Self-excitation push-pull converter
A self-excited push-pull converter technology, applied in the field of DC-DC or DC-AC converters, can solve the problems of wasting electric energy, poor adaptability of working voltage, shortened life, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
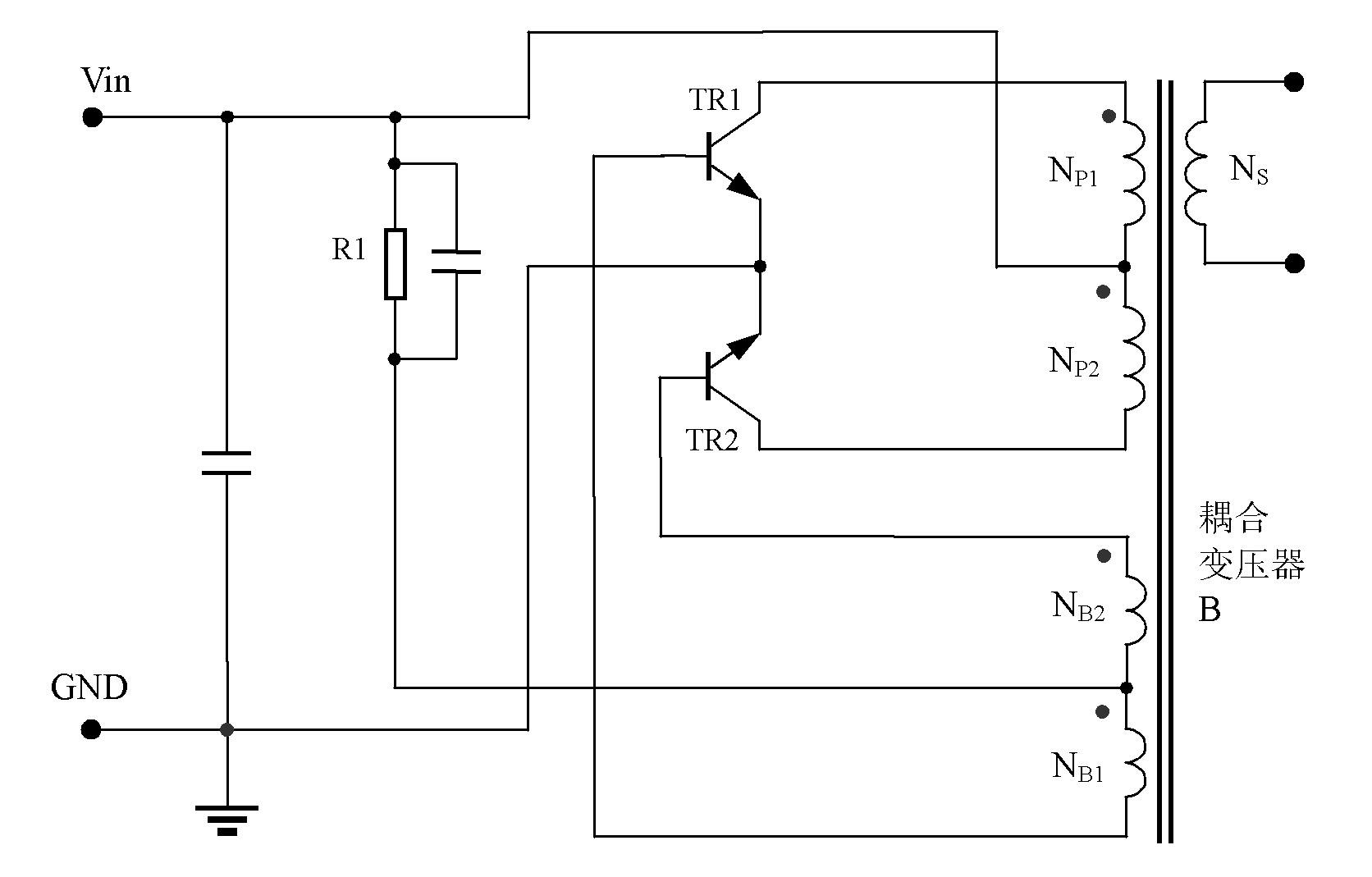
[0060] Figure 8 For the first embodiment, such as Figure 8 As shown, it is a complete self-excited push-pull converter using a constant current source with negative resistance characteristics as a bias, and the main topology of the circuit is a Royer circuit.
