Method for efficient polyculture of environmental-friendly fresh water fishes, shrimps and crabs
An environment-friendly, freshwater fish technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, fish farming, climate change adaptation, etc., can solve problems such as destruction of biodiversity in aquaculture waters, pollution of aquaculture waters, environmental pollution of aquaculture waters, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
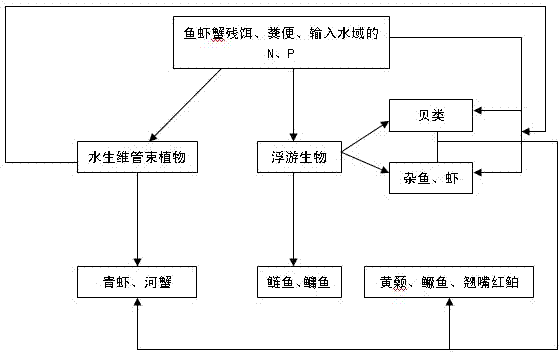
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0020] (1) Use the area within 5 meters along the shore of the breeding waters as the aquatic plant cultivation area, and cultivate aquatic plants such as water chestnut, lotus, water lily, eye vegetable, water hyacinth, and lotus philodendron, so that the coverage rate of aquatic plants accounts for the More than 80% of the cultivation area;
[0021] (2) Take the 20% area of the breeding water area after the aquatic plant cultivation area is removed as the breeding area, and put freshwater shrimp and river crabs in the breeding area. The specification is 30-50 / 500g, 180 per mu;
[0022] (3) The remaining area is the special fish, shrimp, and crab multiplication area. In this area, the fine aquatic plants that fish, shrimps, and crabs like to eat are cultivated, such as bitter grass, reed, calamus, bitter grass, dwarf algae, eye spinach, and hydrilla. The coverage area is greater than 60% of the area of the breeding ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0025] (1) Use the area within 5 meters along the shore of the breeding waters as the aquatic plant cultivation area, and cultivate aquatic plants such as water chestnut, lotus, water lily, eye vegetable, water hyacinth, and lotus philodendron, so that the coverage rate of aquatic plants accounts for the More than 80% of the cultivation area;
[0026] (2) Take the area of 30% of the breeding water area after the aquatic plant cultivation area is removed as the breeding area, and put freshwater shrimp and river crabs in the breeding area. The specification is 30-50 / 500g, 200 per mu;
[0027] (3) The remaining area is the special fish, shrimp, and crab multiplication area. In this area, the fine aquatic plants that fish, shrimps, and crabs like to eat are cultivated, such as bitter grass, reed, calamus, bitter grass, dwarf algae, eye spinach, and hydrilla. The coverage area is greater than 60% of the area of the breedi...
Embodiment 3
[0029] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0030] (1) Use the area within 5 meters along the shore of the breeding waters as the aquatic plant cultivation area, and cultivate aquatic plants such as water chestnut, lotus, water lily, eye vegetable, water hyacinth, and lotus philodendron, so that the coverage rate of aquatic plants accounts for the More than 80% of the cultivation area;
[0031] (2) Take the 25% area of the breeding water area after removing the aquatic plant cultivation area as the breeding area, put green shrimp and river crab in the breeding area, the body length of the green shrimp is 0.8-1cm, put 3000 tails per mu, and the crab The specification is 30-50 / 500g, 150 per mu;
[0032] (3) The remaining area is the special fish, shrimp, and crab multiplication area. In this area, the fine aquatic plants that fish, shrimps, and crabs like to eat are cultivated, such as bitter grass, reed, calamus, bitter grass, dwarf algae, eye spinach, and hydrill...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com