Method for extracting arsenic metal from arsenic trioxide material by two-stage carbon reduction
A technology for arsenic trioxide and metal extraction, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of uncontinuous process, single reduction zone, limited processing capacity, etc., and achieve the effects of improving reduction rate, processing capacity and output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
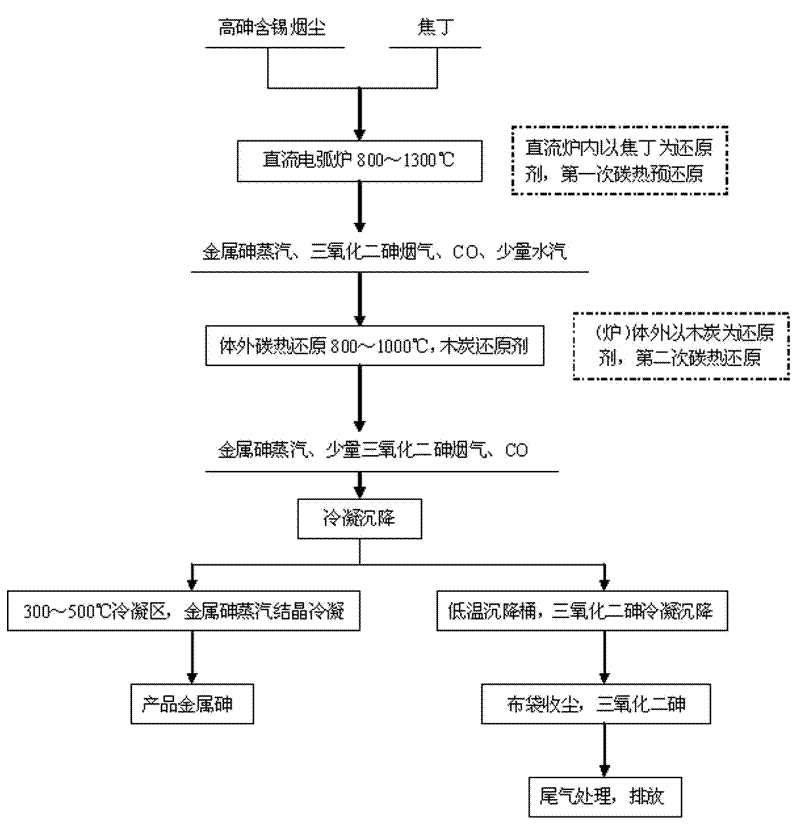
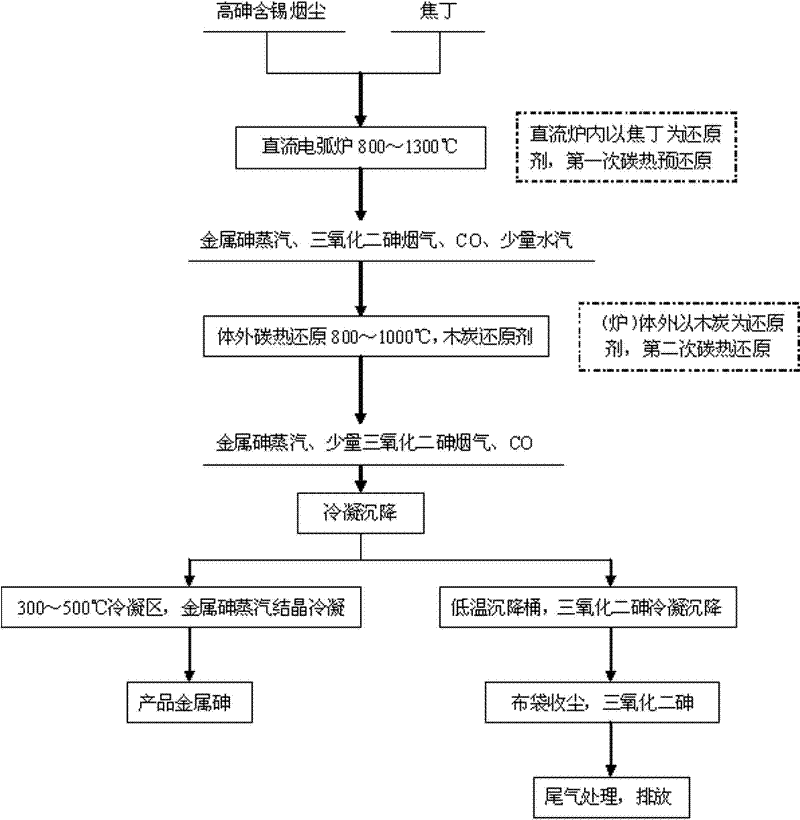
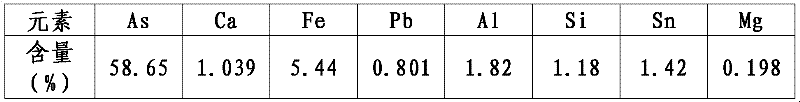
[0029] With arsenic ash as raw material 100.0kg, see Table 1 for specific components, 18.1 kg of carbonaceous primary reducing agent with coke, see Table 2 for specific components, and use cylindrical charcoal (commercially available) as secondary reducing agent, in the ball making machine After pressing the arsenic ash into Φ10mm pellets under pressure, put the arsenic ash and coke in the top hopper of a 100kVA DC submerged arc furnace, and seal the raw material hopper to prevent air from entering. Charcoal is filled in the carbothermal reduction area outside the furnace, and the charcoal hopper is sealed. After checking whether the seals of the metal arsenic vapor condensation and sedimentation chamber are well sealed, turn on the fan exhaust system and control the system pressure at 0-20Pa. When the reduction temperature inside the furnace is 1000°C and the reduction temperature outside the furnace is 800°C, feed materials for carbon thermal reduction. reaction. A part of ...
Embodiment 2
[0035]The raw materials and process are the same as in Example 1, except that the pressure of the control system is 5-20 Pa. When the reduction temperature inside the furnace is 1100°C and the reduction temperature outside the furnace is 900°C for carbothermal reduction reaction, the temperature of the condensation and sedimentation chamber is controlled at Block metal arsenic can be obtained at 340°C. After the reduction is complete, close the flue gas valve on the furnace top, open the bypass valve, and let the unreduced flue gas directly enter the condensation and settling barrel; at the same time, close the front valve of the metal arsenic condensation chamber, open the door of the settling chamber, and take the material to obtain 41.7kg block As for metal arsenic, the reduction rate of metal arsenic is calculated to be 71.1%, and the average purity of the metal arsenic reaches 99.22%.
Embodiment 3
[0037] The raw materials and process are the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the pressure of the control system is 5-15 Pa, when the reduction temperature inside the furnace is 1300°C, and the reduction temperature outside the furnace is 1000°C for carbothermal reduction reaction, the temperature of the condensation and sedimentation chamber is controlled at Block metal arsenic can be obtained at 360°C. After the reduction is completed, close the flue gas valve on the top of the furnace, open the bypass valve, and let the unreduced flue gas directly enter the condensation and settling barrel; at the same time, close the front valve of the metal arsenic condensation chamber, open the door of the settling chamber, and take the material to obtain 44.0kg block As for metal arsenic, the reduction rate of metal arsenic is calculated to be 75.0%, and the average purity of the metal arsenic reaches 99.58%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com