[0061] In order to expound its working principle of the first embodiment of the present invention conveniently, first describe the working principle of the constant current source of negative resistance characteristic in the circuit, the constant current source of negative resistance characteristic is made up of voltage detection circuit, constant current source, output circuit; Voltage detection circuit The positive and negative input terminals of the voltage and output circuit are respectively connected to the positive and negative phases of the input power supply; one end of the constant current source is connected to the positive or negative of the input power supply, and the other end of the constant current sour...
no. 2 example
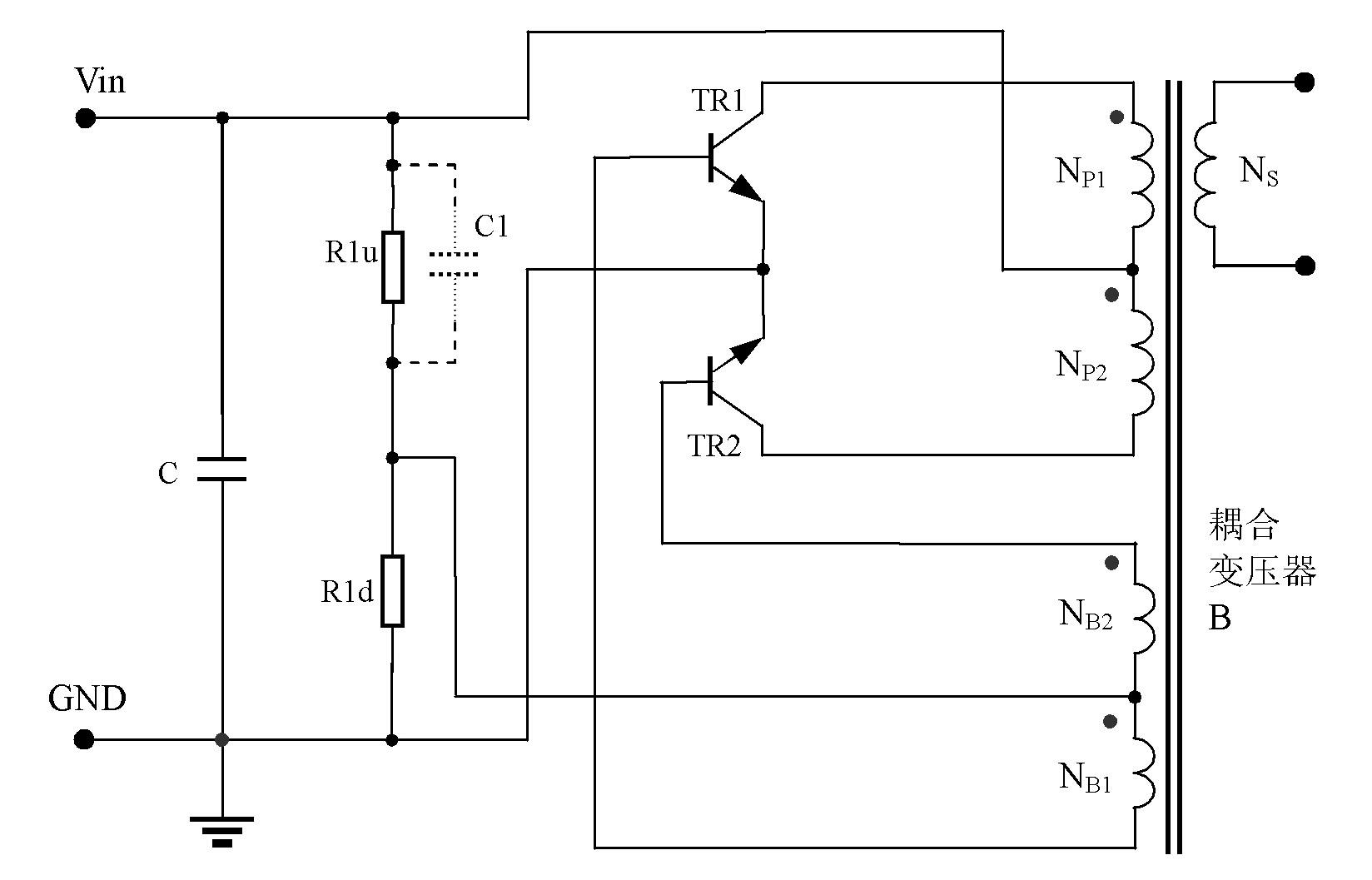
[0103] Figure 15 For the second embodiment, a negative resistance characteristic constant current source INR1 is between the DC loop of the base of the push-pull switching triode and the effective power supply terminal. The difference from the first implementation is that the Figure 8 Capacitor C51, changed to Figure 15 The mid-span is connected between the center tap of the feedback winding of the self-excited push-forward converter and the ground to improve Figure 8 When the working voltage of the circuit is high, the impact of the capacitor C51 on the push-pull switching transistor when the power is turned on.
