Method for determining intermolecular association degree of contribution in hydrophobically-associating type polyacrylamide solution
A technology of polyacrylamide and contribution degree, which is applied in the field of polymer science and experiment to achieve the effect of simple solution preparation and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
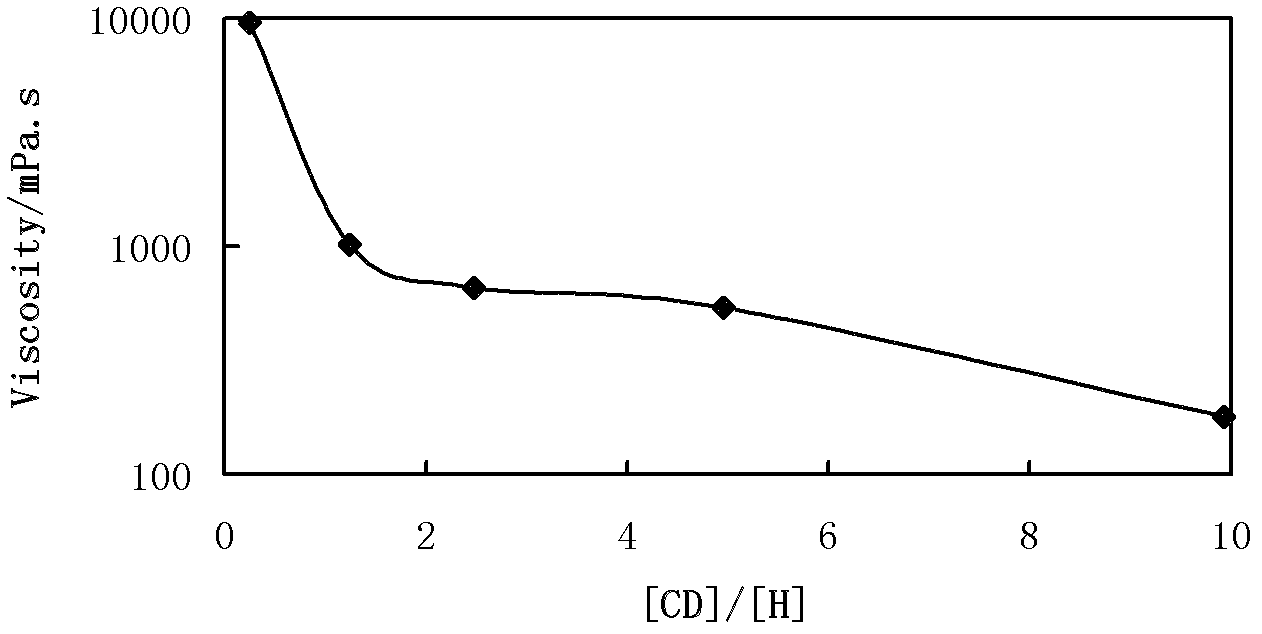
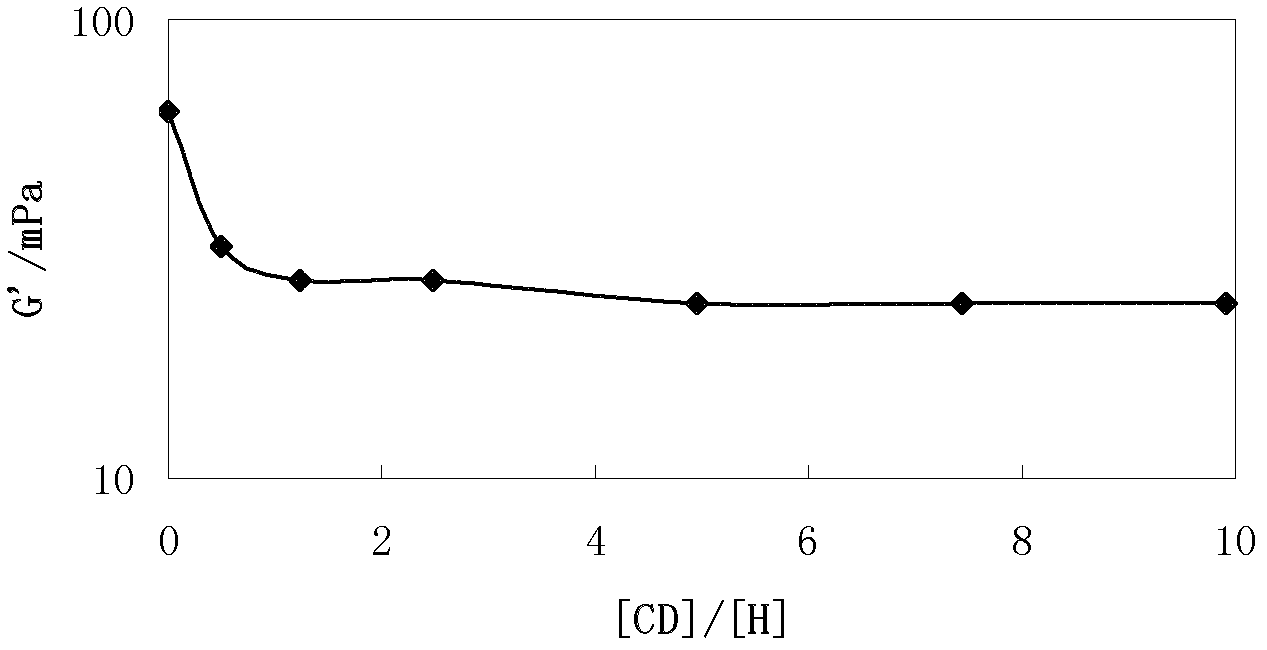
[0041] Example 1, the relationship between cyclodextrin and hydrophobic group molar ratio and intermolecular hydrophobic association
[0042] 1) Associative polyacrylamide (prepared by 0.8 mol acrylamide, 0.2 mol sodium acrylate and 0.005 mol hexadecyl dimethyl allyl ammonium bromide at 50 ° C for 8 hours, the molecular weight is 4.0×10 6 g / mol) was dissolved in deionized water with stirring at 40° C. for 8 hours to obtain a polymer mother liquor with a concentration of 10000 mg / L;
[0043] 2) Dissolving β-cyclodextrin in deionized water with stirring at 30°C for 2 hours to obtain β-cyclodextrin mother liquor with a concentration of 10000 mg / L;
[0044] 3) Mix the polymer mother liquor obtained in step 1), the cyclodextrin mother liquor obtained in step 2) and deionized water with 20°C for 4 hours according to different ratios, and then obtain a series of [CD] / [H] different ( [CD] / [H]=0-10) the hydrophobic association type polyacrylamide solution to be tested;
[0045] 4) F...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2, the repeatability of zero-shear viscosity test results of different concentrations of hydrophobic association polyacrylamide solutions
