Method for forecasting Ac1 point of martensite refractory-steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr
A technology of weld metal and prediction method, applied in chemical property prediction, neural learning method, computer material science and other directions, can solve the problems of wasting time and energy, increasing cost, not suitable for large-scale measurement, etc. energy, increased effects unsuitable for large scale assays
Active Publication Date: 2012-09-12
WUHAN UNIV
View PDF6 Cites 14 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0006] Another purpose of the present invention is to solve the technical problems such as existing in the prior art; 1 A 9% Cr martensitic heat-resistant steel weld metal Ac that wastes time and energy, increases costs and is not suitable for large-scale determination 1 point prediction method
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment
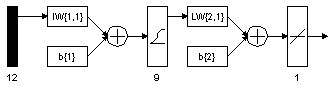
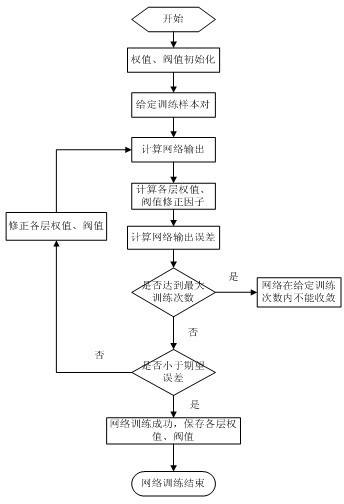
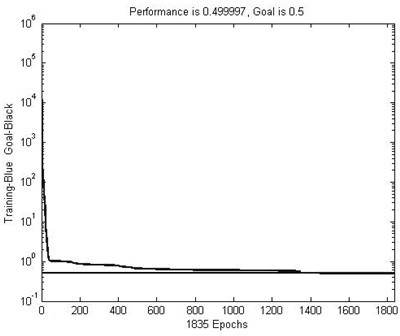
[0075] The BP neural network prediction method involved in the present invention and the traditional expansion method determine the weld metal Ac of 9% Cr martensitic heat-resistant steel 1 Point comparison:
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention relates to a method for forecasting the Ac1 point of martensite refractory-steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr. The A1 point data of T groups of weld metal with different alloy components are obtained by applying an alloy thermodynamics theory through calculation, a neural network based on error back propagation is constructed, the back propagation (BP) network is trained and tested by utilizing the obtained data, and finally, the output threshold of the trained and tested network is corrected by combining the measured data of the Ac1 point of steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr so as to obtain a method which can be used for forecasting the Ac1 point of martensite refractory-steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr. As long as the components (mass fraction) of known weld metal are input, the Ac1 point of weld metal under the condition of the components can be quickly forecasted by utilizing the model. The method for forecasting the Ac1 point of the martensite refractory-steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr can be used for calculating the Ac1 point of martensite refractory-steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr under the condition of some kinds of components so as to provide a basis for selecting the postweld heat treatment temperature of the martensite refractory-steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr. Meanwhile, the method for forecasting the Ac1 point of the martensite refractory-steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr can also be used for directing the alloying design of the welding material of the martensite refractory-steel weld metal with 9 percent of Cr.
Description
technical field [0001] The present invention relates to a metal Ac 1 point prediction method, especially involving a 9% Cr martensitic heat-resistant steel weld metal Ac 1 point forecasting method. Background technique [0002] 9% Cr martensitic heat-resistant steel mainly includes three new types of martensitic heat-resistant steels, P92, P91 and E911, which are widely used in ultra-supercritical boiler main steam pipes, headers and other thick-walled pipes. Low is a major problem when welding this series of steels. In order to improve the toughness of the weld, it is necessary to carry out an alloying design different from the base metal, such as appropriately reducing carbon, silicon, and niobium, and adding austenitic alloying elements such as nickel, manganese, and cobalt, and the corresponding weld metal Ac 1 Points will also change. 9% Cr martensitic heat-resistant steel must be subjected to high-temperature tempering after welding to eliminate welding residual s...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G06N3/08
CPCG16C20/30G16C20/70G16C60/00
Inventor 王学郑江鹏柯洪刚于淑敏
Owner WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com