Escherichia coli engineering bacteria capable of realizing high yield of L-tryptophan
A technology of Escherichia coli and engineering bacteria, applied in the field of microbial breeding and microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of large energy consumption, unfavorable industrialization, waste of intracellular resources, consumption of intracellular resources, etc., and achieves easy industrialization control, simple breeding scheme, and fermentation. short time effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
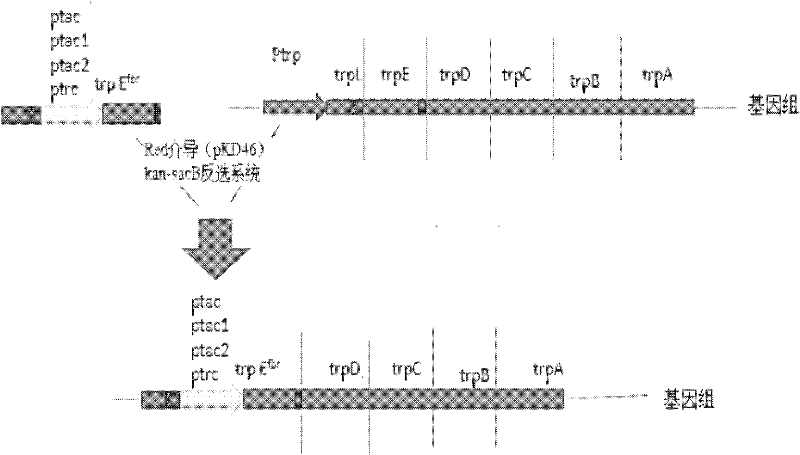
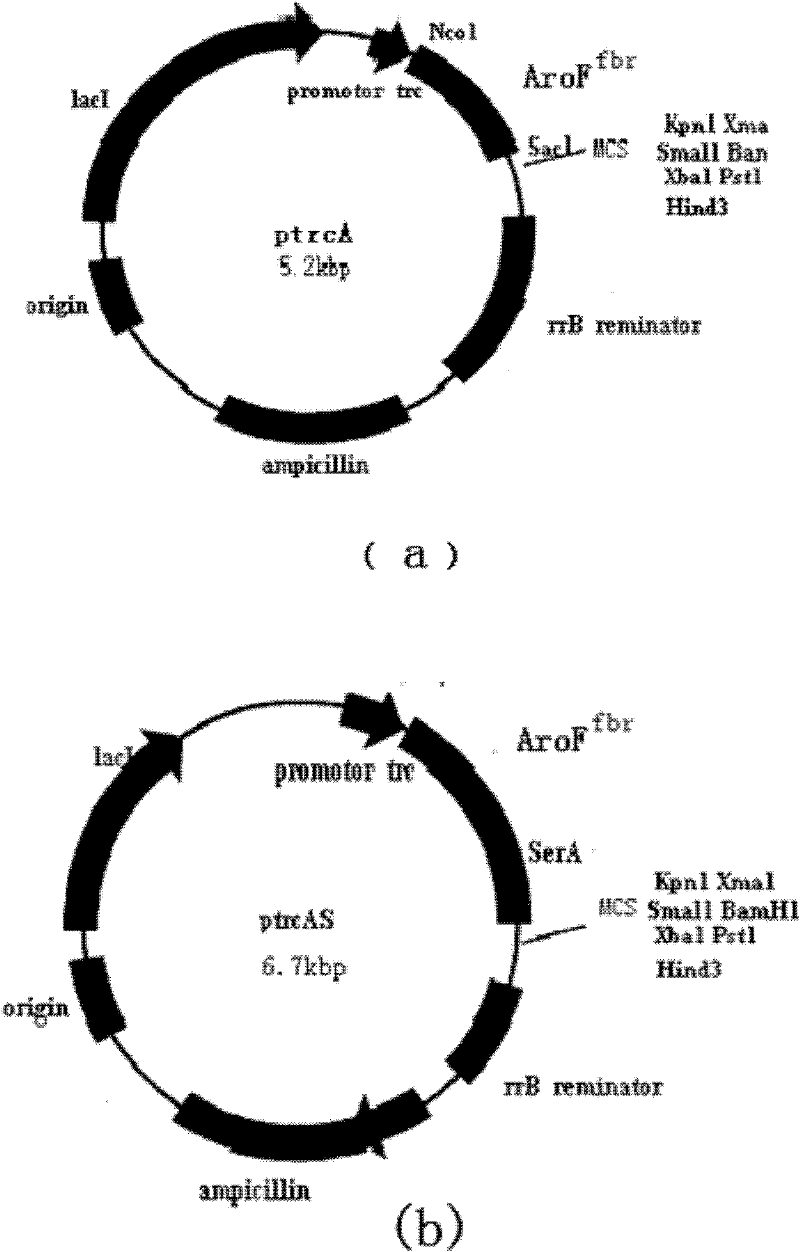
[0028] Example 1 Construction of Escherichia coli Engineering Bacteria with High Production of L-Tryptophan
[0029] 1. tnaA, trpR, tyrR gene knockout
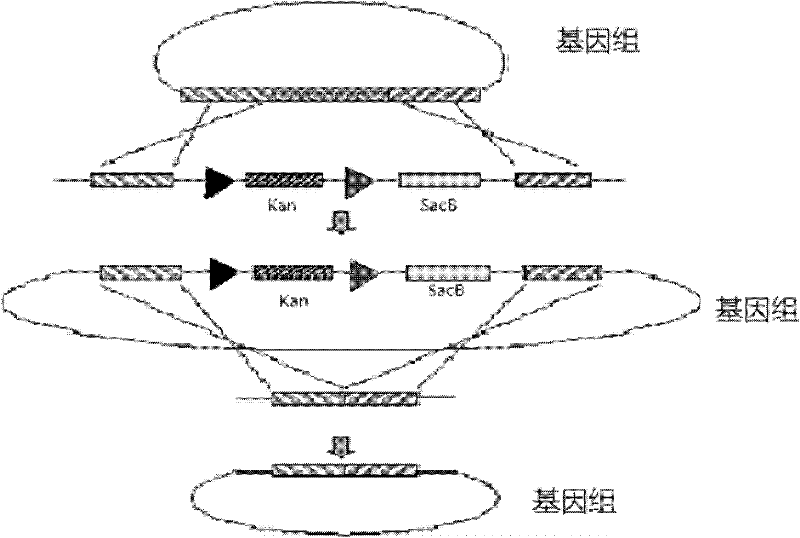
[0030] Using the Red-mediated recombination engineering system, Escherichia coli W3110 was used as the starting bacterium to introduce the heat-sensitive plasmid pKD46, and the kan-sacB reverse selection system was used to knock out the tnaA gene. The method is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the specific method is:
[0031] 1) tnaA gene knockout
[0032] Primers and gene fragments used:
[0033] ptnapuc-1 5'-ATTGAGCCAGTAAAACGTACCACTCGCGCTTCTGACACATGCAGCTCCCGGAGACG-3'
[0034] ptnapuc-2 5'-CGCCAGCATATCGGCATATTTGTAGGTTTCGTGAGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGGAAAC-3'
