Patents
Literature
50 results about "Deubiquitination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
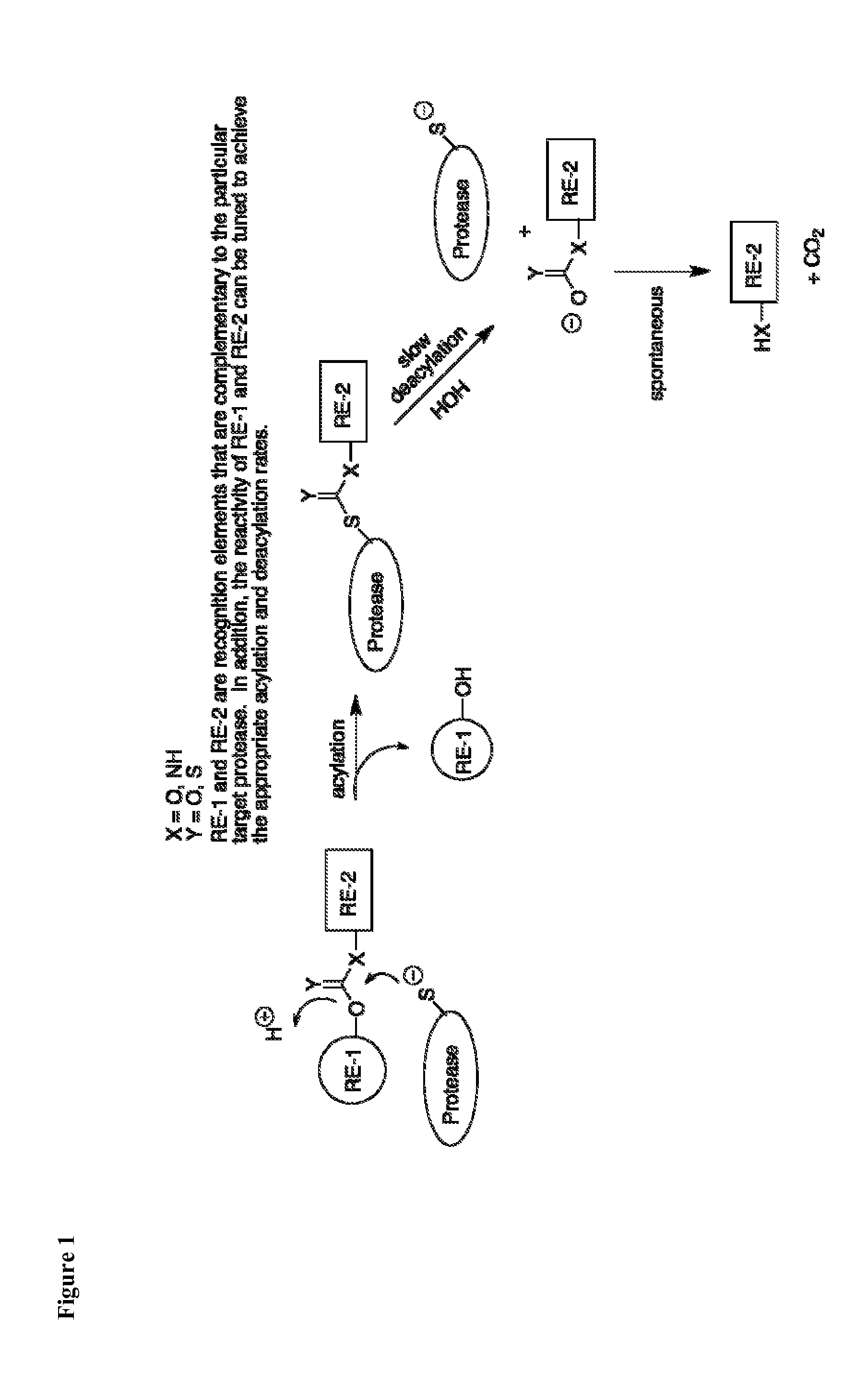
The generation of ubiquitin from proproteins and the processing of polyubiquitin chains to release monomeric ubiquitin. (NCI)
Assay for ubiquitin mediated proteolysis
InactiveUS20080038768A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFluorescenceDeubiquitination
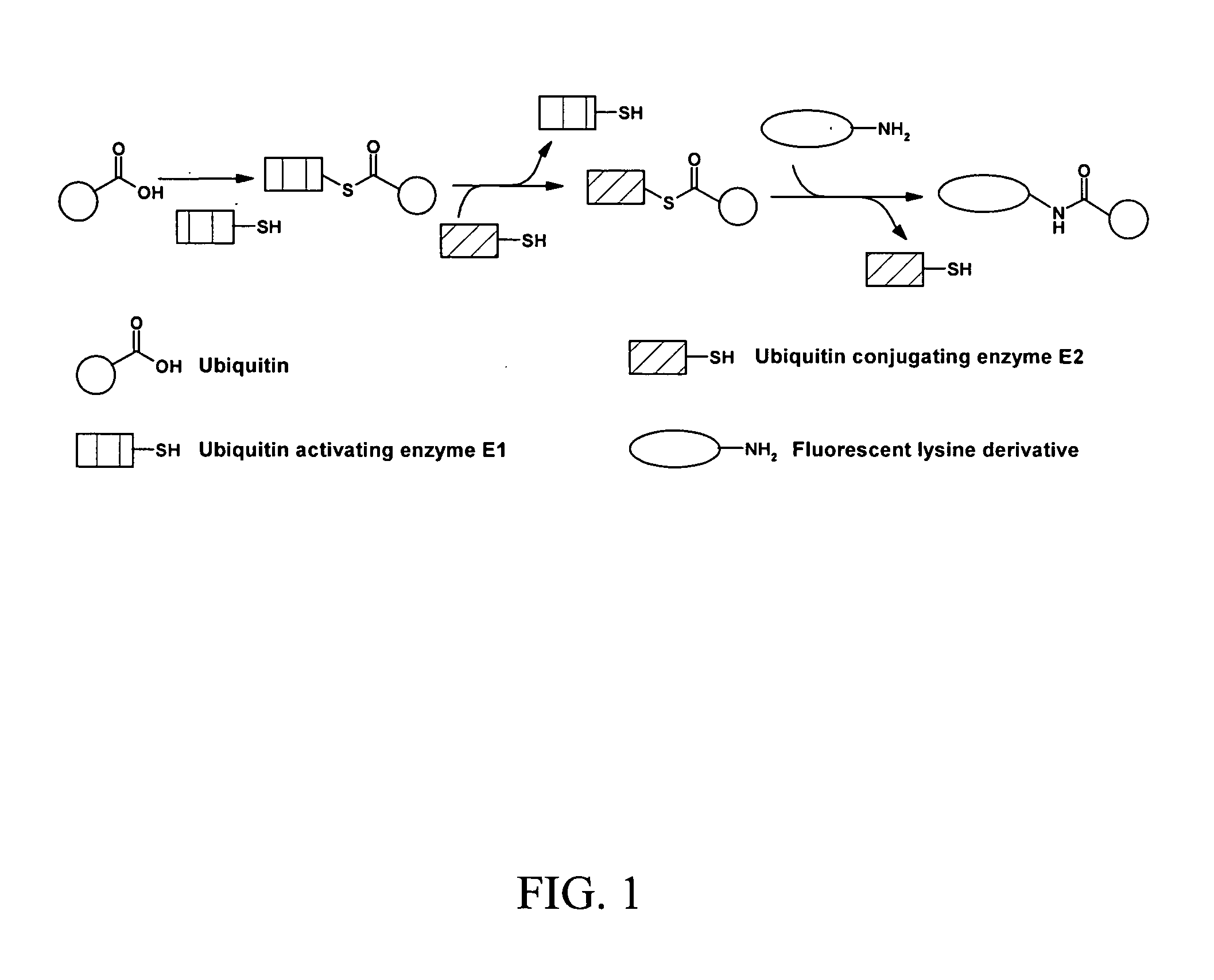
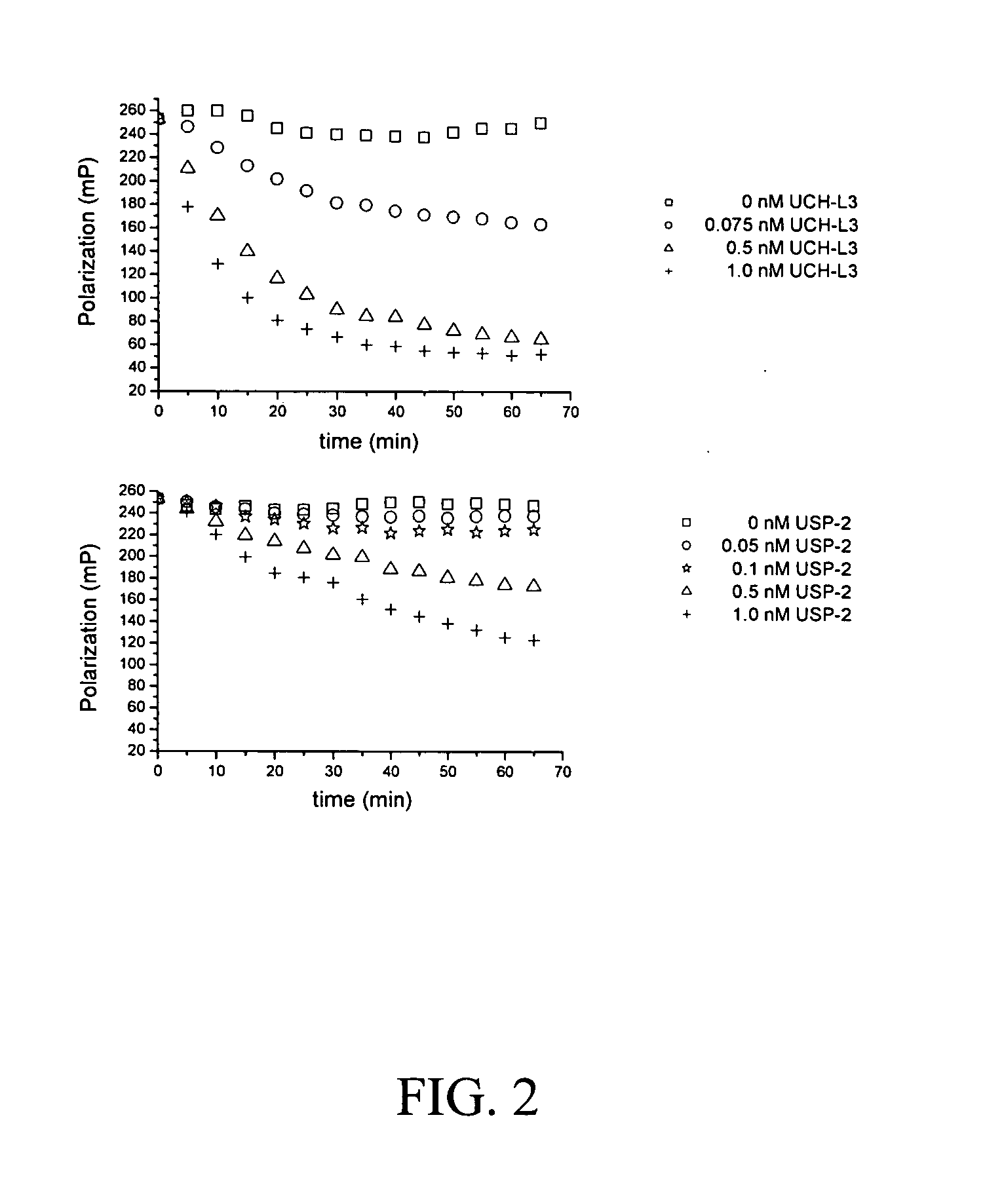
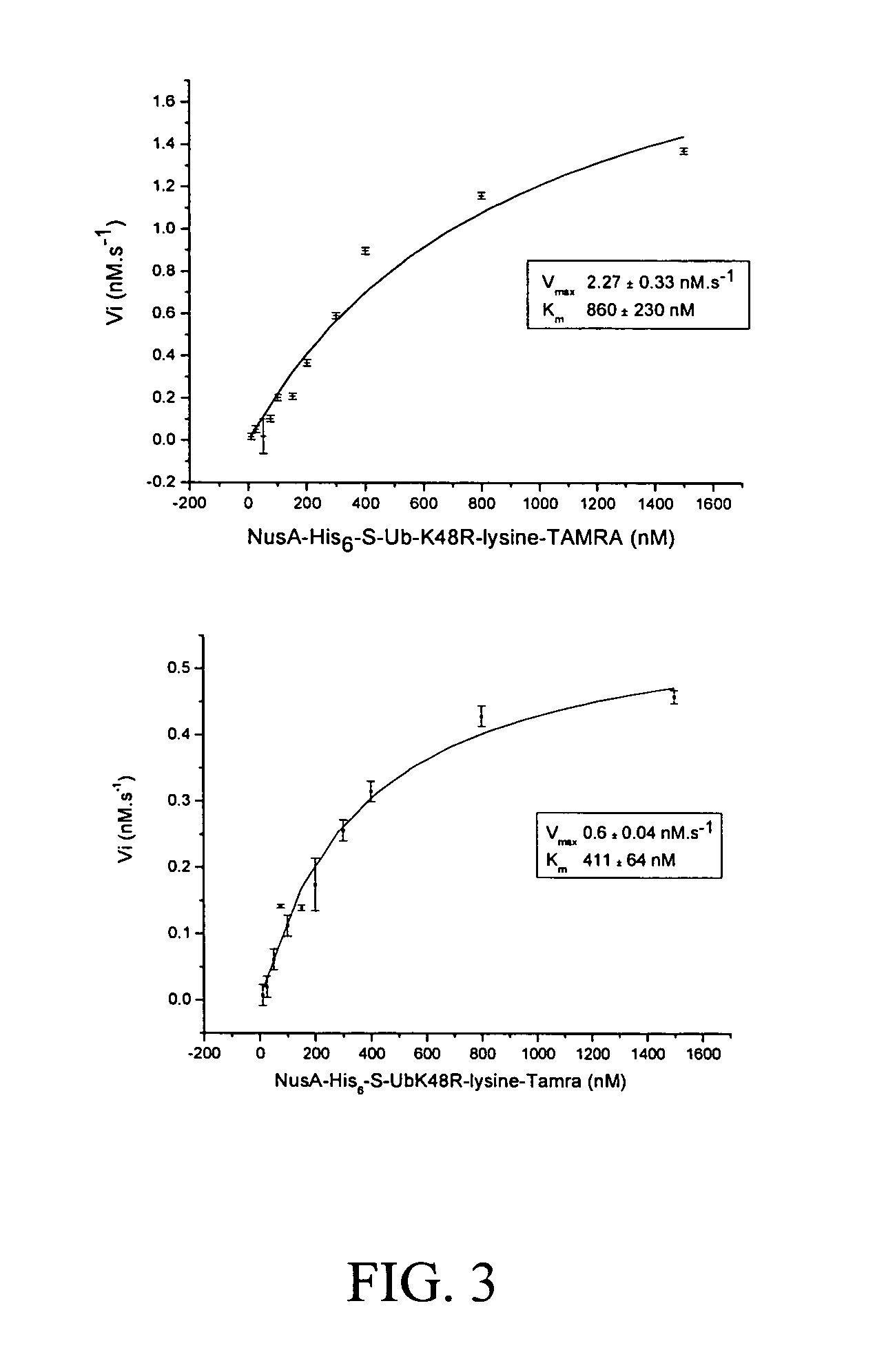
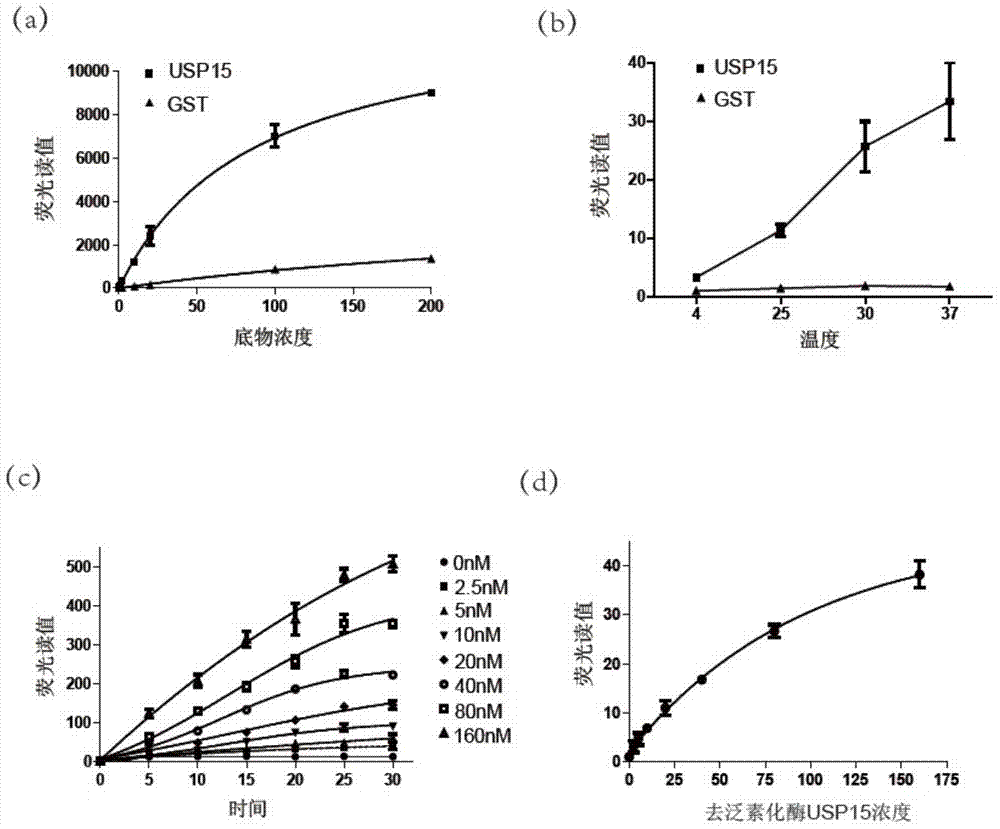
The present invention provides methods and compositions useful in the screening for agents that modulate activity of a deubiquitinating enzyme. In one embodiment, the invention relates to methods for measuring a deubiquitination activity comprising combining a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) with a substrate comprising a ubiquitin moiety and a fluorescently labeled compound under conditions allowing for deubiquitinating activity and measuring an altered fluorescence polarization and / or fluorescence lifetime of the released fluorescently labeled compound The invention also relates to a substrate library comprising peptides of the formula (Z)a(X)mK(X)n(Z)b useful e.g. for the determination of the substrate specificity of a deubiquitinating enzyme.
