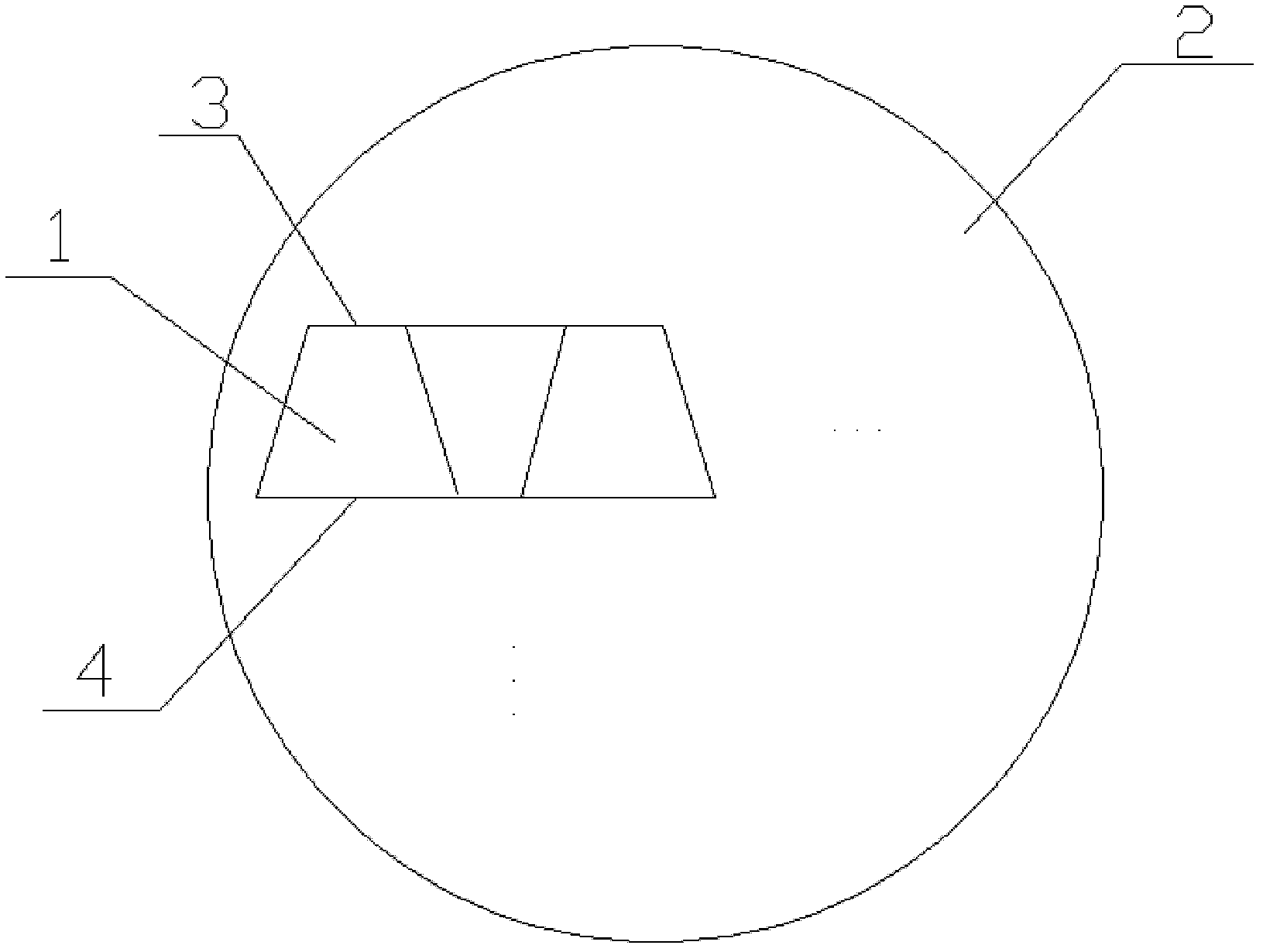Wafer of planar optical waveguide splitter
A planar optical waveguide and splitter technology, applied in the direction of light guides, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large insertion loss temperature changes, poor etching uniformity, wafer waste, etc., to improve process unevenness performance, reduce polarization-dependent loss, and reduce product cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the preferred embodiments described here are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention.
