Compositions and methods for enhancing proteasome activity
A compound and hydrate technology, applied in the field of compositions and methods for improving proteasome activity, can solve problems such as affecting the degradation rate of substrates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0505] Embodiment 1--the synthesis of inhibitor
[0506] Figure 29 One method of preparing the pyrroles of the invention is described. Similar oxadiazole compounds can be prepared by forming a 1,3-oxadiazole instead of an pyrrole. By varying the ring substitution on the arylamine ring 1a, or substituting alkylamines, heteroarylamines, aralkylamines, etc., a wide variety of compounds can be synthesized. Likewise, compound 1e can be reacted with a variety of nucleophiles to provide a variety of compounds. provided below Figure 29 The experimental procedures for the corresponding compounds are shown.
[0507] Synthesis of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,5-dimethylpyrrole (1c). The mixture of 1a (7.65g, 60.0mmol) and 1b (34.2g, 300.0mmol) was heated to 100°C in glacial acetic acid (40mL) for 1 hour, then the solvent was evaporated to dryness, and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain 1c (11.07g , yield: 89.8%).
[0508] Synthesis of 2-chloro-1-[1-(4-...
Embodiment 2
[0510] Example 2 - Usp14 mediates deubiquitination of substrates
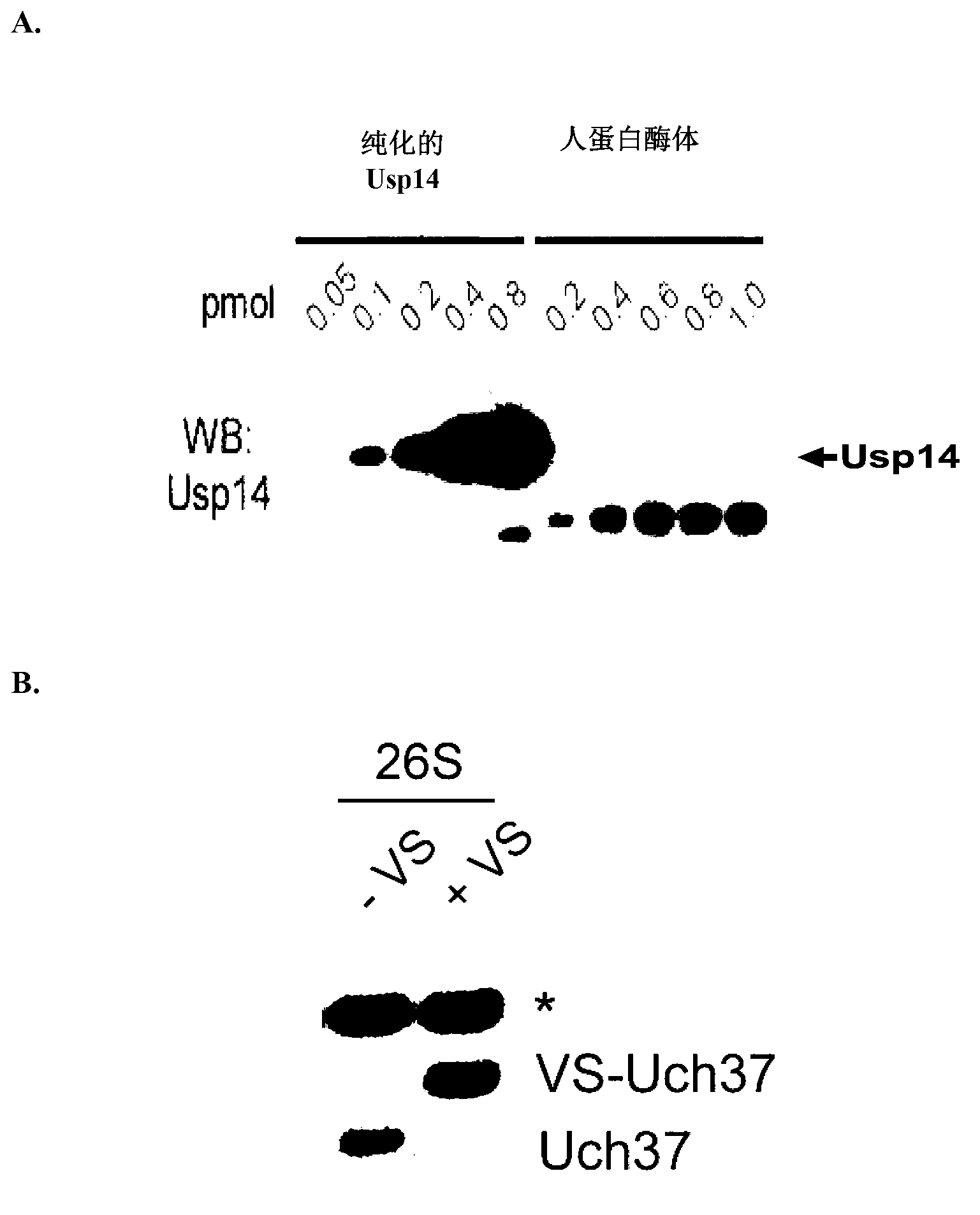
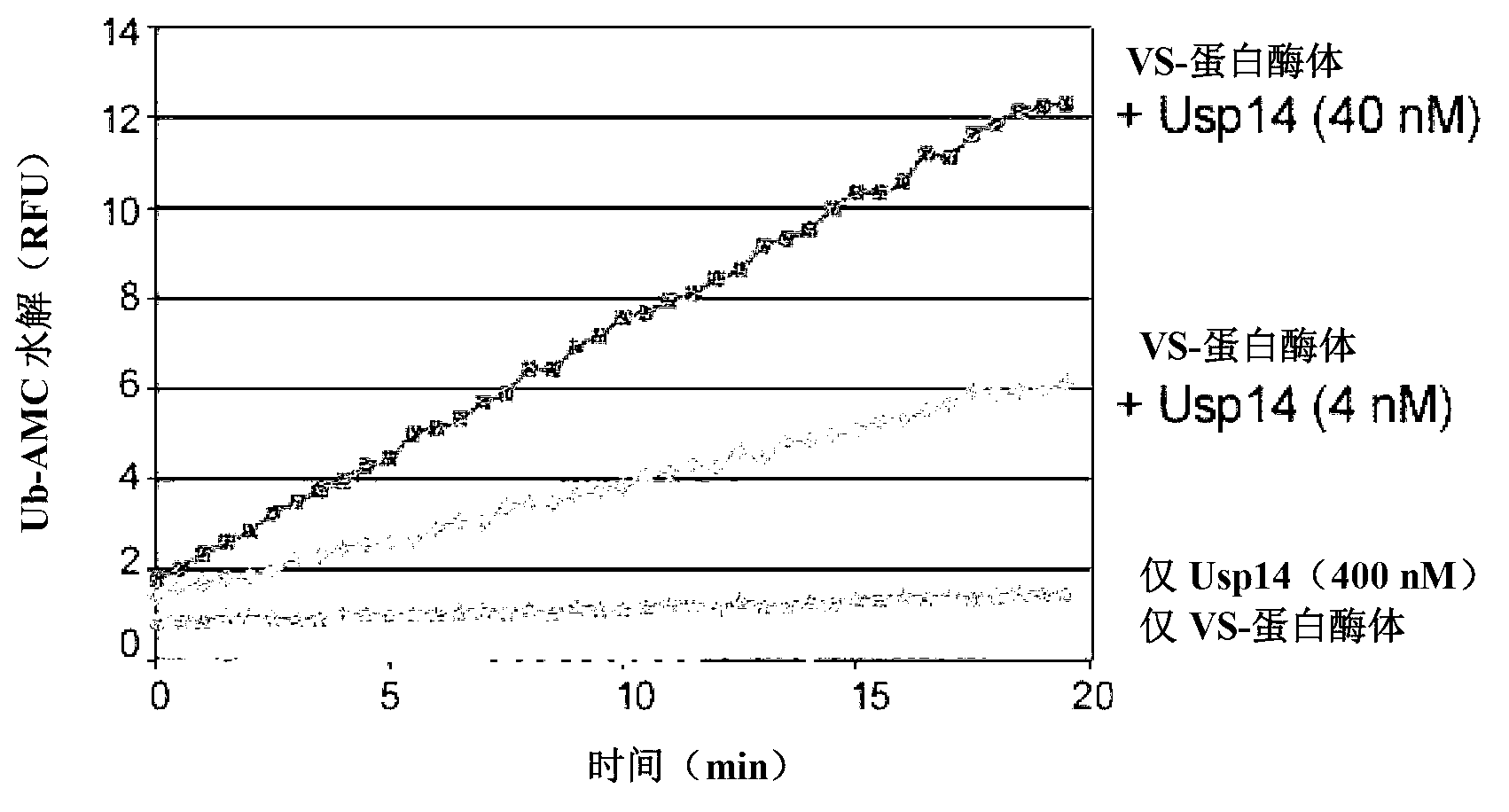
[0511] To test whether Usp14 is a potent inhibitor of the human proteasome, a purification procedure was developed to generate proteasomes lacking detectable levels of the deubiquitinating enzyme Usp14 (modified from Wang et al., (2007), Biochemistry, 46, 3553-3565). Briefly, human proteasomes were large-scale affinity purified from a stable HEK293 cell line harboring HTBH-tagged hRpn11. Cells were lysed in a Dunes homogenizer using lysis buffer containing protease inhibitors (50 mM NaH 2 PO 4 [pH 7.5], 100mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 5mM MgCl 2 , 0.5% NP-40, 5mM ATP, and 1mM DTT). Washed lysates were incubated overnight at 4°C on NeutrAvidin agarose resin (Thermo Scientific). Subsequently, the beads were washed with excess lysis buffer, followed by wash buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 1 mM MgCl 2 and 1mM ATP). To generate VS-proteasomes, 1 to 1.5 μM Ub-VS (Boston Biochem) was added to the resin and incubated...
