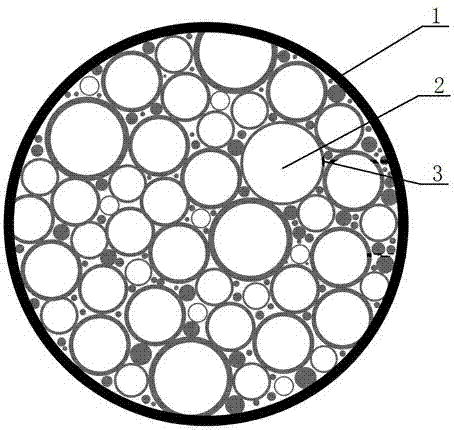
Sustained and controlled release compound fertilizer and its preparation method
A technology of compound fertilizers and granular fertilizers, which is applied in the direction of fertilizer mixtures, fertilization devices, applications, etc., can solve the problems of inability to control the release rates of various nutrients, the inability to achieve differentiation of nutrient release periods, and low fertilizer utilization. Achieve the effects of avoiding nutrient loss, improving consistency, and high fertilizer utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The granules of the above-mentioned slow and controlled release compound fertilizer contain nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium nutrients, and the specific preparation method includes the following sequential steps:
[0023] 1). Prepare nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients separately
[0024] ①. Crushing urea, the basic raw material for nitrogen nutrition, to 60-120 meshes;
[0025] ②. Add the crushed urea into the high-speed mixer and start the high-speed mixer; the temperature in the high-speed mixer is 66°C, and continuously and slowly add (to avoid agglomeration) 3% of the total weight of urea into the high-speed mixer. The colloidal material is in a liquid state, so that each microparticle urea and the colloidal material are fully stirred and mixed, and the stirring time is 5 minutes. The surface of each microparticle urea forms a colloidal film, and each microparticle urea is in the shape of a microcapsule;
[0026] ③. According to steps ① and ②, respecti...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The granules of the above-mentioned slow and controlled release compound fertilizer contain nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium nutrients, and the specific preparation method includes the following sequential steps:
[0032] 1). Prepare nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients separately
[0033] ①. Crush ammonium chloride, the basic raw material for nitrogen nutrition, to 80-120 meshes;
[0034] ②. Add the crushed ammonium chloride into the high-speed mixer and start the high-speed mixer; the temperature in the high-speed mixer is 73°C, and continuously and slowly add 5% of the total weight of urea into the high-speed mixer (to avoid agglomeration). Material-resin, the colloidal material is in a molten state, so that each particulate ammonium chloride and the colloidal material are fully stirred and mixed, and the stirring time is 4min. The surface of each particulate ammonium chloride forms a gelatinous film, and each particulate ammonium chloride is micro Capsul...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The granules of the above-mentioned slow and controlled release compound fertilizer contain nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium nutrients, and the specific preparation method includes the following sequential steps:
[0040] 1). Prepare nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients separately
[0041] ①. Crushing urea, the basic raw material for nitrogen nutrition, to 60-100 meshes;
[0042] ②. Add the crushed urea into the high-speed mixer and start the high-speed mixer; the temperature inside the high-speed mixer is 80°C, and continuously and slowly add 4% of the total weight of urea into the high-speed mixer (to avoid agglomeration). Lipids, colloids, and colloidal materials are in a liquid state, so that the microparticles of urea and the colloidal materials are fully stirred and mixed for 5 minutes. The surface of each microparticle of urea forms a colloidal film, and each microparticle of urea is in the shape of a microcapsule;
[0043] ③. Follow steps ① and ② to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com