[0018] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, a wafer of planar optical waveguide splitters adopts planar optical waveguide splitter chips 1 in the shape of trapezoidal chips, and is arranged on the wafer 2 in reverse order.
[0019] The shape of the trapezoidal chip of the planar optical waveguide splitter chip 1 is an isosceles trapezoid, the upper bottom (short side) is used as the input terminal 3 , and the lower bottom (long side) is used as the output terminal 4 .
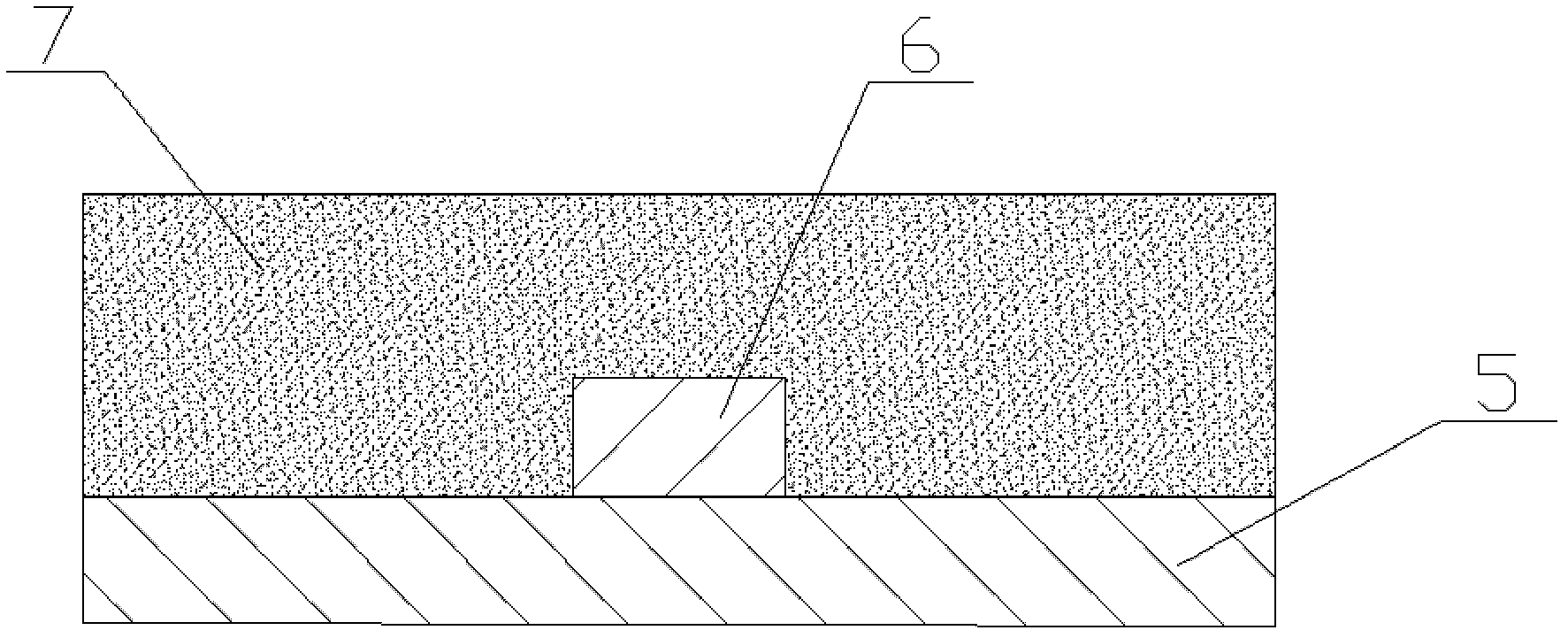
[0020] The substrate 5 of the planar optical waveguide splitter chip 1 is silicon dioxide.
[0021] The specific process is as follows:
[0022] The waveguide core 6 is directly grown on the si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com