Method for detecting initial position of rotor of gearless tractor for elevator
A technology of rotor initial position and gear traction machine, which is applied in the control of generators, electronic commutators, motor generators, etc., and can solve problems such as out of control and misjudgment of control systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
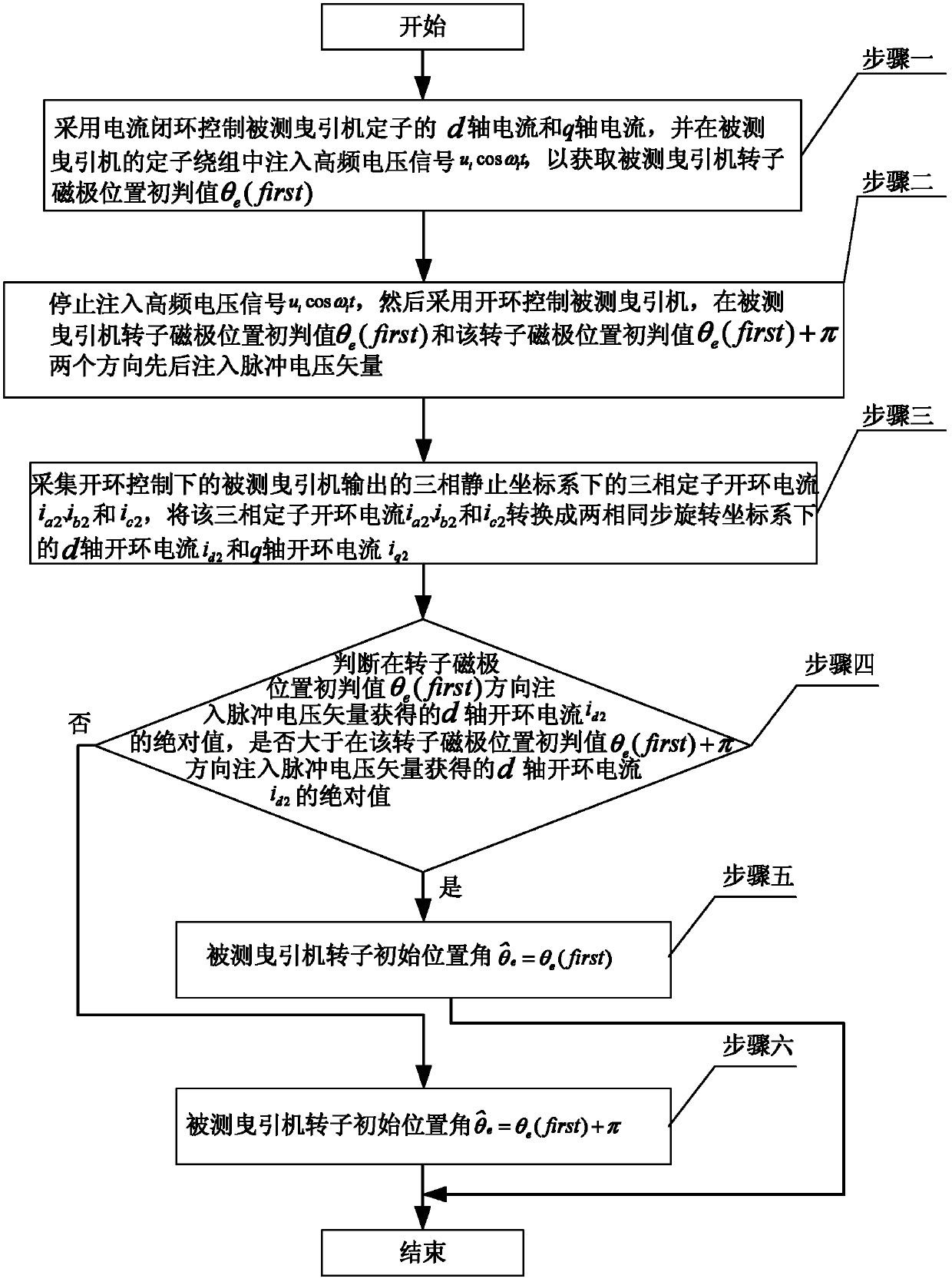
[0038] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 5 Describe this embodiment, the method for detecting the initial position of the rotor of the elevator gearless traction machine described in this embodiment, the traction machine is a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and it includes the following steps:
[0039] Step 1: Use current closed-loop control of the d-axis current and q-axis current of the stator of the traction machine under test, and inject a high-frequency voltage signal u into the stator winding of the traction machine under test i cos ω i t, to obtain the initial judgment value θ of the rotor magnetic pole position of the tested traction machine e (first); where u i Indicates the amplitude of the high-frequency voltage signal, ω i Indicates the frequency of the high-frequency voltage, and t indicates the time;
[0040] Step 2: stop injecting high-frequency voltage signal u i cos ω i t, and then use open-loop control o...
