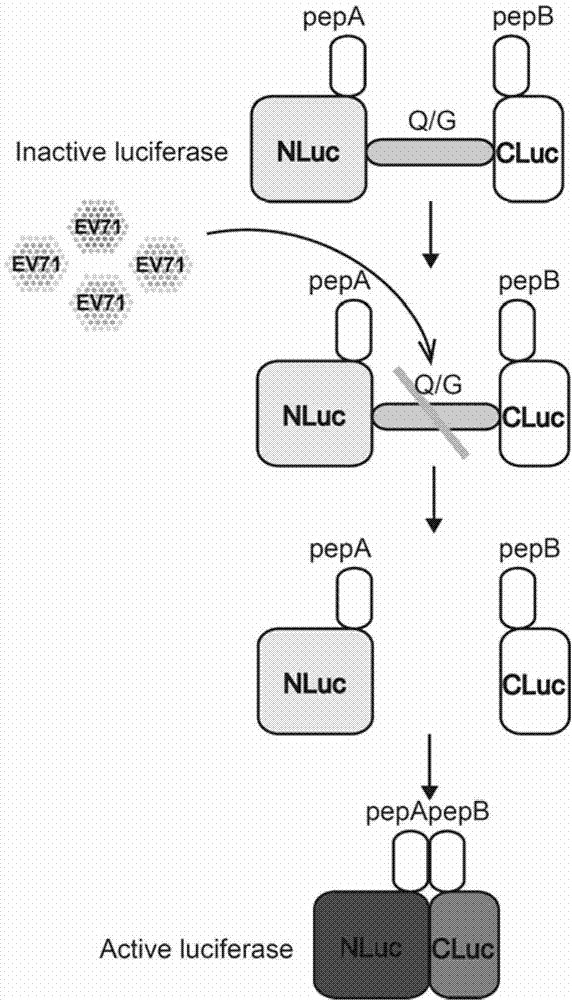
Fusion protein for screening and evaluating anti-enterovirus 71 medicine and application of fusion protein
A fusion protein and enterovirus technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of difficulty in evaluating the anti-EV71 effect of drugs, complicated operation, and lack of evaluation system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
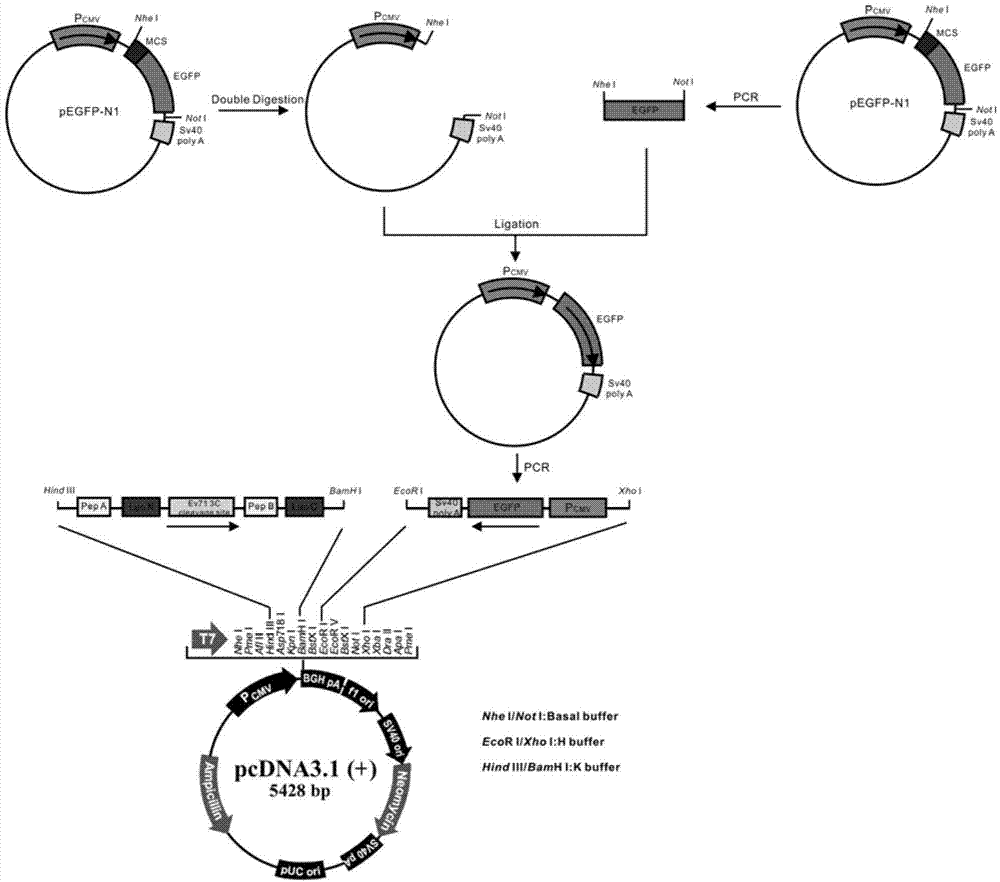
[0062] The construction of embodiment 1 fusion protein ANluc (△ Q / G) BCluc-EGFP eukaryotic expression vector
[0063] 1.1 Construction of pCDNA3.1(+)-EGFP plasmid platform
[0064] First, remove the multiple cloning site in the plasmid pEGFP-N1 (purchased from Clontech, USA) to construct the plasmid pEGFP-N1', then amplify the CMV-EGFP-SV40 fragment, and insert the fragment reversely into pCDNA3.1(+) (purchased from Invitrogen, USA) with multiple cloning sites to construct the vector plasmid pCDNA3.1(+)-EGFP.
