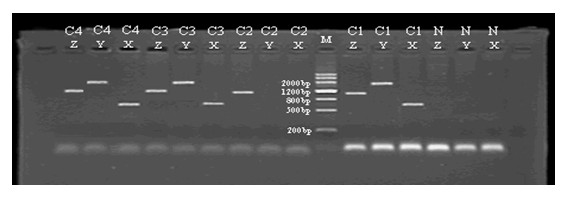
Method for deleting selective marker gene of transgenic poplar
A selection marker and transgenic technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as low deletion efficiency, and achieve the effect of improving deletion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 Preparation of Agrobacterium
[0033] A single colony of Agrobacterium EHA105 was picked, inoculated in 5ml LB medium, and cultured at 28°C and 220rpm for 24h. Add 400??l bacterial solution to 20ml LB medium, culture at 28℃, 220rpm for 3h, until OD 600 Around 0.3. Divide the bacterial solution into 10ml sterile centrifuge tubes and place in ice bath for 10min. Put the centrifuge tube into a centrifuge, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 10min at 4°C. Discard the supernatant, add 5ml of pre-cooled 0.15mol / L NaCl, and gently resuspend. Cool in ice for 30 minutes, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C. Discard the supernatant, add 600??l pre-cooled 0.02mol / L CaCl 2 , and gently resuspend. Add 1??lpX6-GFP plasmid to 200??l of Agrobacterium competent cells, mix gently, and ice-bath for 30min. Freeze in liquid nitrogen for 1 min. 37 ℃ water bath for 3 ~ 5min, quickly placed on ice, ice bath for 1min. join 800??lYEB(str 50 ) culture medium, cultured at 28°C, ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Genetic transformation of Nanlin 895 poplar
[0035] The test-tube seedlings of the transgenic plants of Populus Nanlin 895 were placed on the medium M to subculture by root sprouting and sprouting, and the young and flat 3rd to 5th leaves were selected from the test-tube seedlings that had been subcultured for about 1 month. The size, shape and color are basically the same. Cut off the edge of the leaf and cut it into 0.7~0.8cm 2 The leaf disks are explants, inoculated in such a way that the abaxial surface is in contact with the medium. The culture temperature is 25±2°C, the light is 3000~4000lux, and the light time is 16~18h / d. Pre-culture on T medium for 2~3 days, and the abaxial surface of the leaf disc is in contact with the medium. Pick a single colony of Agrobacterium EHA105 (pX6-GFP plasmid) carrying the GFP gene and inoculate it into YEB liquid medium, culture at 27±1°C, 220-230rpm shaking overnight; transfer 0.8-1mL to 25-30mL YEB liquid medium....
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3 Deletion of selection markers in Nanlin 895 poplar transgenic plants
[0037] After subculture of the transgenic plants of Populus Nanlin 895 obtained through screening, the stem segments of the transgenic resistant plants that had been analyzed and identified were clipped and cultured in leaf disk differentiation medium W' with the selection marker deleted until adventitious buds differentiated. The adventitious buds and the original explants were transplanted into the adventitious bud elongation medium Y' with the selection marker deleted, and subcultured once every 2-3 weeks. After the adventitious buds elongated to about 1.5 cm, each adventitious bud was separated and independently inserted into the rooting medium G' with the selection marker deleted until a complete implant was formed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com