Compositions and methods of treatment using modulators of motoneuron diseases
A motor neuron and disease technology, applied in nervous system diseases, neuromuscular system diseases, drug combinations, etc., can solve problems such as lack of understanding of the fundamental mechanism of motor neuron diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
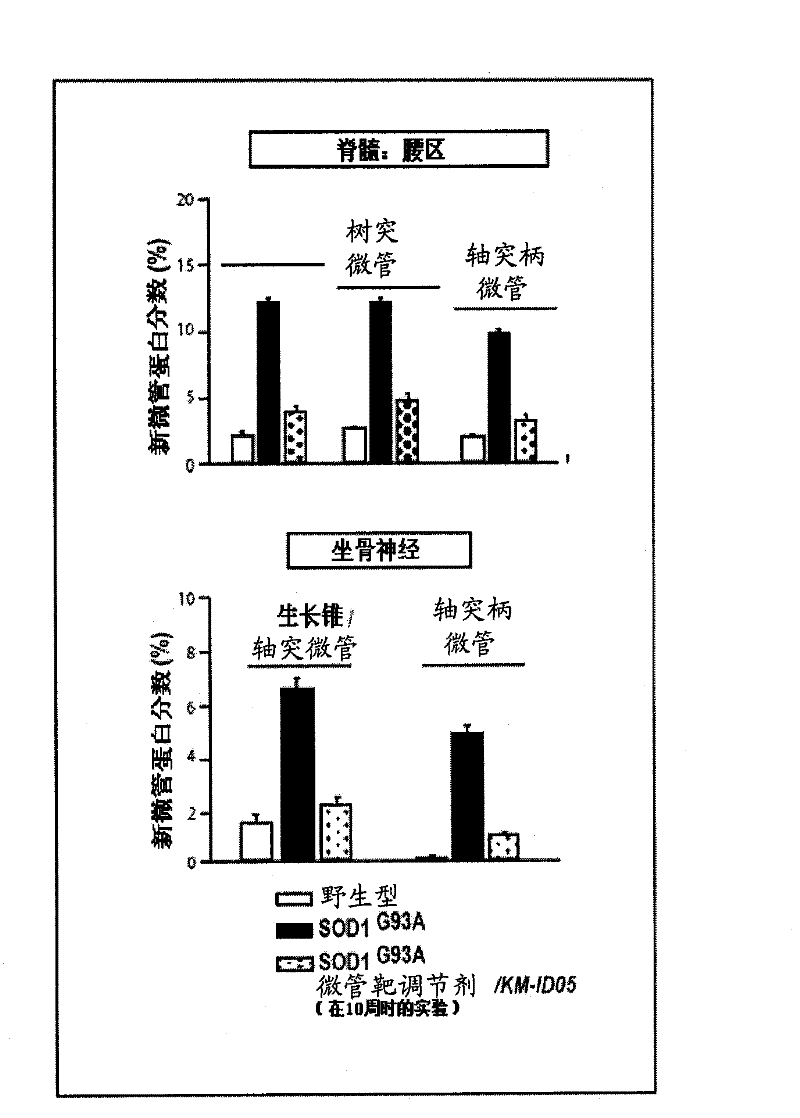
[0232] Example 1: Separation of Tubulin Dimers and Aggregates
[0233] By reviewing previously described protocols (Fanara, P., Oback, B., Ashman, K., Podtelejnikov, A., Brandt, R. Identification of MINUS, a small polypeptide that functions as a microtubule nucleation suppressor. EMBO J. 18, 565-577 (1999); Fanara, P. et al., In vivo measurement of microtubule dynamics using stable isotope labeling with heavy water. Effect of taxanes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 49940-49947 (2004)) slightly Modified to purify tubulin. For ex vivo purification, mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and euthanized by cervical dislocation. The sciatic nerve was cut and isolated as follows. Pull the skin back to expose the muscles of the lower body. The spinal cord was transected with scissors at a location just below the lumbar region and also just above the broad sacral region. Slide the partially opened scissors down the lumbar region of the spine until the scissors touch near the broad ilium port...
