Novel peptides isolated from spider venom, and uses thereof
A venom and terminal amide technology, applied in the field of spider venom peptides, can solve the problems that neurons cannot generate action potentials, and cannot encode and transmit information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0216] Peptide purification and chemical characterization from crude venom
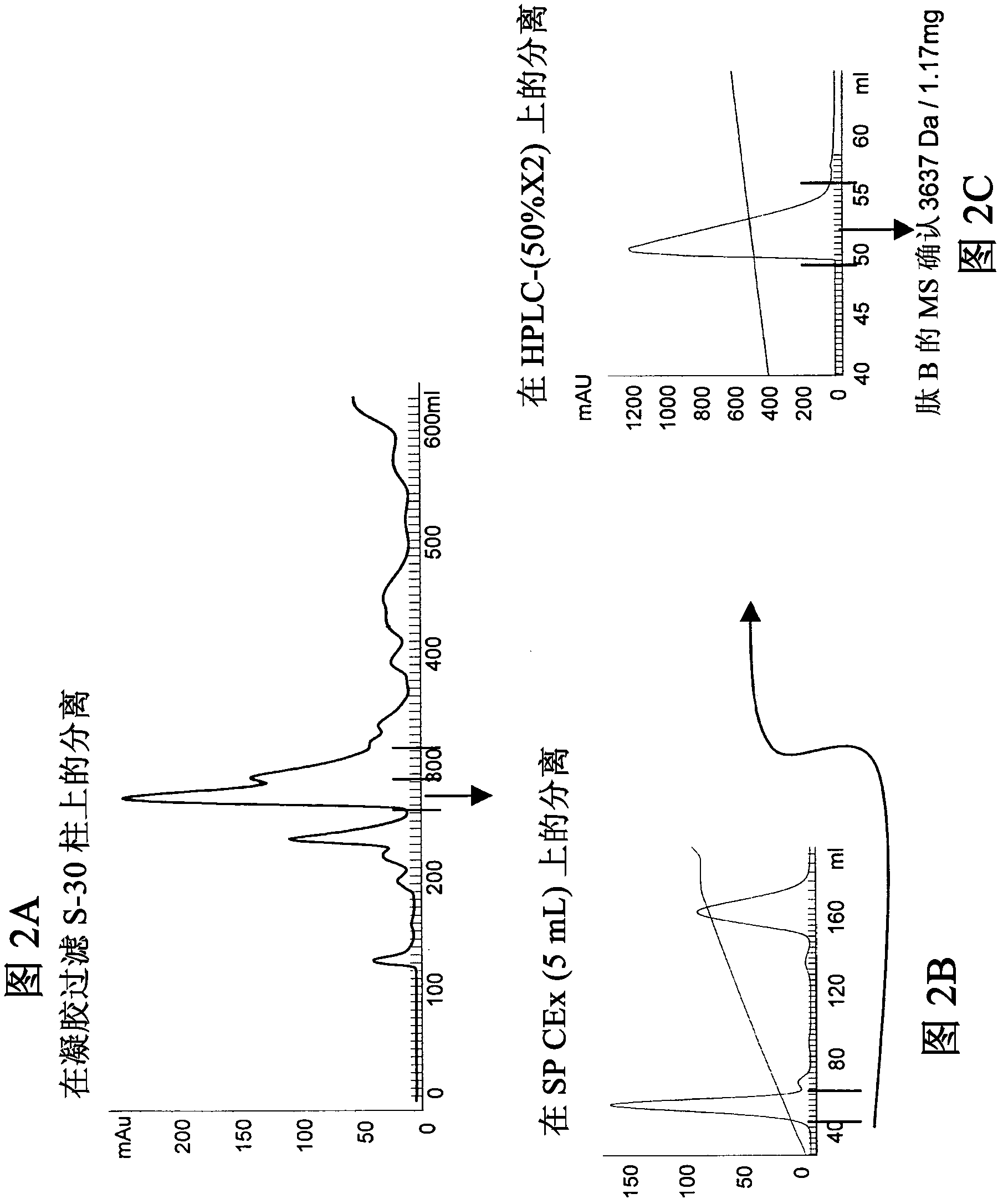
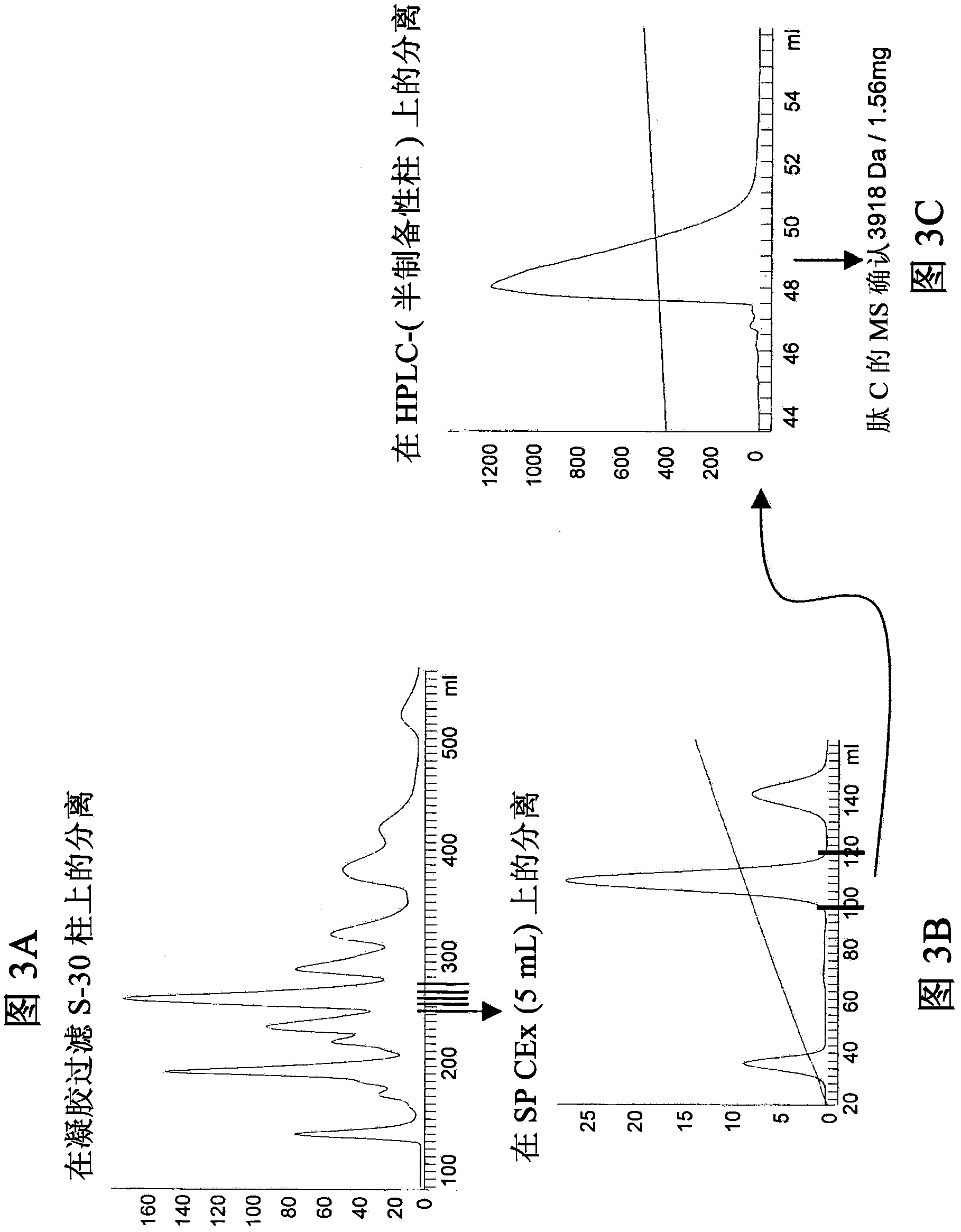
[0217] Peptides A, B, C, D, E and F were isolated from Pterinochilus spp. Usambara (Psp), Metal Blue spider (Hv) and RedMorph Grammostola (RMG) spider venoms using several different chromatography steps (see Figure 1- 6):
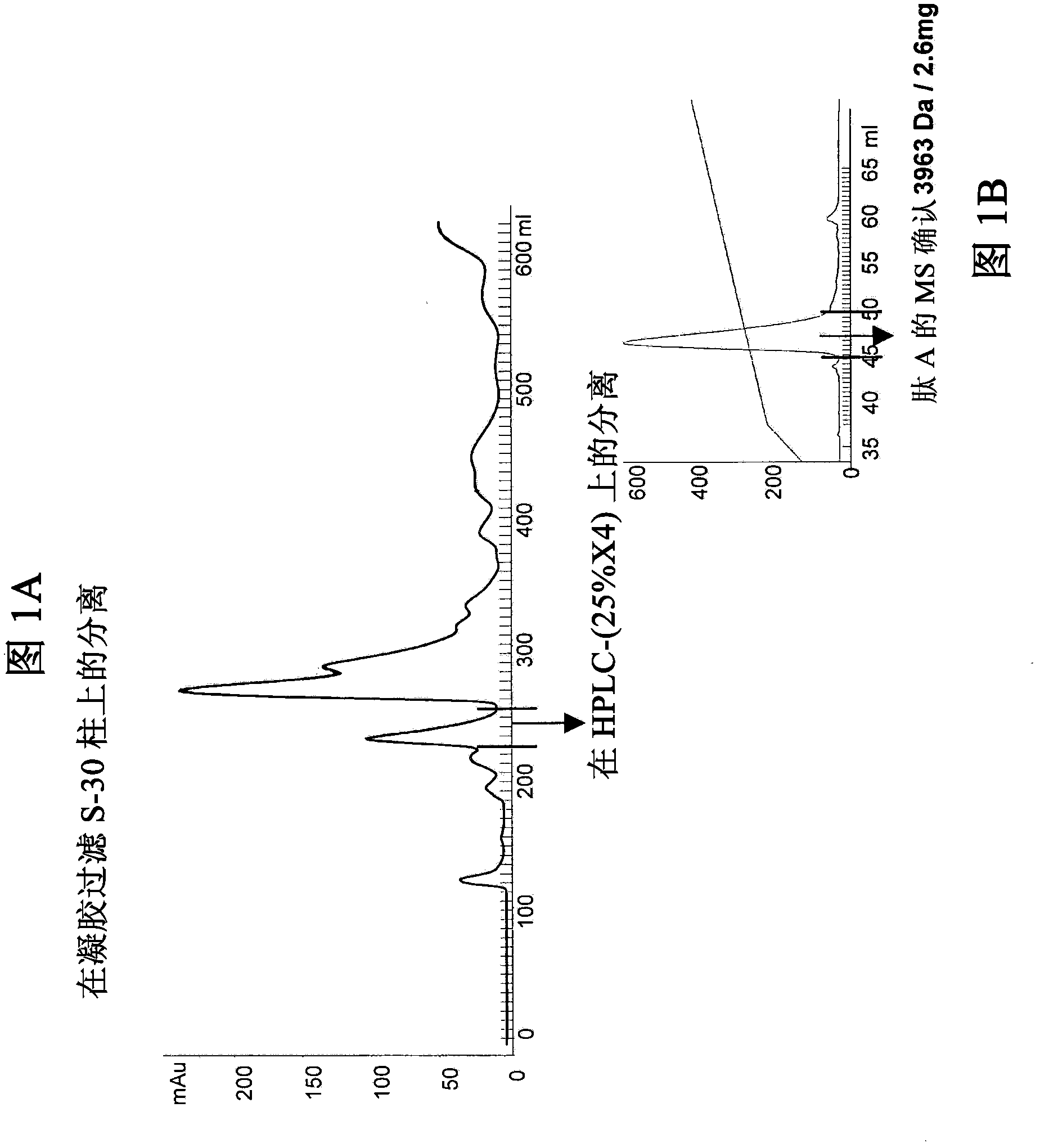
[0218] Chromatographic purification of peptide A from Psp venom
[0219] According to the procedure described in the Methods section, 100 mg of lyophilized crude venom (110 mg by Nanodrop) was loaded on a gel filtration column.
[0220] Fractions (#32-36) were collected, filtered through a 0.22 μm cellulose acetate filter, and 1 / 4 of the sample was loaded into pre-treated solvent A (in 0.1% TFA 5% ACN) equilibrated on a Phenomenex Jupiter