Owner:FILIPUZZI IREOS +2
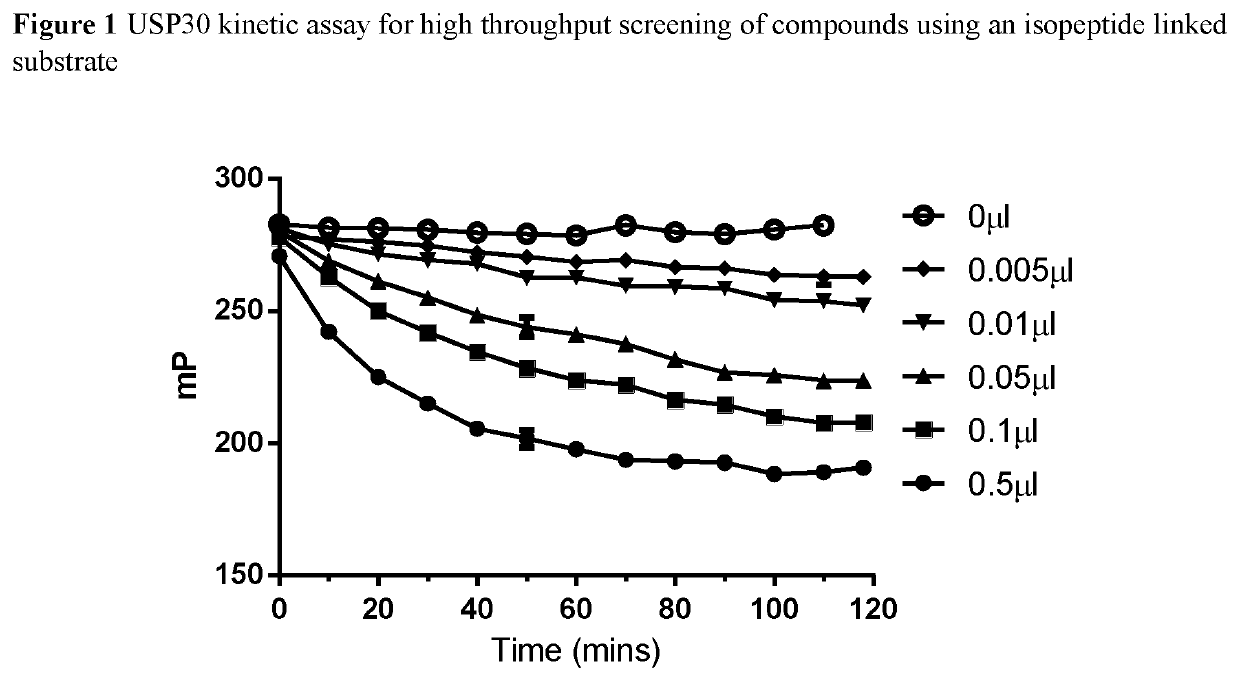
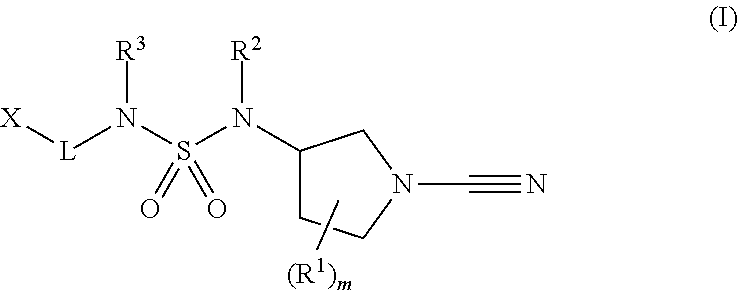
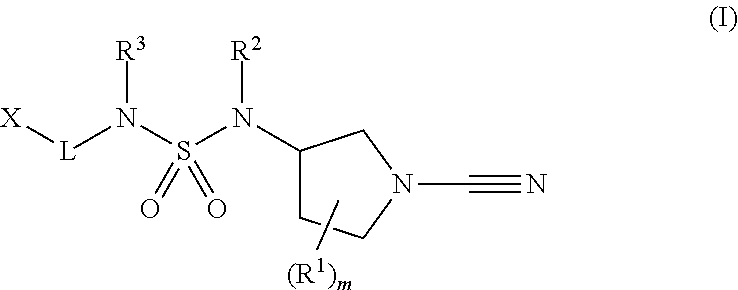
1-cyano-pyrrolidine derivatives as inhibitors of usp30
The present invention relates to novel compounds and methods for the manufacture of inhibitors of deubiquitylatin-enzymes (DUBs). In particular, the invention relates to the inhibition of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase 30 or Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 30 (USP30). The invention further relates to the use of DUB inhibitors in the treatment of conditions involving mitochondrial dysfunction and cancer. Compounds of the invention include compounds having the formula (I) (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, m, L and X are as defined herein.
Owner:MISSION THERAPEUTICS
Kinase and ubiquination assays
InactiveUS20070264678A1Improve throughputReduce the amount of noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisEnergy transferKinase activity
Compositions, including antibodies, polypeptides, and organic molecules, kits, and methods for probing molecular interactions (e.g., deubiquination, ubiquination and kinase activity), e.g., using resonance energy transfer (RET) are provided.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
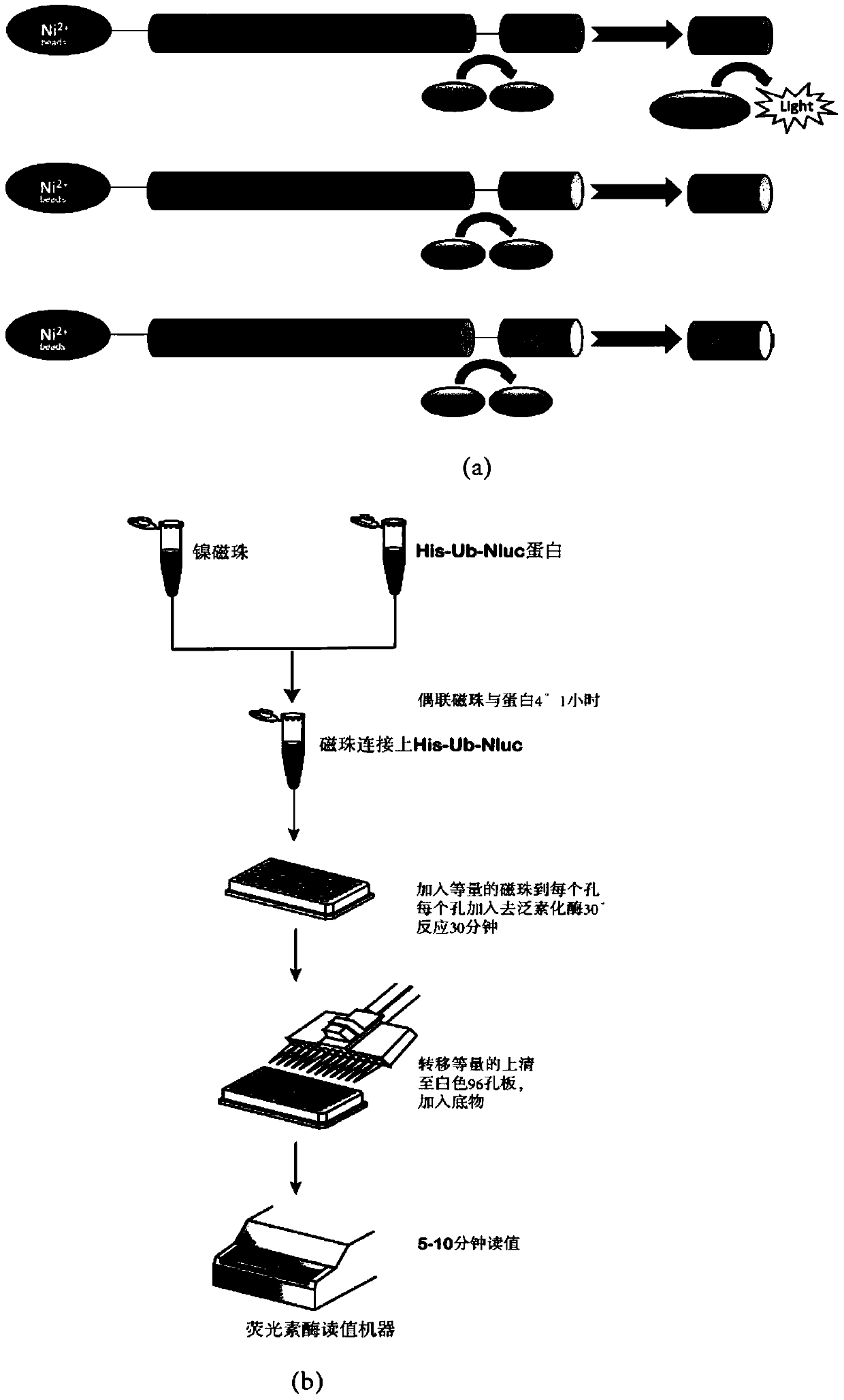
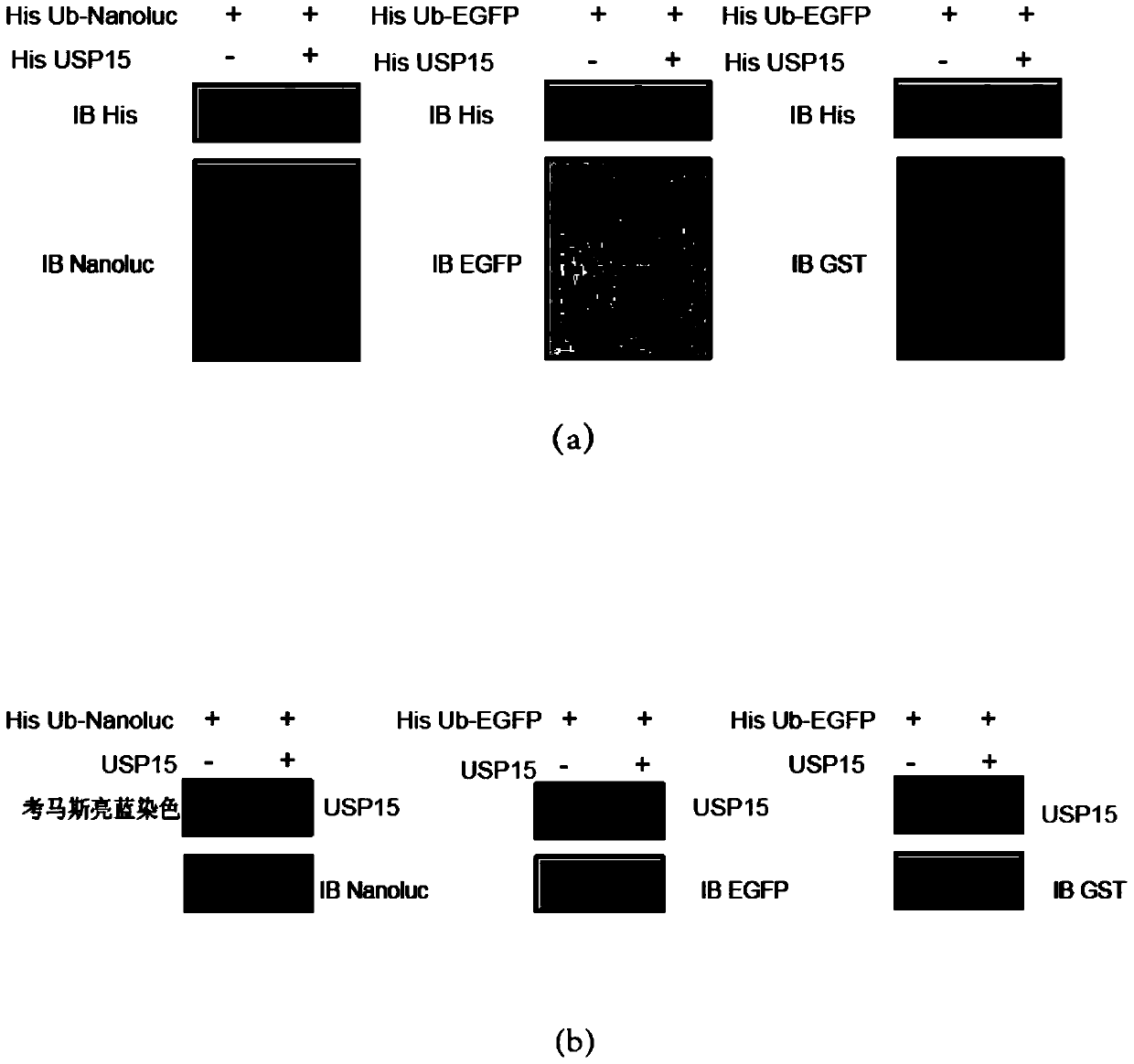
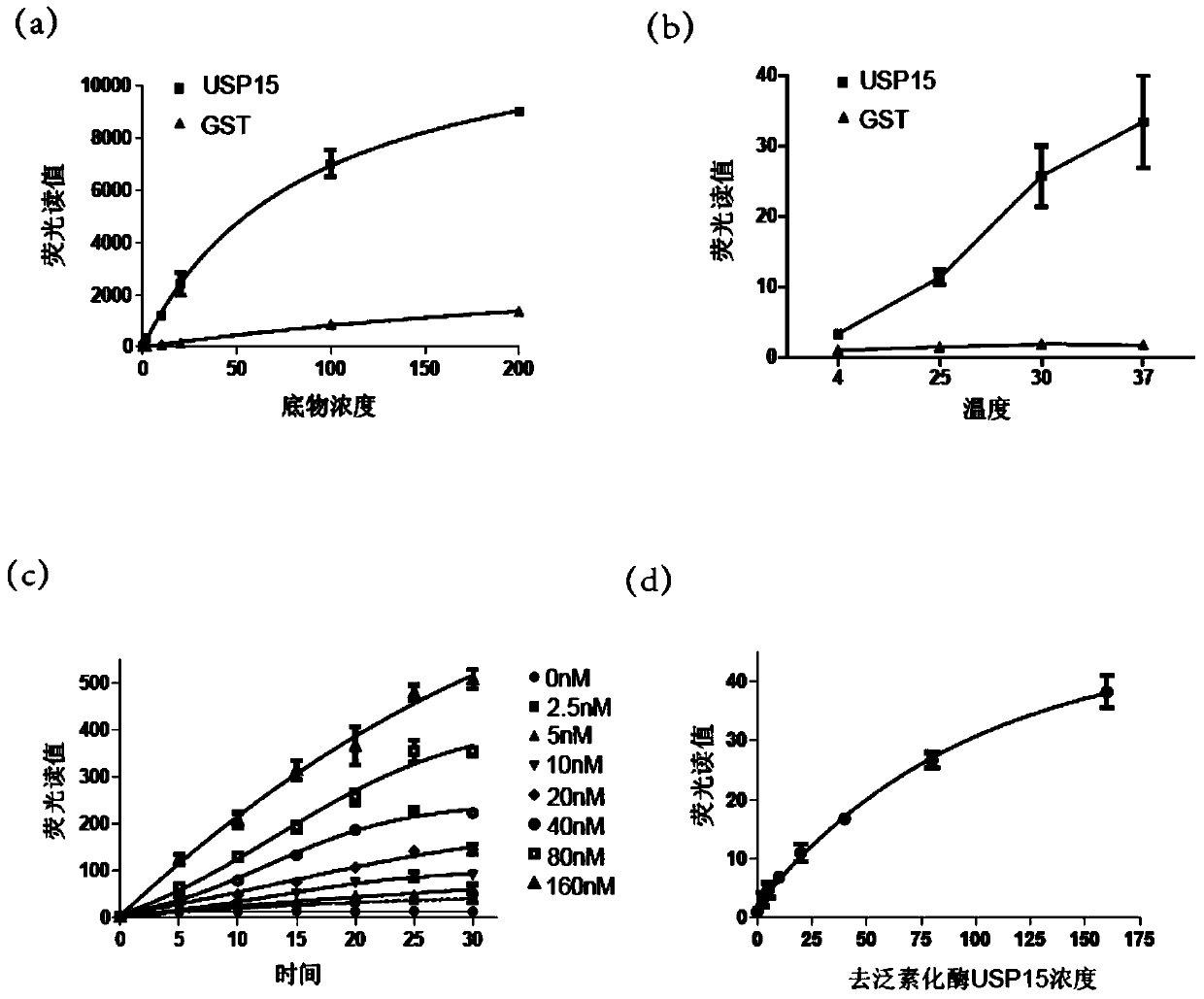
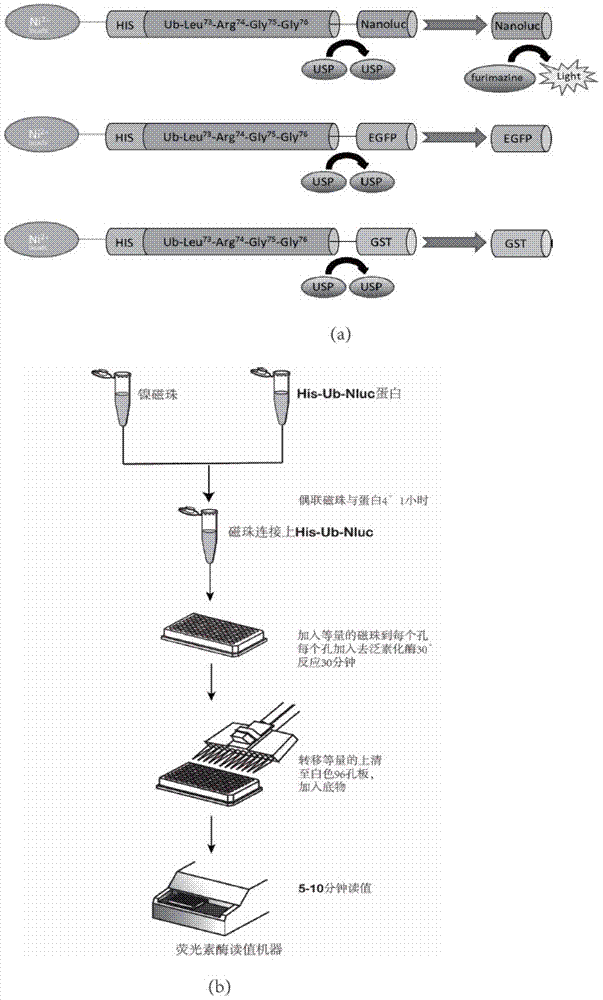
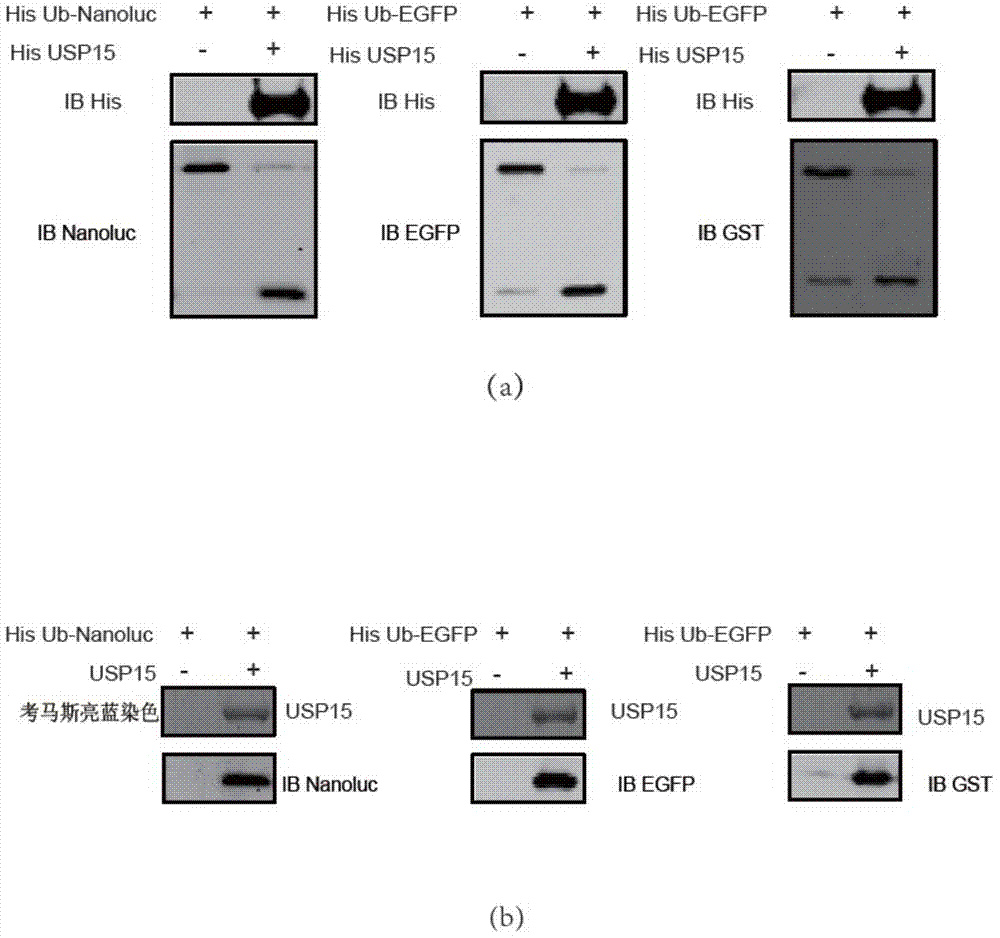
Ub-Nanoluc reporter gene system and Ub-Ub-GS-Nanoluc reporter gene system, constructions and applications thereof
InactiveCN104844704AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesLuciferase GeneEnzyme inhibitor
The present invention discloses an Ub-Nanoluc reporter gene system and an Ub-Ub-GS-Nanoluc reporter gene system, and applications of the Ub-Nanoluc reporter gene system and the Ub-Ub-GS-Nanoluc reporter gene system in deubiquitination enzyme activity detection and deubiquitination enzyme inhibitor throughput-screening, wherein the Ub-Nanoluc reporter gene DNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and the Ub-Ub-GS-Nanoluc reporter gene DNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.4. According to the present invention, the high sensitivity characteristic of luciferase Nanoluc is utilized to provide the method for deubiquitination enzyme activity detection and deubiquitination enzyme inhibitor throughput-screening by using the chemical luminescent reporter gene so as to provide the new action target point and the new ideal for screening and research of new drugs including anticancer drugs, and provide broad application prospects, great enormous benefits, and great social benefits.