Series electrolytic cell system and its method for removing bromate in drinking water
An electrolytic cell and drinking water technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of reducing system processing capacity, increasing post-processing procedures, and expensive electrode materials, etc., to achieve Improve practicability, fast response, no secondary pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
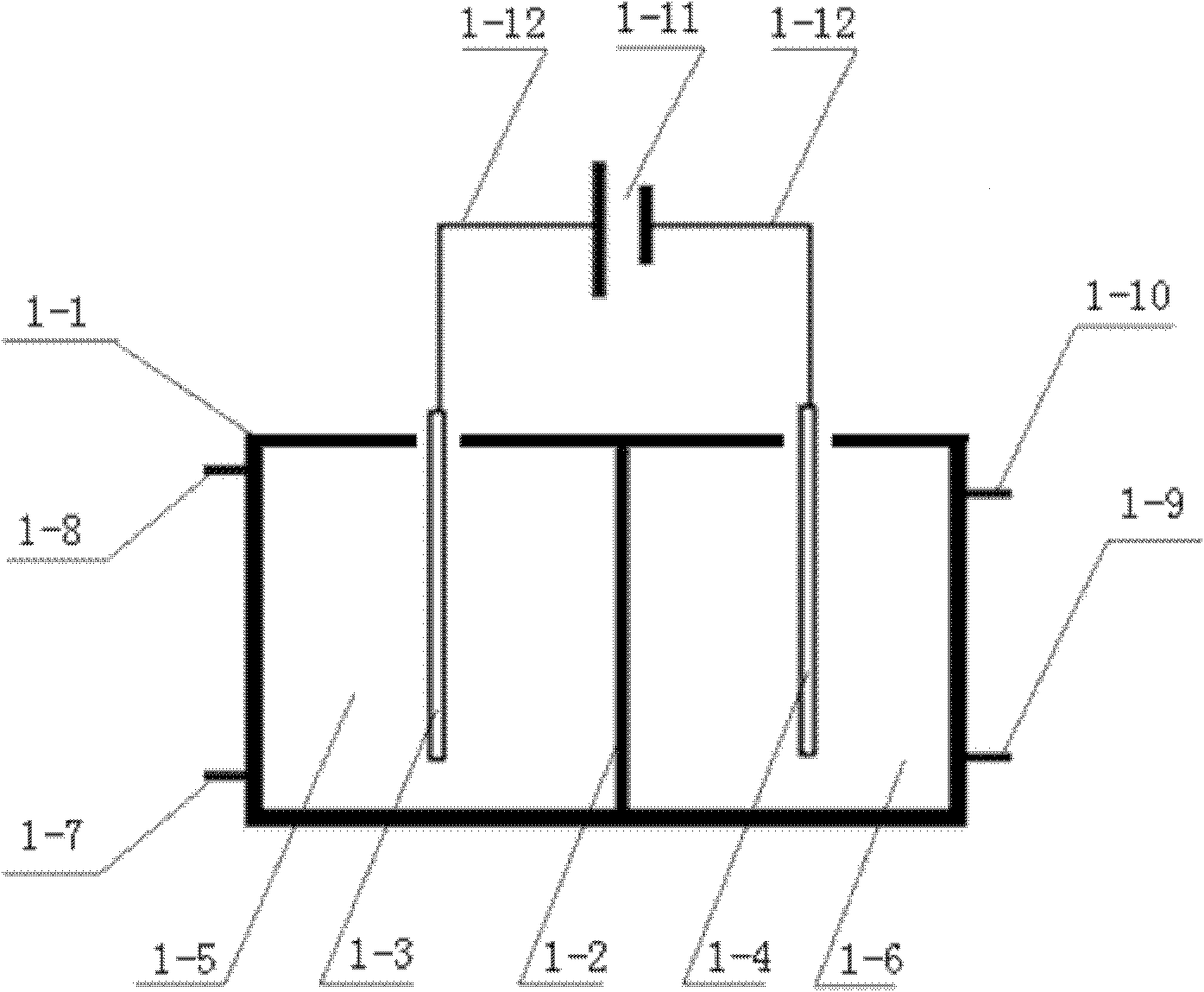
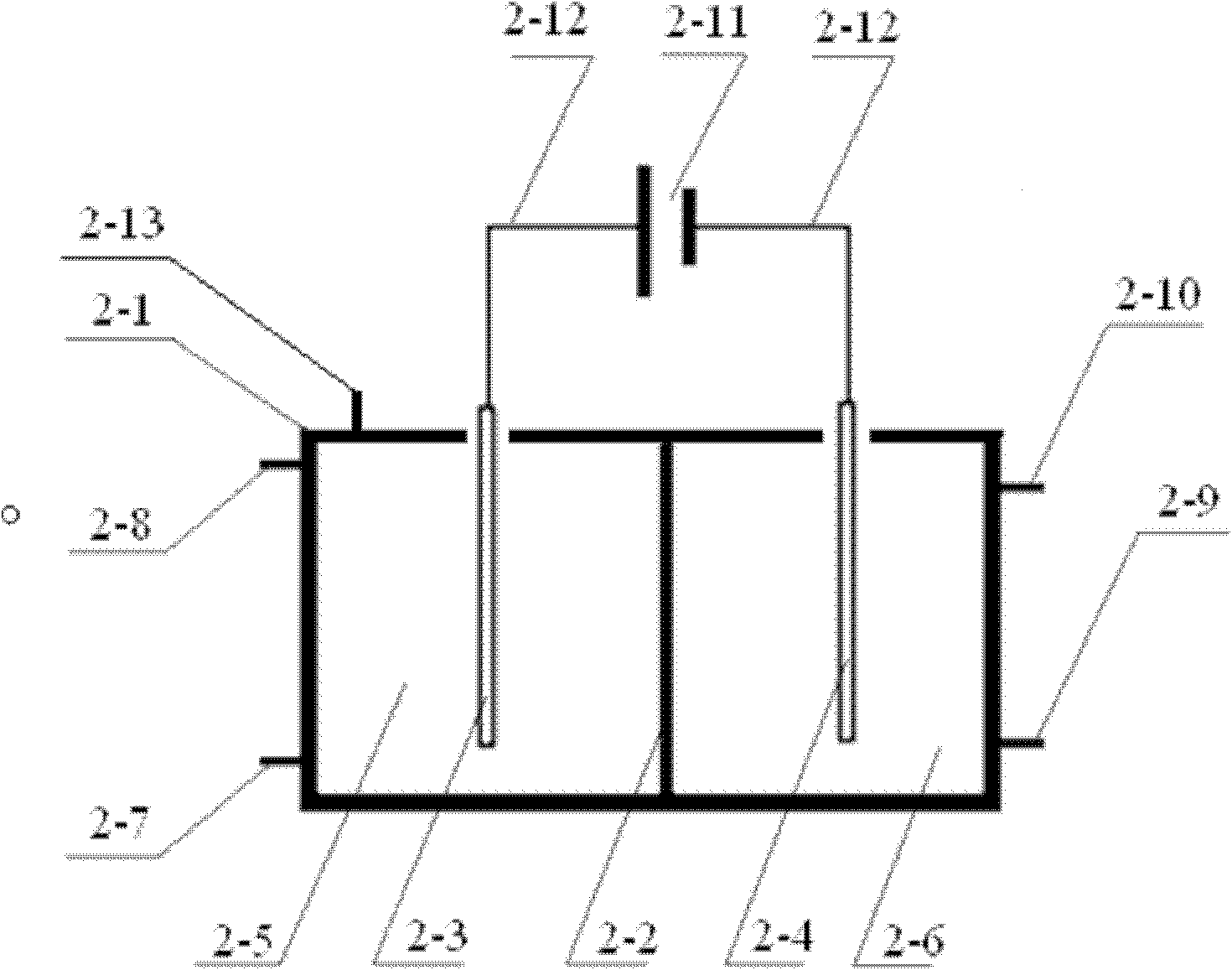
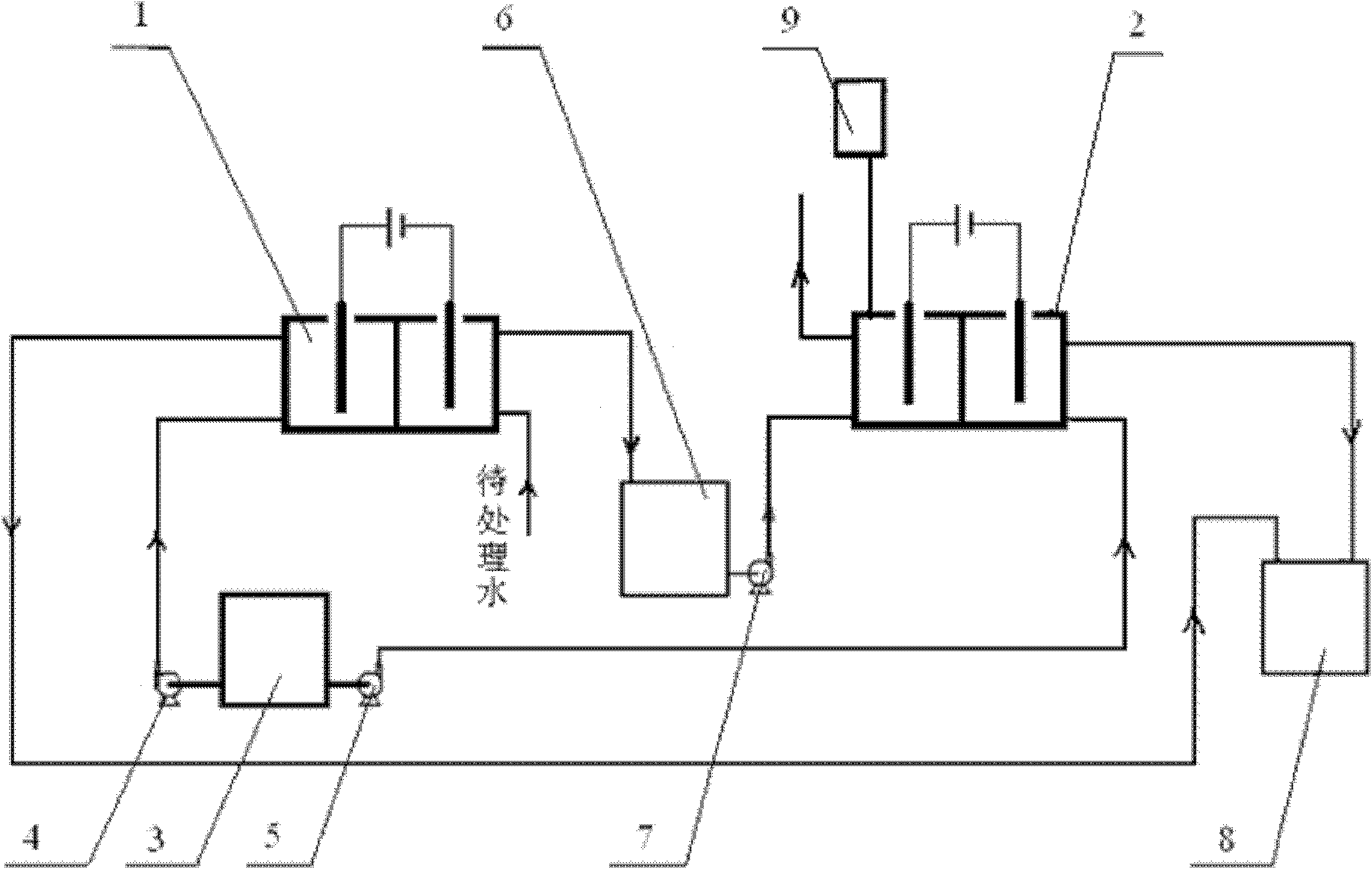
[0009] Specific implementation mode one: (refer to attached figure 1 , 2 and 3) the series electrolytic cell system of the present embodiment includes the first electrolytic cell 1, the second electrolytic cell 2, the first water tank 3, the first water pump 4, the second water pump 5, the middle water tank 6, the third water pump 7, the second Water tank 8 and gas collection device 9; wherein the first electrolytic cell 1 includes a first power supply 