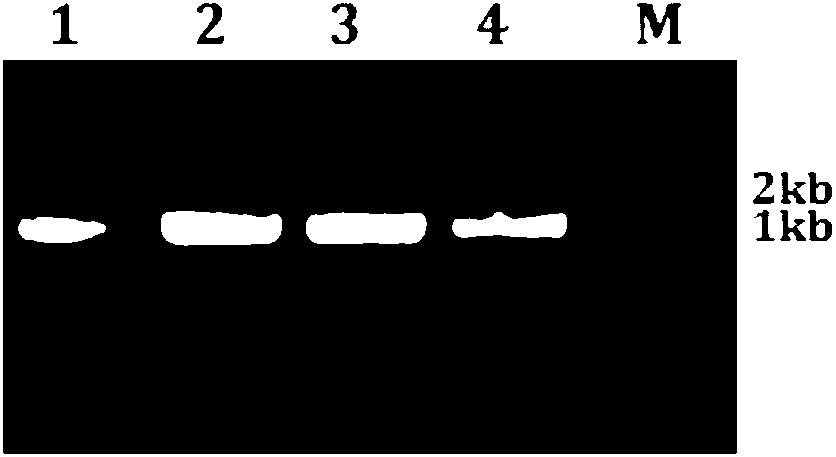Specific molecular markers of eIF4E.a mutation site of Chinese cabbage and application of Specific molecular markers
A mutation site, molecular marker technology, applied in the direction of DNA / RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., to achieve the effect of simple operation, improved screening efficiency, and stable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1. Cloning of eIF4E.a in different Chinese cabbage inbred lines
[0035] 1.1 Chinese cabbage genomic DNA extraction
[0036] (1) Put the leaves of Chinese cabbage seedlings into a liquid nitrogen pre-cooled mortar, and grind them into powder in liquid nitrogen;
[0037] (2) After the liquid nitrogen evaporates to dryness, transfer it to a 2ml centrifuge tube immediately, add about 0.6ml of CTAB extract preheated to 65°C for every 100mg of material, after melting, vigorously shake and mix the sample, place it in a 65°C water bath for 40- 60 minutes to lyse the cells;
[0038] (3) After the lysis is complete, take out the sample and let it cool down to room temperature completely. Add an equal volume of chloroform (chloroform), gently invert to mix, and place at room temperature for 10 minutes;
[0039] (4) Centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 15 minutes at room temperature;
[0040] (5) Use a pipette to carefully suck out the upper aqueous phase, add it to a new 1.5ml...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 Development of dominant ASM markers
[0062] 2.1 Primer design
[0063] Carefully compare the genome sequences of BrA.eIF4E.a1, BrA.eIF4E.a2, BrA.eIF4e.a1, and BrA.eIF4e.a2. The regions with large differences are between 150-600bp, and the key is located in the exon region Therefore, for the difference between the wild type and the mutant, site-specific primers were designed with Primer Premier 5.0 software. The forward primer sequence related to mutant detection is Fm: 5'-GGAAGCTCCTTACGATCCGTCTTCT-3', the forward primer related to wild type detection is FW: 5'-GGAAGCTCCTTACGATCCGTCTTCAC-3', and the universal reverse primer is RWm: 5 '-TGGCACAGATAGGATCCTCCCAC-3'. The primers were synthesized by Beijing Huada Gene Company.
[0064] 2.2 Acquisition of ASM mark:
[0065] (1) Amplification using (FW+RWm) and (Fm+RWm) primer combinations in anti- / sensitivity materials respectively: the preparation of PCR reaction solution and amplification conditions are as des...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3 Identification of different resources of Chinese cabbage by ASM markers
[0069] (1) Genomic DNA extraction of different Chinese cabbage resources: 8 different Chinese cabbage materials were randomly selected, and the genomic DNA of these materials was extracted as described in 1.1.
[0070] (2) PCR amplification: The preparation and amplification conditions of the PCR reaction solution are as described in item (2) of 1.2.
[0071] (3) Detection of PCR products is as described in item (3) of 1.2. Test results such as Image 6 As shown, A: FW+RWm combination amplification result; B: Fm+RWm combination amplification result; M molecular weight standard DL2000, 1-8 are eight Chinese cabbage materials. It can be seen from the figure that 1-4 are wild type and 5-8 are mutants. The identification efficiency of the two sets of primers for homozygous wild type and mutants was 100%.
[0072] (4) Sequencing verification of the eIF4E site was as described in 1.2. The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com