Substrate temperature control method
A technology for controlling substrates and substrates, used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, ion implantation plating, gaseous chemical plating, etc., can solve problems such as temperature rise, clean room safety risks, leakage, adhesion pollution, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
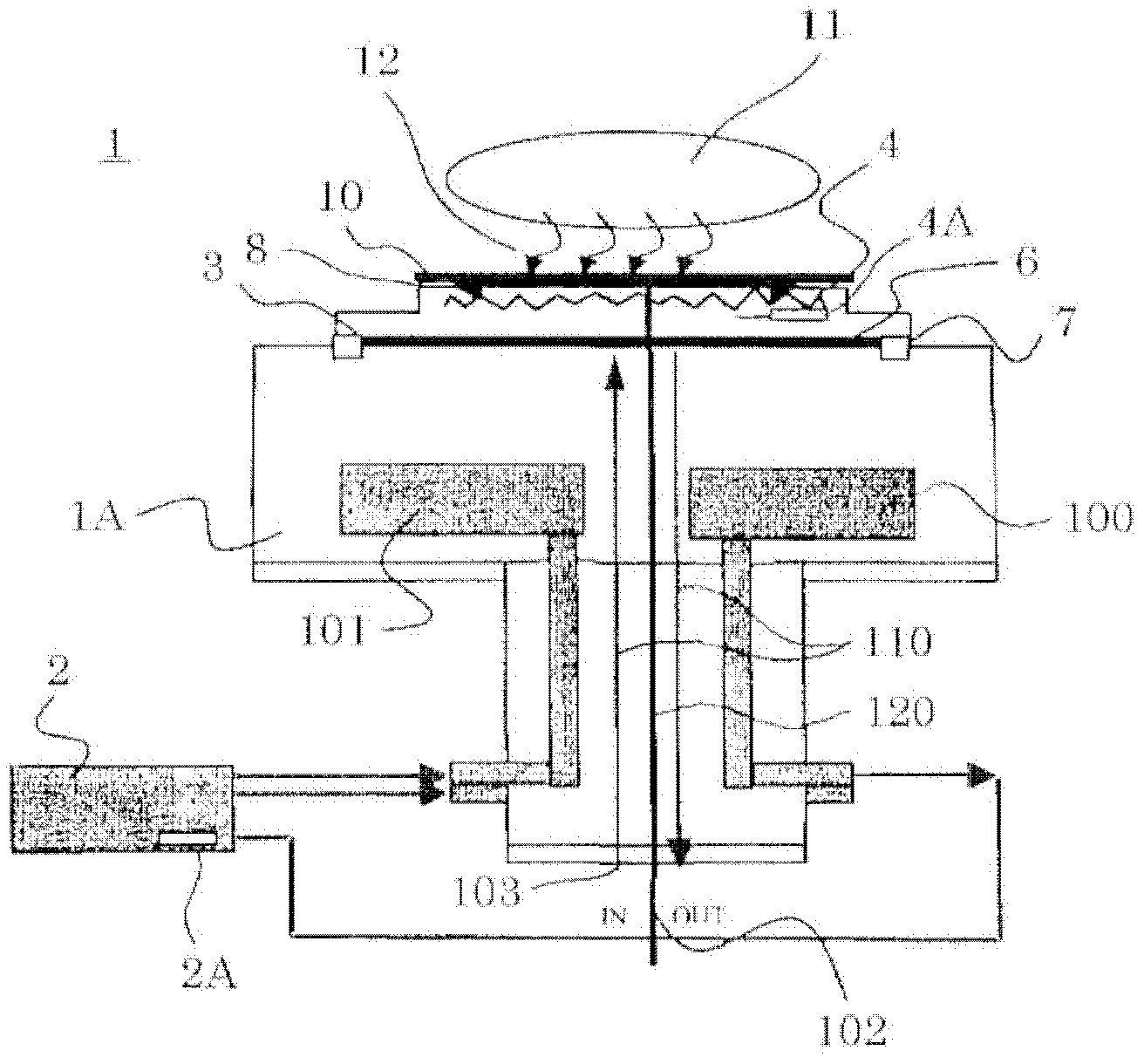
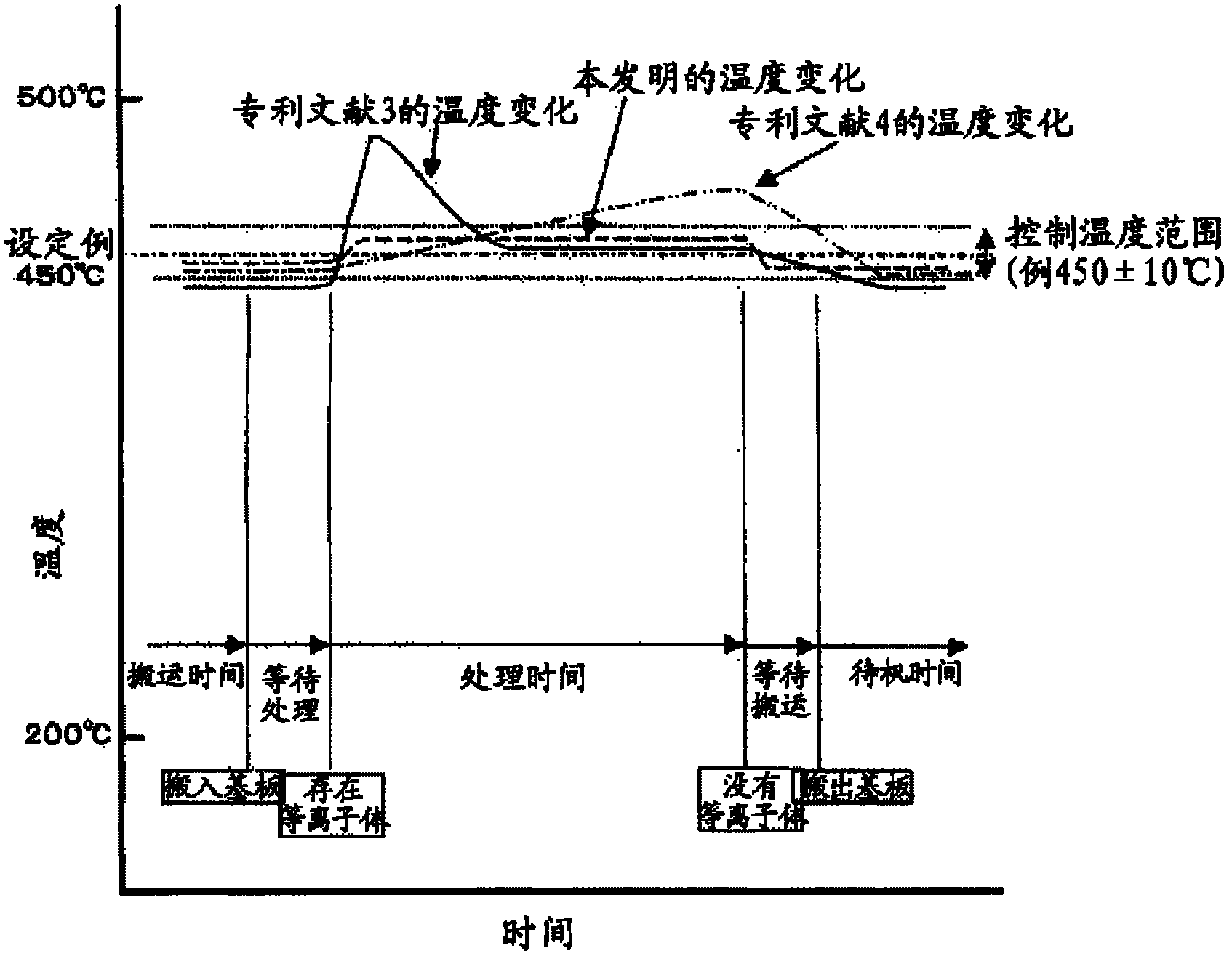
[0034] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing the first embodiment of the substrate holding device of the present invention. figure 2 It is an explanatory diagram showing the temperature change of the substrate holding device of the present invention in relation to the conventional temperature change.
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, the substrate holding device 1 according to the first embodiment is installed in a vacuum container (not shown) of a plasma processing device which is a representative device of a sputtering device. This substrate holding device 1 holds a substrate 10 by electrostatic attraction on an electrostatic chuck 3 disposed on the substrate holding side (upper part) of the holding device main body 1A.
