Diagenesis simulation experiment device
A technology for simulating experimental devices and diagenesis, which can be used in measuring devices, material inspection products, suspension and porous material analysis, etc., and can solve the problems of low automation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
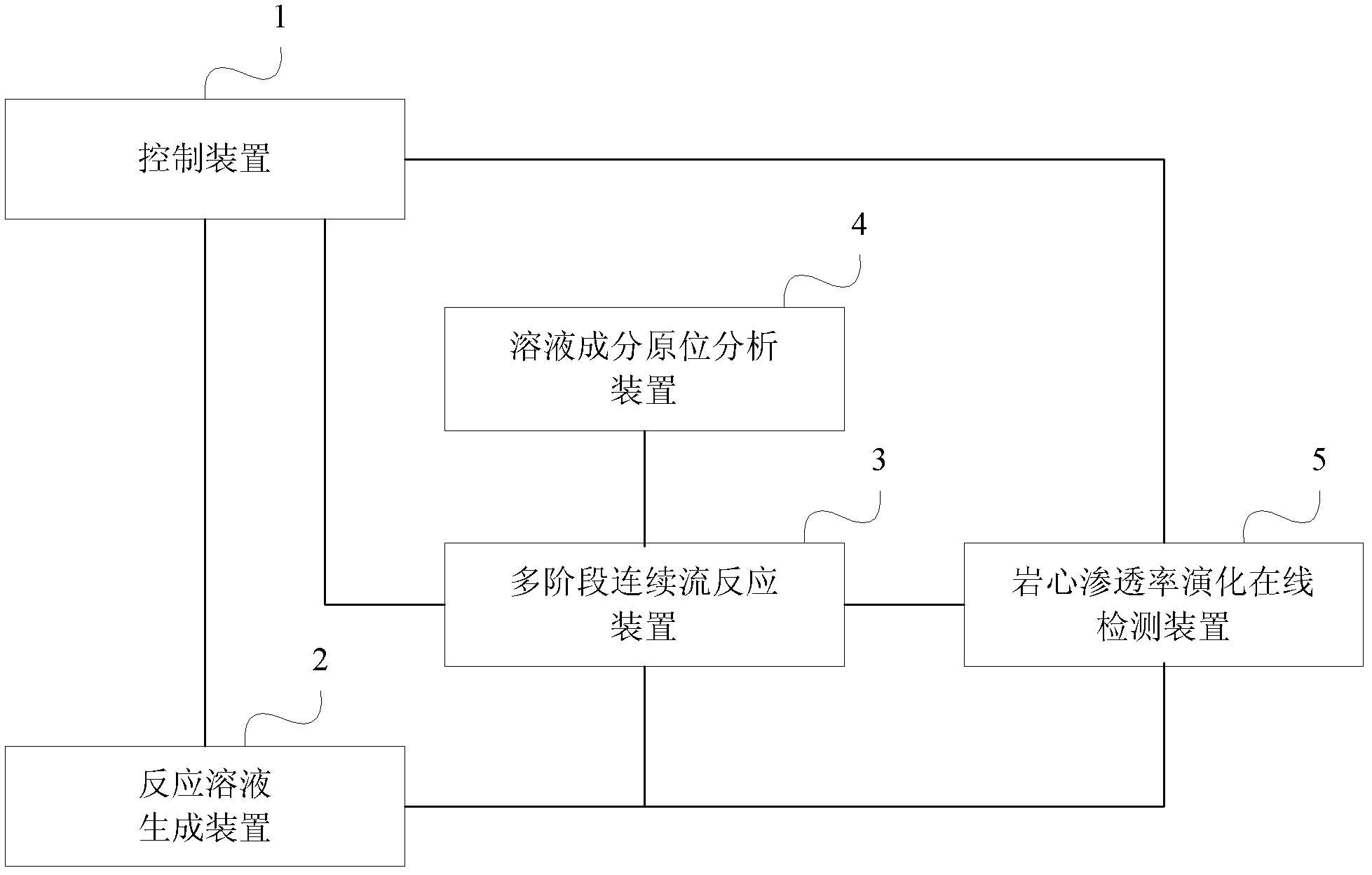
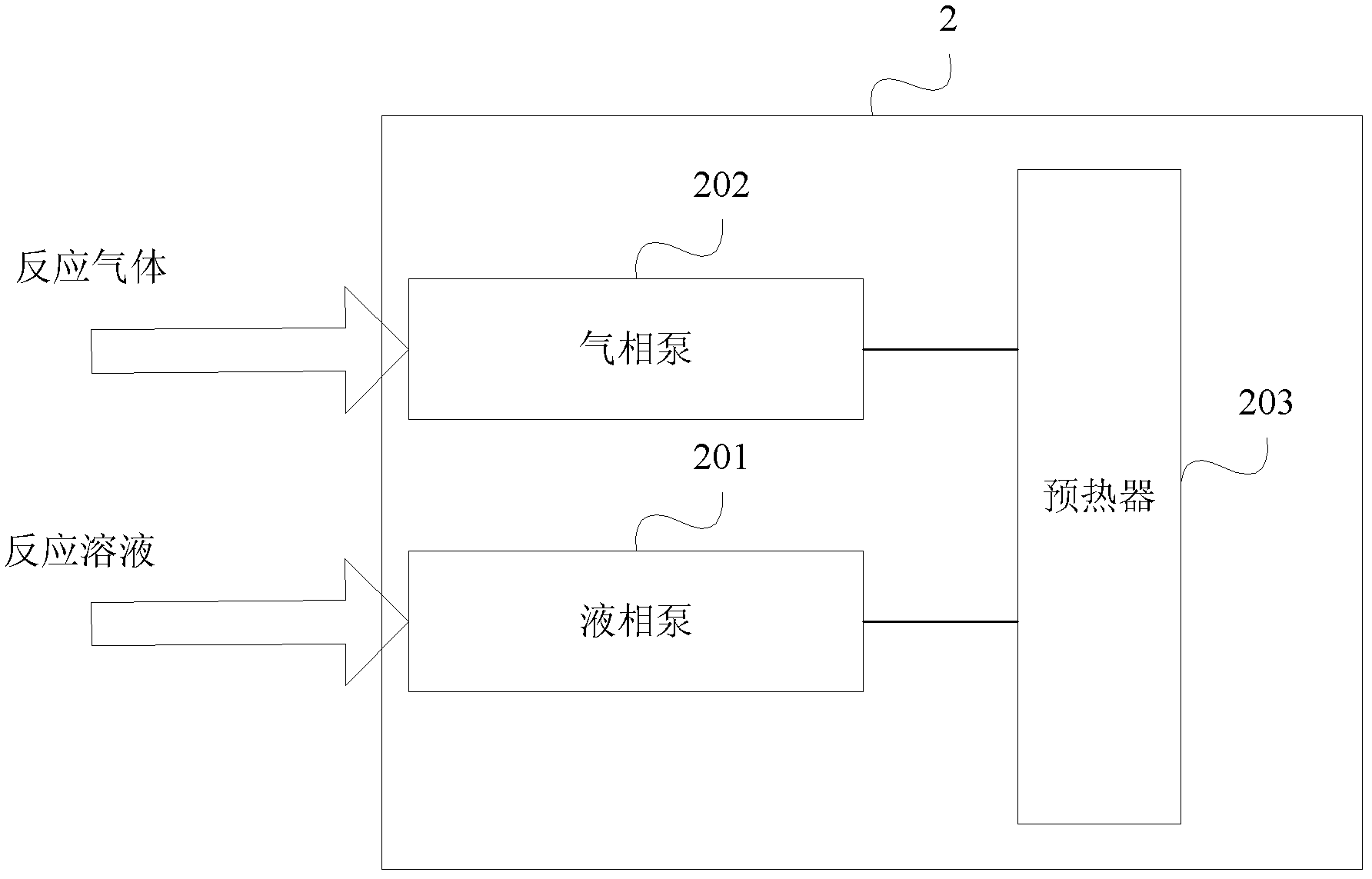
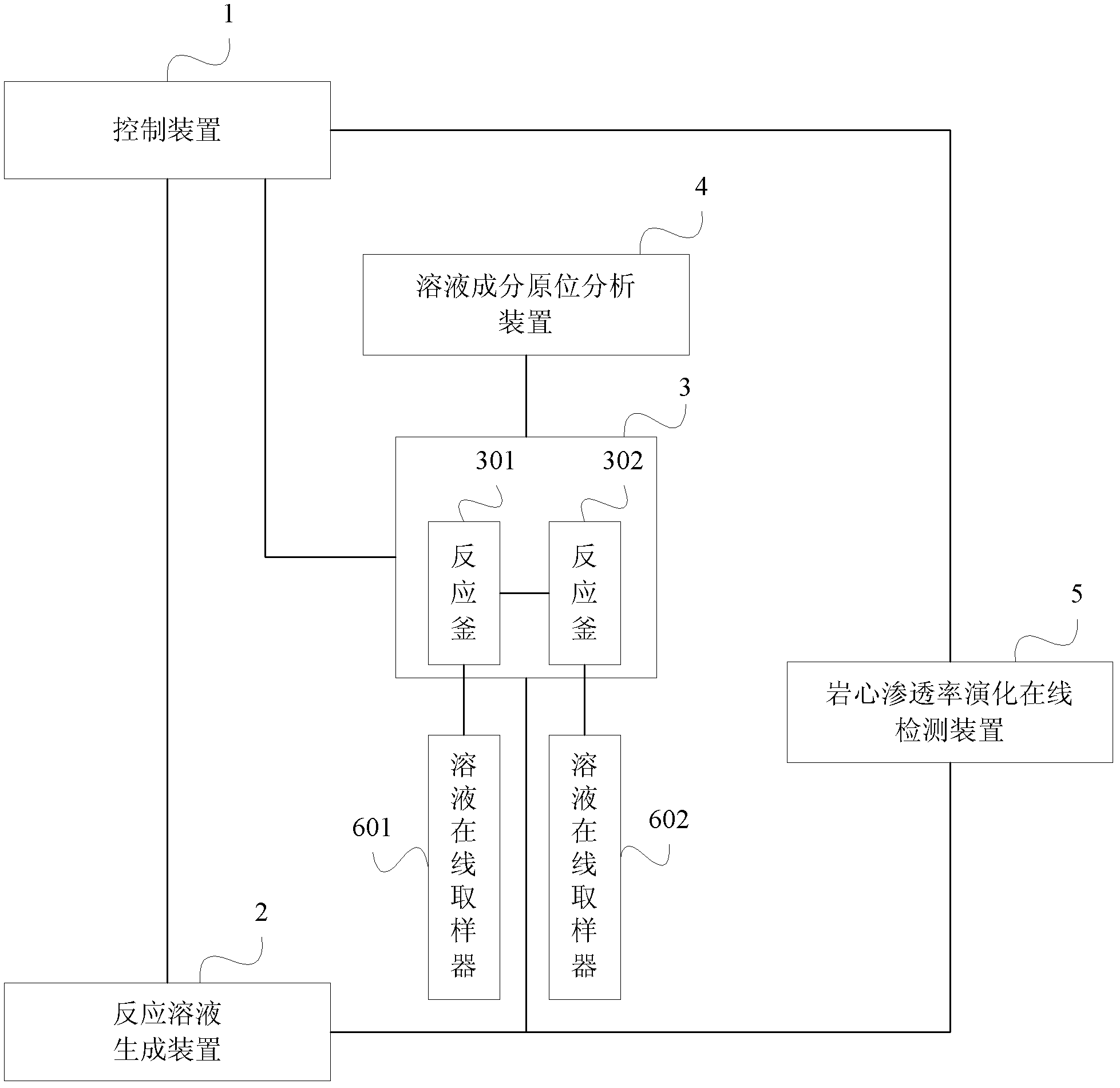
[0043] Figure 12It is a structural schematic diagram of a specific embodiment of the diagenesis simulation experiment device of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the experimental device of the present invention includes reactor R1, reactor R2, gas phase pump F1, liquid phase pump F2, preheater W1, temperature changer W2, overvoltage protector C1, overvoltage protector C2, temperature