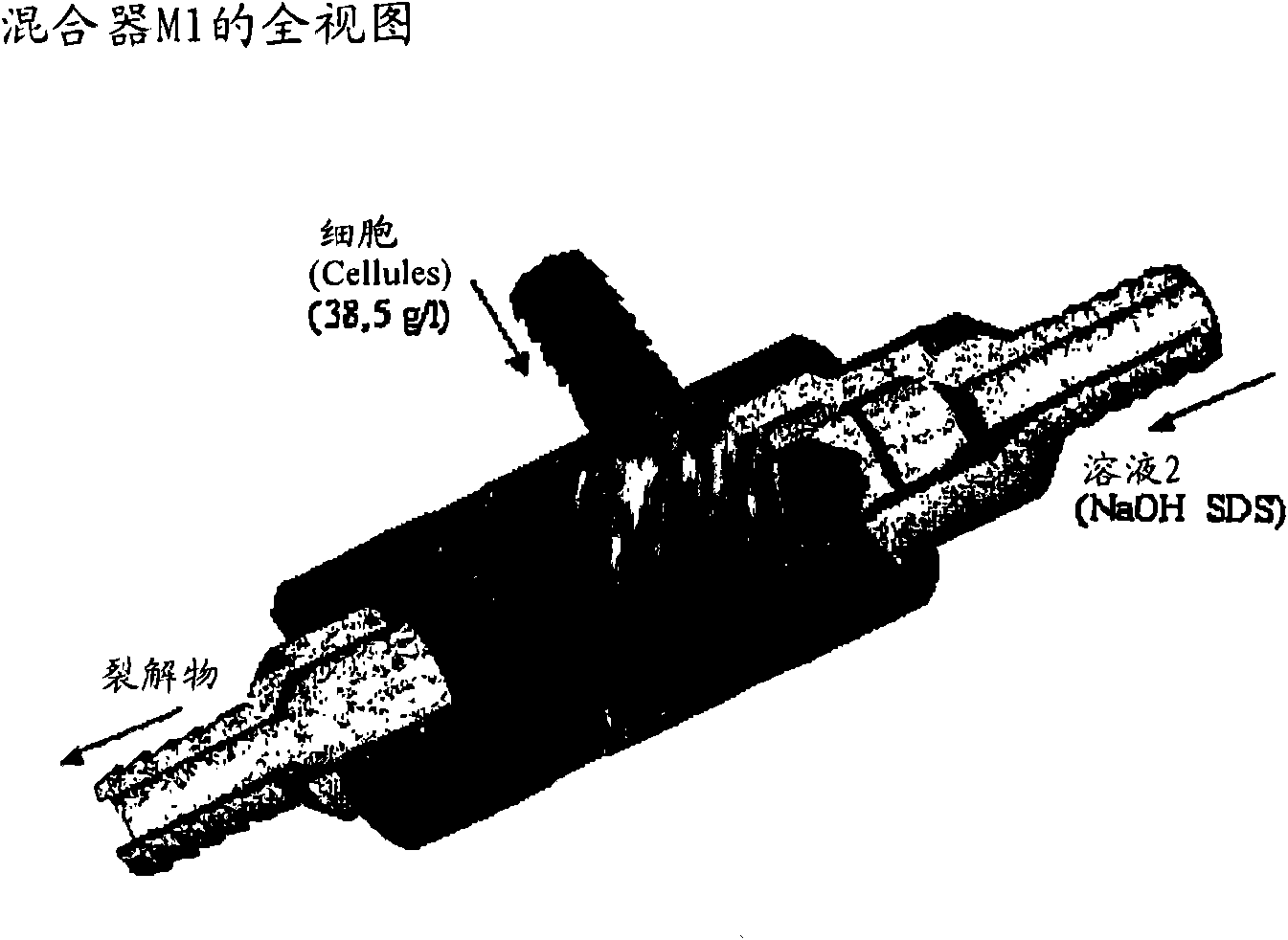
[0271] 1) Mixing: cells (in solution 1) + solution 2 (M1 + 3m of 6mm tube). SDS lyses cells to begin, as long as the DNA is not denatured and there is no risk of fragmentation.
[0272] 2) After the lysis is completed, the gDNA is denatured (13m 16mm tube).
[0273] 3) Mixing: lysate + solution 3 (6 mm tube of M2 + 3m).
[0274] 4) Collect the neutralized lysate at 4°C.
[0275] 5) Settling flocs and large fragments of gDNA overnight at 4°C.
[0276] Continuous lysis can be performed using the following conditions:
[0277] - Solution 1: EDTA 10 mM, Glucose (Glc) 9 g / l and Tris HCl 25 mM, pH 7.2.
[0278] - Solution 2: SDS 1% and NaOH 0.2N.
[0279] - Solution 3: acetic acid 2M and potassium acetate 3M.
[0280] - Flow rate 60 l / h: solution 1 and solution 2.
[0281] - Flow rate 90 l / h: solution 3.
[0282] - The cells are adjusted to 38.5 g / l with solutio...
Embodiment 3
[0300] The column used was a 1 ml HiTrap column activated with NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide, Pharmacia), connected to a peristaltic pump (output 2 The sequence of the group is as follows: 5'-GAGGCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1).
[0301] The buffers used in this example are as follows:
[0302] Coupling buffer: 0.2M NaHCO 3 , 0.5M NaCl, pH 8.3.
[0303] Buffer A: 0.5M ethanolamine, 0.5M NaCl, pH 8.3.
[0304] Buffer B: 0.1M Acetate, 0.5M NaCl, pH 4.
[0305] The column was washed with 6 ml of 1 mM HCl, then the oligonucleotide (50 nmol in 1 ml) diluted in coupling buffer was applied to the column for 30 minutes at room temperature. Wash 3 times successively with 6 ml of buffer A and 6 ml of buffer B. The oligonucleotide is thus covalently bound to the column via a CONH bond. Store the column at 4 °C in PBS, 0.1% NaN 3 Medium, and can be used at least 4 times.
[0306] The following two oligonucleotides were synthesized: oligonucleotide 4817:
[0307] 5'-GATCCGAAGAA...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com