Distance measuring device and image pickup device
A technology of distance measuring device and camera element, which is applied in the direction of measuring device, focusing device, measuring distance, etc., which can solve the problems of low degree of freedom and distance measurement, and achieve the effect of improving the degree of freedom of setting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
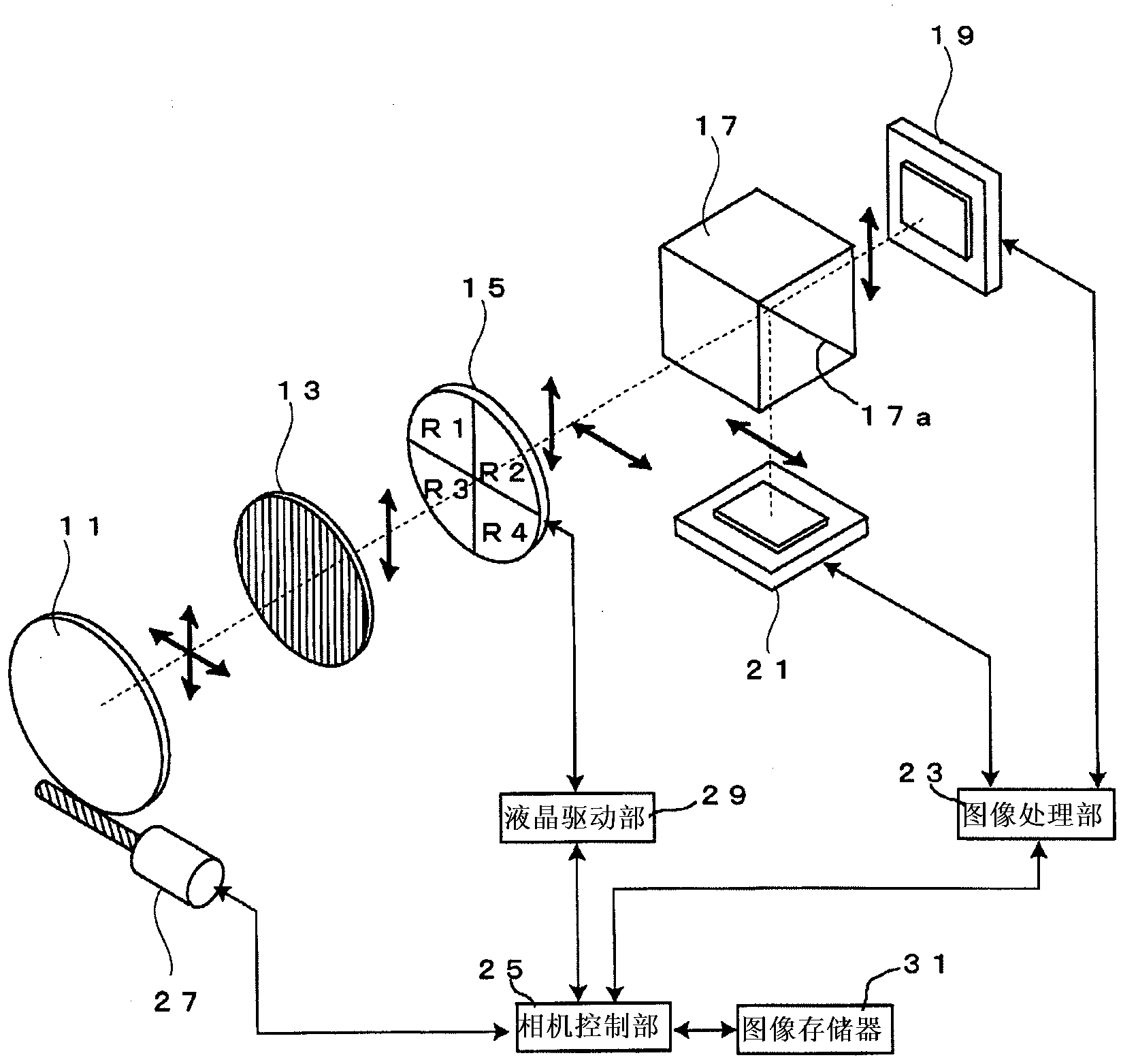
[0035] figure 1 The first embodiment of the distance measuring device of the present invention is shown. In this embodiment, the present invention is applied to an imaging device including a camera.
[0036] The imaging device includes: an objective lens 11, a polarizing element 13, a liquid crystal rotator 15, a polarization separation element 17, a first imaging element 19, a second imaging element 21, an image processing unit 23, a camera control unit 25, an AF driving mechanism 27, a liquid crystal driving Part 29, image memory 31.
