Digital linear servo pump
A servo pump, digital technology, applied in the field of digital linear servo pumps, can solve the problems of high cost, low drive efficiency, heat generation, etc., achieve high drive stiffness and precision, overcome heat generation problems, and improve the effect of smoothness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] In order to further understand the invention content, characteristics and effects of the present invention, the following examples are given, and detailed descriptions are as follows in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
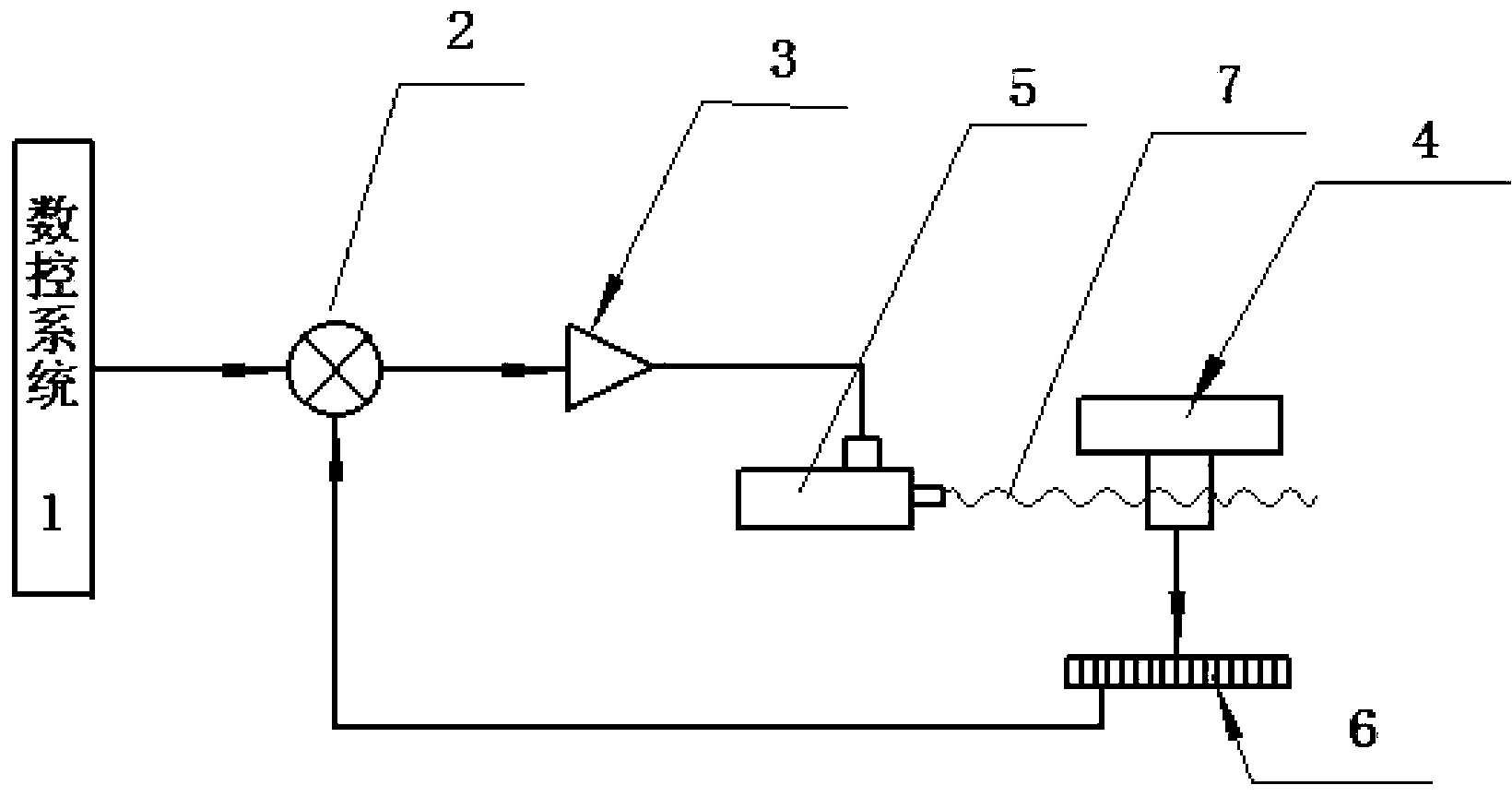
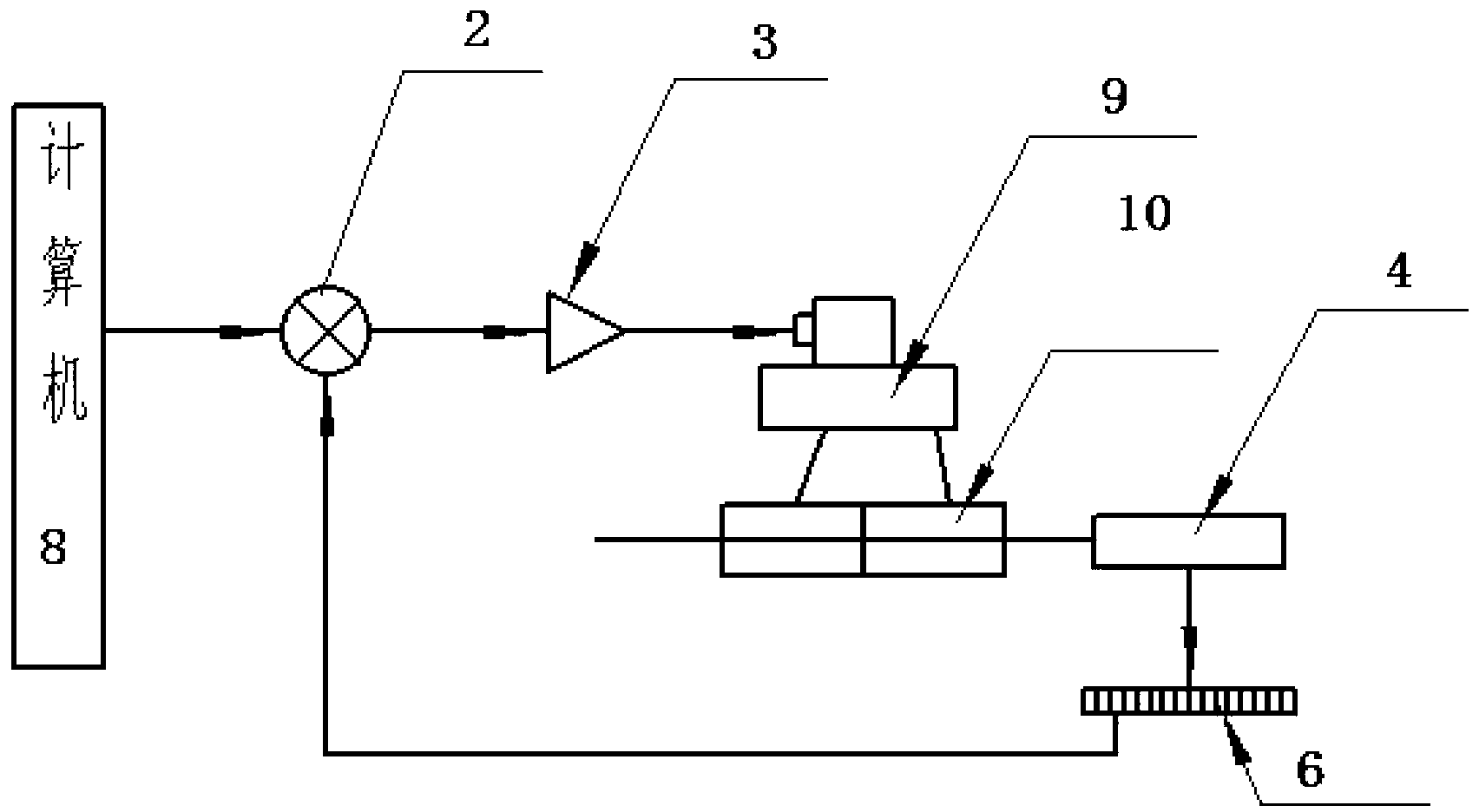
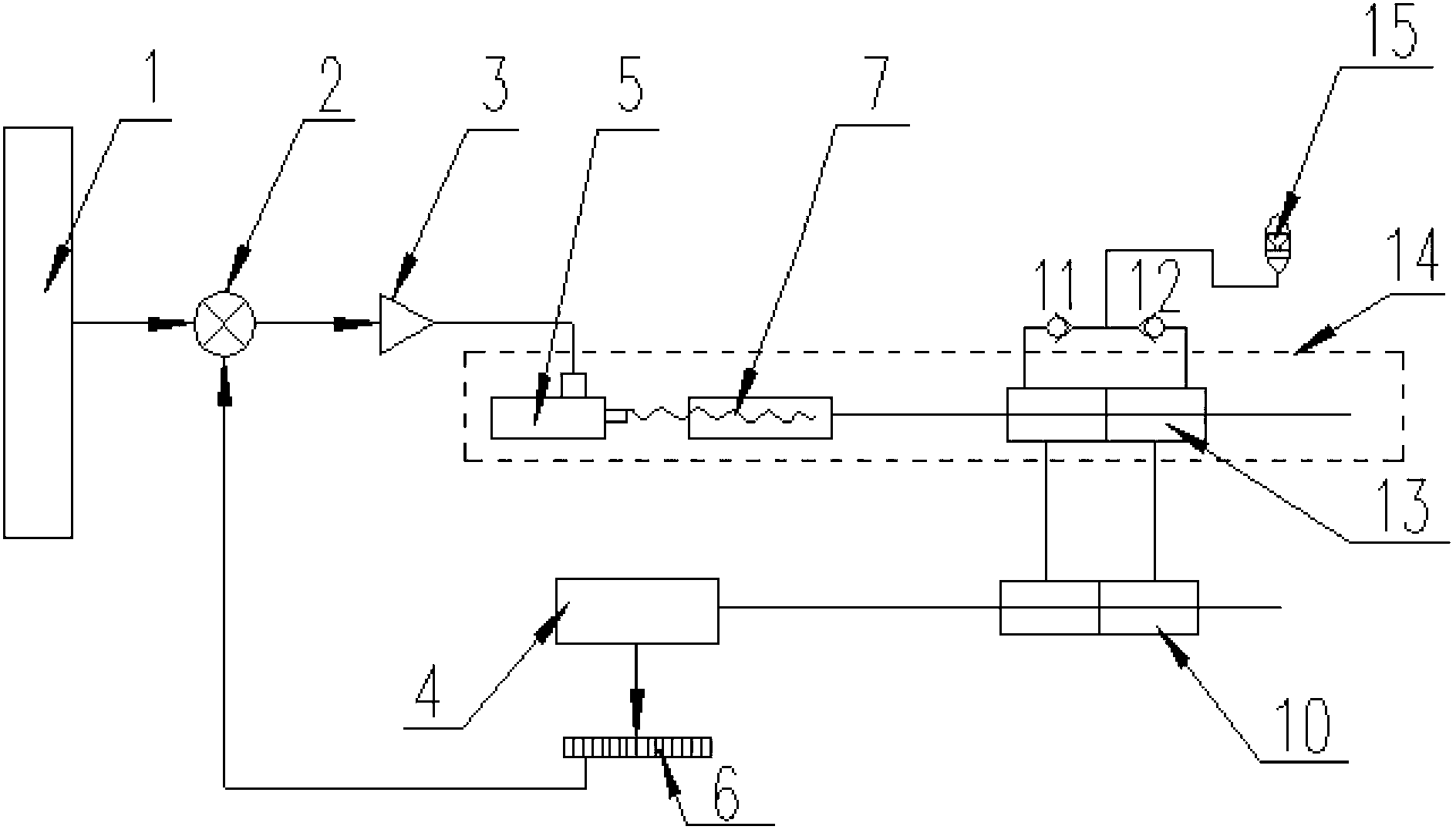
[0028] The digital linear servo pump of the present invention combines a servo motor, a ball screw and an oil cylinder to form a digital linear servo pump,
[0029] Such as image 3 As shown, the digital linear servo pump of the present invention includes a numerical control system 1, a comparator 2, and a servo amplifier 3 connected in sequence. The output of the servo amplifier 3 is connected to a linear oil pump 14, and the linear oil pump 14 passes through a pipeline Connected to the first oil cylinder group 10 , the piston of the first oil cylinder group 10 is connected to and drives the machine tool table 4 , and the machine tool table 4 is connected to the comparator 2 through the grating 6 .
[0030] The linear oil pump 14 includes a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com