[0035] ptnaA 5'-ATTGAGCCAGTAAAACGTACCACTCGCGCTGAAACCTACAAAATATGCCGATATGCTGGCG-3'
[0036] Using ptnapuc-1 and ptnapuc-2 as primers, and using the plasmid pUC18-KS as the template, the PCR product was electrotransformed into Escherichia coli W3110 (pKD46), cultured on a 50m...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Example 2 Fermentation of Escherichia coli Engineering Bacteria with High Production of L-Tryptophan
[0119] Take the four L-tryptophan-producing strains obtained in Example 1 as an example.
[0120] (1) Medium:
[0121] Shake flask seed medium (1L): Yeast powder 5g, peptone 10g, NaCl 10g, add water to prepare;
[0122] Primary seed medium (1L): glucose 10g, ammonium sulfate 5g, MgSO 4 1g, trisodium citrate 1g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 5g, yeast extract 5g, CaCl 2 0.02g, FeSO4 7H 2 O 0.05g, trace elements 1ml, pH 6.8;
[0123] Among them, trace element solution (1L): Na 2 MoO 4 2H 2 O 0.15g, H 3 PO 3 1g, CoCl 0.5g, CuSO 4 0.5g, MnCl 0.3g, ZnSO 4 1.2g.
[0124] Fermentation medium (1L): glucose 20g, ammonium sulfate 10g, MgSO 4 2g, trisodium citrate 1g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 10g, yeast extract 8g, CaCl 2 0.2g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.1g, trace elements 2ml, antifoaming agent 5 drops, pH 6.8.
[0125] (2) Determination of tryptophan conten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com