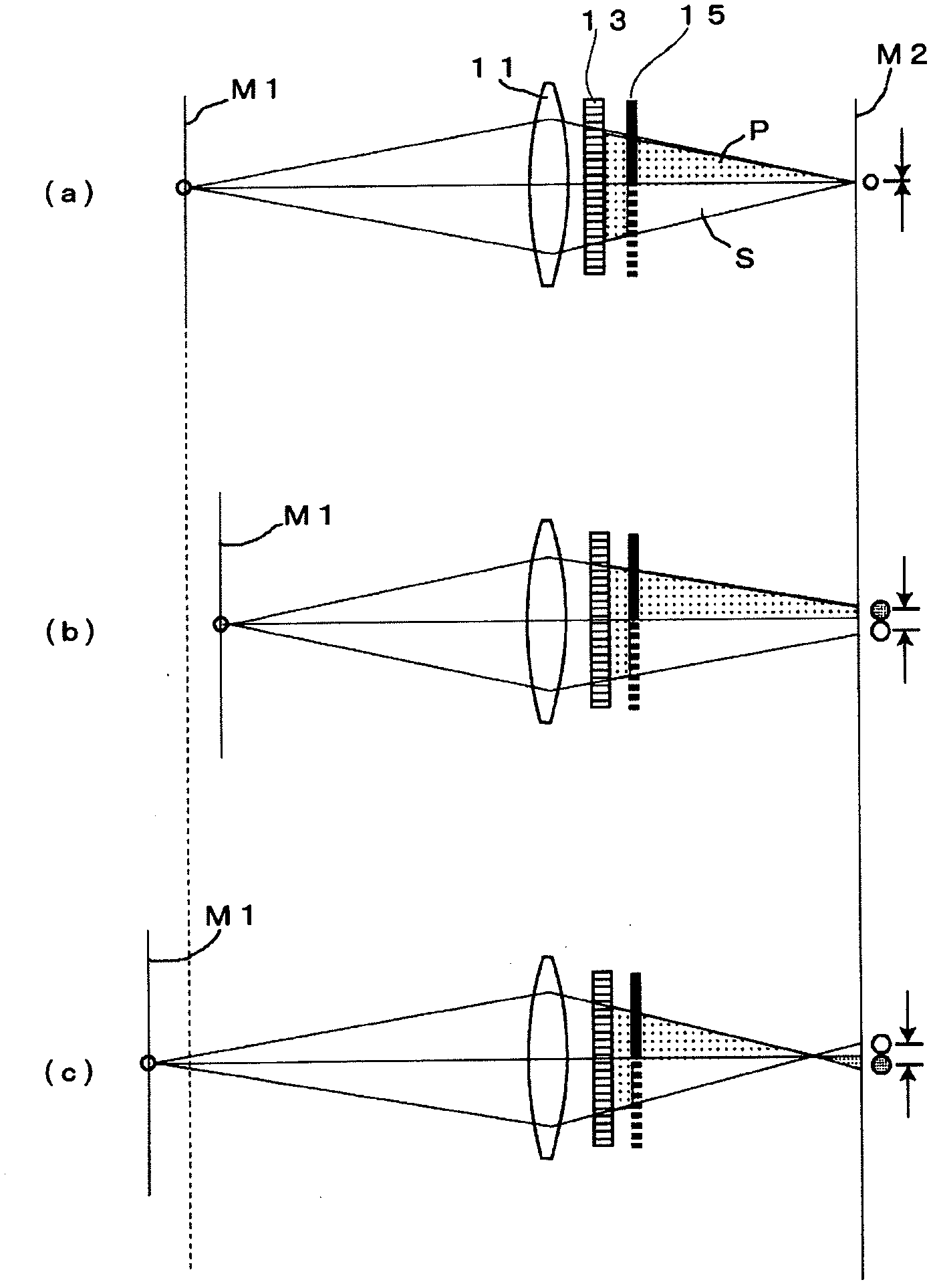
[0037] A polarizing element 13 is provided at the pupil position of the objective lens 11 . The polarizing element 13 is constituted by a polarizing filter for aligning the polarization axis of the light from the objective lens 11 to, for example, P-polarized light.
