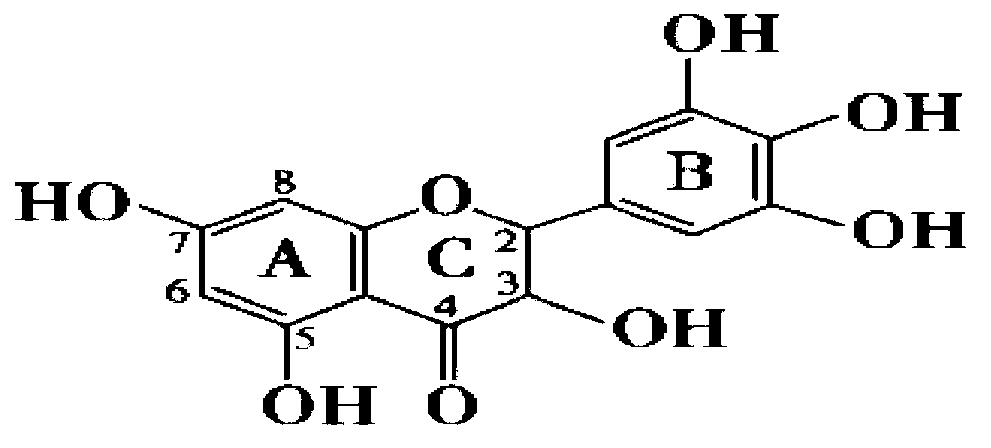
Method for extracting dihydromyricetin and Ampelopsis grossedentata polysaccharide from Ampelopsis grossedentata
A technology of dihydromyricetin and vine tea, applied in the direction of organic chemistry and the like, can solve the problems of low extraction efficiency, low extraction purity, complicated extraction process, etc., and achieves improved extraction rate and purity, good operation safety, and simple process. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] A method for extracting dihydromyricetin and vine tea polysaccharide from vine tea, it comprises the following steps:
[0023] (1) Dry the fresh vine tea stems and leaves, and then crush them into 100-mesh vine tea particles;
[0024] (2) Soak the above vine tea granules in a solvent, and the ratio of solid to liquid between vine tea granules and solvent is 1:8;
[0025] (3) Add the mixed solvent to the microwave countercurrent extraction equipment for microwave extraction, repeat the operation 3 times, each extraction time is 10 minutes, and obtain the extract;
[0026] (4) Heat the extract to 40°C, first filter the suspension with a ceramic membrane, and then pass the obtained filtrate through the ultrafiltration membrane while it is hot, and the molecular weight cut-off of the ultrafiltration membrane is 8000 Daltons;
[0027] (5) The filtrate is concentrated, crystallized and dried;
[0028] (6) The part that failed to filter through the ultrafiltration membrane w...
Embodiment 2
[0033] A method for extracting dihydromyricetin and vine tea polysaccharide from vine tea, it comprises the following steps:
[0034] (1) Dry the fresh vine tea stems and leaves, and then crush them into 90-mesh vine tea particles;
[0035] (2) Soak the above-mentioned rattan tea granules in a solvent, the ratio of solid to liquid of rattan tea granules and solvent is 1:20;
[0036] (3) Add the mixed solvent to the microwave countercurrent extraction equipment for microwave extraction, repeat the operation twice, each extraction time is 15 minutes, and obtain the extract;
[0037] (4) Heat the extract to 50°C, first filter the suspension with a ceramic membrane, and then pass the obtained filtrate through the ultrafiltration membrane while it is hot, and the molecular weight cut-off of the ultrafiltration membrane is 50,000 Daltons;
[0038] (5) The filtrate is concentrated, crystallized and dried;
[0039] (6) The part that failed to filter through the ultrafiltration membr...
Embodiment 3
[0044] A method for extracting dihydromyricetin and vine tea polysaccharide from vine tea, it comprises the following steps:
[0045] (1) Dry the fresh vine tea stems and leaves, and then crush them into 95-mesh vine tea particles;
[0046] (2) Soak the above-mentioned rattan tea particles in a solvent, and the ratio of solid to liquid between rattan tea particles and solvent is 1:10;
[0047] (3) Add the mixed solvent to the microwave countercurrent extraction equipment for microwave extraction, repeat the operation 5 times, each extraction time is 8 minutes, and obtain the extract;
[0048] (4) Heat the extract to 45°C, first filter the suspension with a ceramic membrane, and then pass the obtained filtrate through the ultrafiltration membrane while it is hot, and the molecular weight cut-off of the ultrafiltration membrane is 20,000 Daltons;
[0049] (5) The filtrate is concentrated, crystallized and dried;
[0050] (6) The part that failed to filter through the ultrafilt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com