Synchronous motor and system for driving synchronous motor
A synchronous motor and drive system technology, applied in synchronous machines, synchronous motors with stationary armatures and rotating magnets, motor control, etc., to solve problems such as torque reduction and inability to generate maximum torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0125] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the rotor is arranged not only on the outer peripheral side of the stator but also on the inner peripheral side, and accordingly, the stator has stator teeth not only on the outer diameter side of the stator but also on the inner diameter side of the stator. tooth.
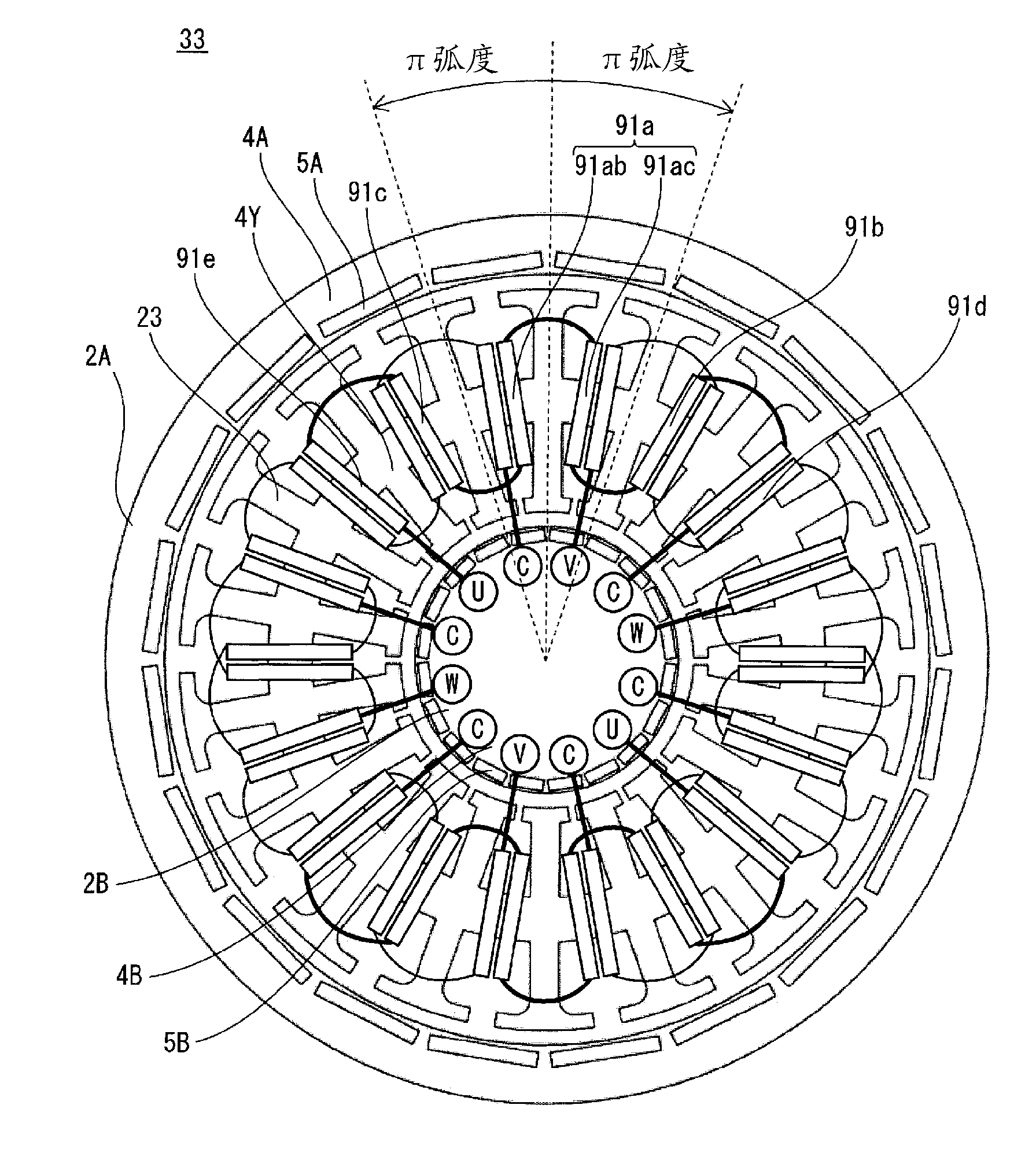
[0126] Figure 5 It is a plan view of the synchronous motor of this embodiment.
