Method and reagent for regulation and control of germ layer differentiation of embryonic stem cell and early embryo
A technology of embryonic stem cells and nuclei, applied in embryonic cells, biochemical equipment and methods, animal cells, etc., can solve problems such as unclear research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0233] Preparation of Competent Bacteria and Preparation of Plasmid DNA
[0234] Preparation of competent bacteria (rubidium chloride method)
[0235] Use an inoculation loop to pick a small amount of frozen strains and inoculate them on a solid LB agar plate, and incubate at 37°C for 12-15 hours. Pick a single clone, inoculate into 30ml SOB liquid medium, and culture overnight (12-15 hours) at 37°C on a shaker. The next day, take 8ml of the bacterial solution and inoculate it into 200ml of SOB, and shake it on a shaker at 37°C until OD 590 = 0.3 to 0.5. Place the bacterial solution in a salt ice bath for 15 minutes, then centrifuge at 4°C, 4000g, for 5 minutes. Resuspend the bacteria with 64ml of pre-cooled buffer I, bath in salt ice for 15 minutes, centrifuge at 4°C, 4000g, for 5 minutes. Resuspend the bacteria with 16ml of pre-cooled buffer II on ice, and then immediately distribute them into pre-cooled Ep tubes, each 100ul, quick-freeze with liquid nitrogen, and store ...