specific Embodiment approach 2
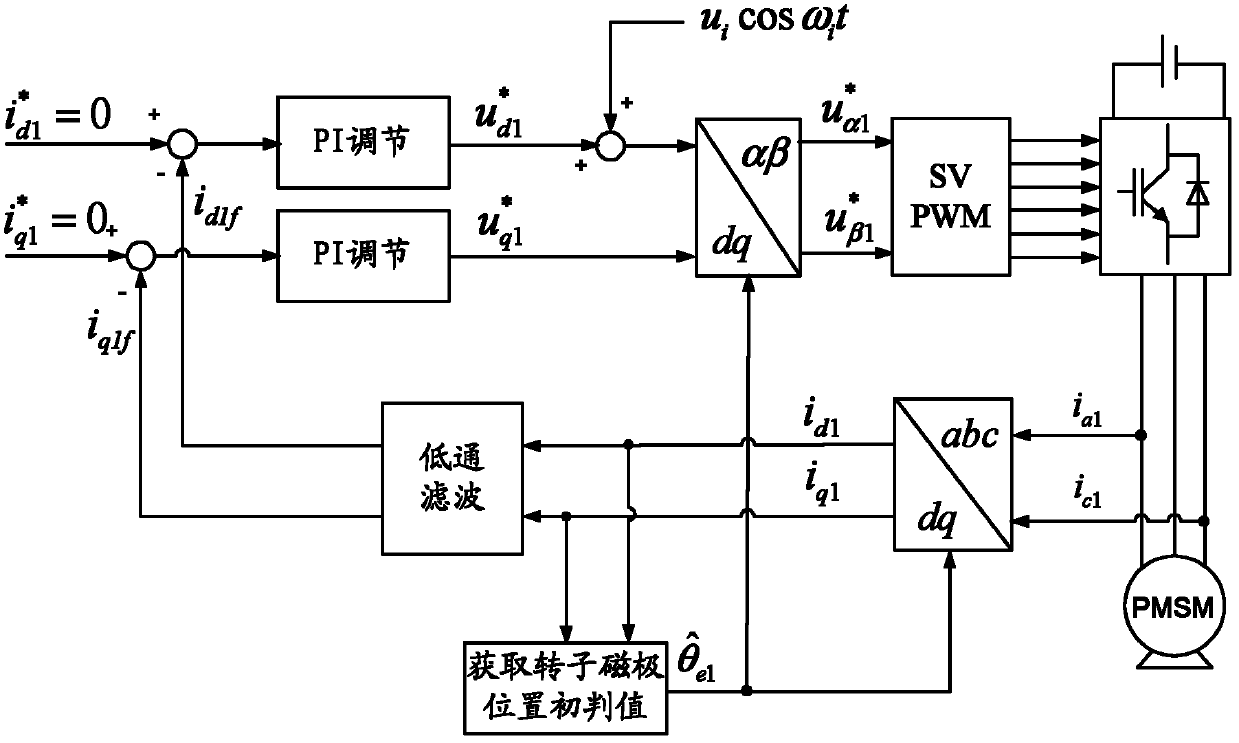
[0048] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 2 , image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1. In step 1 of this embodiment, the initial judgment value θ of the rotor magnetic pole position of the measured traction machine is obtained. e The specific method of (first) is:
[0049] Step 11: Initialize the d-axis closed-loop given current of the stator of the traction machine under test q-axis closed-loop given current and the given position angle of the measured traction machine rotor Make it all 0;
[0050] Step 1 and 2: set the d-axis closed-loop current of the stator The d-axis closed-loop current feedback value i of the stator d1f After making a difference, the d-axis closed-loop given voltage of the stator is formed through PI adjustment The d-axis closed-loop given voltage with high frequency voltage signal u i cos ω i t is superimposed to form a stator d-axis close...
