Force-feedback-based robot micro-wound operation simulating system
A technology of minimally invasive surgery and simulation system, applied in the field of computer virtual simulation system, can solve problems such as immature system, force feedback distortion, robot motion simulation distortion, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing realism and realizing digitalization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
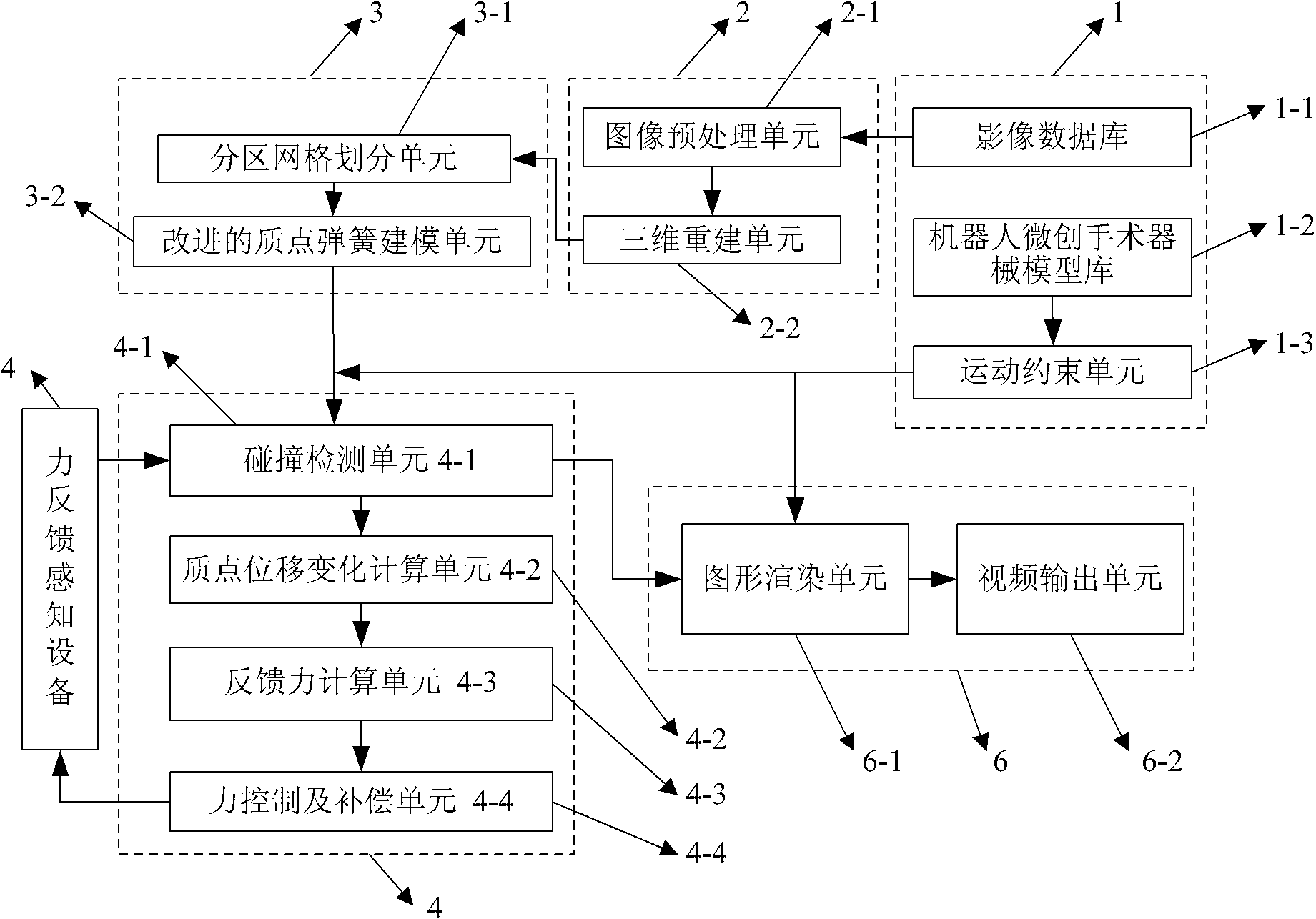
[0029] Specific implementation mode one, seefigure 1 This embodiment will be described. The robot minimally invasive surgery simulation system based on force feedback described in this embodiment is composed of a force feedback sensing device 5, a force feedback module 4, a database module 1, an image processing module 2, a physical modeling module 3 and a graphics rendering module 6. The feedback module 4 outputs a control signal to the force feedback sensing device 5, and the force feedback sensing device 5 outputs a force feedback signal to the force feedback module 4, and the force feedback module 4 outputs a collision signal to the graphics rendering module 6, and the image processing module 2 receives from the database module 1 Reading image data, the image processing module 2 outputs three-dimensional reconstruction information to the physical modeling module 3, and the physical modeling module 3 outputs physical model information to the force feedback module 4, and the ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0037] Specific implementation mode two, see figure 1 This embodiment will be described. This embodiment is an illustration of an embodiment of the database module 1 described in the first specific embodiment. The database module 1 described in this embodiment consists of an image database 1-1, a robot minimally invasive surgical instrument model library 1- 2 and motion constraint units 1-3, where:
[0038] Image database 1-1, used to store medical image raw data;
[0039] Robotic minimally invasive surgical instrument model library 1-2, used to store component models of minimally invasive surgical robots and various surgical instrument model data;
[0040] The motion constraint unit 1-3 is used to store each component stored in the robot minimally invasive surgical instrument model library 1-2 and the kinematic constraint connection relationship and motion law between various surgical instruments.
[0041] The raw medical image data described in this embodiment includes im...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0045] Specific implementation mode three, see figure 1 This embodiment will be described. This embodiment is a further description of the robot minimally invasive surgical instrument model library 1-2 and the motion constraint unit 1-3 described in the second specific embodiment. The robot minimally invasive surgical instrument model library 1-2 described in this embodiment In the model data in 2, different materials are assigned to the model of each moving part, and different diffuse reflection lights are set. In this way, the display of the robot kinematic units in the virtual environment can be enhanced.
[0046] The motion constraint related data in the motion constraint unit 1-3 specifies the position and posture of the robot according to the DH algorithm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com