Embodiment 1
[0346] Example 1, Calcinuerin-NFAT signaling pathway is necessary for ES cell germ layer differentiation
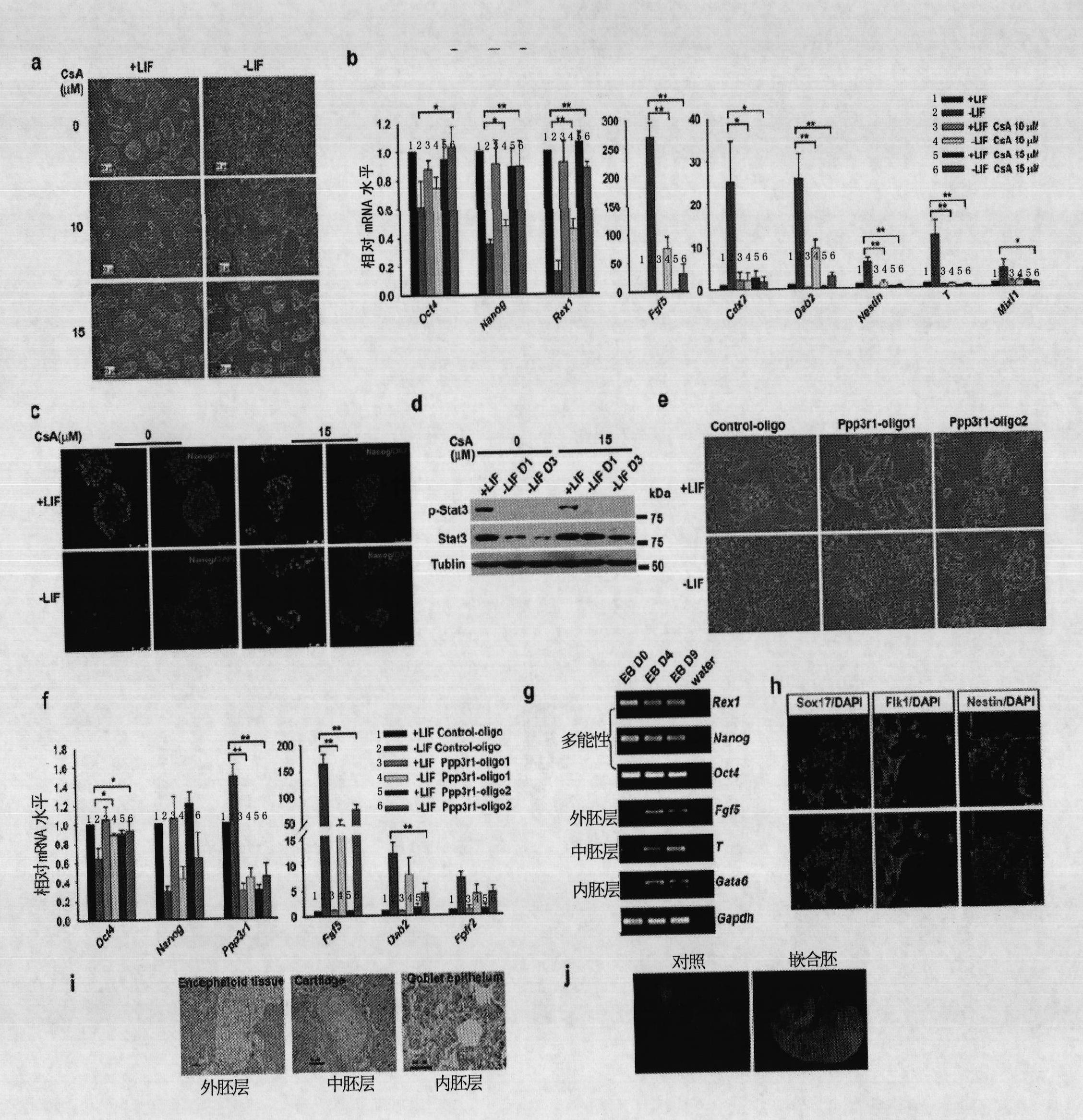
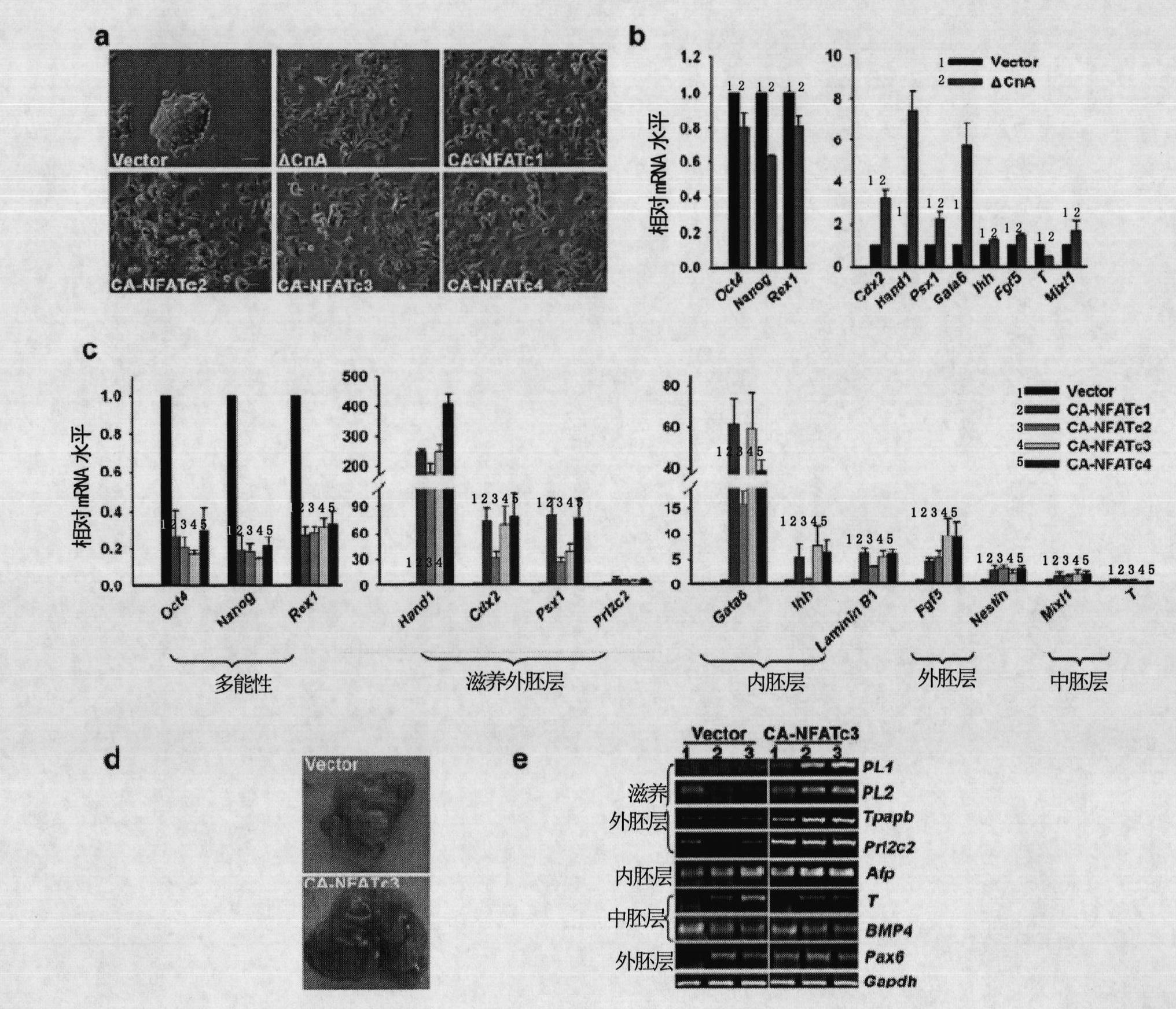
[0347] After the PB transposon mutated the endogenous gene Ppp3r1 of ES cells, ES cells could not undergo normal germ layer differentiation under the condition of removing LIF to induce ES cell differentiation, suggesting that the Calcinuerin-NFAT signaling pathway potentially plays an important role in regulating the germ layer differentiation of ES cells .
[0348] To test this hypothesis, the present inventors treated ES cells with the calcinuerin inhibitor CsA, and examined cell morphology and gene expression with the addition of LIF (+LIF) or withdrawal of LIF (-LIF). After the ES cells were cultured without LIF, the cell morphology differentiated significantly, and the germ layer differentiation marker genes Fgf5, Cdx2, Dab2, Nestin, T, and Mixl1 were all significantly increased, while the pluripotency marker genes Oct4, Nanog, and Rex1 were all decreased ( figure ...