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Regulation of HIF protein levels via deubiquitination pathway
InactiveUS20050049309A1Lower protein levelReduced activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnticarcinogenPropanoic acid
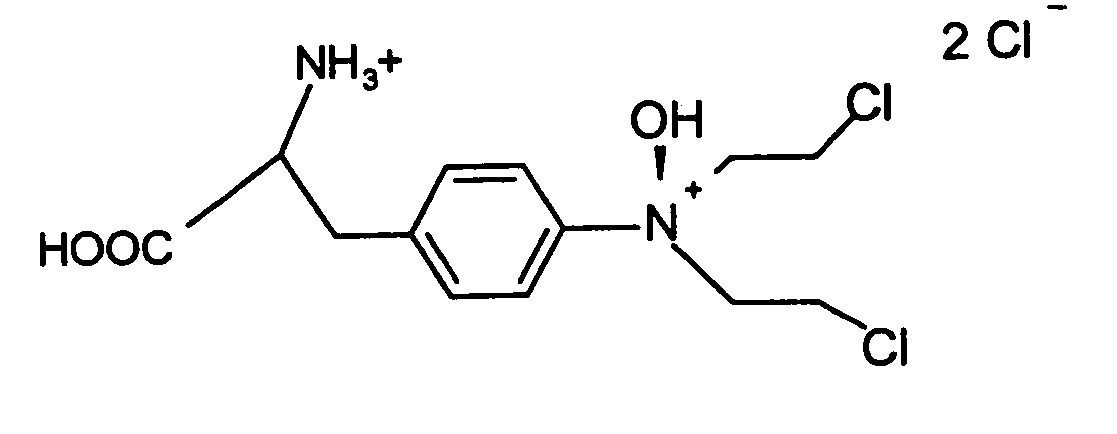
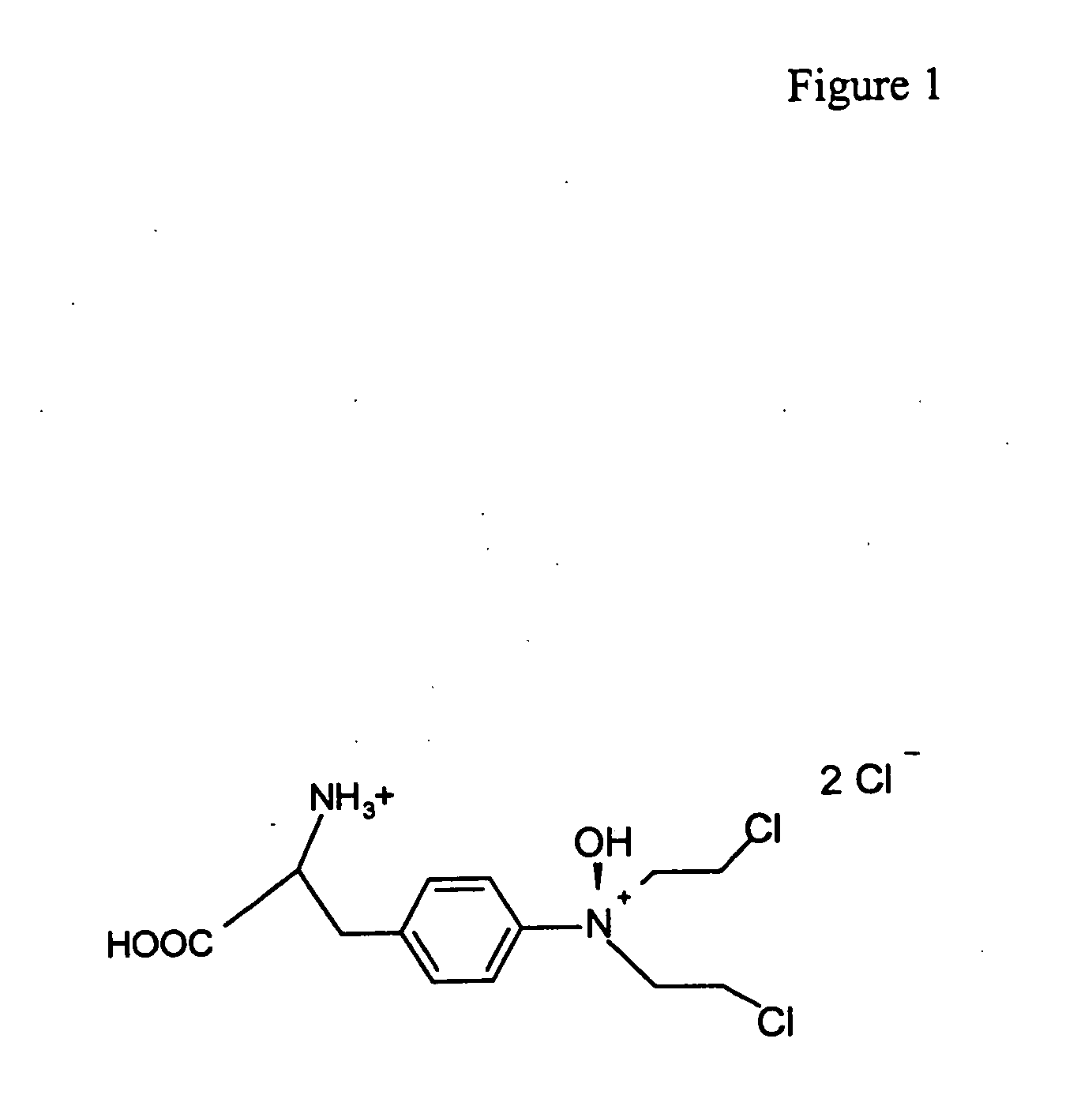
The hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) transcription factor is an important regulator of the cellular response to hypoxia. The activity of HIF-1 is regulated by the level of the HIF-1α subunit, HIF-1α, which is rapidly degraded under normoxic conditions by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. HIF-1α levels increase under hypoxic conditions. Many human cancers also show constitutively increased HIF-1α levels. PX-478 or S-2-amino-3-[4′-N,N,-bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl propionic acid N-oxide dihydrochloride, is a novel anticancer agent, and is capably of decreasing both constitutive and hypoxia induced HIF-1α protein levels and HIF-1 transactivation in vitro and in vivo. In method embodiments, the administration of PX-478 is independent of the pathways of HIF-1α regulation involving the von Hippel-Lindau protein and p53. PX-478 causes an increase in polyubiquitinated HIF-1α levels due to inhibition of HIF-1α deubiquitination. The levels of other proteins whose proteasomal breakdown is mediated by ubiquitination are not affected by PX-478. Deubiquitination is a novel pathway for the regulation of cellular HIF-1α levels and PX-478 is a specific inhibitor of the pathway. Therapeutic compounds for regulating cellular HIF-1α levels and methods of regulating cellular HIF-1α levels are herein provided.
Owner:PROLX PHARMA +1
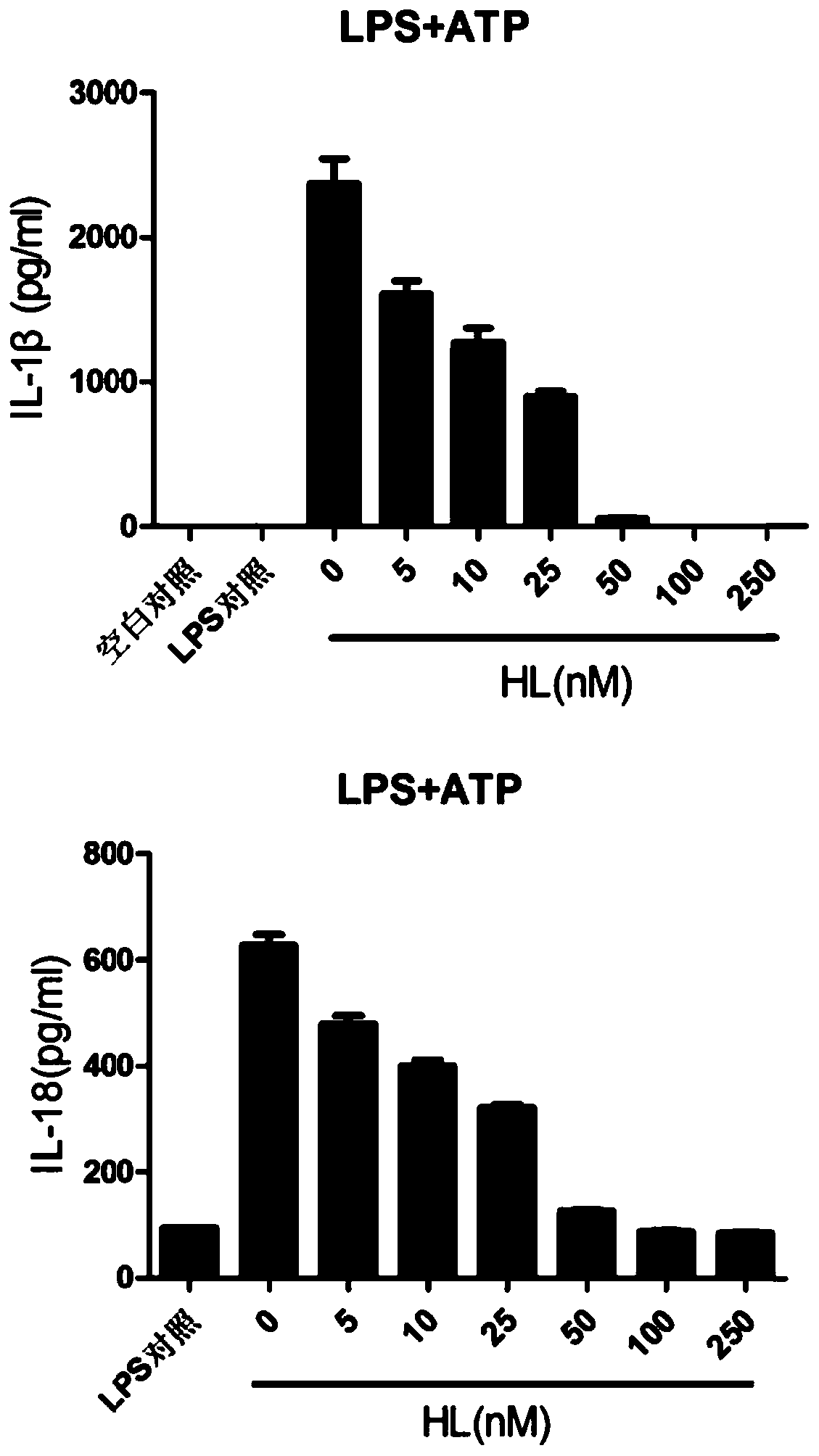
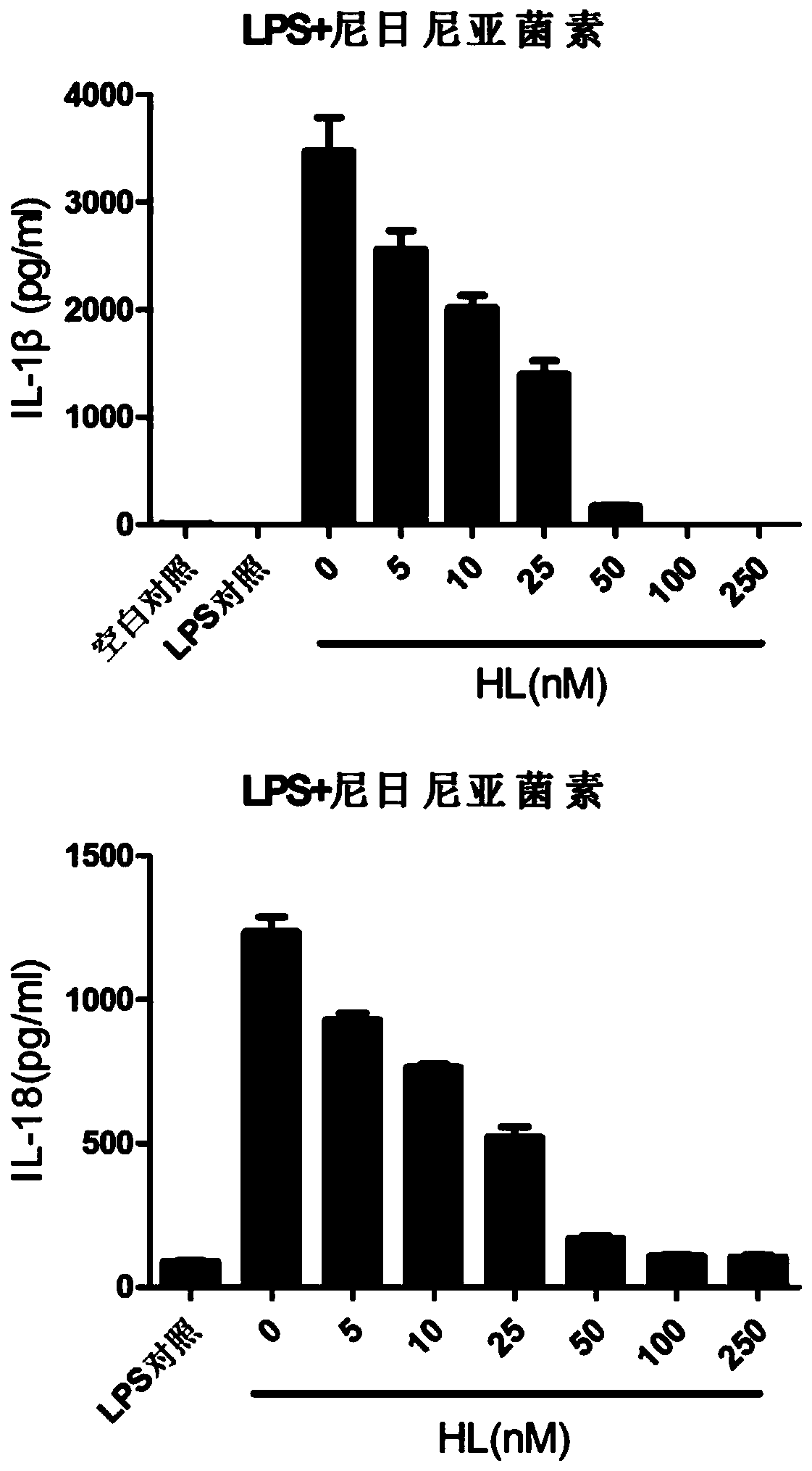
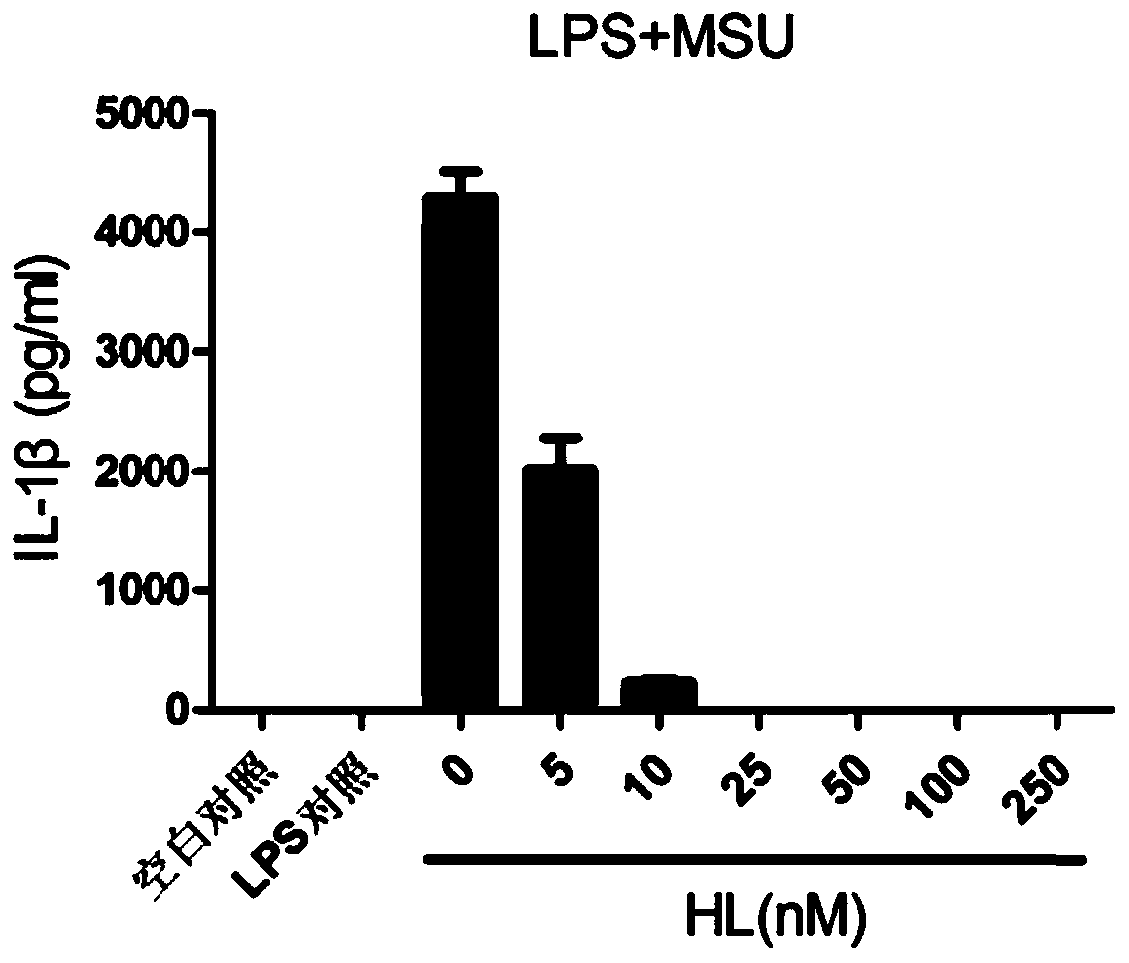
Application of holomycin in inhibition of activation of NLRP3 inflammasome
ActiveCN108815158AInhibit bindingInhibition formationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseIn vivo
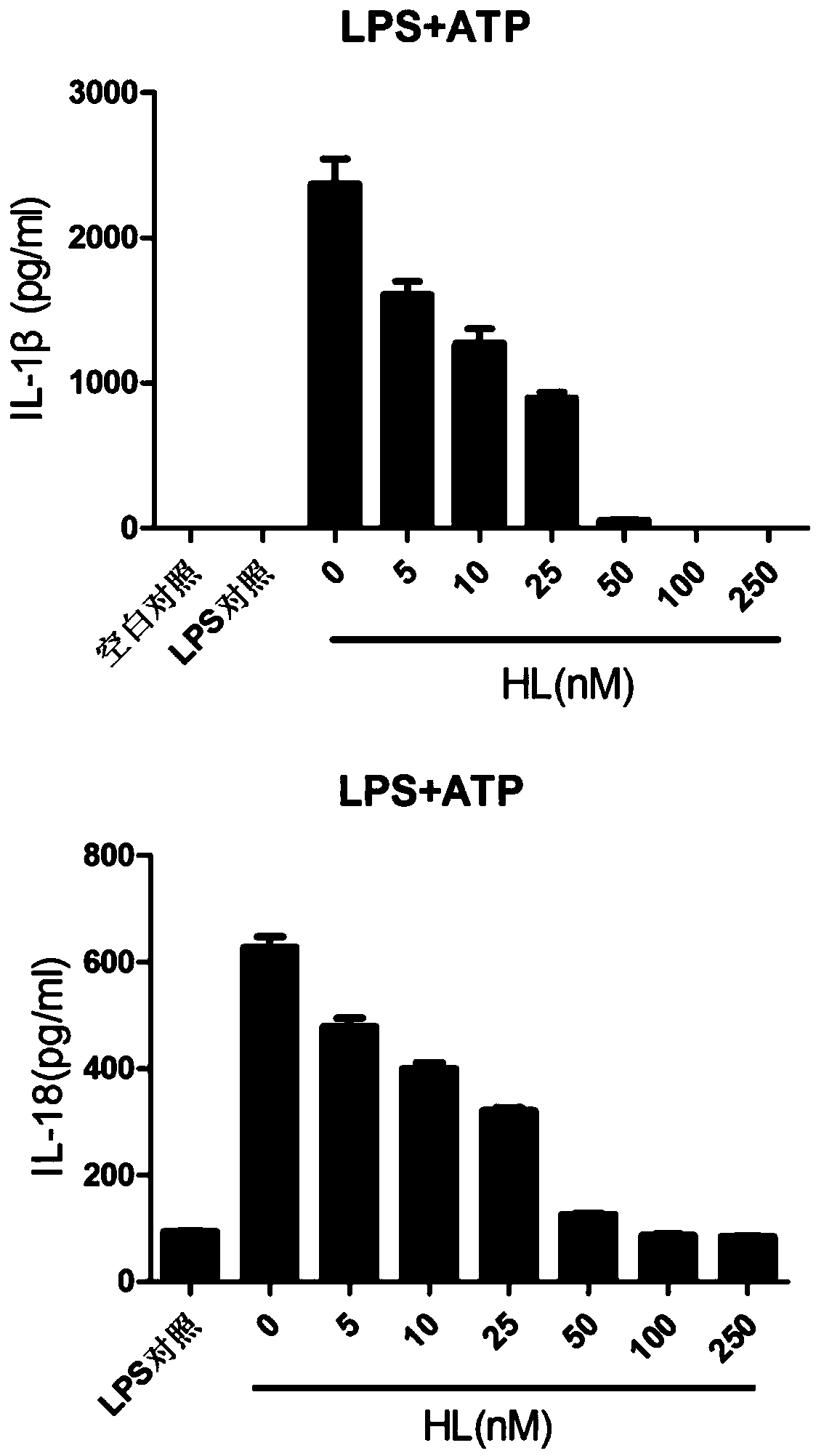
