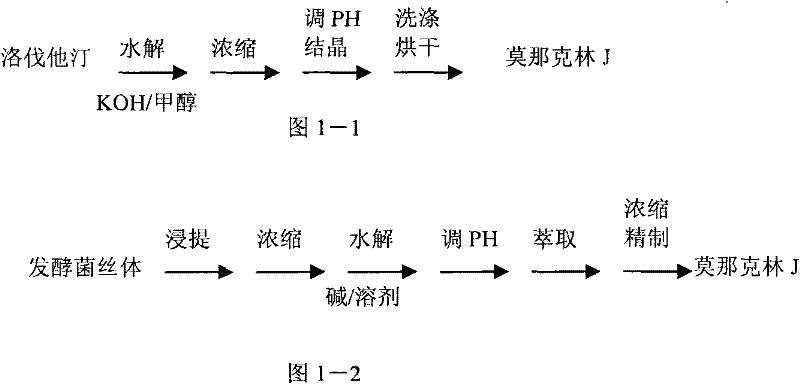
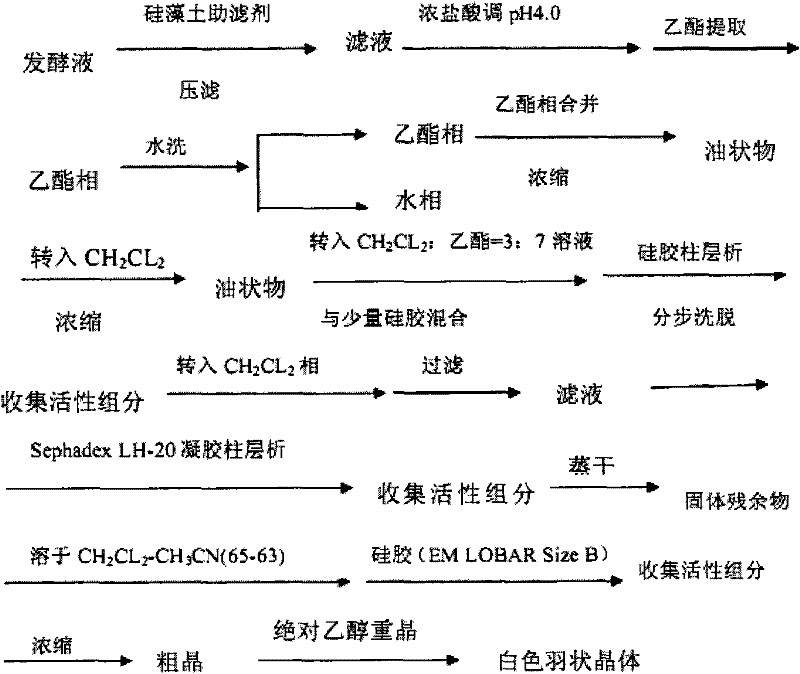
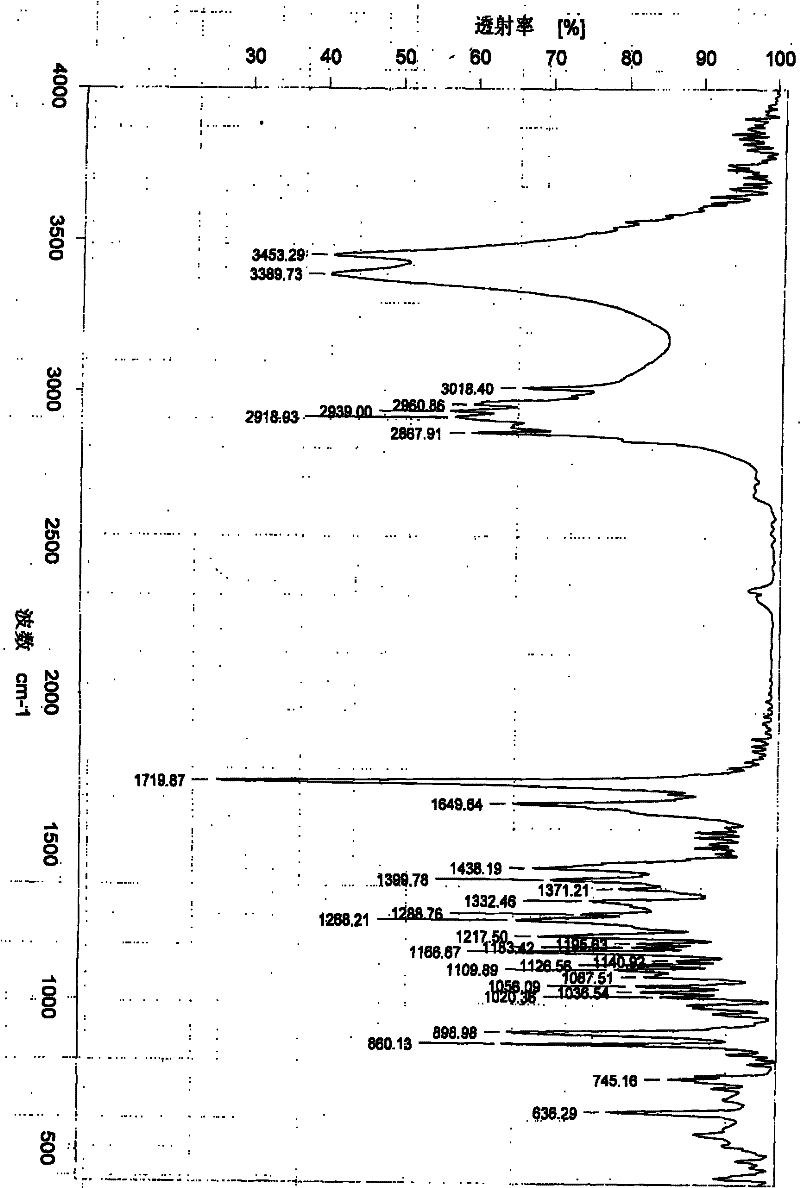
Method for preparing monacolin J
A technology for monacolin and lovastatin is applied in the new process field for preparing monacolin J, which can solve the problems of high cost, cumbersome process steps and the like, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple process steps and less environmental harm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Weigh 100 g of Aspergillus terreus obtained by plate and frame filtration after fermentation, add 800 mL of ethanol, stir at 75° C. for 30 min, cool to room temperature, and then filter. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and ethanol was recovered. The obtained concentrate contained 8.91 g of lovastatin (lactone type). Dissolve 40g of sodium hydroxide in 200mL of water, dissolve completely and add to the concentrate. The reaction was stirred at 83 °C for 12 h. The conversion rate of lovastatin was 100%. Concentrated hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to 200 mL of the reaction liquid in an ice-water bath to adjust the pH to 3.5, and stirred for 30 min. Subsequently, an equal volume of ethyl ester was added to extract for 3 times, dried by adding anhydrous sodium sulfate, and then concentrated under reduced pressure. 7.17 g of monacolin J in trihydroxy acid form (ring-opening acid form) was obtained with a yield of 96.24%.
Embodiment 2
[0041] Weigh 100 g of Aspergillus terreus obtained by plate and frame filtration after fermentation, add 800 mL of ethanol, stir at 25° C. for 30 min, cool to room temperature and filter. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and ethanol was recovered. The obtained concentrate contains 8.54 g of lovastatin (lactone type). Dissolve 60g of sodium hydroxide in 200mL of water, dissolve completely and add to the concentrate. The reaction was stirred at 75 °C for 6 h. The conversion rate of lovastatin was 99.46%. Concentrated hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to 200 mL of the reaction liquid in an ice-water bath to adjust the pH to 4.0, and stirred for 30 min. Subsequently, an equal volume of ethyl ester was added to extract for 3 times, dried by adding anhydrous sodium sulfate, and then concentrated under reduced pressure. 6.83 g of monacolin J in trihydroxy acid form (ring-opening acid form) was obtained with a yield of 95.66%.
Embodiment 3
[0043]Weigh 100 g of Aspergillus terreus obtained by plate and frame filtration after fermentation, add 1200 mL of ethanol, stir at 55° C. for 30 min, cool to room temperature and filter. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and ethanol was recovered. The obtained concentrate contained 9.14 g of lovastatin (lactone type). Dissolve 30g of sodium hydroxide in 200mL of water, dissolve completely and add to the concentrate. The reaction was stirred at 80 °C for 37 h. The conversion rate of lovastatin was 98.82%. Concentrated hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to 200 mL of the reaction liquid in an ice-water bath to adjust the pH to 4.0, and stirred for 30 min. Subsequently, an equal volume of ethyl ester was added to extract for 3 times, dried by adding anhydrous sodium sulfate, and then concentrated under reduced pressure. 7.08 g of monacolin J in trihydroxy acid form (ring-opening acid form) was obtained with a yield of 92.59%.
[0044] The NMR data of mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com