Preparation method for lithium ion battery electrode material
A lithium-ion battery and electrode material technology, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low conductivity, low ion diffusion coefficient, poor cycle stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
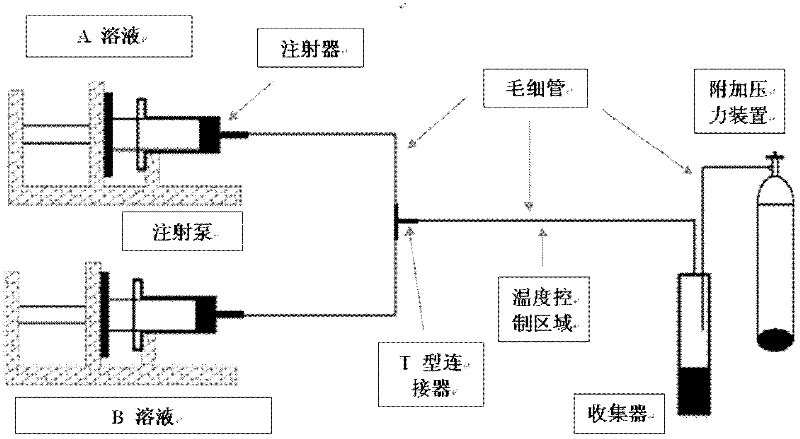
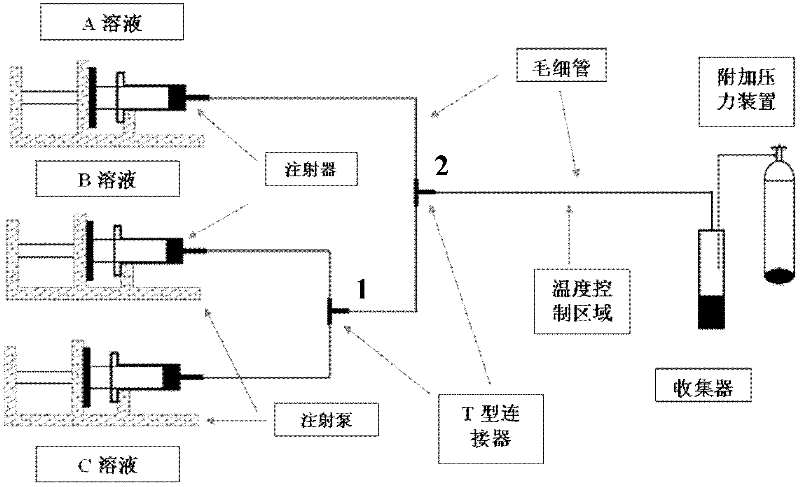
[0022] Synthesis process see figure 1 : first pass inert gas such as N into two parts of distilled water or deionized water 100ml 2 Or Ar to remove oxygen in water; weigh 94.01mg of Li according to the ratio of the amount of ionic species 1:1:1 3 C 6 h 5 o 7 4H 2 O, 2780.2 mg of FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 1320.6mg of (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 .
[0023] Li first 3 C 6 h 5 o 7 4H 2 Dissolve O in solution A, then FeSO 4·7H 2 O is dissolved in solution A; (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 Soluble in solution B; Fe in solution 2+ , Li + with PO 4 3- The ion concentration is 0.1mol / l, and finally the two solutions are sealed respectively. Use two clean syringes to extract liquid A and liquid B respectively, install them on the syringe pumps respectively, and press them with capillary and T-shaped connectors. figure 1 The method is connected, the end of the capillary in the reaction zone is connected to a closed receiving device, and the receiving device is connected to the air pressure bottle to...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Synthesis process see figure 1 And embodiment 1: first respectively to two parts (A, B liquid: Fe in the solution 2+ , Li + with PO 4 3- Ion concentration is 0.01mol / l) distilled water or deionized water 100ml into an inert gas such as N 2 Or Ar to remove oxygen in water; weigh 9.40 mg of Li according to the ratio of the amount of ionic species 1:1:1 3 C 6 h 5 o 7 4H 2 O, 278.02 mg of FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 132.06mg of (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 .
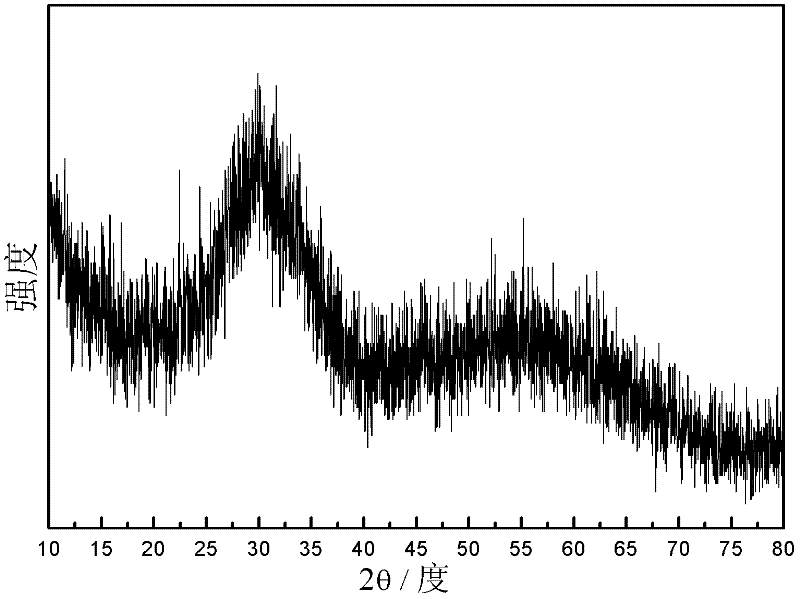
[0026] Li first 3 C 6 h 5 o 7 4H 2 Dissolve O in solution A, then FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O is dissolved in solution A; (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 Dissolve in solution B; finally seal the two solutions separately. Use two clean syringes to extract liquid A and liquid B respectively, and install them on the syringe pumps respectively. The adjustment parameters are as follows: heating temperature T=200°C, quartz capillary length 30cm inner diameter 250μm, additional pressure P=0Psi, liquid flow rate V =3ml / h, after drying, the amorphous phos...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Synthesis process see figure 1 And embodiment 1: first respectively to two parts (A, B liquid: Fe in the solution 2+ , Li + with PO 4 3- Ion concentration is 0.1mol / l) distilled water or deionized water 100ml into an inert gas such as N 2 or Ar to remove oxygen in water, then weigh 94.01mg of Li 3 C 6 h 5 o 7 4H 2 Dissolve O in solution A, then weigh 2780.2mg of FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in liquid A; additionally weighed 1320.6 mg of (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 Dissolve in solution B; finally seal the two solutions separately. Use two clean syringes to extract a certain amount of liquid A and liquid B respectively, and then install them on the syringe pumps respectively. The adjustment parameters are as follows: heating temperature T=200°C, quartz capillary length 30cm inner diameter 250μm, additional pressure P=200Psi, liquid flow rate respectively It is V=3ml / h, and the amorphous phosphate Fe-based positive electrode material is obtained after drying.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com