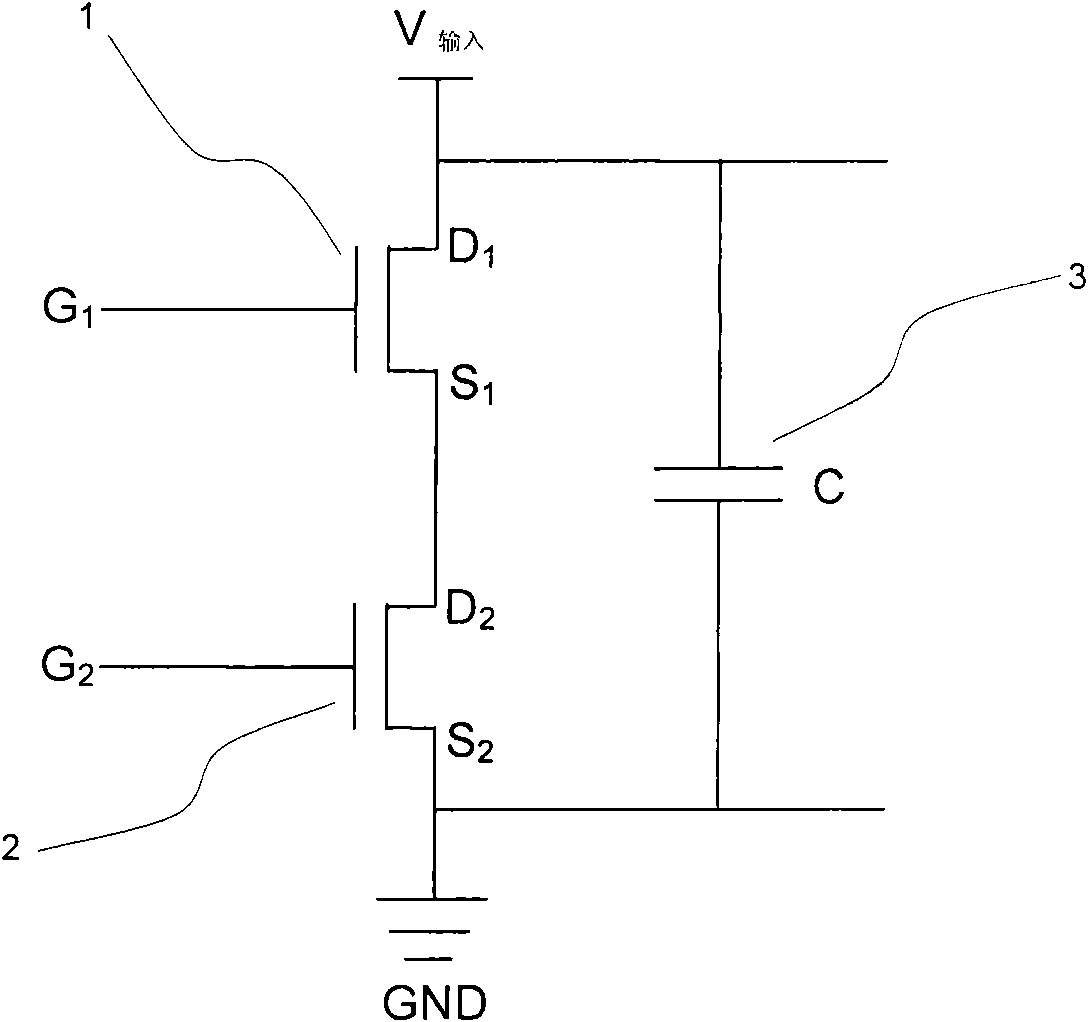
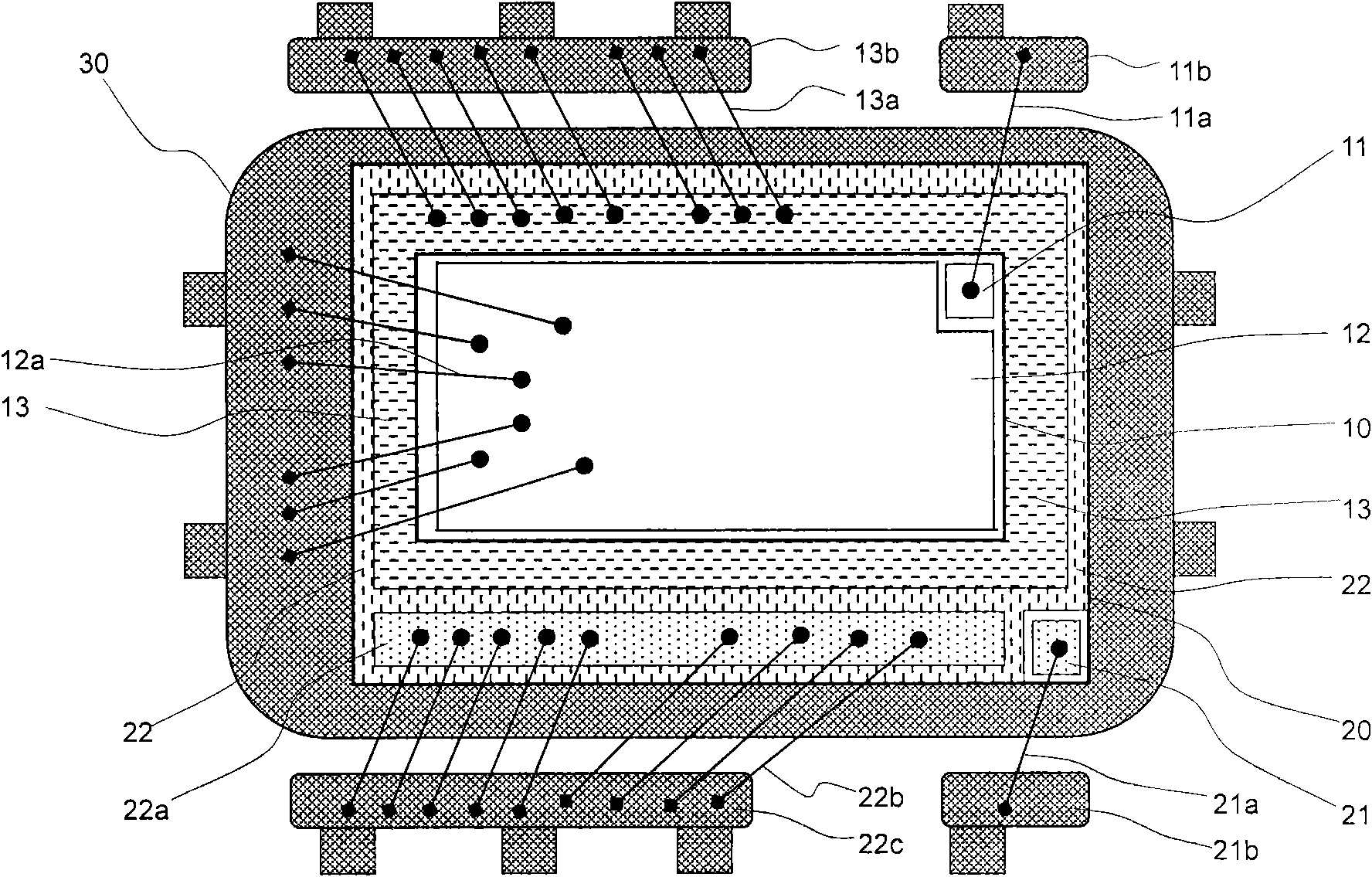
Metal-oxide semiconductor field effect transistor integrated with capacitor
A technology of field effect transistors and capacitors, which is applied in the field of metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors and its preparation, and can solve problems such as chip functional failure and wafer particle fragmentation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
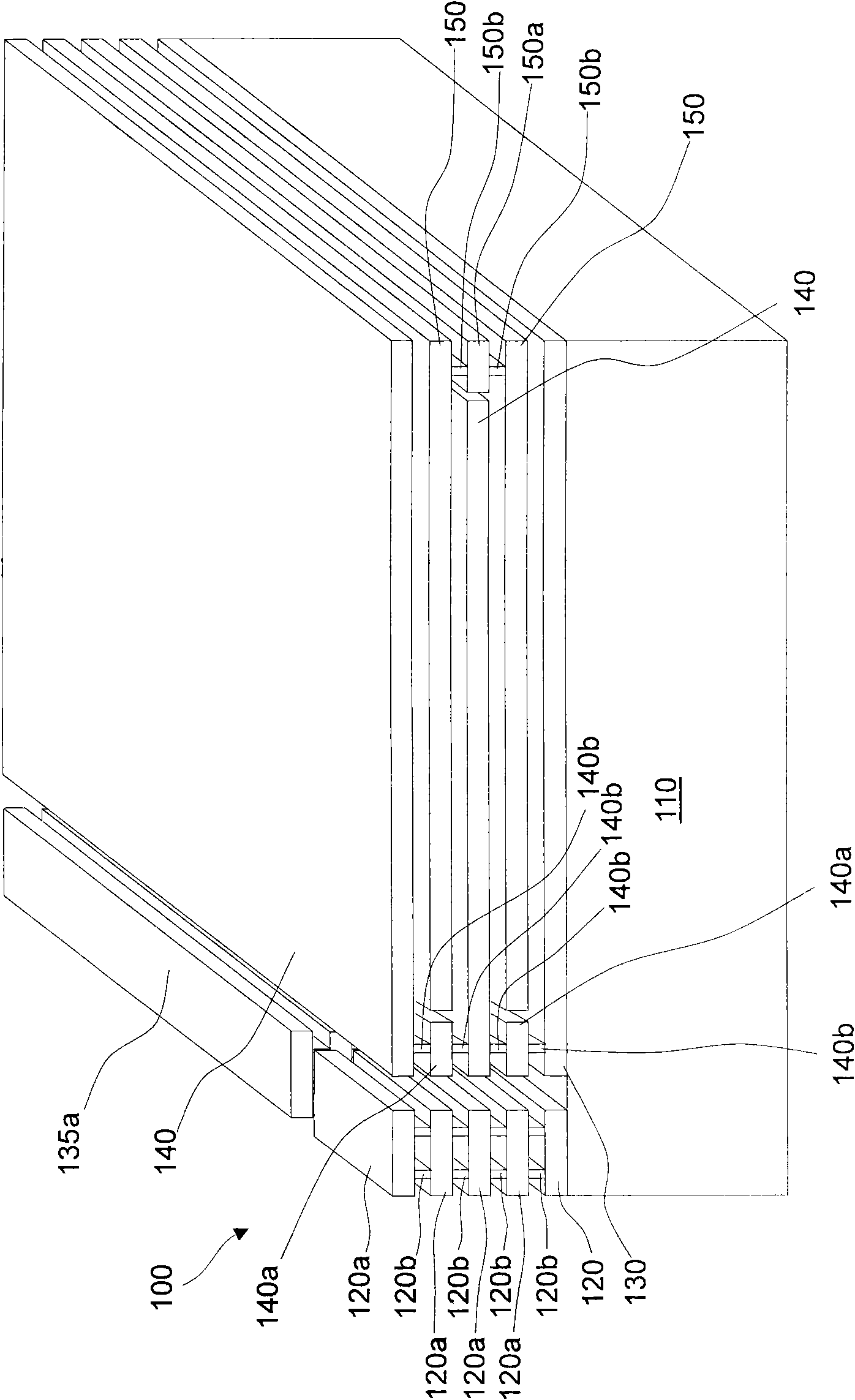
[0052] see Figure 2A (Schematic diagram of three-dimensional structure), 2B-2F (Schematic plan view of the level where each layer of capacitive plates are located correspondingly from bottom to top in the schematic diagram of three-dimensional structure), on a silicon chip substrate 110 top surface is provided with The gate metal layer 120 (referred to as the second electrode metal layer) of the MOS field effect transistor 100 gate electrode (referred to as the second electrode) constituting the low side (LowSide), and the source electrode constituting the MOS field effect transistor 100 (referred to as the second electrode) The source metal layer 130 (referred to as the first