Detector T1, temperature detector T2, condenser W3, reverse pressure controller P, gas-liquid separator S, in-situ observation pool B1, in-situ observation pool B2, optical fiber probe X and spectrum of the solution composition in-situ analysis device Analyzer G, sampling tube Q1, sampling tube Q2 and valves V4, V5, V11, V12 of solution online sampler, core holder R3 of real-time online permeability detection device, differential pressure detector P1, manual pump F3, and There are also a multi-stage continuous flow reaction device and a heating device (not shown) of a real-time onli...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The function of the present invention in diagenesis research will be introduced below through a specific experiment.
[0052] In clastic rock formations, a large amount of carbonate cements can be observed, but it is difficult to find secondary pores formed by the dissolution of carbonates. Instead, the spaces formed by the dissolution of aluminosilicates such as feldspar are secondary pores. This phenomenon is inconsistent with the general understanding that carbonate rocks are more soluble than silicate rocks. Geologists proposed a carbonate regression dissolution model to explain the above phenomenon, that is, a relatively low-temperature shallow buried environment is more conducive to the dissolution of carbonate minerals, and it was proved by thermodynamic calculations. However, there are many unfavorable factors for the proof and interpretation of diagenetic models by means of thermodynamic calculations: 1) the data of thermodynamic calculations mostly come from r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com