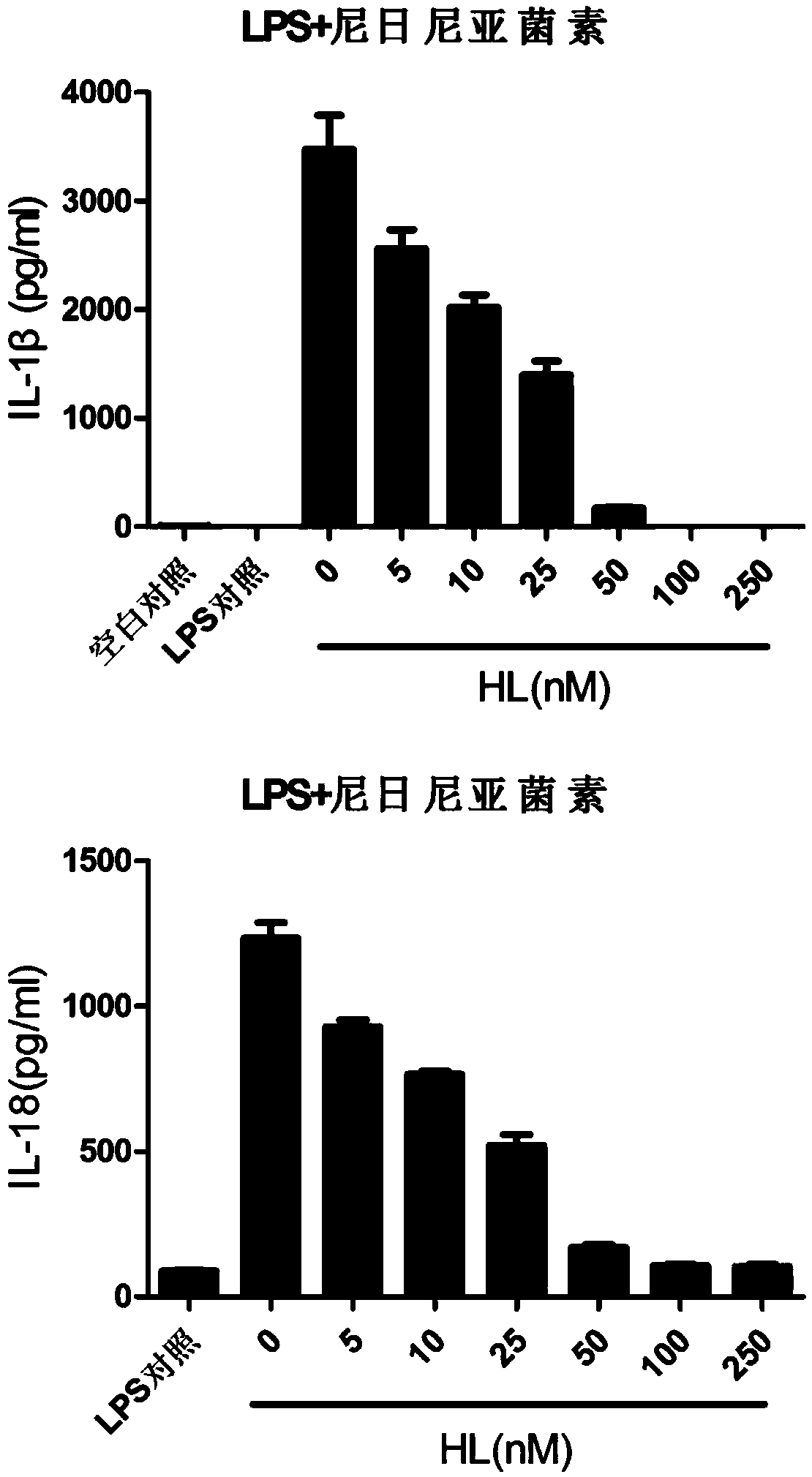
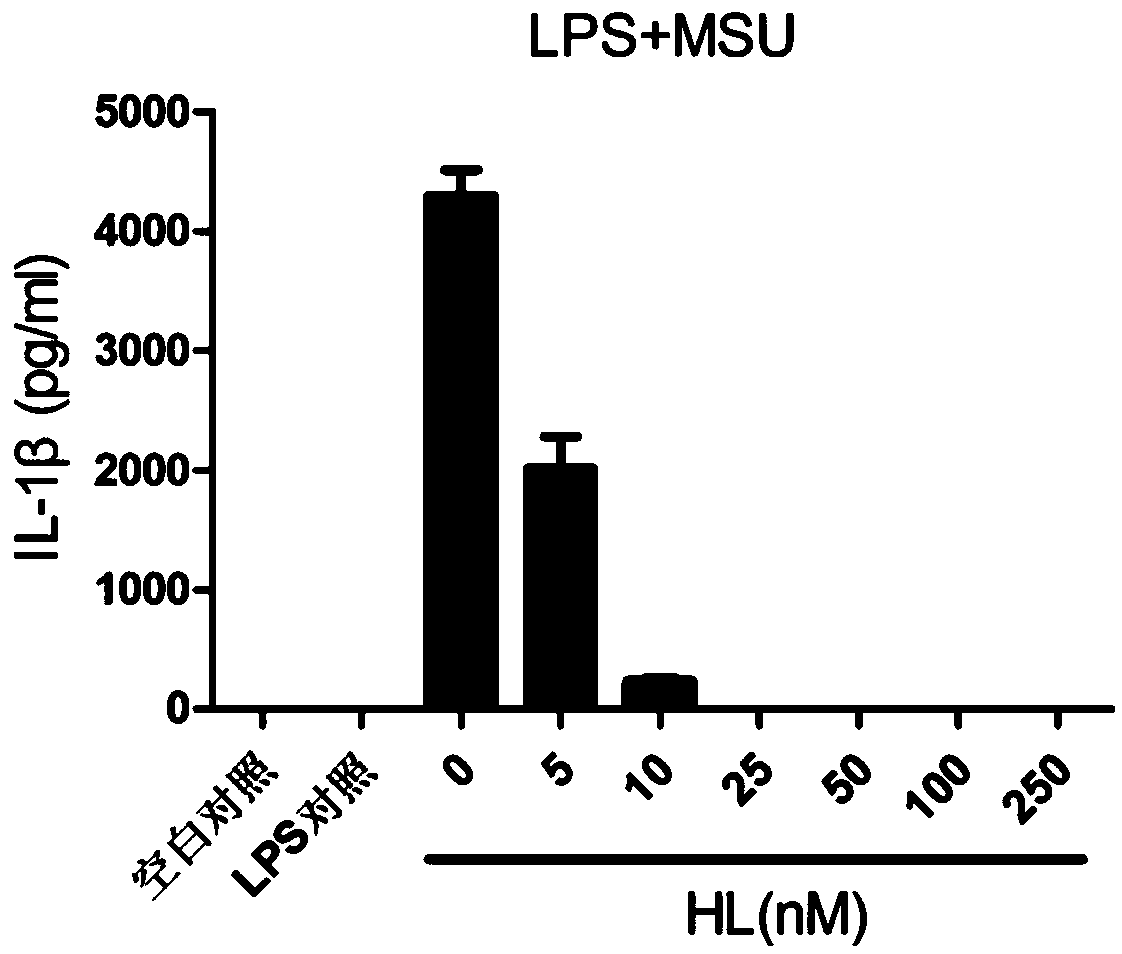
The invention relates to the field of biology and medicine and discloses an application of holomycin in inhibition of the activation of an NLRP3 inflammasome. The holomycin can inhibit NLRP3 protein self-deubiquitination under agonist stimulation, binding of NLRP3 to an ASC protein, formation of ASC spots and activation of Caspase-1, and finally inhibit IL-1 beta and IL-18 secretion. The holomycincan inhibit monosodium urate-induced peritonitis in vivo. Therefore, holomycin can be used a specific drug for treatment on NLRP3 abnormal activation-related diseases.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
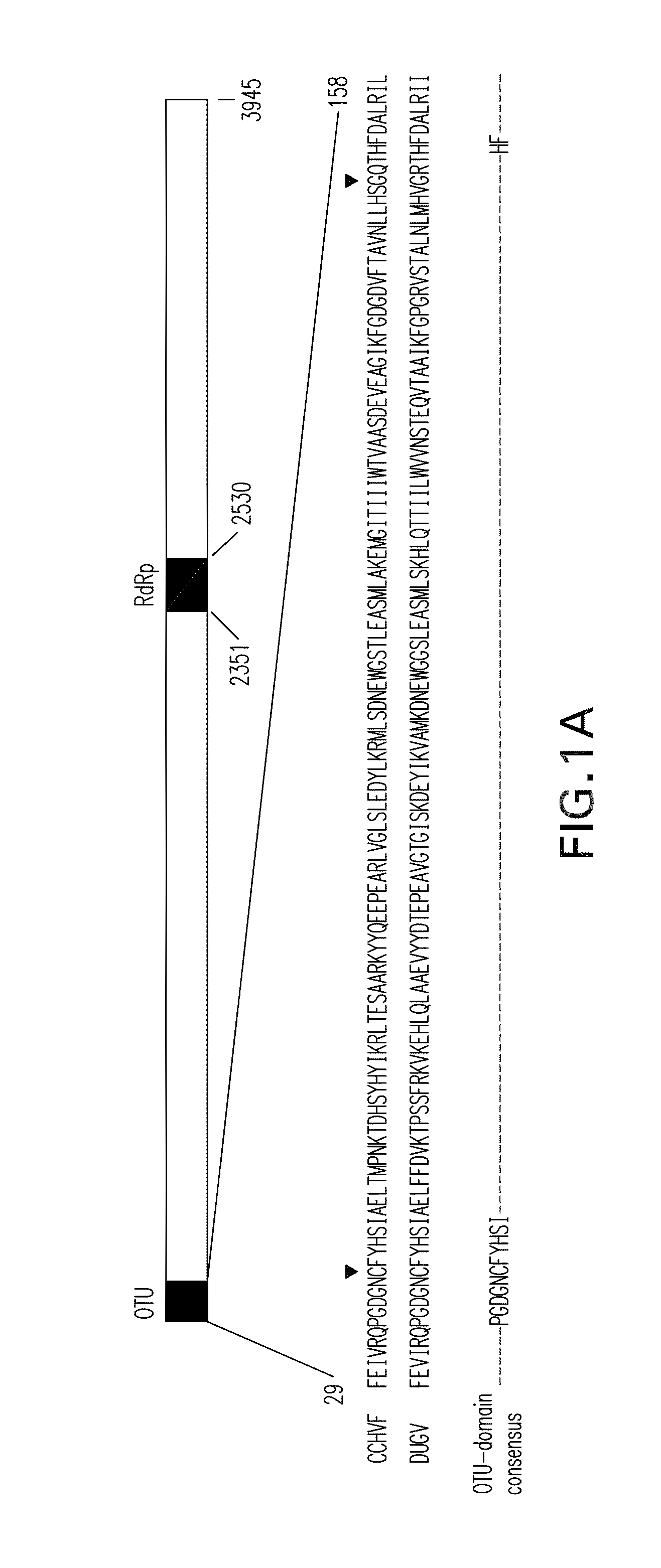
METHODS OF PREVENTING AND TREATING VIRAL INFECTIONS BY INHIBITING THE DelSGYLATION ACTIVITY OF OTU DOMAIN-CONTAINING VIRAL PROTEINS
InactiveUS20110033498A1Reduce capacityReduce and eliminate abilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseISG15ADAMTS Proteins
Viruses having an impaired ability to deISGylate ISG15 conjugates, in particular, viral mutants comprising a mutation in the viral genome that reduces or eliminates the ability of the viral OTU domain-containing protein encoded by the viral genome to deISGylate ISG15 conjugates and / or deubiquitinate ubiquitinated proteins and / or deNeddylate Neddylated proteins are disclosed. Such viral mutants may be used in the formulation of immunogenic compositions for inducing an immune response and preventing, managing and / or treating a viral infection. Also disclosed are methods for identifying anti-viral compounds, in particular, methods of identifying compounds that reduce or inhibit the deISGylation activity and / or deubiquitination and / or deNeddylation activity of a viral OTU domain-containing protein. The compounds identified using such methods may be used as antiviral agents for the prevention, treatment and / or management of viral infections.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Inhibitors of deubiquitinating proteases
InactiveUS20160090351A1Prevent and treat diseaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityUbiquitinated Proteins
Disclosed are small molecule inhibitors of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), and methods of using them. Certain compounds display a preference for specific ubiquitin specific proteases (USPs).
