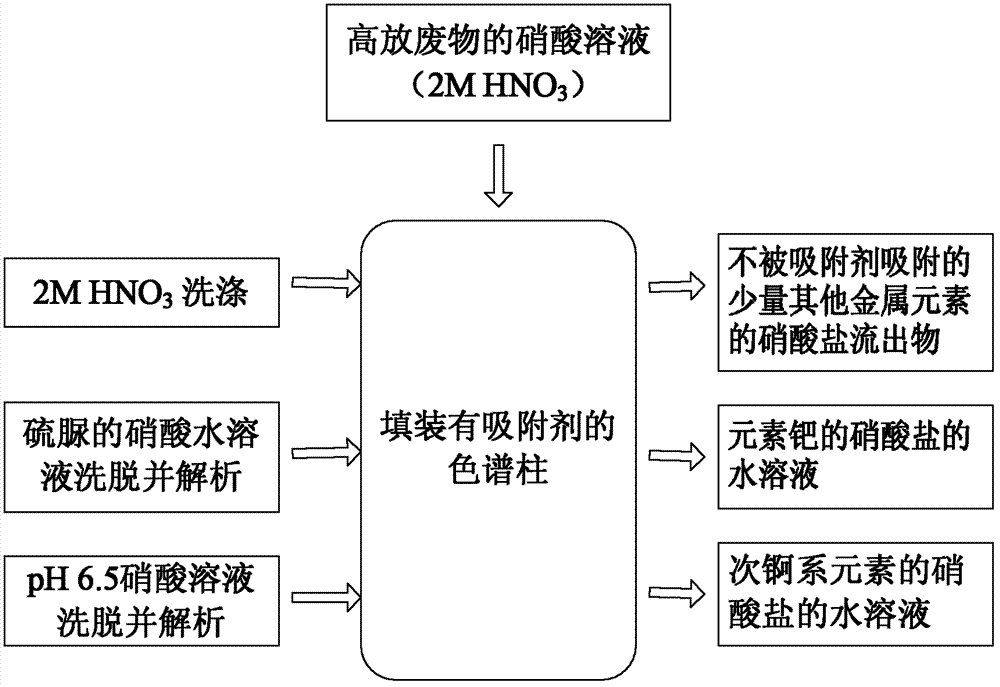
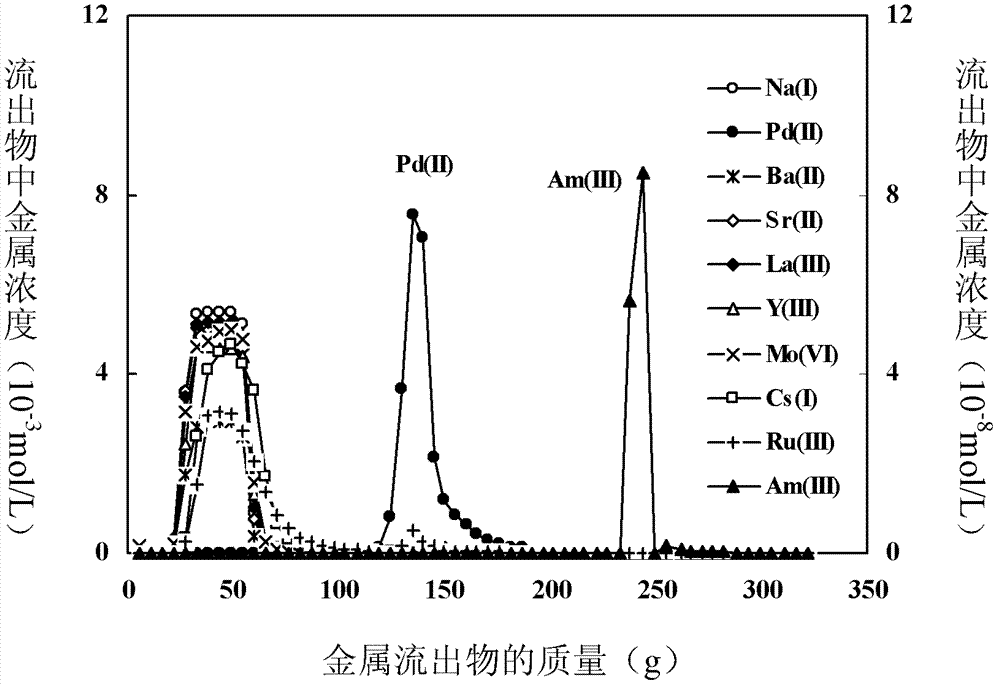
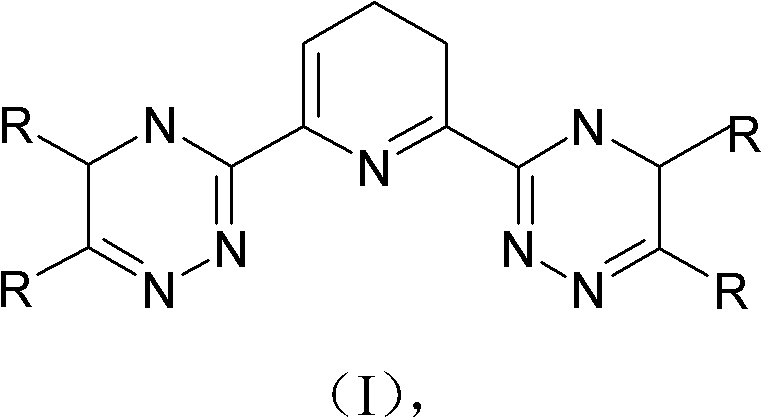
Method for separating element palladium and sub-actinide elements from high-level waste
A technology for high-level radioactive waste and minor actinides, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, solid adsorbent liquid separation, etc., to achieve safe and effective treatment and disposal, high selectivity, simple and efficient methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The preparation of embodiment 1 adsorbent
[0040] Dissolve 100 grams of 2,6-bis-(5,6-di-n-butyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)-pyridine in 1000 mL of dichloromethane and mix well; add 300 grams of coating polymer macroporous SiO 2 (SiO 2 -P) Stir evenly to volatilize most of the dichloromethane until the material is in a nearly dry state, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 45° C. for 24 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The preparation of embodiment 2 adsorbent
[0042] Dissolve 100 g of 2,6-bis-(5,6-dimethyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)-pyridine in 1500 mL of dichloromethane and mix well; add 600 g of coating polymer macroporous SiO 2 (SiO 2 -P) Stir evenly to volatilize most of the dichloromethane until the material is in a nearly dry state, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 45° C. for 24 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Preparation of Adsorbent
[0044] Dissolve 100 grams of 2,6-bis-(5,6-diethyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)-pyridine in 3000 mL of dichloromethane and mix well; add 1500 grams of coating polymer macroporous SiO 2 (SiO 2 -P) Stir evenly to volatilize most of the dichloromethane until the material is in a nearly dry state, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 45° C. for 24 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com