Method for estimating oxide semiconductor thin film and method for managing quality of oxide semiconductor thin film
A technology of oxide semiconductors and evaluation methods, applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring devices, measuring electrical variables, etc., to achieve the effects of improving productivity, accurate quality management, and improving yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
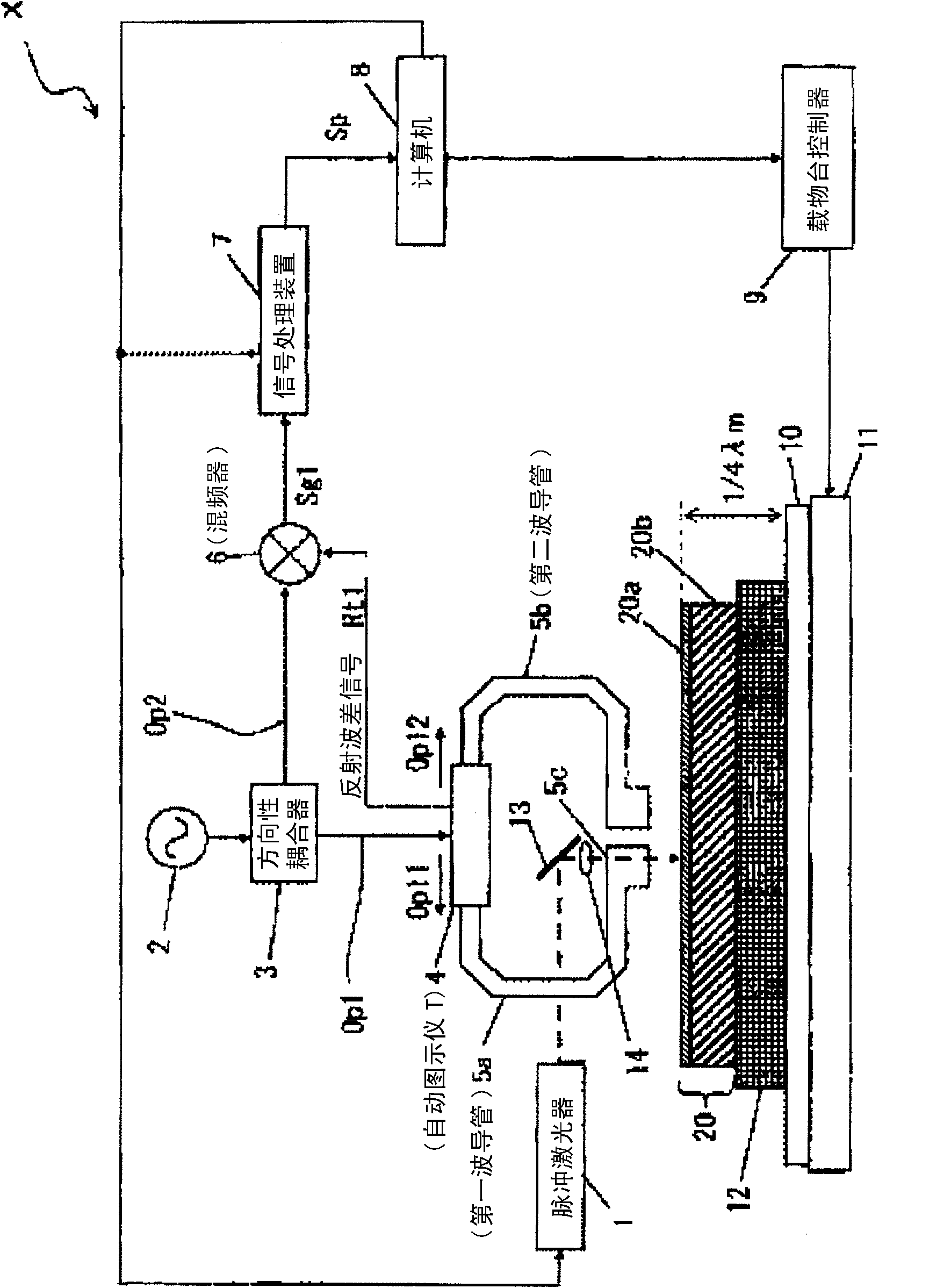
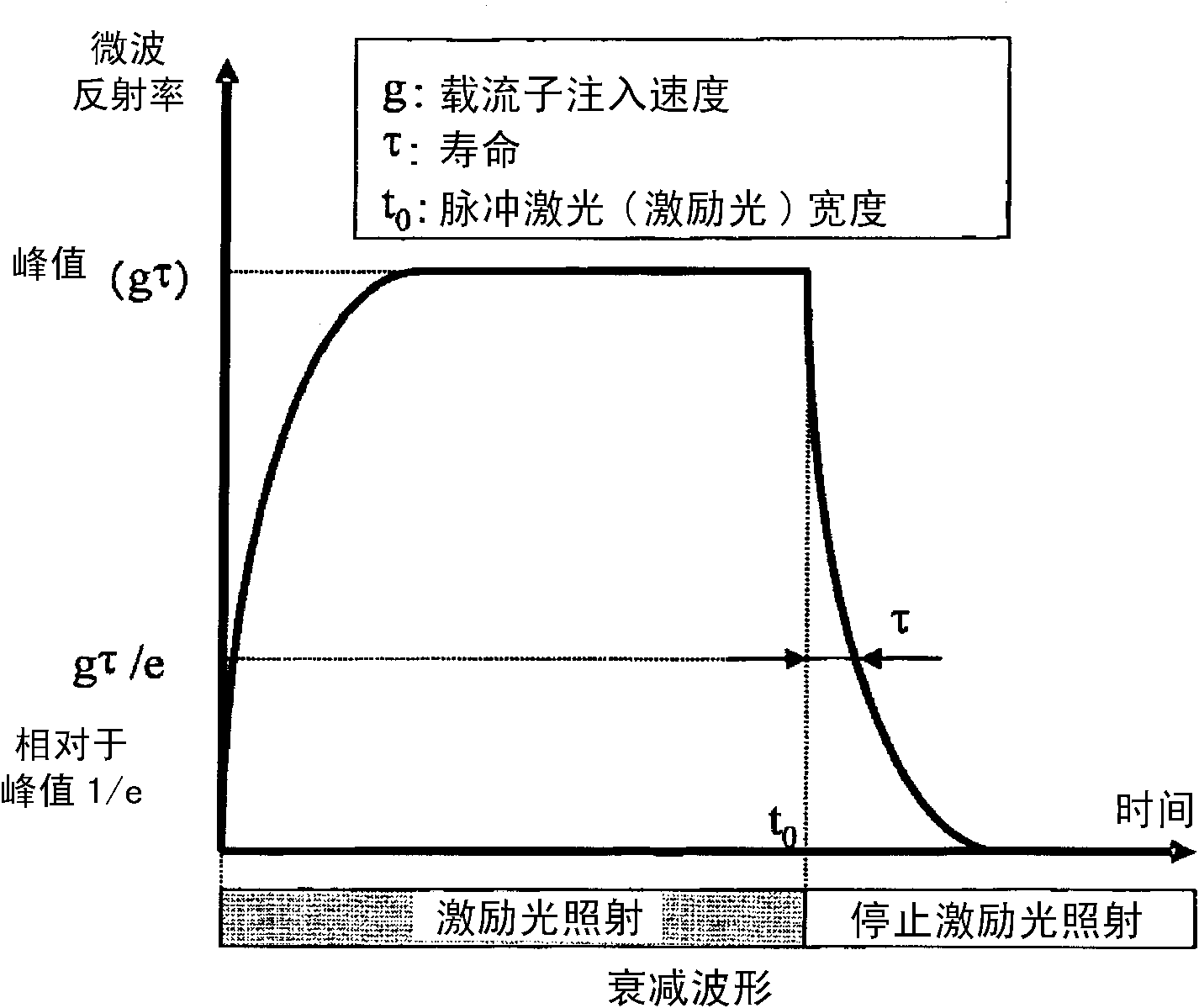
[0114] In Example 1, the correlation between the carrier mobility and the lifetime value or the peak value of the oxide semiconductor thin film was investigated by performing the following experiments.
[0115] First, a sample of an amorphous oxide semiconductor thin film (InGaZnO) was produced for measuring lifetime by the microwave photoconductivity attenuation method. First, an oxide semiconductor thin film was formed by a sputtering method on a glass substrate (EAGLE2000 manufactured by Corning: 6 inches) under the following conditions.
[0116] Sputtering target composition: 1nGaZnO 4 (In:Ga:Zn=1:1:1)
[0117] Substrate temperature: room temperature
[0118] Film thickness of oxide semiconductor layer: 100nm
[0119] Oxygen addition amount: O 2 / (Ar+O 2 ) = 2%
[0120] Next, in order to change the mobility of the oxide semiconductor thin film, a pre-annealing treatment was performed under the following conditions to obtain a sample (Sample Ne. 1 was not subjected to...
Embodiment 2
[0150] In Example 2, the following oxide semiconductor thin film samples were produced in order to measure and evaluate the lifetime in-plane distribution of the sample using the microwave photoconductivity attenuation method (using the same apparatus as in Example 1).
