Low-heating-value gas burner
A low calorific value gas and burner technology, applied in the direction of gas fuel burners, burners, combustion methods, etc., can solve the problems of low flame temperature, inability to burn low calorific value gas, and unstable combustion, etc., to achieve safe operation and occupy space Effects of small, expensive equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
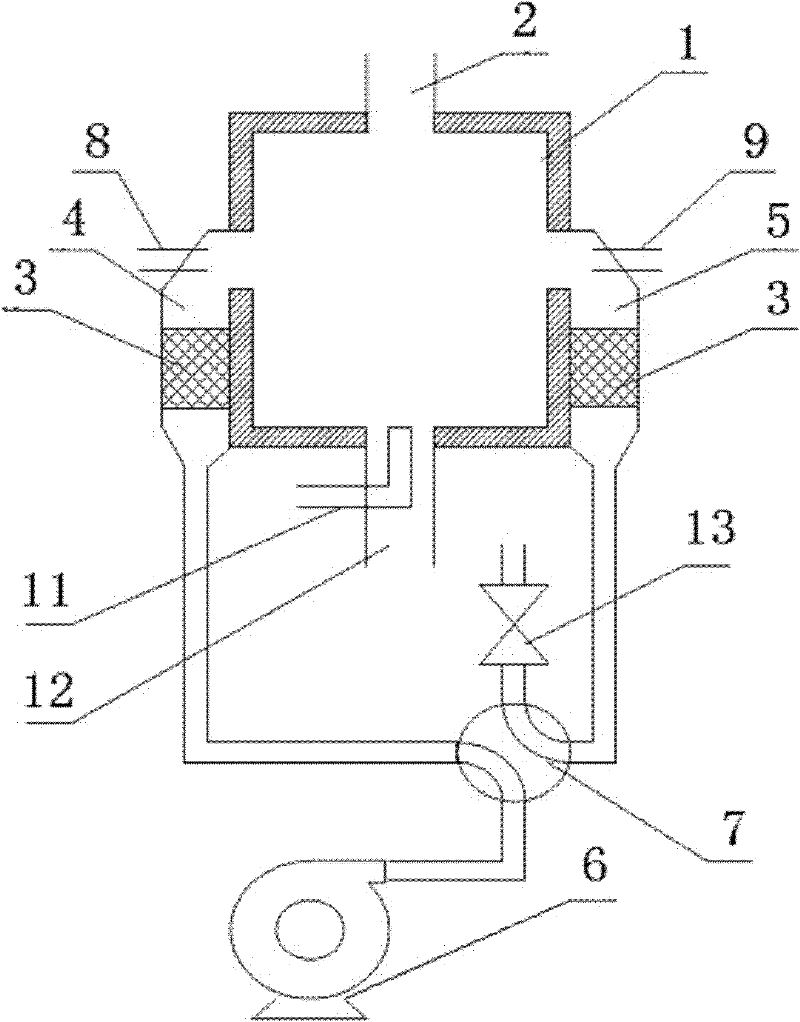
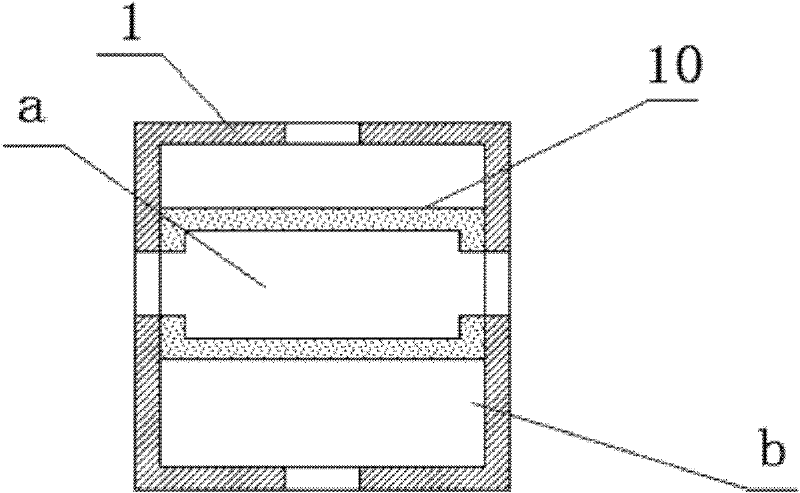
[0028] Example 1: Combining figure 1 As shown, it is a preferred embodiment of a low calorific value gas burner, which consists of a combustion chamber 1, a single heat storage device, a main gas delivery device (not shown in the figure), a main air delivery device (not shown in the figure) ) and a high temperature exhaust device (not shown in the figure). The top of the combustion chamber 1 is provided with a high-temperature gas outlet 2, and the high-temperature gas outlet 2 is connected with a high-temperature exhaust device through a pipeline; At the same time, a main gas nozzle 11 and a main air nozzle 12 are provided, which are respectively connected with the main gas delivery device and the main air delivery device through pipelines.