reverse phase HPLC column (5u, C18, 300A, 250 x 4.6mm, 00G-4053-EO, S / No397274-10). Proteins were eluted by step gradient using solvent A (= 5% ACN in 0.1% TFA) and 60% ACN in 0.1% TFA as mobile phase (= buffer B), run at a constant flow rate o...
Embodiment 2
[0250] Refolding of synthetic peptides
[0251] According to Schnolzer, M. et al., (1992) In situ neutralization in BOC-chemistry solid phase peptide synthesis, Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 40, 180-193, and Atherton, E. et al., (1989) Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (IRL, Oxford, U.K.), produced synthetically by solid-phase synthesis procedures by chemical synthesis using BOC (tert-butoxycarbonyl) or Fmoc (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl) solid-phase peptide synthesis Peptides A, B, C, D, E and F were provided as lyophilized powders with a purity of 70-95%. Each peptide was then subjected to a different refolding procedure as described below to achieve correct folding and the same biological activity as the venom-purified native peptide.
[0252] Peptide A refolding
[0253] Crude synthetic peptides were dissolved in 0.1 M Tris buffer pH 8.5 at a protein concentration of 5 mM and then reduced with 20 mM DTT for 1 hour at room temperature (RT). The reduced peptide was added to a fo...
Embodiment 3
[0279] In vitro biological activity of isolated pure peptides
[0280] For TTX-sensitive Na V 1.3 and TTX tolerant Na V 1.8 Channels were tested for blocking activity. Each of these is stably expressed in mammalian cell lines and elicits channel currents by appropriate voltage stimulation. Toxin activity is examined by measuring current before, during (usually at increasing doses) and after perfusion of the toxin. The proportion of inhibitory currents at each toxin dose was measured in at least three separate cells and the mean ± SD was plotted.
[0281] Peptide A inhibits Na V 1.3 and Na V 1.8 channels with apparent IC 50 1.75 and 2.5 μM, respectively.
[0282] Peptide B inhibits Na V 1.3 channels where the apparent IC 50 is 230 nM.
[0283] Peptide C inhibits Na V 1.3 channels where the apparent IC 50 was 1.2 μM.
[0284] Peptide D inhibits Na V 1.3 channels where the apparent IC 50 is 160 nM.
[0285] Peptide E inhibits Na V 1.3 channels where the apparent ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com