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
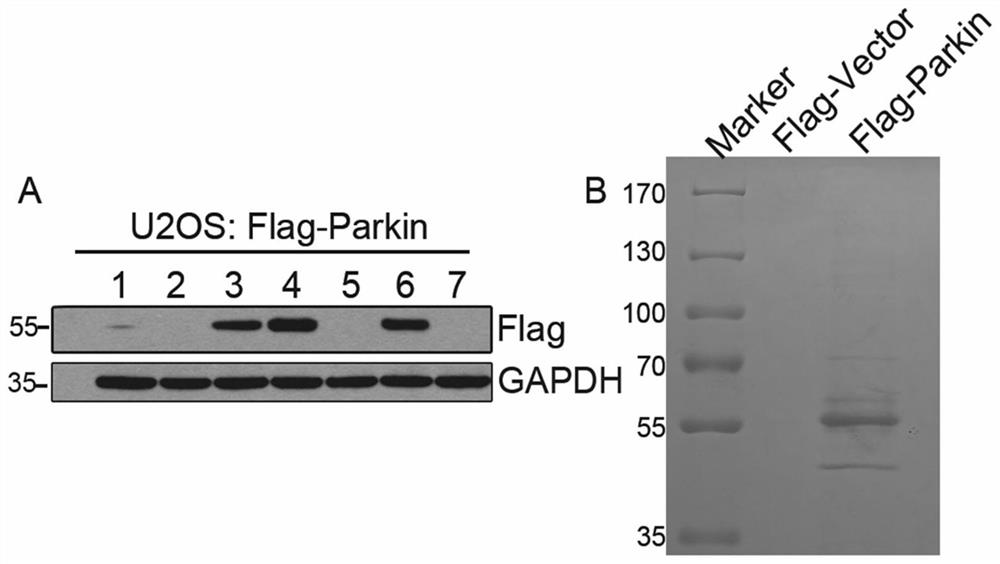
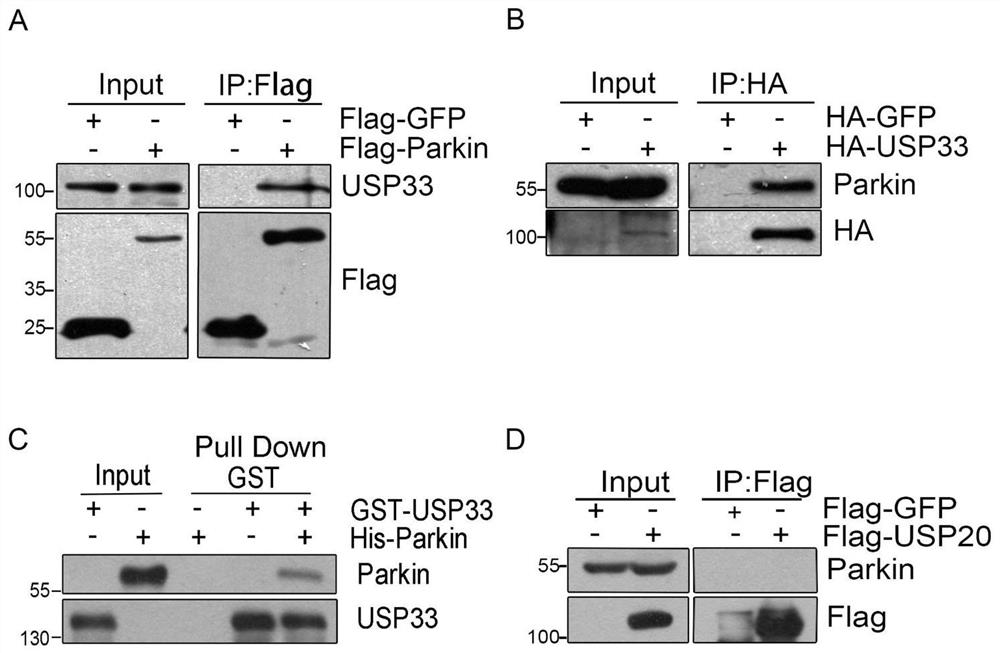
Application of USP33 as drug target in preparation of drugs
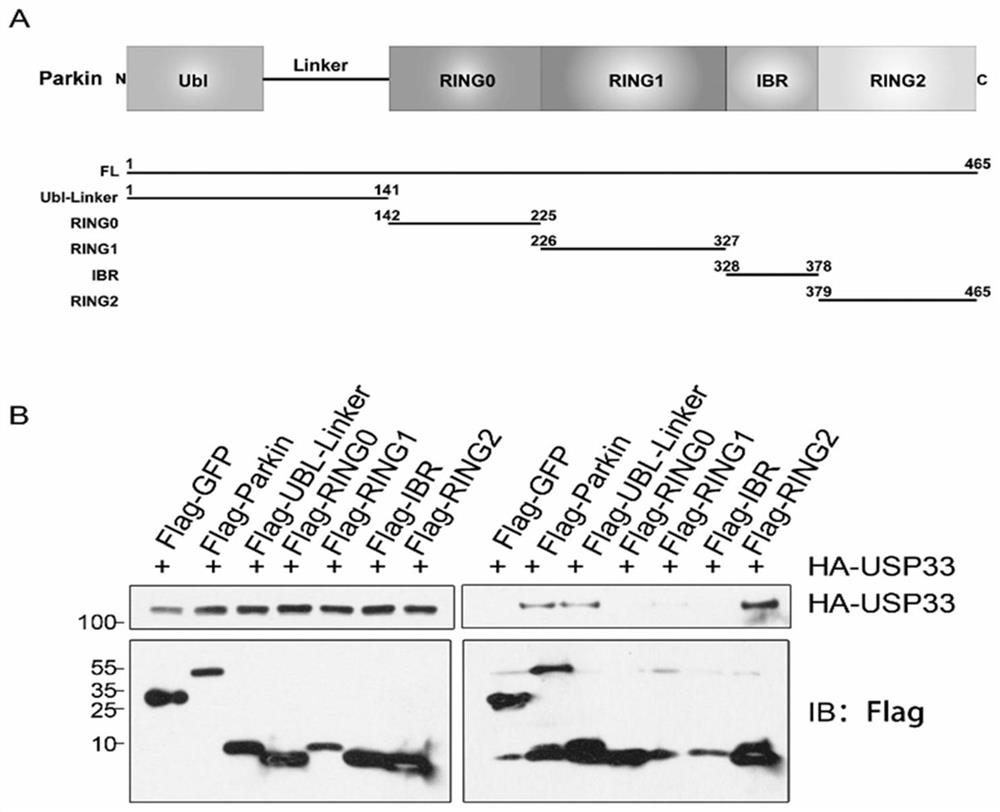
ActiveCN111748531APromote autophagyGreat application potentialCompound screeningNervous disorderApoptosisDrug target
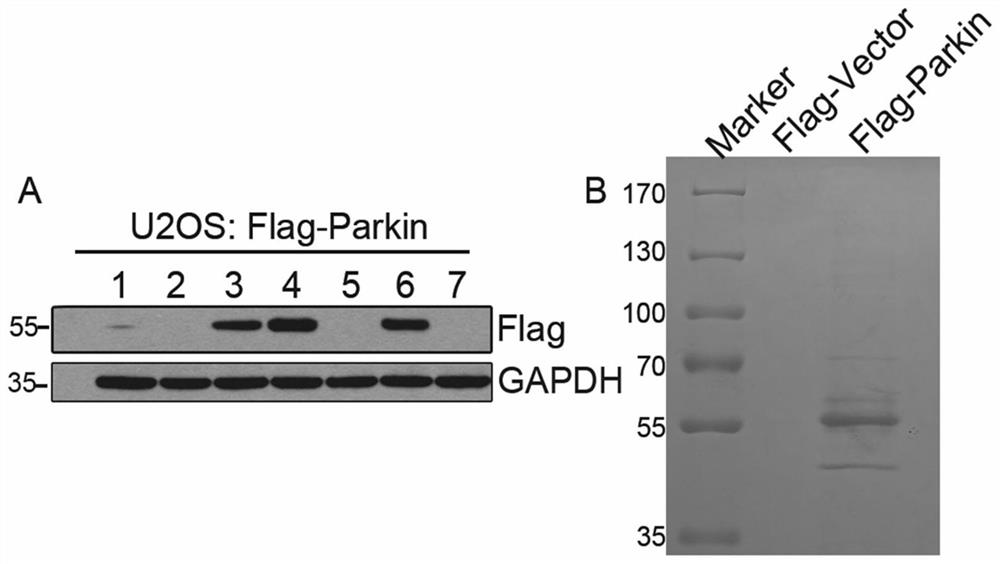
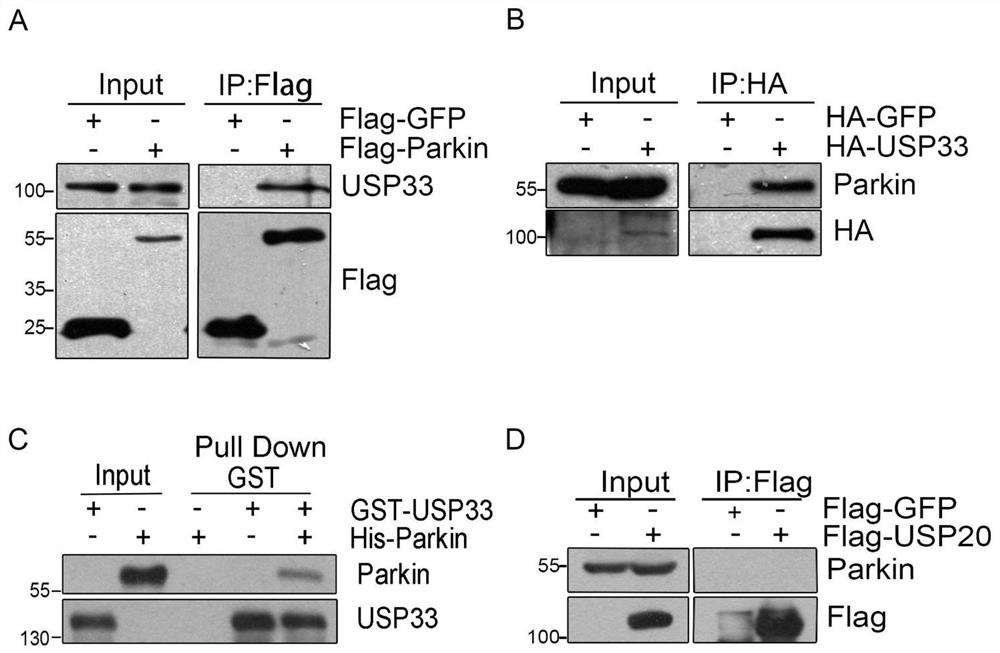
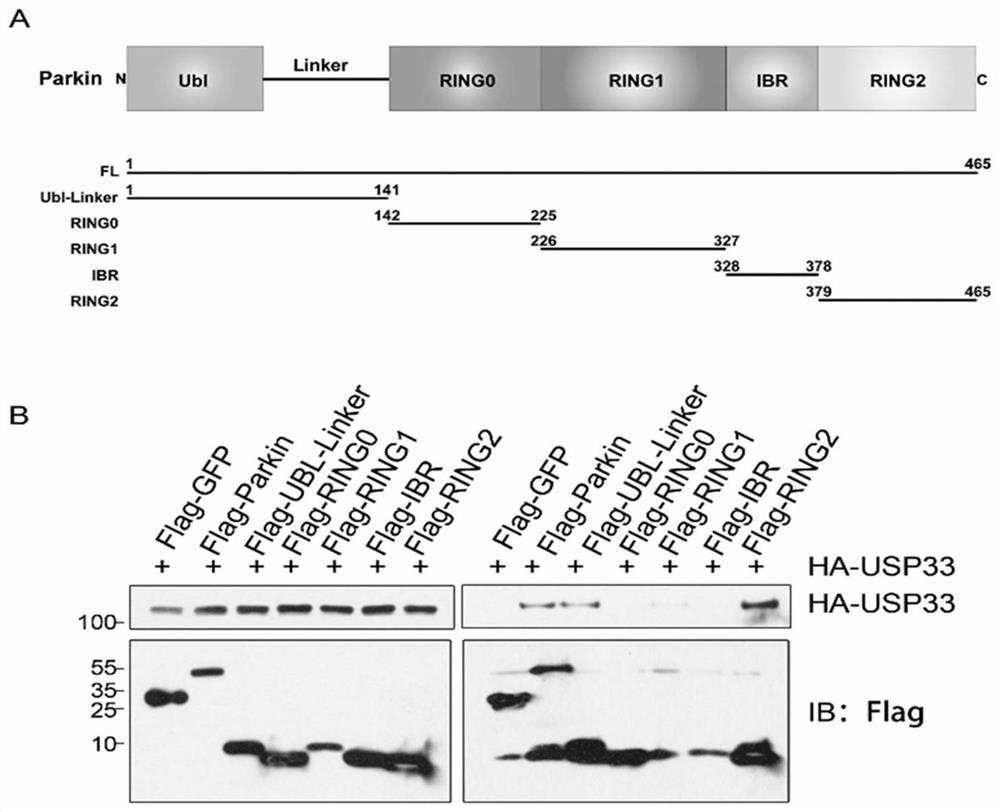
The invention provides an application of USP33 as a medication target in preparation of drugs, and belongs to the field of protein engineering. According to the invention, the deubiquitination enzymeUSP33 interacting with Parkin is discovered by utilizing co-immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry technologies, so that the USP33 is further discovered to be positioned on the outer membrane of mitochondria, and the E3 ligase Parkin can be modified by deubiquitination. When the USP33 is knocked down, Parkin transposition to mitochondria can be promoted; therefore, mitochondrial autophagy is enhanced to remove damaged mitochondria; USP33 regulates mitochondrial autophagy by influencing deubiquitination of Parkin, apoptosis of nerve cells under MPTP treatment can be inhibited by knocking down USP33, USP33 can be used as a medication target for preparing a medicine, and good application potential and value are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Application of ubiquitination pathway related factor in regulating and controlling functions of regulatory T cell
InactiveCN108144049APromote transcriptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticRegulatory T cellUbiquitinated Proteins
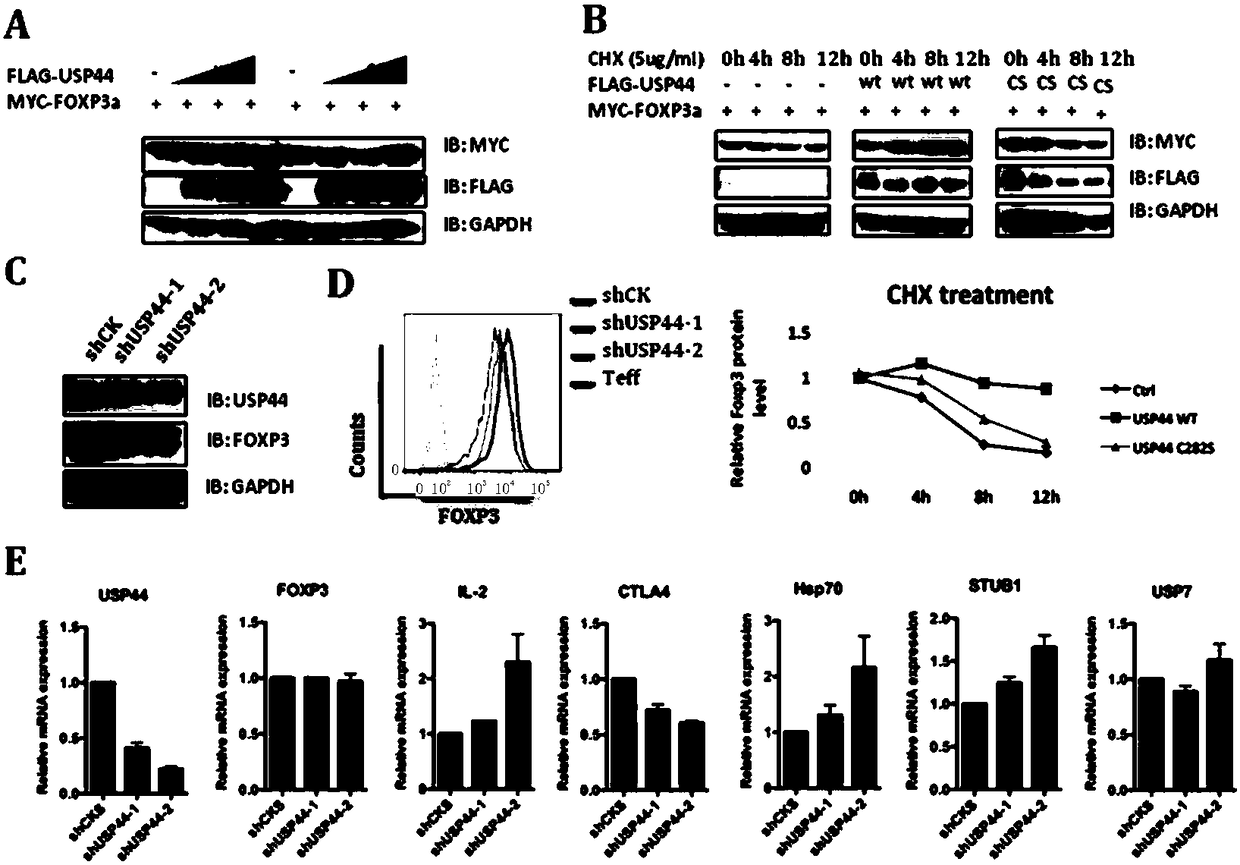
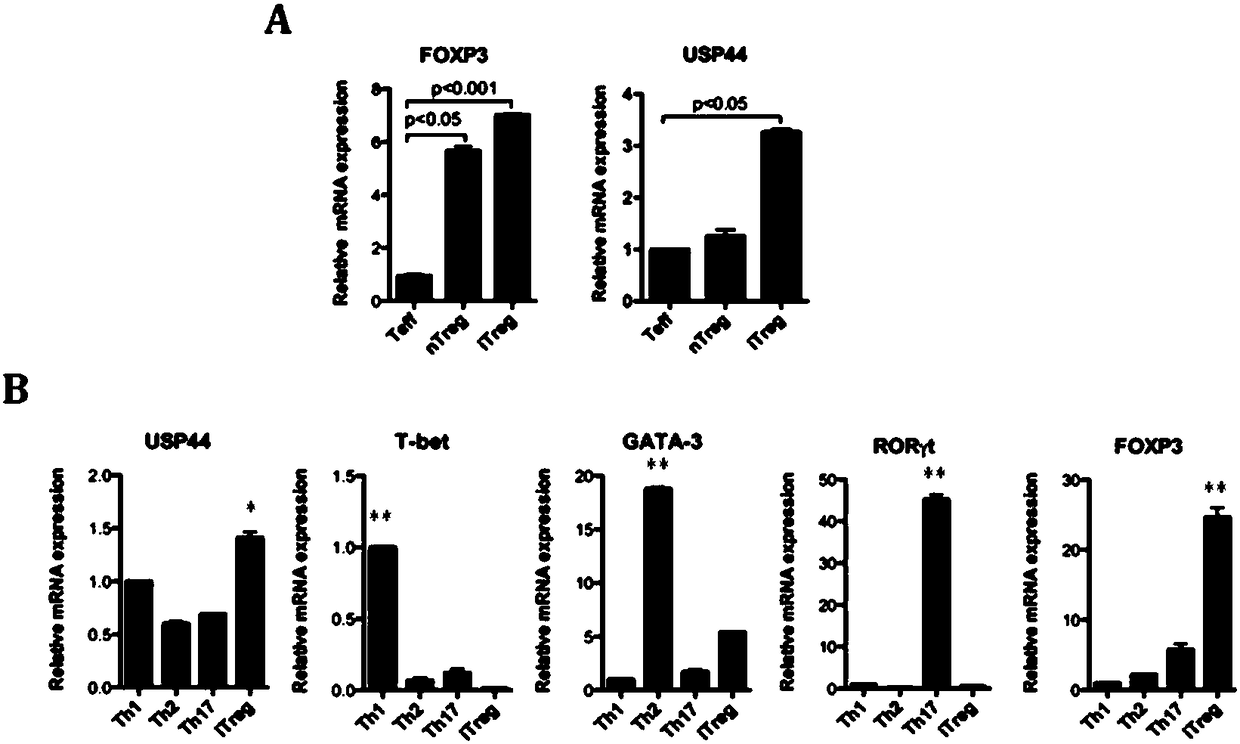
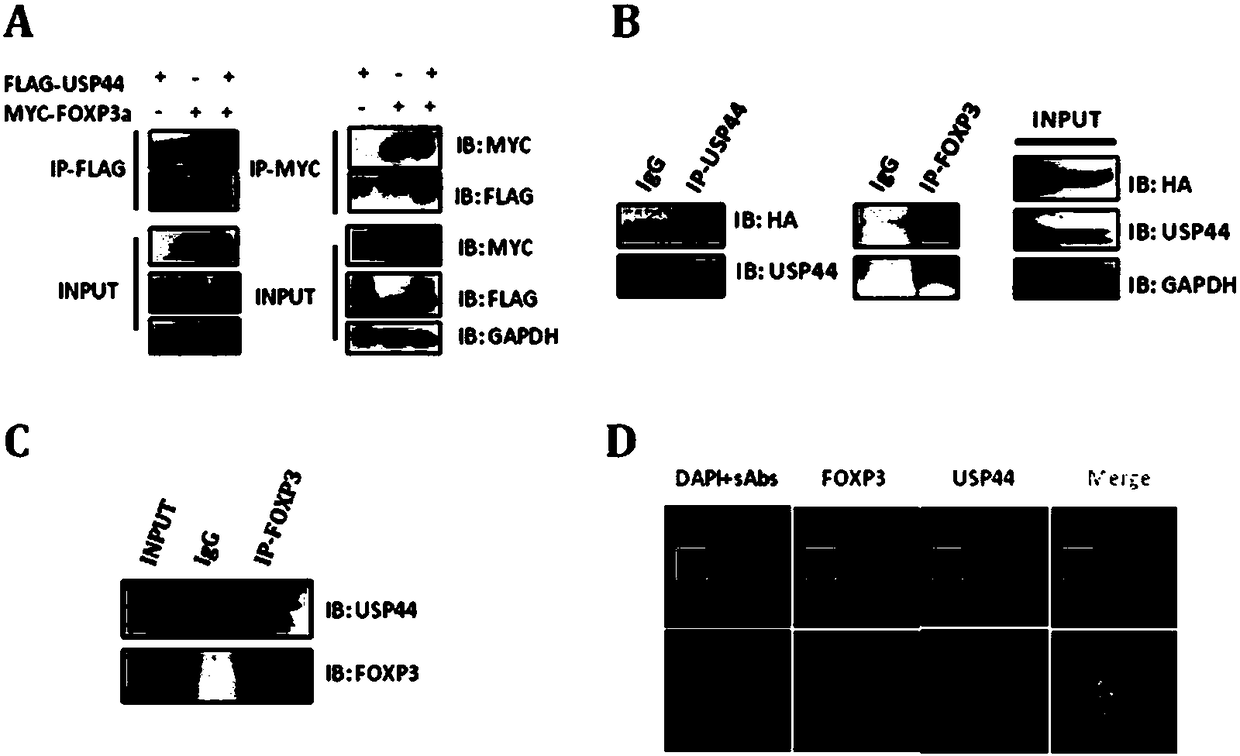
The invention relates to an application of a ubiquitination pathway related factor in regulating and controlling functions of a regulatory T cell. Specifically, the invention relates an application ofthe ubiquitination pathway related factor and an agonist or an antagonist thereof in preparing a preparation or a reagent for regulating FOXP3 or the regulatory T cell, wherein the ubiquitination related factor is selected from gene coding proteins USP44 and USP7 of a ubiquitination protein family. The novel regulatory factor provided by the invention, by regulating transcriptional regulatory activity of the FOXP3 on a target gene thereof, can regulate and control the regulatory T cell and the balance of an immune system.