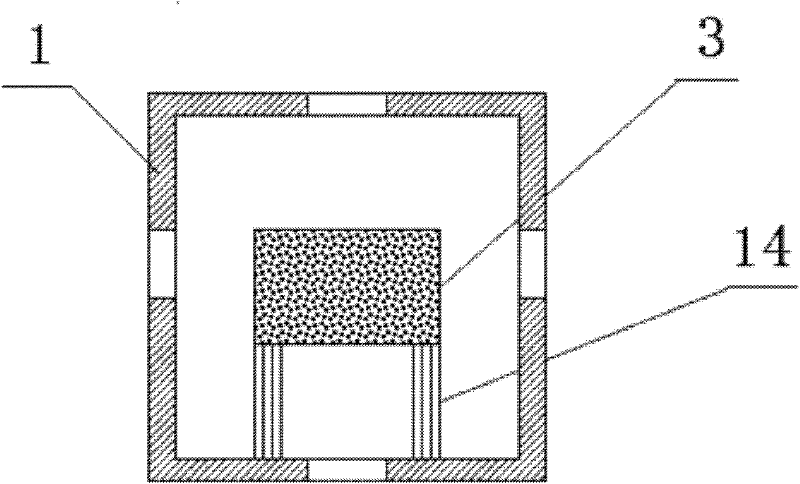
[0029]The alternate heat storage device in this embodiment consists of the left and right regenerators 4, 5 symmetrically distributed on both sides of the combustion chamber 1, the left and right gas nozzles 8, 9, the air delivery devic...
Embodiment 2
[0037] In this embodiment, two alternate heat storage devices are used, that is, four heat storage chambers are arranged on the side of the combustion chamber 1, so that when the two heat storage chambers 4 and 5 in one alternate heat storage device are 7. When reversing, the two regenerators in the other alternate heat storage device can continuously and stably alternately work in the heat storage and heat release states, so as to ensure that the pressure field and temperature field in the combustion chamber 1 will not be too large. Large fluctuations, maintaining the stability of high temperature outlet gas temperature and flow.
[0038] Others of this embodiment are the same as Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0040] In the present embodiment, the gas nozzles 8 and 9 on the left and right sides are not provided, and the gas is all sent in through the bottom of the combustion chamber 1 . That is, at the initial stage, the main gas nozzle 11 injects low calorific value coal gas and combusts the air blown in from the left and right regenerators 4 and 5. At this time, the high-temperature gas outlet 2 is closed, and the left and right regenerators 4 and 5 are reversing in four directions. Under the action of the valve 7, it operates alternately. After the combustion chamber 1 reaches the set high temperature (1200°C), the flow rate of the main gas nozzle 11 is increased and the main air nozzle 12 and the high-temperature gas outlet 2 are opened at the same time. The high-temperature gas is discharged from the high-temperature gas outlet 2. Discharged for heating and calcination.
[0041] Others of this embodiment are the same as Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com