1-11, a first tank body 1-1, a first anode 1-3, a first cathode 1-4 and a first ion exchange membrane 1 -2, with graphite as the first cathode 1-4, with carbon felt as the first anode 1-3, the first ion exchange membrane 1-2 divides the first cell 1-1 into the first anode area 1-5 and The first cathode region 1-6, the first cathode 1-4, the first power supply 1-11 and the first anode 1-3 are connected with the first titanium wire lead 1-12, on the side wall of the first anode region 1-5 The lower part is provided with a first ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0011] Specific embodiment two: the method for removing bromate in drinking water by using the series electrolytic cell system described in specific embodiment one is carried out in the following steps: 1. The drinking water to be treated is fed from the first The second water inlet 1-9 of an electrolytic cell leads into the cathode area 1-6 of the first electrolytic cell 1, and the bromide ion concentration of the water to be treated is 0.1mg / L~2mg / L, and simultaneously the first water tank 3 The deionized water inside is passed into the first anode area 1-5 of the first electrolytic cell 1 by the first water pump 4, and second, the first power supply 1-11 applies a voltage of 1.3V to 8V, and the current density is controlled to be 1mA / cm 2 ~5mA / cm 2, the water in the first anode area 1-5 is discharged into the second water tank 8, and the water in the first cathode area 1-6 is discharged into the intermediate water tank 6; three, the water in the intermediate water tank 6 is...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0013] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is that in step one, the drinking water to be treated is fed from the cathode area water inlet 1-10 of the first electrolytic cell 1 at a speed of 5mL / min to 30mL / min. into the cathode zone 1-6 of the first electrolytic cell 1. Others are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com