Owner:INST PASTEUR OF SHANGHAI CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
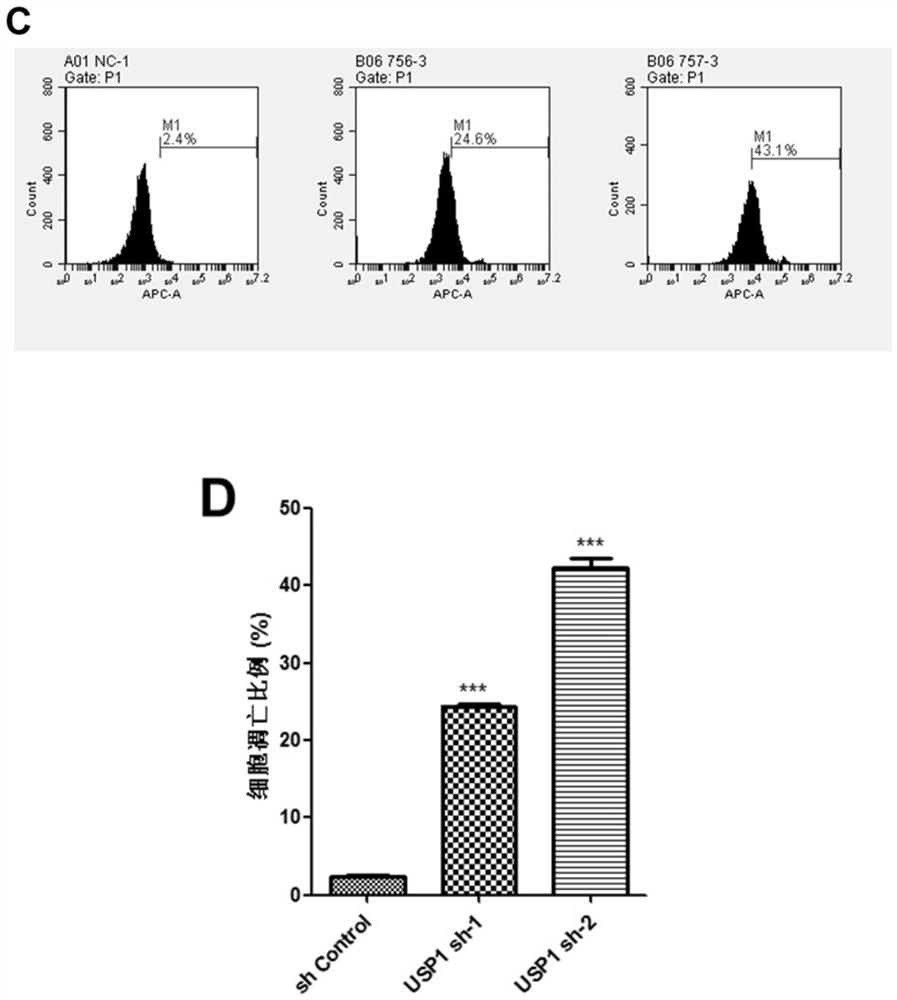
Application of substance for reducing USP1 expression in preparation of medicine for treating children T-series acute lymphoblastic leukemia
ActiveCN111926018ASlow down proliferationPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsLymphocyteOncology
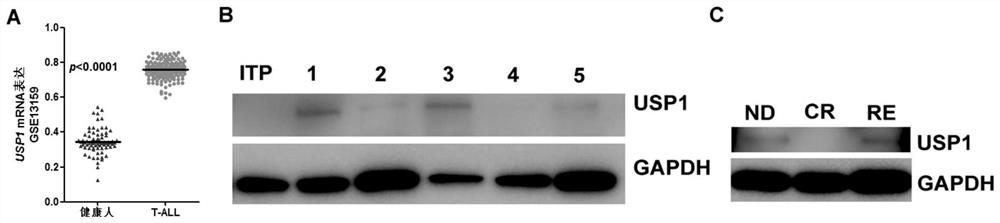
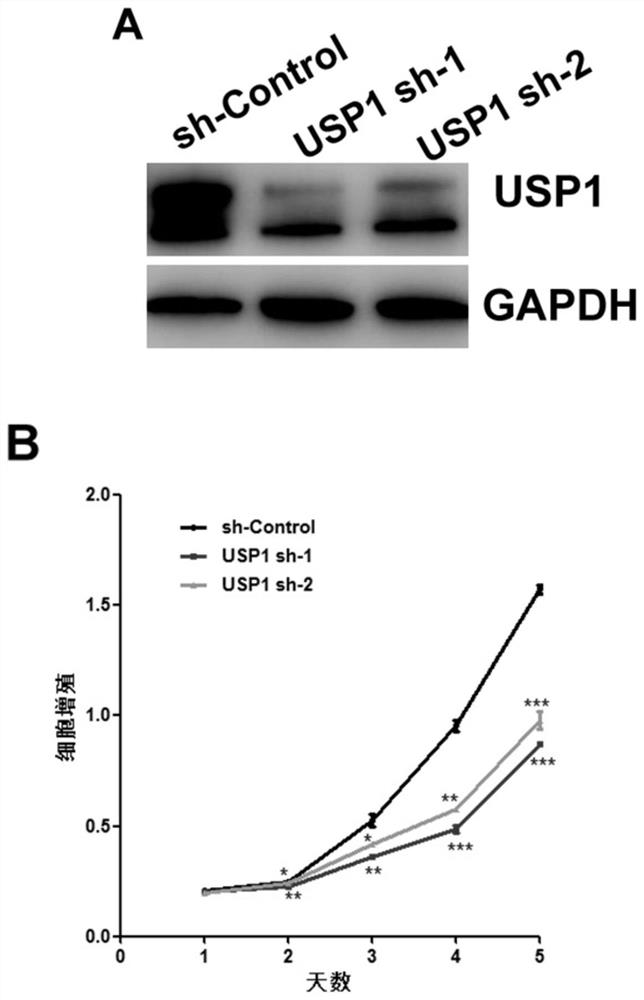
The invention discloses application of a substance for reducing USP1 expression in preparation of a medicine for treating children T-series acute lymphocytic leukemia. The invention discloses short hairpin RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) for forming a stem-loop structure. The short hairpin RNA is shRNA-1 or shRNA-2. The deubiquitination enzyme USP1 has the effects of inhibiting cell apoptosis and promotingcell proliferation in T-series acute lymphocytic leukemia cells, and the invention proves that inhibition of USP1 expression can promote apoptosis of tumor leukemia cells and inhibit proliferation ofleukemia cells. The invention provides a novel way for the treatment of T-series acute lymphocytic leukemia, and the deubiquitinase USP1 is expected to become a potential target for anti-leukemia treatment and has a very wide application prospect in the medical field.
Owner:BEIJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
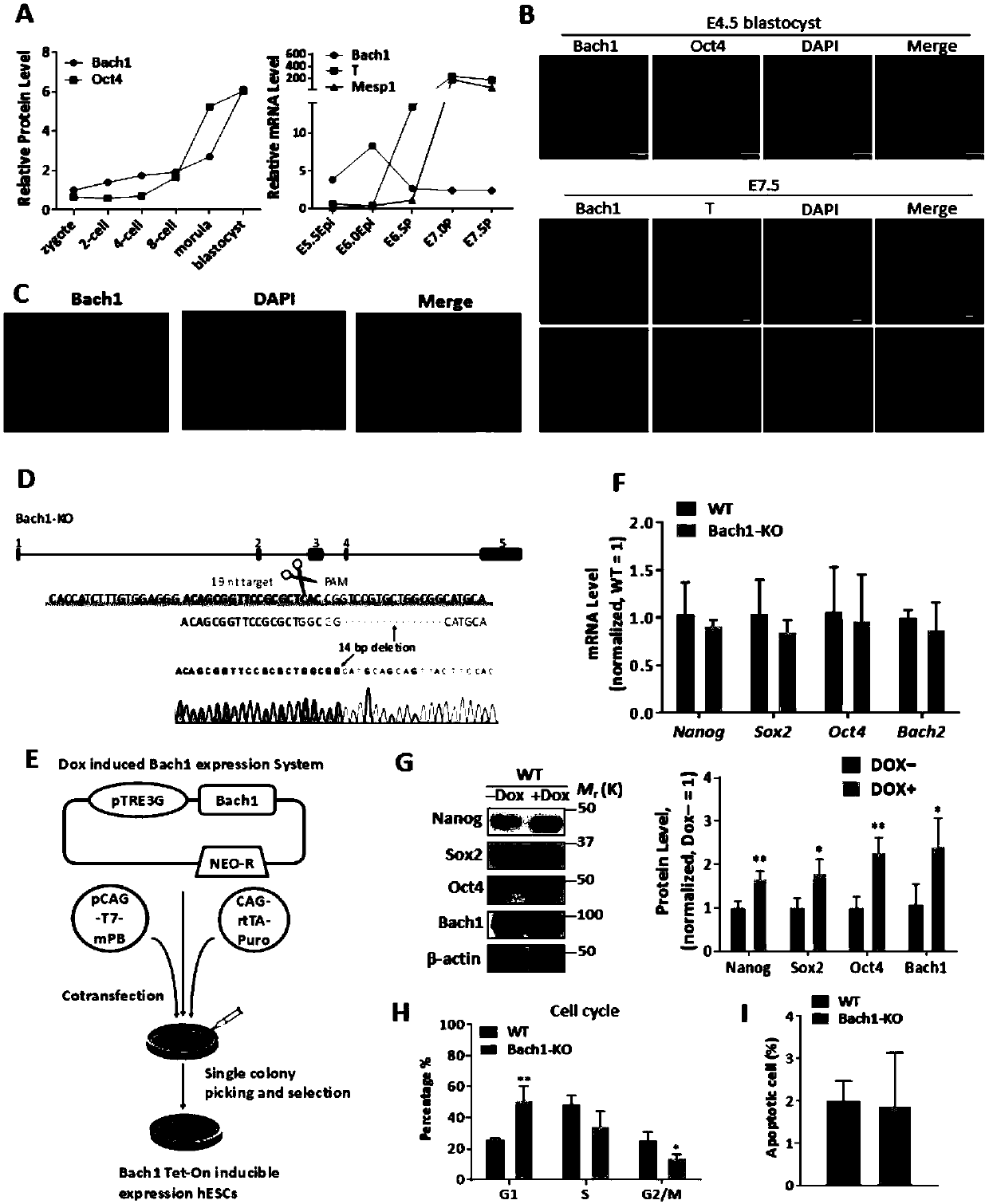
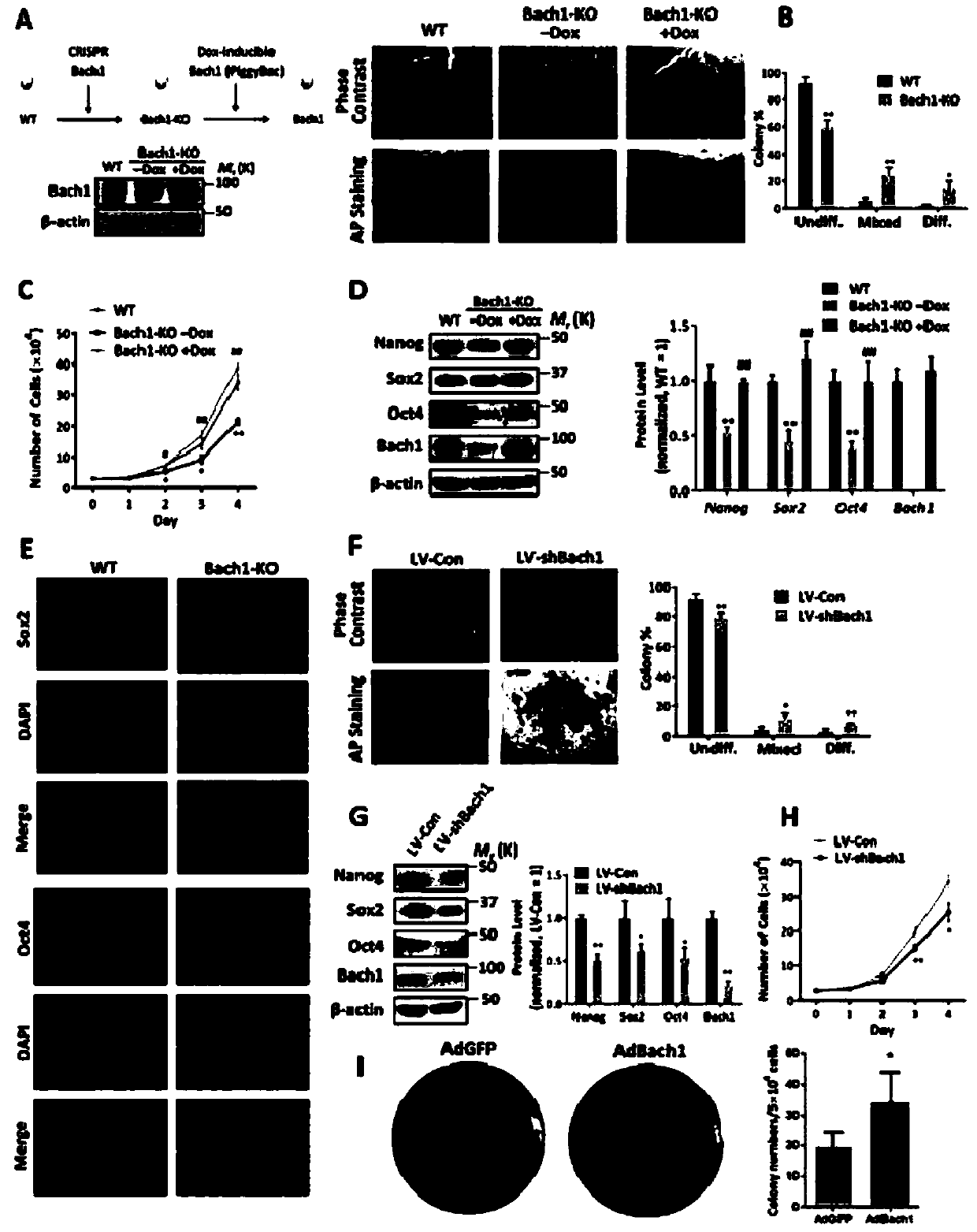
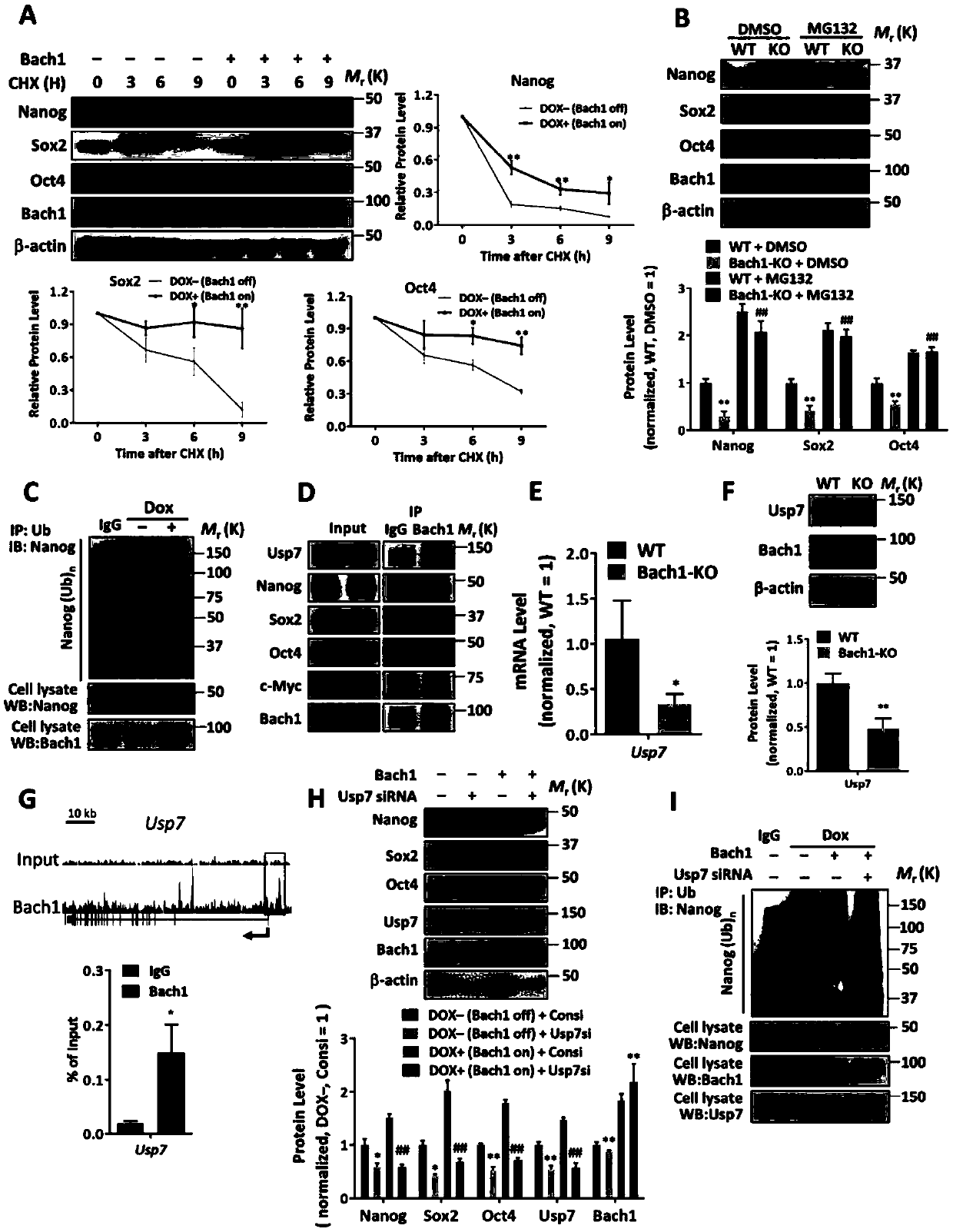
Modified Bach1 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN109517826ARegulation of pluripotencyRegulate self-renewalGenetically modified cellsUnknown materialsNODALProteinase activity
The invention relates to a modified Bach1 gene and an application thereof to pluripotency, self-updating, proliferation, reprogramming and differentiation of a stem cell. Due to the modification of the Bach1 gene of a transcription factor, the BACH1 protein activity or expression of the cell is inhibited or increased, and furthermore, the cell interacts with a deubiquitinated protease Usp7, a pluripotent factor Nanog, Sox2 and / or Oct4, a PRC2 complex, a Wnt / beta-catenin signal channel and / or an Nodal / Smad2 / 3 signal channel, so that the self-updating, proliferation and / or differentiation of thestem cell are regulated.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
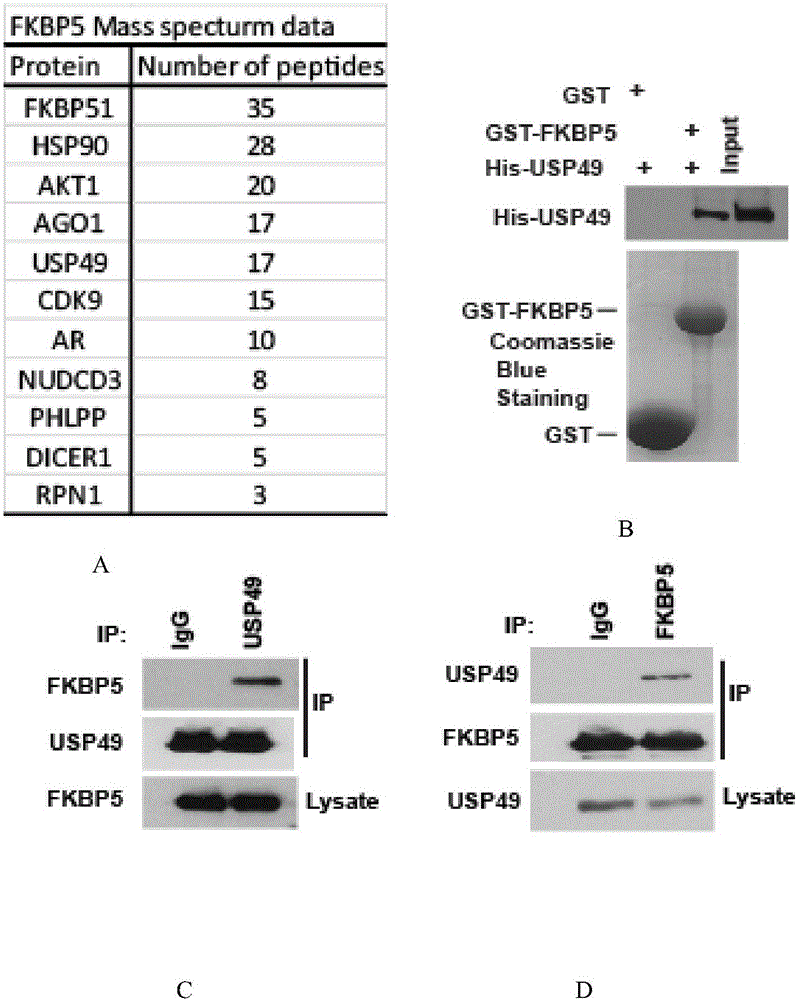
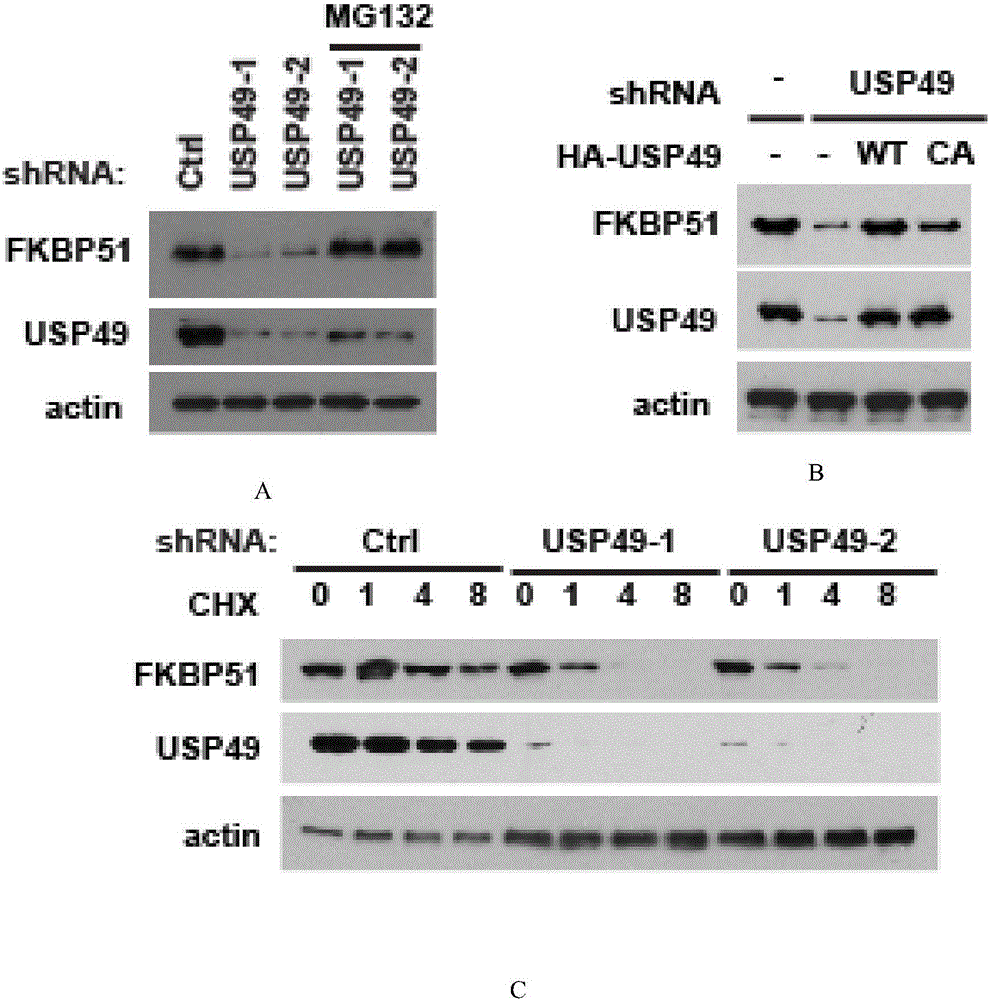
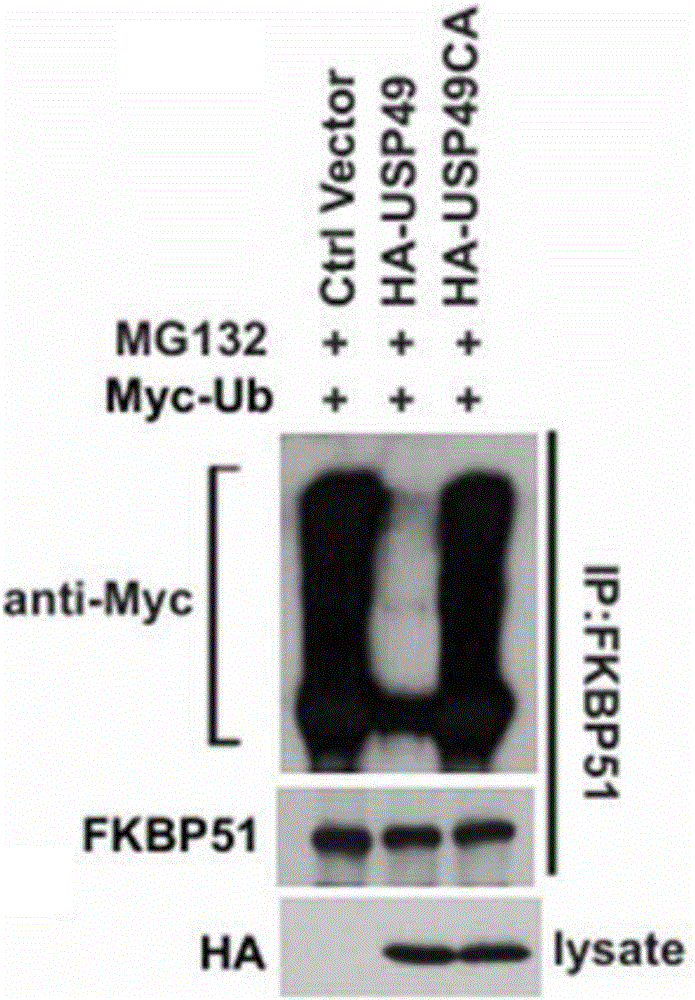
Application of USP 49 (ubiquitin-specific protease 49)