[0065] According to the cDNA sequence of EGFP (Genebank number: GI1377911), the primer sequence for PCR amplification of the EGFP gene fragment was designed as follows:
[0066] P1 (upstream primer): 5'-ATATATGCTAGCATGGTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGA-3'
[0067] P2 (downstream primer): 5'-ATATAGCGGCCGCTTACTTGTACAGCTCGTCCA-3'
[0068] The primer sequences for amplifying the CMV-EGFP-SV40 fragment are as follows:
[0069] P3 (upstream primer):
[0070] 5'-GCGCGCTCGAGTAGTTATTAATAGTA...
Embodiment 2
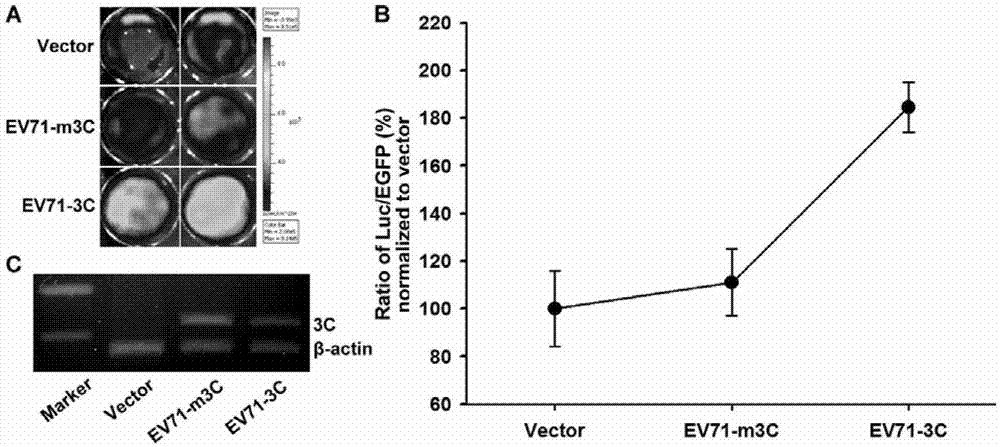
[0097] Example 2 The use of intracellular transfection to express the carrier of the EV713C protein to verify the effect of the fusion protein
[0098] 1. Construction of vector pEGFP-3C
[0099] 1.1 Construction of pEGFP-C1 plasmid platform
[0100] Using pcDNA3.1 (+) (purchased from Invitrogen, USA) as the basic plasmid backbone, the EGFP nucleic acid fragment with a flexible link at the 3' end was amplified from the pEGFP-N1 plasmid (purchased from Invitrogen, USA), and the green fluorescent protein EGFP The gene fragment was inserted into the pcDNA3.1 (+) plasmid to construct the pEGFP-C1 plasmid platform.
[0101] According to the cDNA sequence design of EGFP (Genebank number: GI1377911), the 3' end of PCR amplification was designed with a flexible linker (5'GGTGGAGGCGGTTCAGGCGGAGGTGGCTCTGGCGGTGGCGGATCG3')
[0102] The primer sequence of the EGFP gene fragment is as follows:
[0103] P9 (upstream primer): 5'-ATATATAGCTAGCATGGTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGAGCT-3'
[0104] P10 (downst...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com