Wavelength-tunable laser based on March-Zehnder interferometer and reflecting grating
A technology for tuning lasers and reflection gratings, which is applied to devices that control the output parameters of lasers, structures of optical resonators, etc., can solve problems such as a wide tunable range, and achieve the effect of avoiding the assembly process, obvious performance and price advantages.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
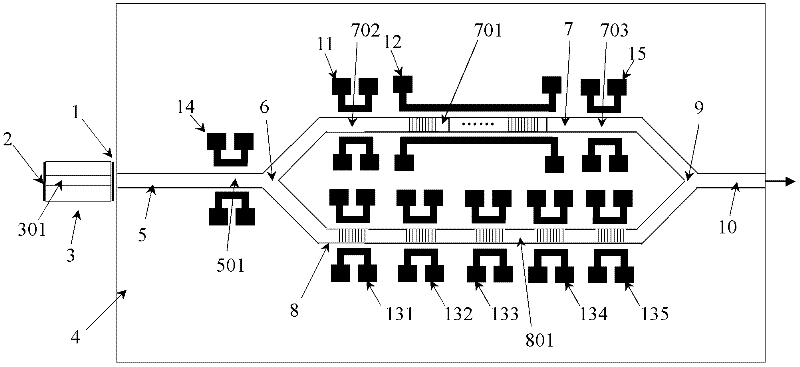
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, the schematic diagram of the top view structure of the wavelength tunable laser based on the compound MZI and reflection grating according to the first embodiment of the present invention, it includes an active gain chip 3, which is used to generate broadband spontaneous emission photons as an excitation light source; The source photonic chip 4 serves as an external cavity to provide wavelength tunable feedback, and generates laser output with tunable wavelength. Each of the active gain chip 3 and the passive photonic chip 4 has a waveguide (optical waveguide), and the two chips are coupled and docked through the waveguide core; the docking of the active gain chip 3 and the passive photonic chip 4 is by placing the Optimal coupling is achieved by precise optical alignment of the waveguide core.
[0042] The waveguide in the passive photonic chip 4 includes an input waveguide 5, a first coupler 6, a second coupler 9, a first waveguide arm 7, a...
Embodiment 2
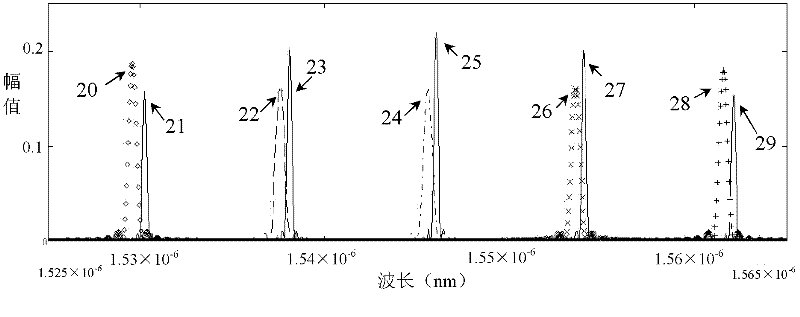
[0062] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the structural principle diagram of the second embodiment of the present invention, the structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of the first embodiment, the difference is that the mirror of the second mirror section 801 is also a sampling grating or a superstructured grating, and the second The two sides of the waveguide core of the reflector section 801 are symmetrically provided with metal electrodes 13 . Such as Figure 5 As shown, the free spectral ranges of the sampling gratings or superstructure gratings of the second mirror section 801 and the first mirror section 701 are different but close; their corresponding comb reflection peaks 30, 31; 32, 33; 34, 35; 36, 37; 38, 39 have similar reflection strengths. The laser coupling phase adjustment section 702 is arranged between the first coupler 6 and the first mirror section 701, and the laser power phase adjustment section 703 is arranged between the second coupler 9 ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the structural principle diagram of the second embodiment of the present invention, the structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of the first embodiment, the difference is that: the mirror of the first mirror section 701 is composed of a waveguide Bragg grating, and the waveguide Bragg grating The number of at least two, the specific number can be set according to the needs of tuning, the number of waveguide Bragg gratings in this embodiment is five. The electrodes 121, 122, 123, 124, and 125 of the first mirror section are symmetrically arranged on both sides of the waveguide core of each waveguide Bragg grating; the mirror of the second mirror section 801 is a sampling grating or a superstructure grating The wavelengths of the reflection peaks of each waveguide Bragg grating are respectively close to the wavelengths of the corresponding reflection peaks in the comb-shaped reflection peak distribution of the sampling gratin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com