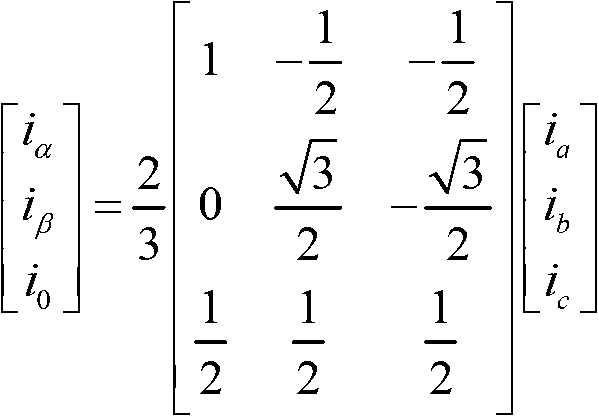Method for determining initial position angle of rotor of permanent-magnetic synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, rotor initial position technology, applied in the control of generator, motor generator control, control of electromechanical transmission and other directions, can solve the problems of low precision, failure of motor start, complex processing steps, etc., to achieve high current Sampling accuracy, small possibility of misjudgment, and concise follow-up processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
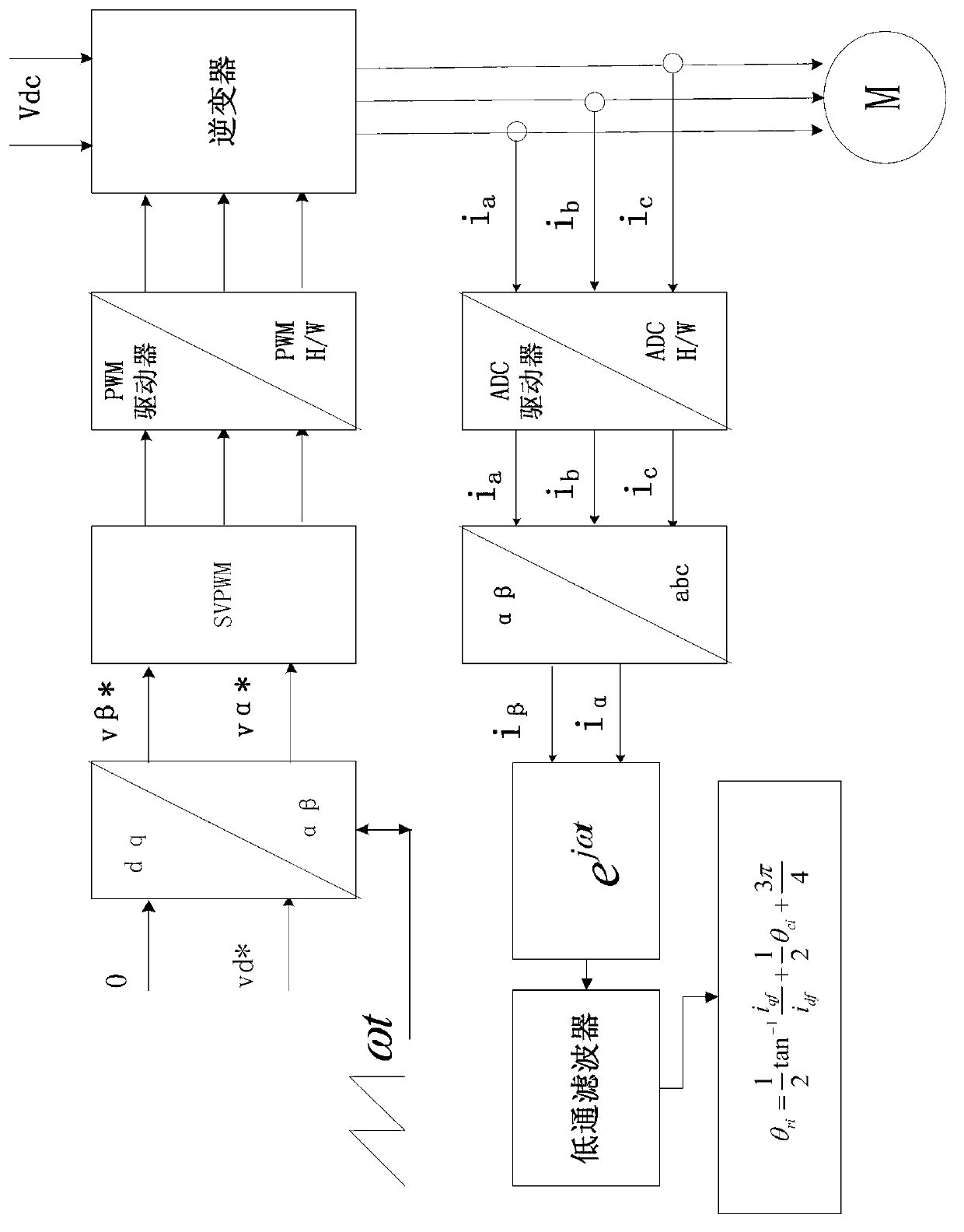
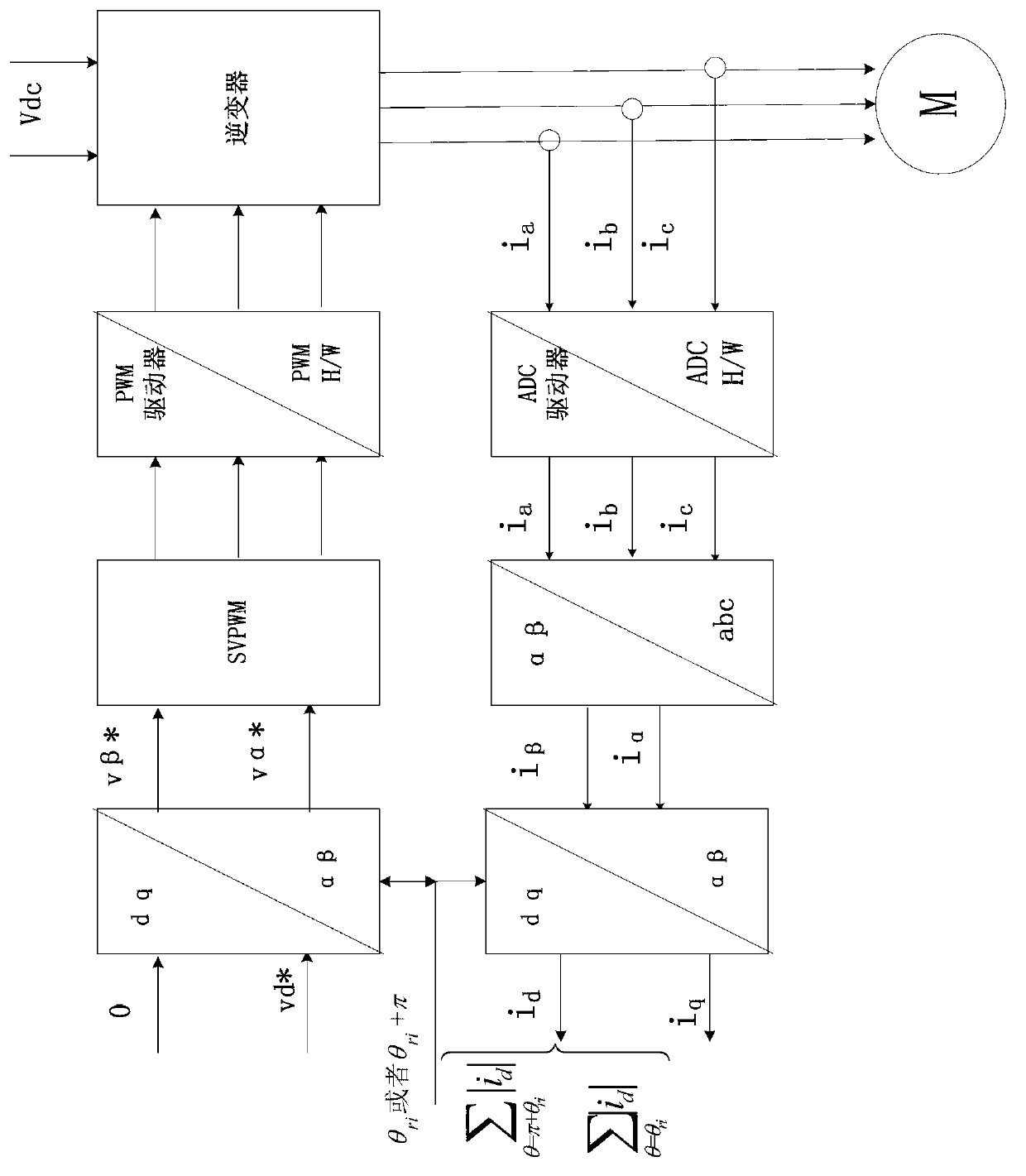
[0022] combined with figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a method for determining the initial position angle of the rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor according to an embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0023] Step 1, inject amplitude U, angular frequency ω, and initial phase θ into the stator winding of the permanent magnet synchronous motor under test ci The high-frequency rotating voltage vector signal of the
[0024] The high-frequency torque generated by the high-frequency rotating voltage vector signal is not enough to make the measured permanent magnet synchronous motor rotate, so it can ensure that the motor is in a static state during the identification process; in addition, the injected high-frequency rotating voltage vector signal The angular frequency ω is much higher than the rated operating frequency of the tes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com