ActiveCN105802945AStabilized protein levelsSignificant technological progressPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDeubiquitinationFKBP5
The invention provides an application of USP 49 (ubiquitin-specific protease 49) in preparation of a drug for preventing or treating pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. An amino acid sequence of the USP 49 is represented as SEQ ID NO:1. The deubiquitinating enzyme USP49 interacting with FKBP5 protein is provided, a degradation and stabilization mechanism of the FKBP5 protein as well as molecular regulation for an FKBP5-AKT pathway by the deubiquitinating enzyme USP49 is determined, the function and the molecular mechanism of the pathway in the occurrence and development processes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma are provided, new basis is provided for treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, and USP49 has direct guidance significance for personalized medical treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL
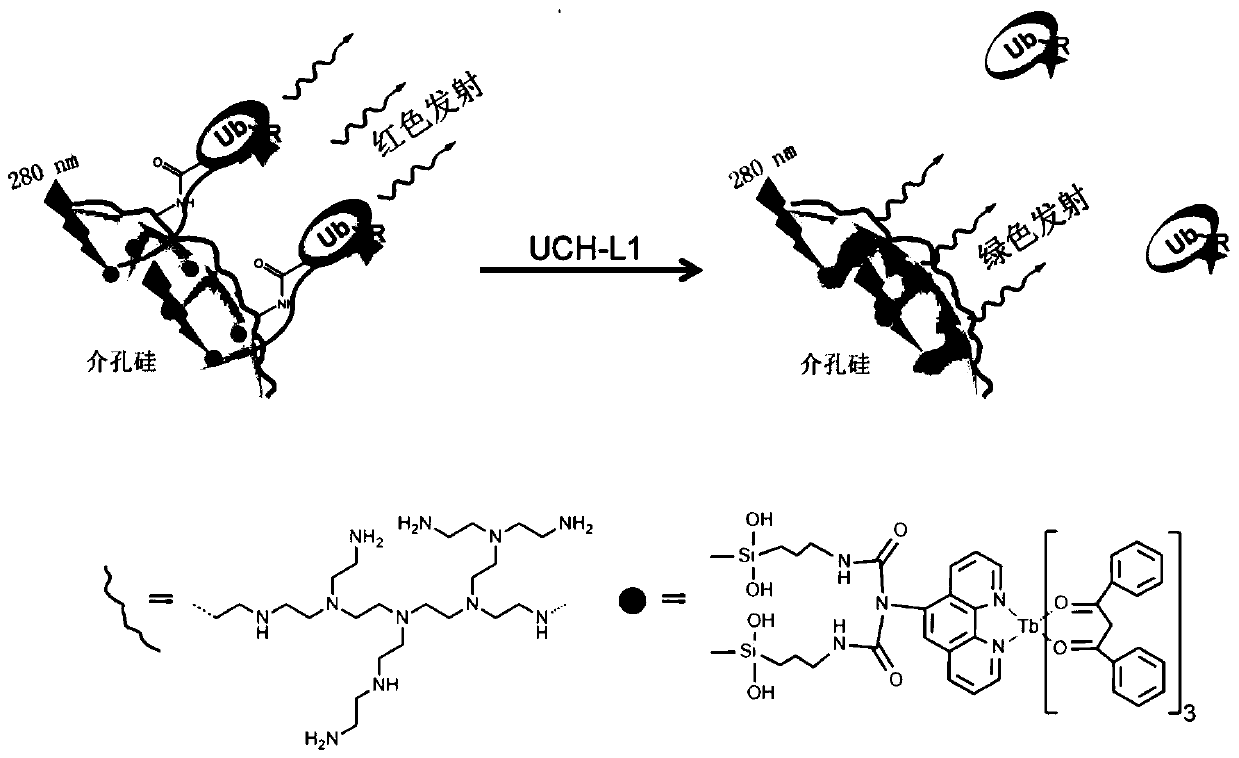
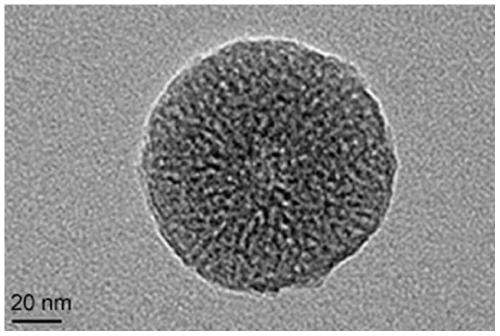
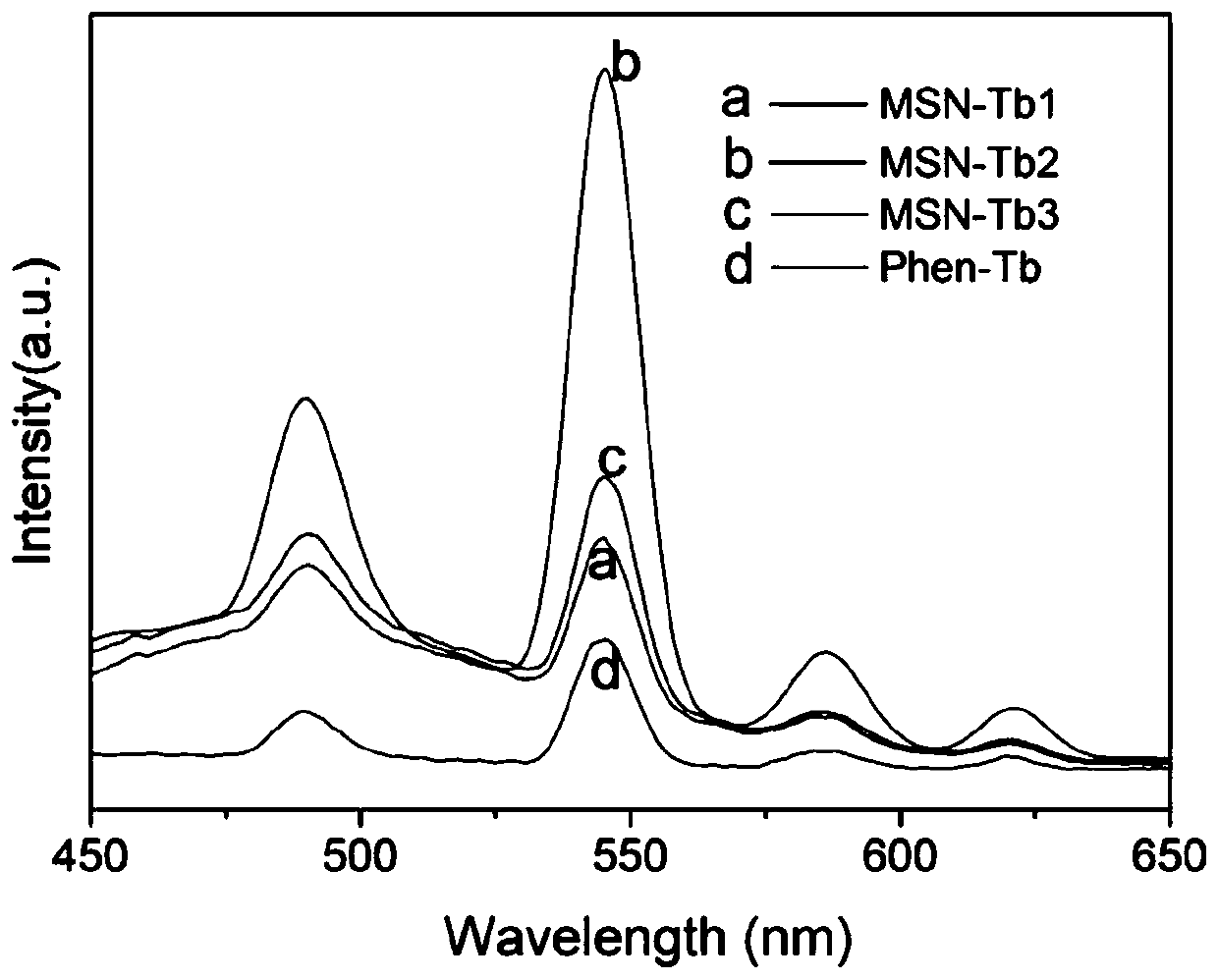
Preparation method of nano fluorescent probe for detecting deubiquitination enzyme
ActiveCN111154481AAvoid vibrationHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsNanoparticlePhenanthroline
The invention belongs to the technical field of deubiquitination enzyme fluorescence detection, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a nano fluorescent probe for detecting deubiquitination enzyme. The preparation method comprises following steps: dispersing mesoporous silicon nano particles into a dichloromethane solution containing phenanthroline-silicon, carrying out reactions toobtain mesoporous silicon-phenanthroline nano particles; mixing mesoporous silicon-phenanthroline nano particles and TbCl3.6H2O in ethanol, refluxing, adding 1,3-diphenyl-1,3-propanedione, carrying out reactions to obtain a nano fluorescent probe precursor; suspending the nano fluorescent probe precursor in a polyethyleneimine water solution to coat polyethyleneimine to obtain a polyethyleneiminemodified nano fluorescent probe precursor; dispersing the polyethyleneimine modified nano fluorescent probe precursor into the mixed solution, and stirring to obtain the nano fluorescent probe. The preparation process is simple, the period is short; and the prepared nano fluorescent probe has good sensitivity and selectivity for detection of UCH-L1.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
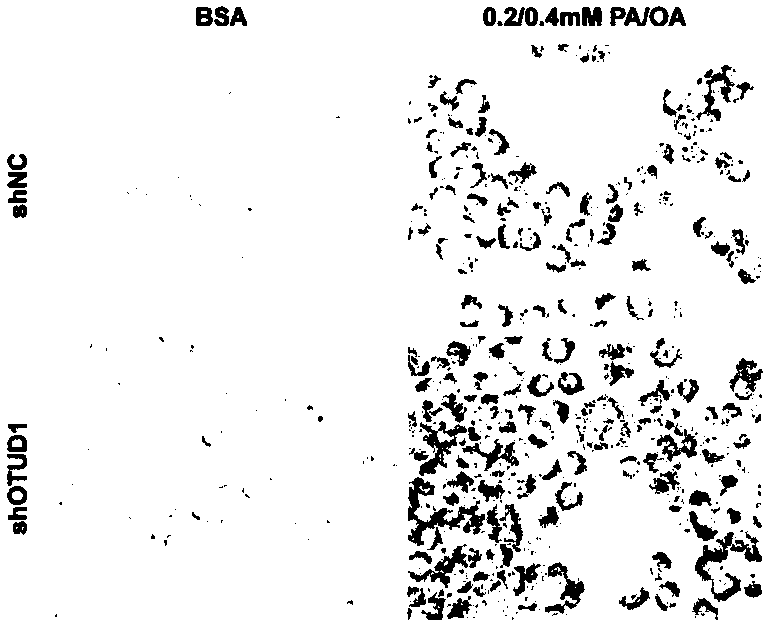
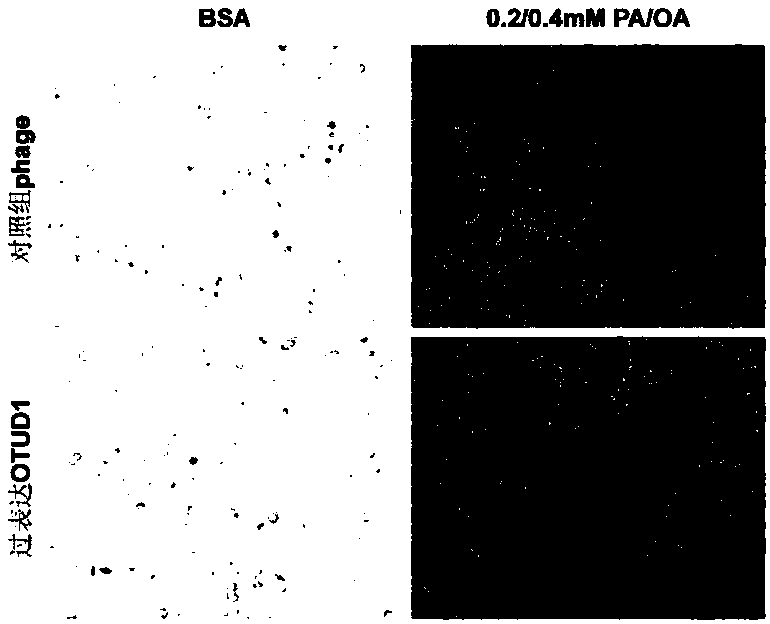
Application of OTU Domain-Containing Deubiquitinase 1 in preparation of medicines for treating fatty liver and related diseases