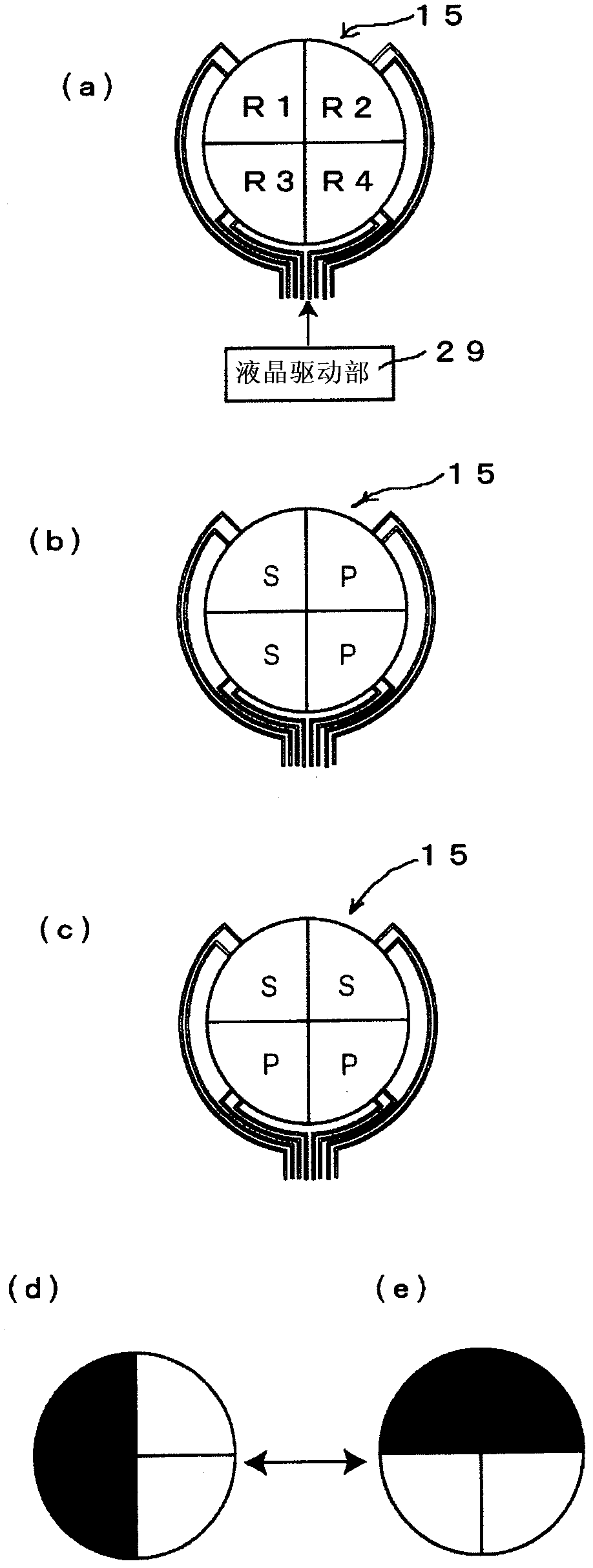
[0038] The liquid crystal rotator 15 electrically changes the polarization axis of light. Such as figure 2 As shown in (a), the light transmission surface of the liquid cry...
no. 2 approach
[0050] Figure 4 It shows the second embodiment of the distance measuring device of the present invention. In this embodiment, the present invention is applied to an imaging device including a camera. In addition, in this embodiment, the same code|symbol is attached|subjected to the same element as 1st Embodiment, and detailed description is abbreviate|omitted.
[0051] The imaging device includes: an objective lens 11, a liquid crystal shutter 33, a pupil splitting liquid crystal rotator 35, a polarization separation element 17, a first imaging element 19, a second imaging element 21, an image processing unit 23, a camera control unit 25, and an AF drive mechanism 27 , a liquid crystal drive unit 29 , and an image memory 31 .
[0052] A liquid crystal shutter 33 is provided at the pupil position of the objective lens 11 . The liquid crystal shutter 33 includes a first polarizing element 37 , a pupil mask liquid crystal rotator 39 , and a second polarizing element 41 .
[...
no. 3 approach
[0072] Figure 9 A third embodiment of the imaging device of the present invention is shown.
[0073] In this embodiment, the drive area of the pupil mask liquid crystal rotator 39A is finely divided.
[0074] Such as Figure 9 As shown in (a), the pupil-mask liquid crystal rotator 39A finely divides the drive area like a general dot-matrix liquid crystal display. More functions can be realized by driving the fine driving area according to the situation.
[0075] (1) if Figure 9 As shown in (b), by setting the same transmission region as a simple fixed pattern, it is possible to function as a pupil mask.
[0076] (2) if Figure 9 As shown in (c), at the time of exposure, the transmissive region is provided as a concentric circle with respect to the optical axis, and can function as a diaphragm.
[0077] (3) if Figure 9 As shown in (d), by adjusting the amount of transmission in the transmission area together with the aperture drive, it is possible to adjust the amou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com