example 2
[0234] Example 2: Isolation of cold stable microtubules
[0235] A slight modification of the previously described protocol was used to isolate cold-stable microtubules (Pirollet, F., Derancourt, J., Haiech, J., Job, D., Margolis, R.L. Ca( 2+ )-calmodulin regulated effectors of microtubule stability in bovine brain. Biochemistry 31, 8849-8855 (1992)). Briefly, in the presence of 1.5mM CaCl 2 The ice-cold MSB (Fanara, P., Obaek, B., Ashman, K., Podtelejnikov, A., Brandt, R. Identification of MINUS, a small polypeptide that functions as a microtubule nucleation suppressor. EMBO J.18, 565- 577 (1999)), the ratio of buffer to cell pellet or brain tissue was set at a ratio of 1.4:1 (volume / weight). After 2 minutes on ice, EGTA was added to a final concentration of 3 mM and the mixture was homogenized for an additional 1 minute on ice. The extract was centrifuged at 150,000 x g for 30 min at 4°C and the supernatant collected. Microtubule assembly was initiated by incubating supe...
example 3
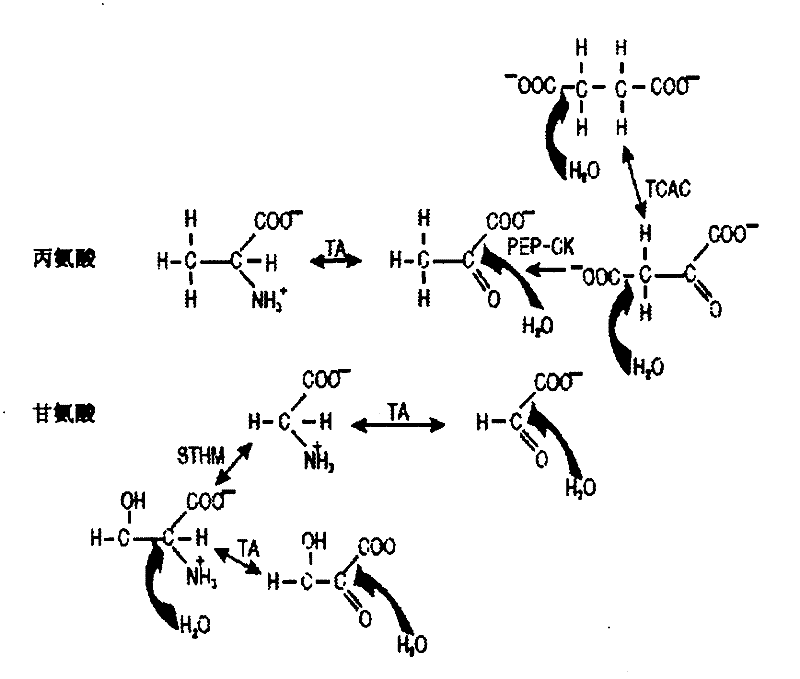
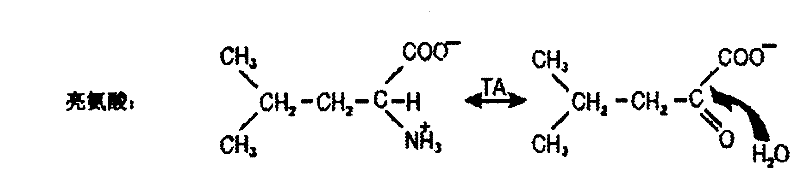
[0236] Example 3: GC / MS analysis of tubulin
[0237] Tubulin samples were hydrolyzed by treatment with 6N HCl at 110°C for 16 hours. Derivatization of protein-derived amino acids to pentafluorobenzyl derivatives and measurement by GC / MS 2 Incorporation of H into alanine, as detailed elsewhere (Fanara, P. et al., In vivo measurement of microtubule dynamics using stable isotope labeling with heavy water. Effect of taxanes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 49940 -49947 (2004)). 2 The enrichment of H was calculated as the percentage increase of the alanine derivative present as the (M+1) mass isotopologue over the natural abundance.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com