Embodiment 3
[0516] Example 3 - Usp14 inhibits proteasomal degradation
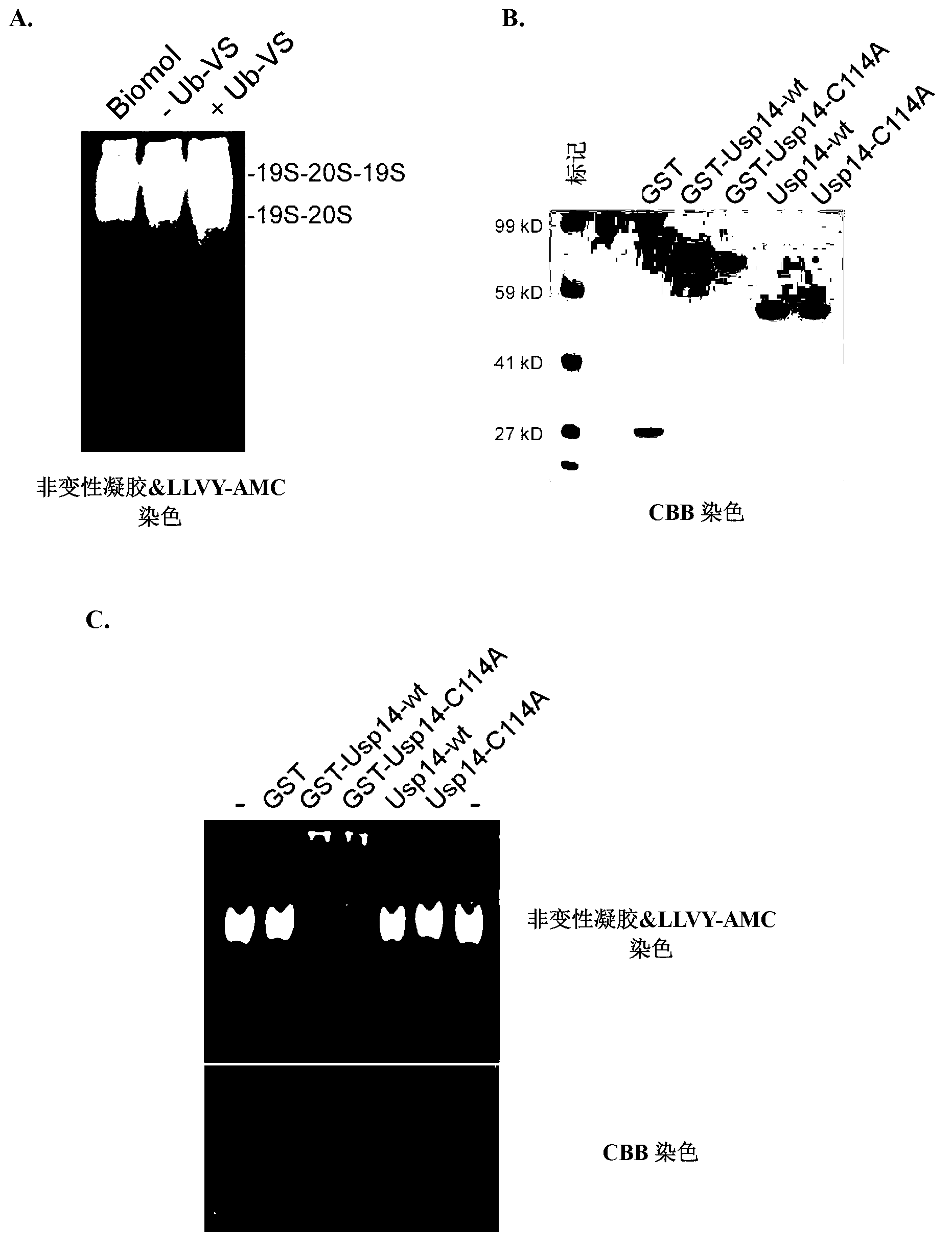
[0517] The effect of Usp14 on the degradation of ubiquitinated substrates was examined in an in vitro degradation assay using the ubiquitin-dependent proteasome substrate polyubiquitinated cyclin B (Ub n -ClnB). In these experiments, Ub n -ClnB was co-incubated with human proteasome (4nM) containing wild-type or catalytically inactive Usp14 (60nM). The catalytically inactive Usp used in these experiments was Usp14-C114A, which contains a mutation in the active deubiquitinating site of Usp14. Notably, both wild-type Usp14 and Usp14-C114A were able to bind to mammalian proteasome 26S ( figure 2 ). Such as Figure 5As shown, Usp14 strongly inhibits the degradation of cyclin B, while the active site mutant of Usp14 has no inhibitory effect. Active site mutants deficient for Ub n -Inhibition of ClnB degradation suggests that the activity of wild-type Usp14 to trim ubiquitin chains is required for Usp14 to inhibit p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com