[0104] like Figure 15 As shown, it is not only possible to achieve Figure 8 At the same time, since C1 is connected to the ground wire, the capacitor C1 is no longer like Figure 8 Like the middle capacitor C51, there is an inrush current to the base and emitter of the triode. On the contrary, in this implementation, since the voltage across the capacitor...
no. 3 example
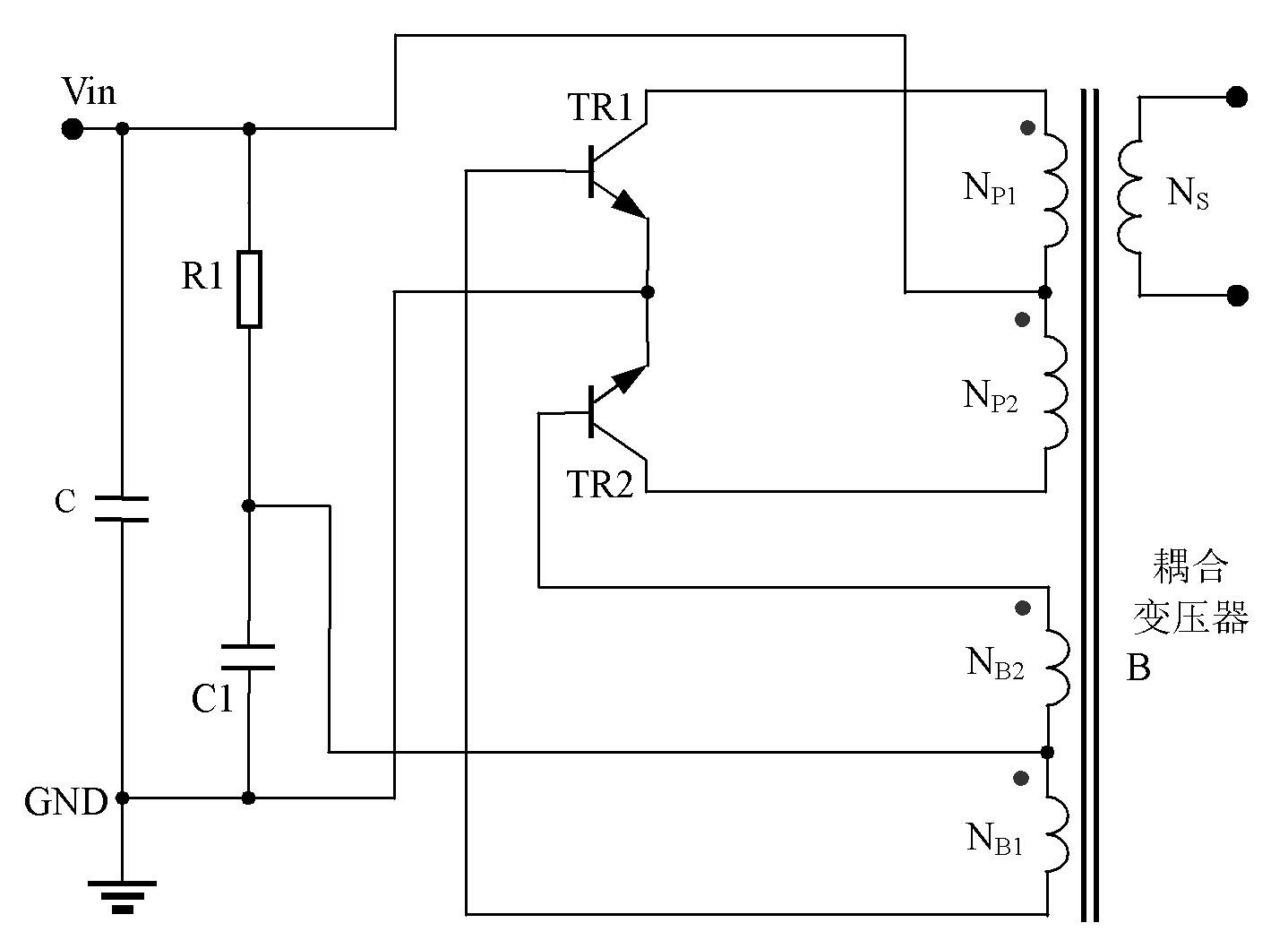
[0107] Figure 16 For the third embodiment, between the DC loop of the base of the push-pull switching transistor and the effective power supply terminal is a constant current source INR1 with negative resistance characteristics, which is corresponding to the prior art image 3 innovative inventions.
[0108] The working principle of the circuit of the third embodiment is: the negative resistance constant current source INR1 replaces the original bias resistor R1, but the current direction is the same, when Figure 16 When the operating voltage of the self-excited push-pull converter increases for some reason, due to the existence of the negative resistance characteristic constant current source INR1, the current provided to the base of TR2 of the two push-pull transistors TR1 is reduced until it is turned off. Observe the collector current of one of the triodes for comparison. When using the existing technology, as the operating voltage increases, the required saturation cur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com