Embodiment 2
[0351] Example 2, Calcinuerin-NFAT signaling pathway is activated during ES cell differentiation
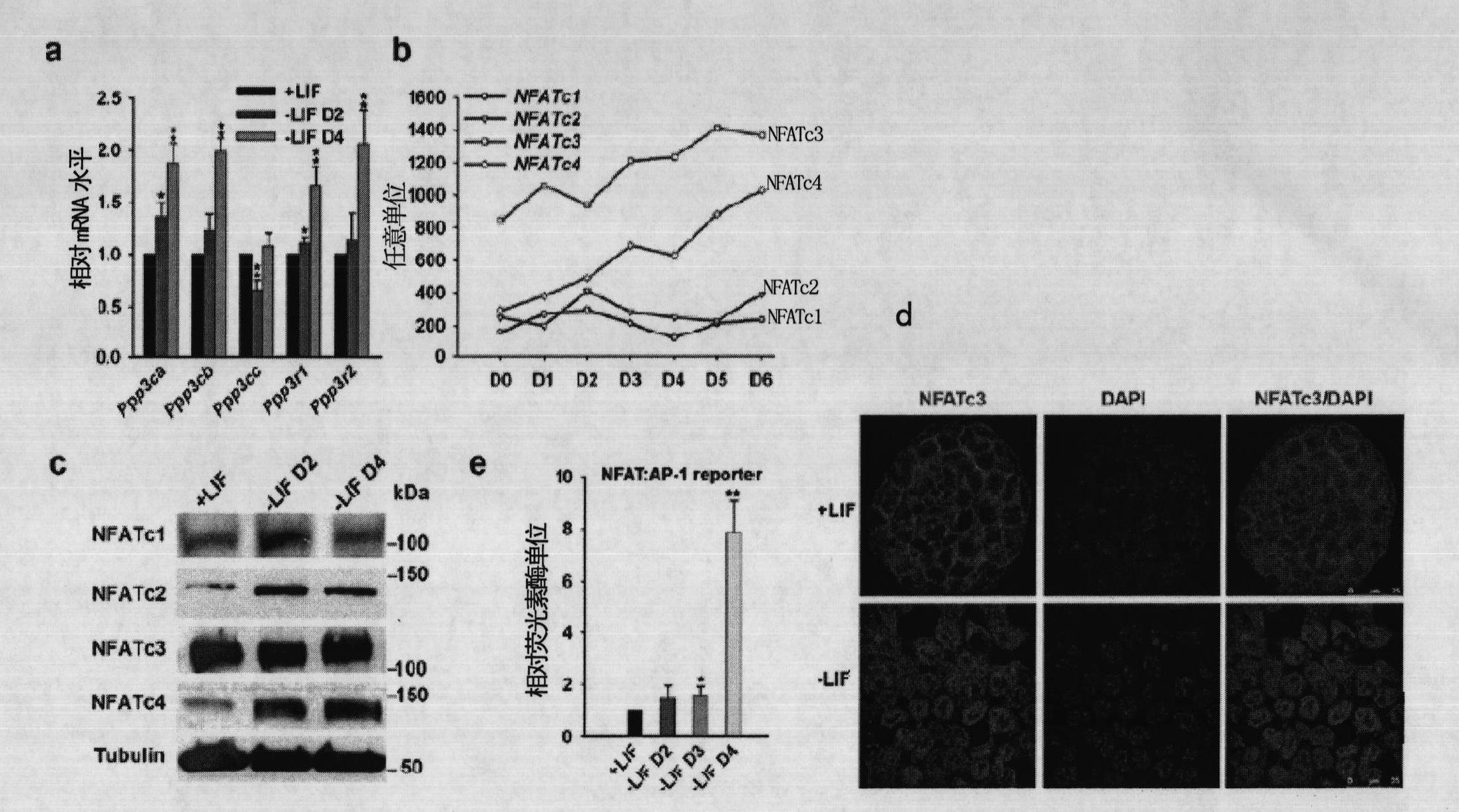
[0352] The present inventors further detected the expression of Calcinuerin-NFAT signaling pathway in ES cell differentiation process. The transcription levels of each subunit of Calcinuerin increased during the differentiation of ES cells induced by LIF removal ( figure 2 a).
[0353] Western blot and microarray data showed that NFATc3 and NFATc4 among NFAT family members were at high expression levels in mouse ES cells. The protein level of NFATc4 increased significantly during the differentiation of ES cells, while the protein level of NFATc3 was always highly expressed ( figure 2 b, c).
[0354] Notably, NFATc3 localizes to the cytoplasm in undifferentiated ES cells, whereas it localizes to the nucleus after withdrawal of LIF ( figure 2 d), showing that NFATc3 is activated during ES cell differentiation.
[0355] The present inventors further detected the activity of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com