Method for preparing polysulfonate microporous fibre non-woven fabric
A technology of non-woven fabrics and polysulfones, applied in the field of preparation of microporous fiber non-woven fabrics, which can solve the problems of high processing temperature, low solubility, unfavorable microcellular foaming, etc., and achieve the effect of high tensile strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
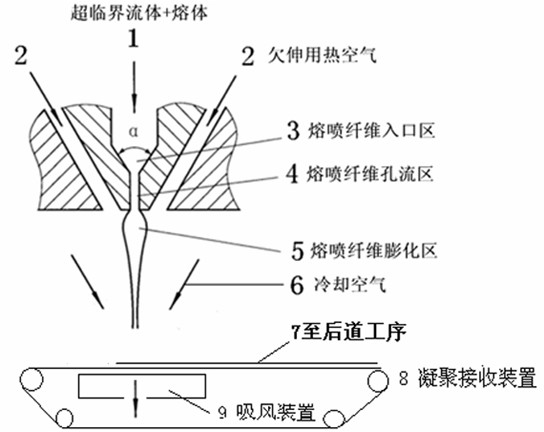
[0030] The solid chips of polyarylsulfone resin are fed quantitatively to the screw, and the solid chips of polysulfone resin are conveyed and preheated in the screw feeding section, and then compacted and gradually melted in the screw compression section. In the screw melting section, supercritical fluid N with a temperature of 50-380°C and a pressure of 7-40MPa 2 Inject into the polysulfone melt through the injection device, supercritical N 2 The mass ratio to polysulfone polymer is 1:250-1:100 to form a homogeneous polysulfone melt. In the filter section, the homogeneous polysulfone melt should pass through the filter medium to filter out impurities and catalyst remaining after polymerization. In the part of the metering pump, the homogeneous polysulfone melt is metered (10-500000g / h) by the gear metering pump to precisely control the fineness and uniformity of the fibers. Such as figure 1 As shown, the arrow A in the figure indicates the injection direction of the homog...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The solid chips of polyarylsulfone resin are fed quantitatively to the screw, and the solid chips of polysulfone resin are conveyed and preheated in the screw feeding section, and then compacted and gradually melted in the screw compression section. In the melting section of the screw, the supercritical fluid N with a temperature of 50°C and a pressure of 7MPa 2 Inject into the polysulfone melt through the injection device, supercritical N 2 The mass ratio of polysulfone polymer to polysulfone polymer is 1:250 to form a homogeneous polysulfone melt. In the filter section, the homogeneous polysulfone melt should pass through the filter medium to filter out impurities and catalyst remaining after polymerization. In the part of the metering pump, the homogeneous polysulfone melt is metered (10-500000g / h) by the gear metering pump to precisely control the fineness and uniformity of the fibers. Such as figure 1 As shown, the arrow A in the figure indicates the injection d...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The polysulfone resin (polyethersulfone) solid chips are quantitatively fed to the screw, and the polysulfone resin solid chips are conveyed and preheated in the screw feeding section, and then compacted and gradually melted in the screw compression section. In the screw melting section, supercritical fluid N with a temperature of 260°C and a pressure of 20MPa 2 Inject into the polysulfone melt through the injection device, supercritical N 2 The mass ratio with polysulfone polymer is 1:150 to form a homogeneous polysulfone melt. In the filter section, the homogeneous polysulfone melt should pass through the filter medium to filter out impurities and catalyst remaining after polymerization. In the part of the metering pump, the homogeneous polysulfone melt is metered (10-500000g / h) by the gear metering pump to precisely control the fineness and uniformity of the fibers. Such as figure 1 As shown, the arrow A in the figure indicates the injection direction of the homog...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com