specific Embodiment approach 3
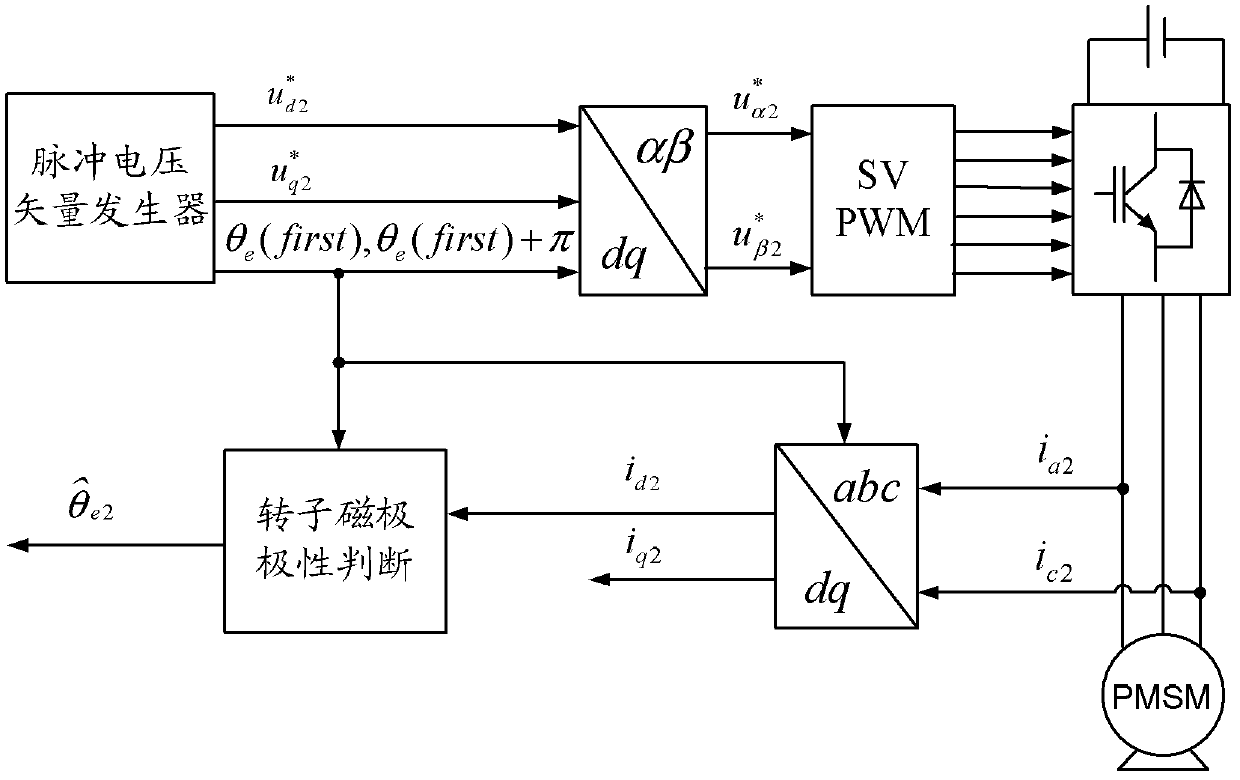
[0089] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination image 3 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1 or 2. The specific method of using open-loop control of the traction machine under test in step 2 of this embodiment is:
[0090] Using a pulse voltage vector generator to form a two-phase synchronous rotating coordinate system for the stator d-axis open-loop given voltage and stator q-axis open-loop given voltage And the stator d-axis open-loop given voltage and stator q-axis open-loop given voltage Convert the two-phase synchronous rotating coordinate system to the two-phase stationary coordinate system to obtain the stator voltage reference value in the two-phase stationary coordinate system and The stator voltage reference and The control of the traction machine under test is realized through the output of the three-phase inverter bridge to the traction machine under test, and the three-phase inverter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com