[0069] Adopt the zero-shear viscosity test determined by the present invention (implementation example 1 step 4)) and calculation method to carry out repeatability test to the zero-shear viscosity of embodiment 1 gained associative polyacrylamide, experimental result is as follows:
[0070] Table 1. Repeatability of zero-shear viscosity test results
[0071]
[0072] According to the experimental results in the table, the average error of the zero-shear viscosity parallel test results obtained by adopting the rheological test procedure determined by the present invention is less than 3%.
Embodiment 3
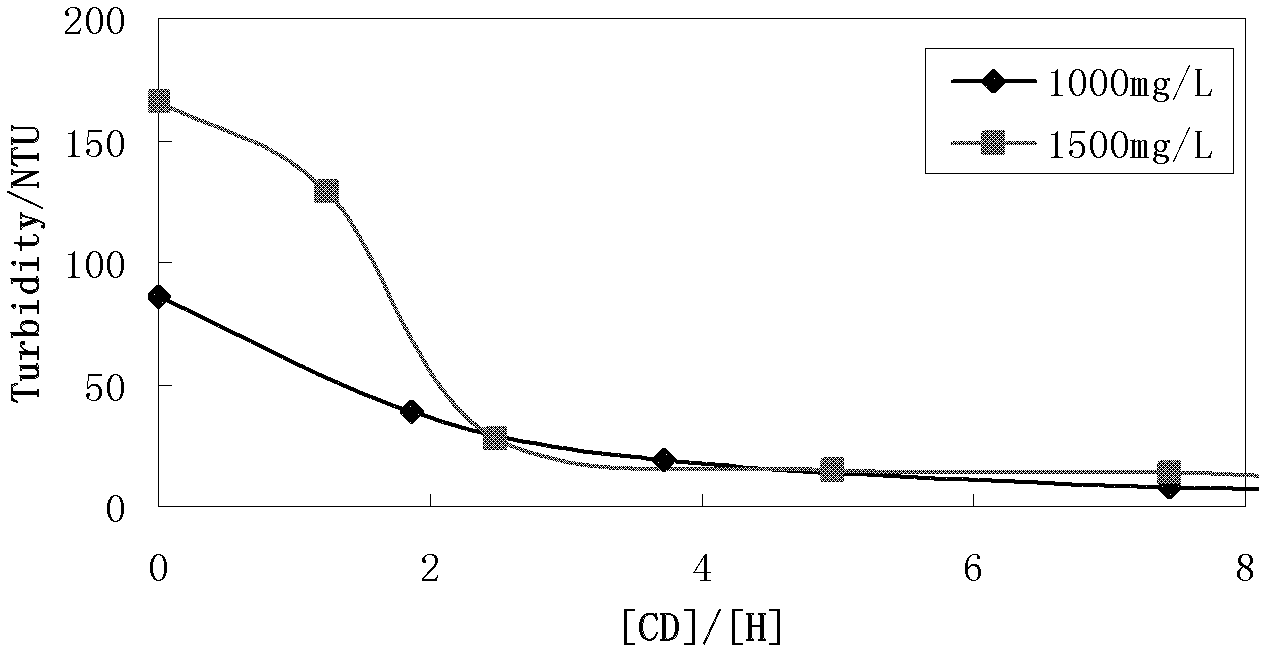
[0073] Example 3, Comparison of the degree of contribution of intermolecular associations in different concentration intervals
[0074] 1) Associative polyacrylamide (obtained from 0.8mol acrylamide, 0.2mol sodium acrylate and 0.005mol hexadecyldimethylallyl ammonium bromide by copolymerization at 50°C for 8 hours, molecular weight 4.0×10 6 g / mol) was dissolved in deionized water with stirring at 50° C. for 6 hours to obtain a polymer mother liquor with a concentration of 10000 mg / L;
[0075] 2) Dissolving β-cyclodextrin in deionized water with stirring at 35°C for 1 hour to obtain β-cyclodextrin mother liquor with a concentration of 10000 mg / L;
[0076] 3) Stir and mix the polymer mother liquor, cyclodextrin mother liquor and deionized water obtained in steps 1) and 2) at 25°C for 3 hours to obtain the associative polyacrylamide solution to be tested; the associative polyacrylamide Solution 300-2000mg / L, [CD] / [H]=0 and 4.
[0077] 4) For the hydrophobic association polyacr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com