[0036]The holding device main body 1A is, for example, a disk-shaped or cylindrical support member that supports a semiconductor wafer as a substrate 10 . A circulating medium flow path 100 through which a circulating medium (cooling medium) 10...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
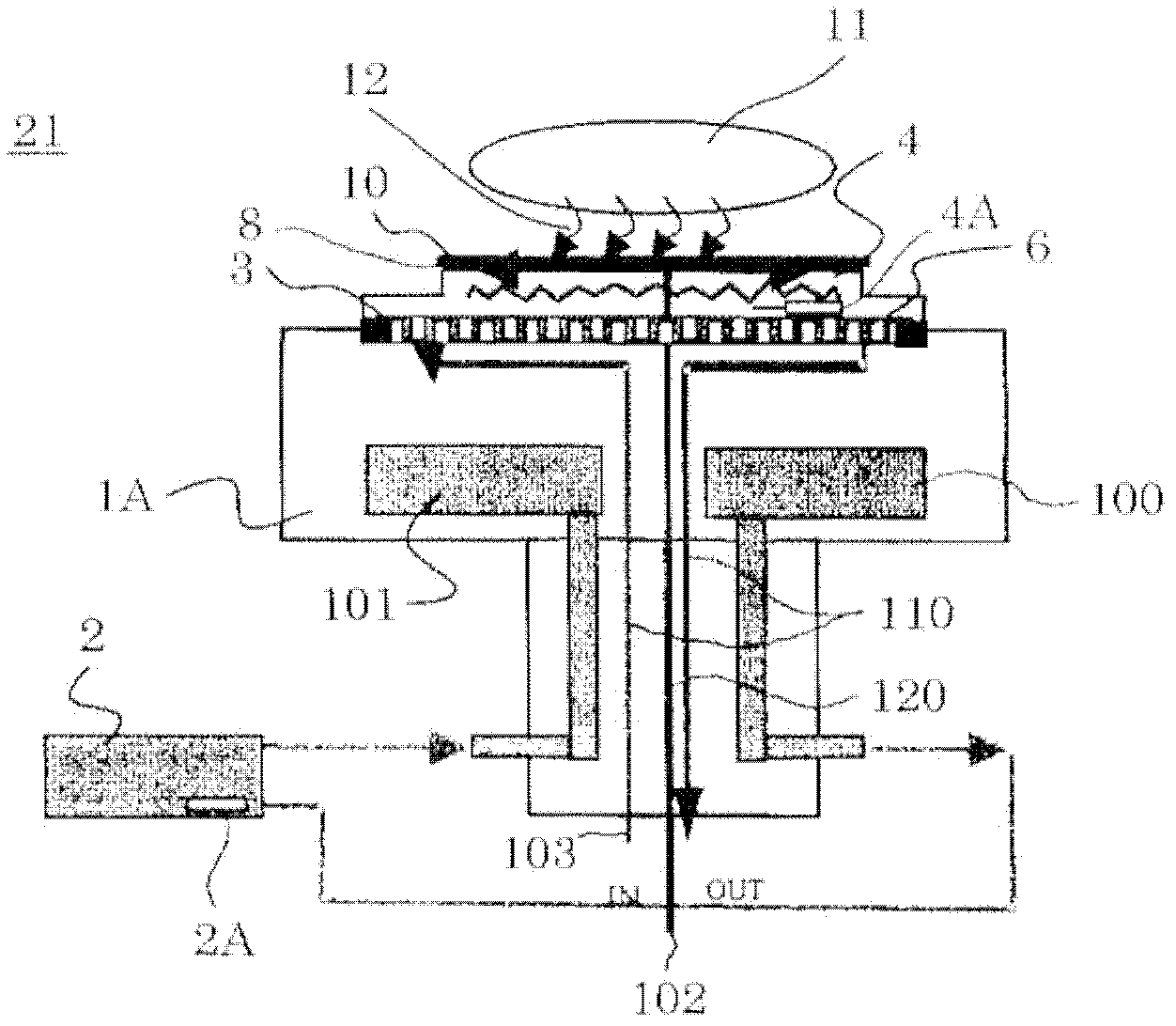
[0054] image 3 It is a schematic diagram showing the substrate holding device of the second embodiment. Figure 4 is a cross-sectional view showing the cross-sectional structure of the variable heat transfer energy member. The same reference numerals will be attached to the same components as those in the first embodiment for description.
[0055] The substrate holding device 21 of the second embodiment is a substrate holding device having the same specification as that of the first embodiment, in which the heat transfer energy variable member 6 defined and formed in the gap between the holding device main body 1A and the electrostatic chuck 3 is changed. constructed.
[0056] That is, the heat transfer energy variable member 6 in the second embodiment is divided and formed by arranging the first plate-shaped body 16 and the second plate-shaped body 17 facing each other. The first plate-shaped body 16 and the second plate-shaped body 17 has arc-shaped cooling fins 16A, 17A...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0059] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram showing the third embodiment of the substrate holding device of the present invention. figure 2 It is an explanatory diagram showing the temperature change of the substrate holding device of the present invention in relation to the conventional temperature change.
[0060] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the substrate holding device 1 of the third embodiment is installed in a vacuum chamber (not shown) of a plasma processing device typified by a sputtering device. This substrate holding device 1 holds a substrate 10 by electrostatic attraction on an electrostatic chuck 3 disposed on the substrate holding side (upper part) of the holding device main body 1A.
[0061] The holding device main body 1A is, for example, a disk-shaped or cylindrical support member that supports a semiconductor wafer as a substrate 10 . A circulating medium flow path 100 through which a circulating medium (cooling medium) 101 flows is defined and formed in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com