[0151] The oxide semiconductor thin film was formed using the Co-Sputter method of simultaneously discharging two sputtering targets with different compositions. By fixing the substrate directly under the middle of the two sputtering targets, it is possible to form a thin film in which the amount of elements composed of the two sputtering targets is inclined in the surface of the substrate. In addition, the same glass plate as that of Example 1 was used as the substrate.
[0152] Co-sputter film formation conditions are as follows.
[0153] Sputtering target composition: ZnO, ZnSnO (the composition ratio of Zn:Sn is 3:2)
[0154] Substrate temperature: room temperature
[0155] Film thickness of the substra...
Embodiment 3
[0166] In Example 3, in order to determine and evaluate the in-plane distribution of the lifetime of the sample by the microwave photoconductivity decay method (using the same apparatus as in Example 1), the following oxide semiconductor thin film samples were prepared.
[0167] The oxide semiconductor thin film was formed using the Co-Sputter method in which three sputtering targets with different compositions were simultaneously discharged. By fixing the substrate directly under the middle of the three sputtering targets, a thin film in which the elemental amounts of the three sputtering targets are made up can be formed on the surface of the substrate. In addition, the same glass plate as that of Example 1 was used as the substrate.
[0168] Co-sputter film formation conditions are as follows.
[0169] Sputtering target composition: ZnO, ZnSnO (the composition ratio of Zn:Sn is 3:2), Al 2 o 3
[0170] Substrate temperature: room temperature
[0171]Film thickness of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com