electrode metal layer), the source metal layer 130 includes an extension structure 135 . The drain (not shown) of the MOS field effect transistor 100 is formed on the bottom surface of the silicon substrate 110, and the source (not shown) and gate (not shown) of the MOS field effect transistor 100 are f...
Embodiment 2
[0057] see Figure 3A (Schematic diagram of three-dimensional structure), 3B-3F (Schematic plan view of the level where each layer of capacitor plate is located correspondingly from bottom to top in the schematic diagram of three-dimensional structure), on a silicon chip substrate 210 top surface is provided with The gate metal layer 220 (referred to as the second electrode metal layer) of the MOS field effect transistor 200 gate electrode (referred to as the second electrode) constituting the low side (LowSide), and the source electrode constituting the MOS field effect transistor 200 (referred to as the second electrode) The source metal layer 230 (referred to as the first electrode metal layer), the source metal layer 230 includes an extension structure 235 . The drain (not shown) of the MOS field effect transistor 200 is formed on the bottom surface of the silicon substrate at 210, and the source (not shown) and the gate (not shown) of the MOS field effect transistor 200 a...
Embodiment 3
[0062] In fact, with the continuous improvement of the dielectric constant of the dielectric used in the capacitor, the above-mentioned embodiment is slightly cumbersome, and the general capacitor does not need so many multi-layer capacitor plates as in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 or 2, as a further improvement of the above-mentioned embodiment Improvement, the following content will provide a more concise implementation.
[0063] see Figure 4A(Schematic diagram of three-dimensional structure), 4B-4E (Schematic diagram of the planar view of the level where each layer of capacitor plate is located correspondingly from bottom to top in the schematic diagram of three-dimensional structure), the MOS field effect transistor 300 is integrated with a bypass capacitor, Wherein: the gate metal layer 320 (referred to as the second electrode metal) of the gate electrode (referred to as the second electrode) of the MOS field effect transistor 300 (referred to as the second electrode...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com