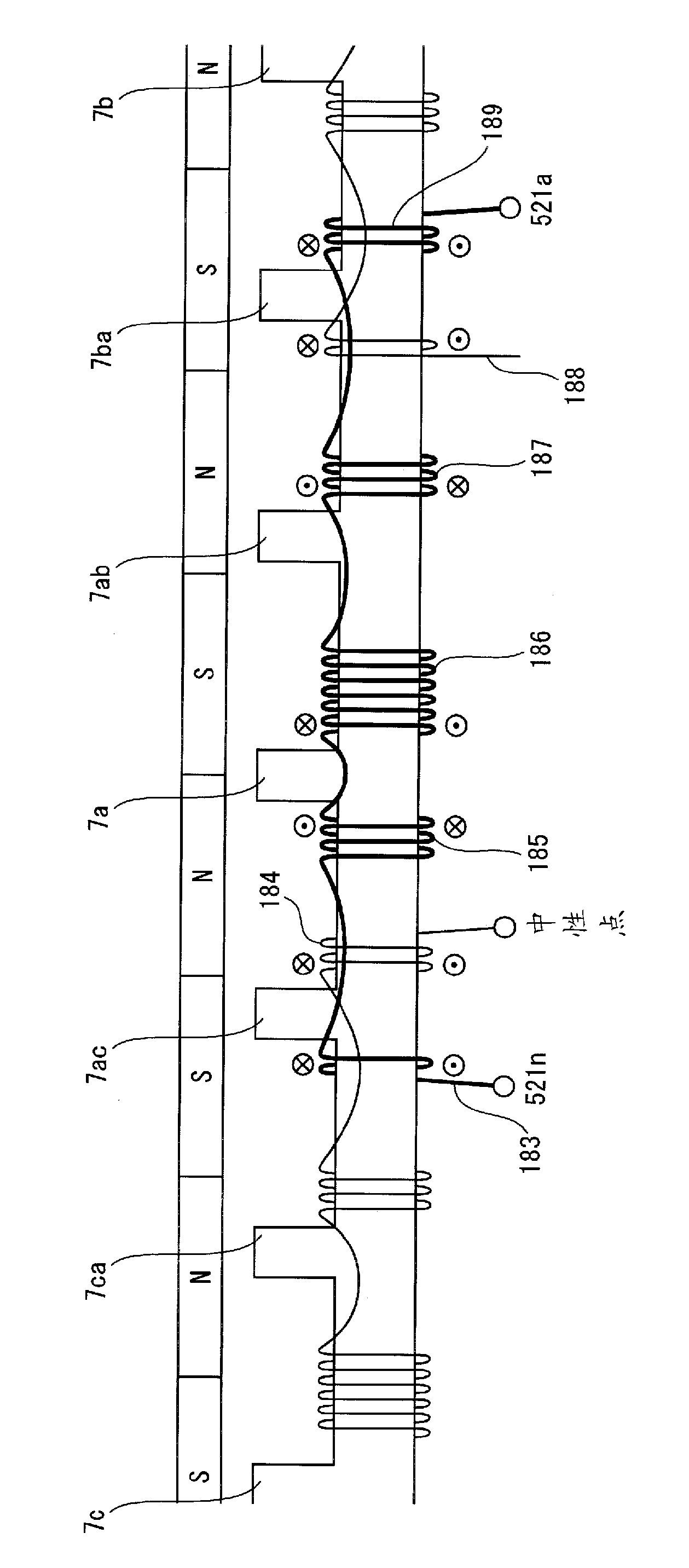
[0127] Figure 6 It is a schematic diagram of the winding structure of the synchronous motor of this embodiment.
[0128] Synchronous motor 33 is composed of rotors 2A, 2B and stator 23 .
[0129] The rotor 2A outside the stator 23 includes a rotor core 4A and 20 permanent magnets 5A, and the permanent magnets 5A are arranged at equal intervals on the rotor core 4A along the circumferential direction of the rotor. The pair of magnetic poles that alternately arrange N poles and S poles composed of permanent magnets 5A form an electrical angle of 2π radi...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0133] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment lies in the number of turns of the winding and the connections.
[0134] The winding is configured such that two types of stator windings are respectively wound on two adjacent stator yoke portions, and one type of stator winding is wound on each of the stator yoke portions on both sides of the two consecutive stator yoke portions. Hereinafter, differences from the first embodiment will be mainly described.
[0135] 3.1. Structure
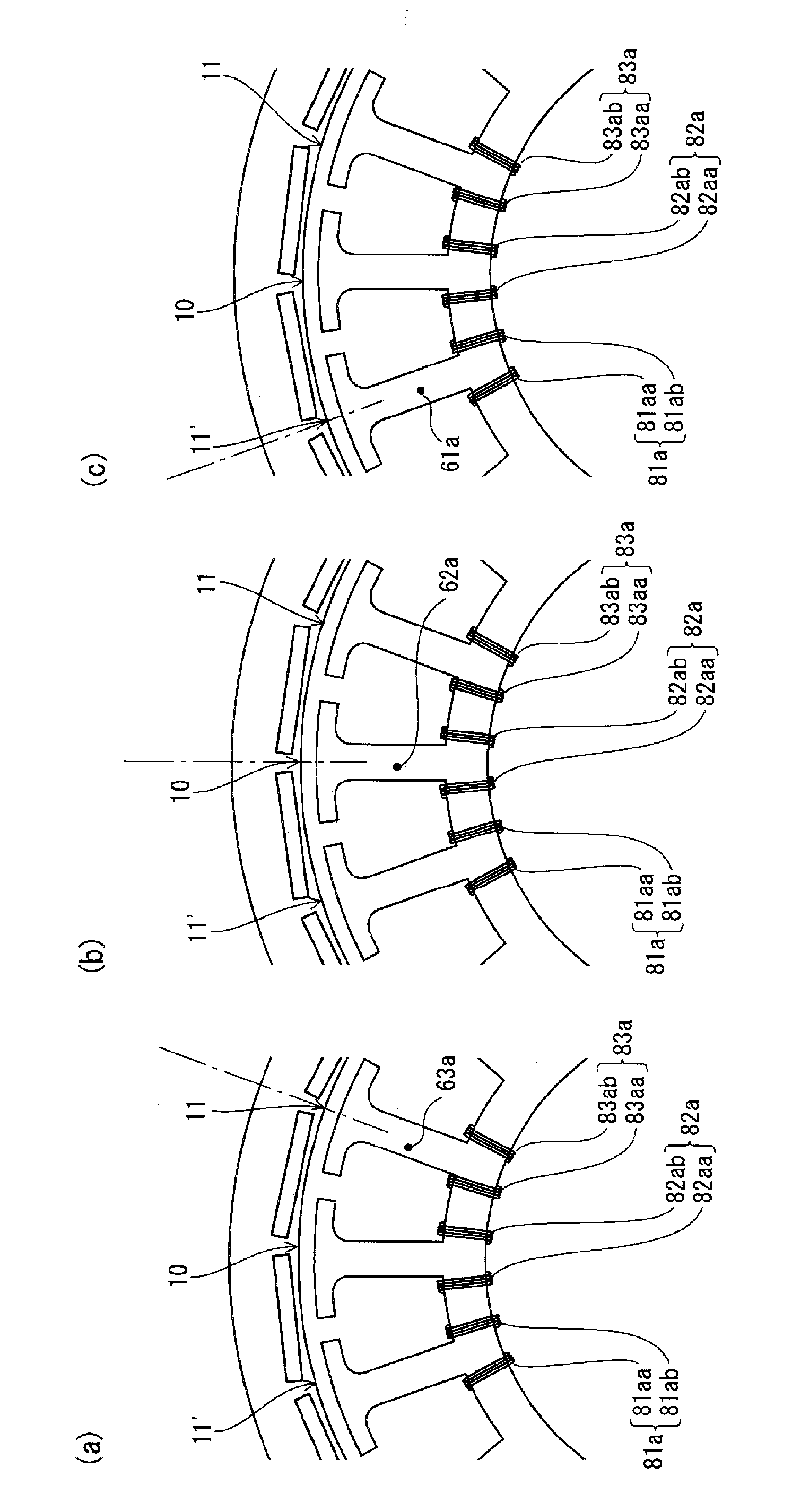
[0136] Figure 7 is a plan view of the synchronous motor of this embodiment, Figure 8 is the winding structure diagram of a synchronous motor, Figure 9 is a vector diagram representing the magnitude and phase of the magnetic field.
[0137] Synchronous motor 51 is composed of rotor 2 and stator 13 .
[0138] The rotor 2 is the same as the first embodiment, and the stator 13 is also the same as the first embodiment except for the structure of the stator winding.
[0139] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com