The invention discloses an application of OTU Domain-Containing Deubiquitinase 1 in preparation of medicines for treating fatty liver and related diseases. According to the invention, a normal human hepatocyte L02 cell line is taken as a research object, lentivirus can be used for constructing an OTUD1 knockout and overexpression vector system, and an OTUD1 gene knockout or overexpressed L02 cellis obtained. The function of the OTUD1 gene in fatty degeneration is researched through a palmitic acid (PA) and oleic acid (OA) combination-induced fatty liver cell model. The result displays that under same PA+OA stimulation, compared with the L02 cell normally expressed by the OTUD1 gene, the red fat droplets in the L02 cell knockouted by the OTUD1 gene are large and multiple; and on the contrary, and the red fat droplets in the L02 cell overexpressed by the OTUD1 gene are small and less. The result shows that the OTUD1 gene can obviously inhibit liver lipid deposition and inhibit generation of fatty liver.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
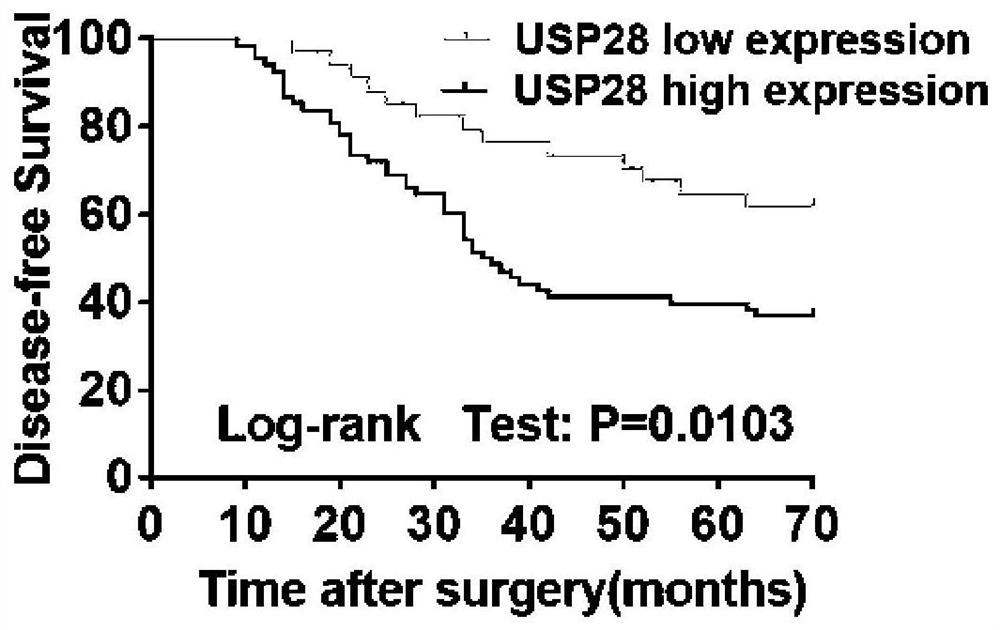
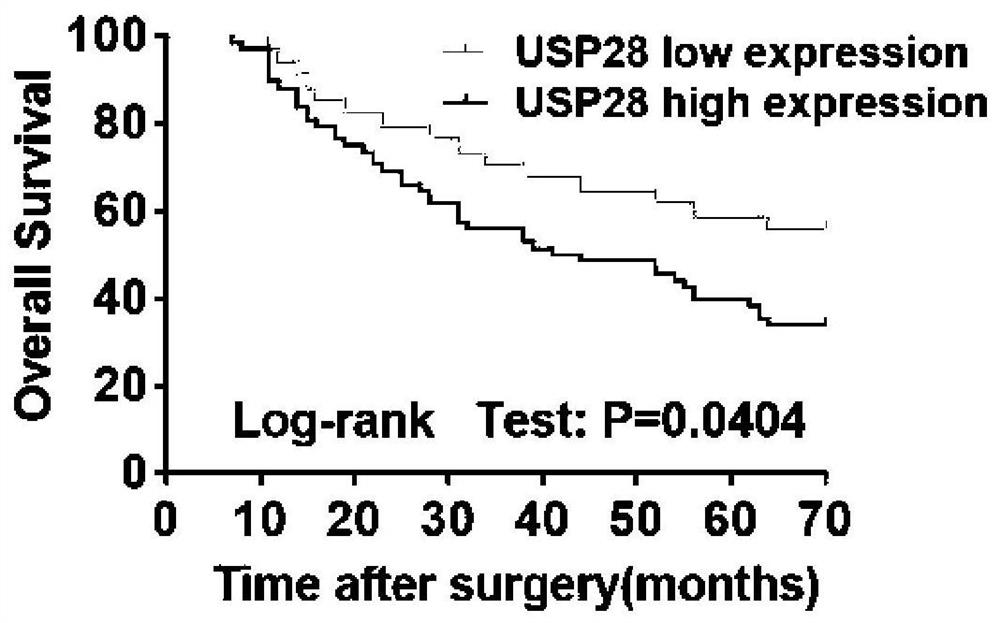
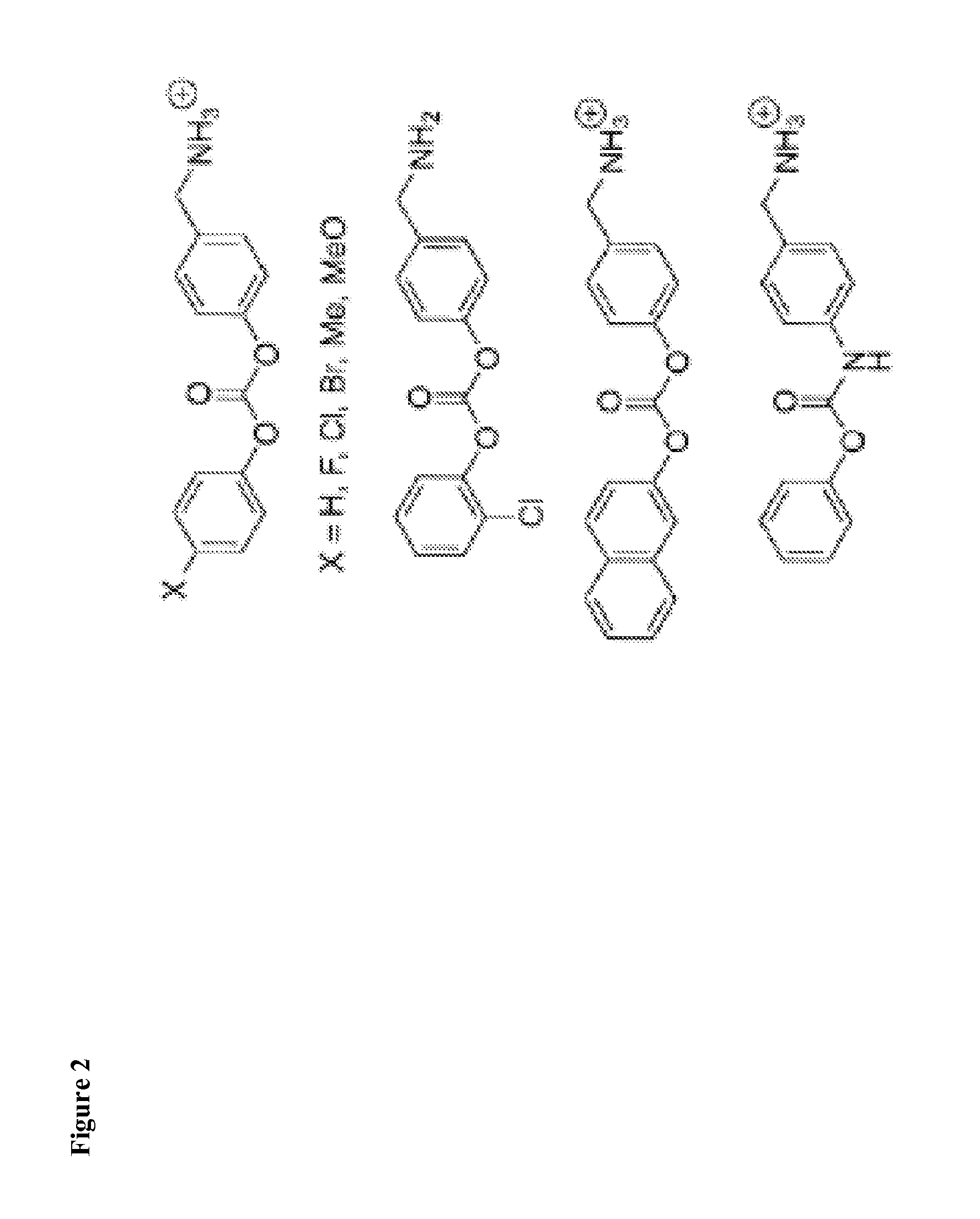
Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel
InactiveCN112604001AExpression up-regulationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemPancreas CancersOncology
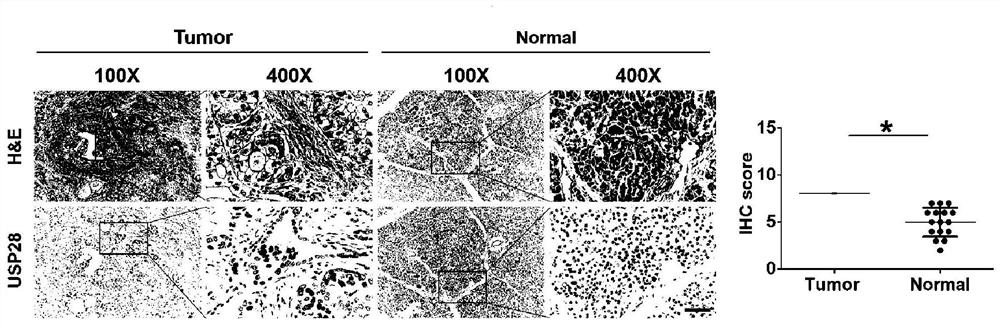
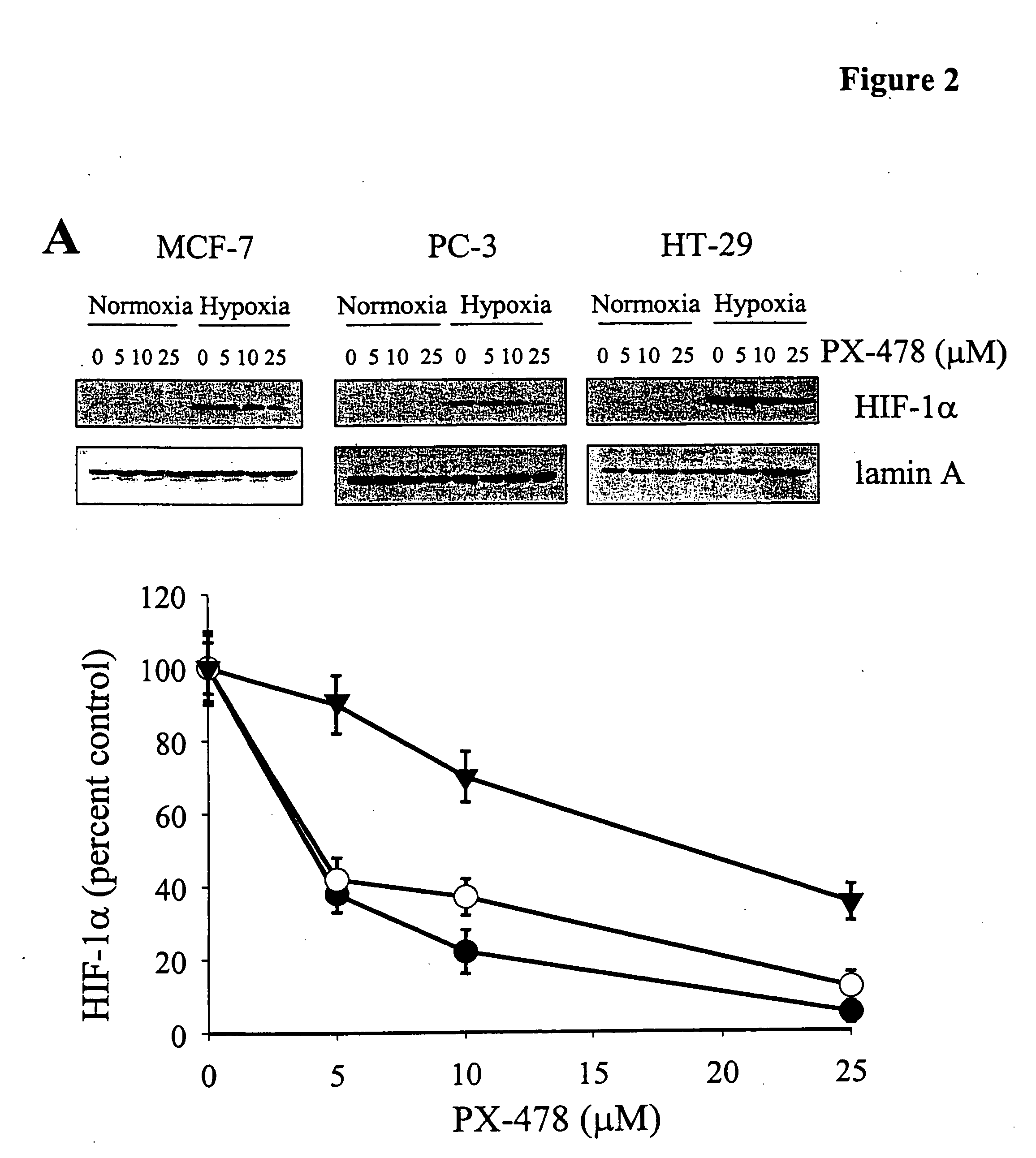
The invention relates to an application of a GATA4 inhibitor in inhibiting an NF-[kappa]B / STAT3 signal channel, and according to earlier-stage research, USP28 regulates the stability of MYC through deubiquitination so as to promote up-regulation of the expression quantity of MYC; then a GATA4 promoter region is demethylated, so the expression of GATA4 is up-regulated; The process of 'inflammatory cancer transformation' of pancreas is promoted by activating two inflammation-related signal channels, namely NF-[kappa]B / SASP and Reg3[beta] / STAT3. The application has the advantages that the transcription factor GATA4 is taken as an entry point, the discussion that USP28 / MYC / GATA4 signal axis promotes pancreas inflammatory cancer transformation is taken as the center, the formation cause of pancreas cancer is understood from the new perspective of transformation, and a new method and thought are provided for preventing and treating pancreas cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Novel hypoxia signal regulation molecule and application thereof
ActiveCN111265658AInhibit transferSuppress generationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseCancer cell
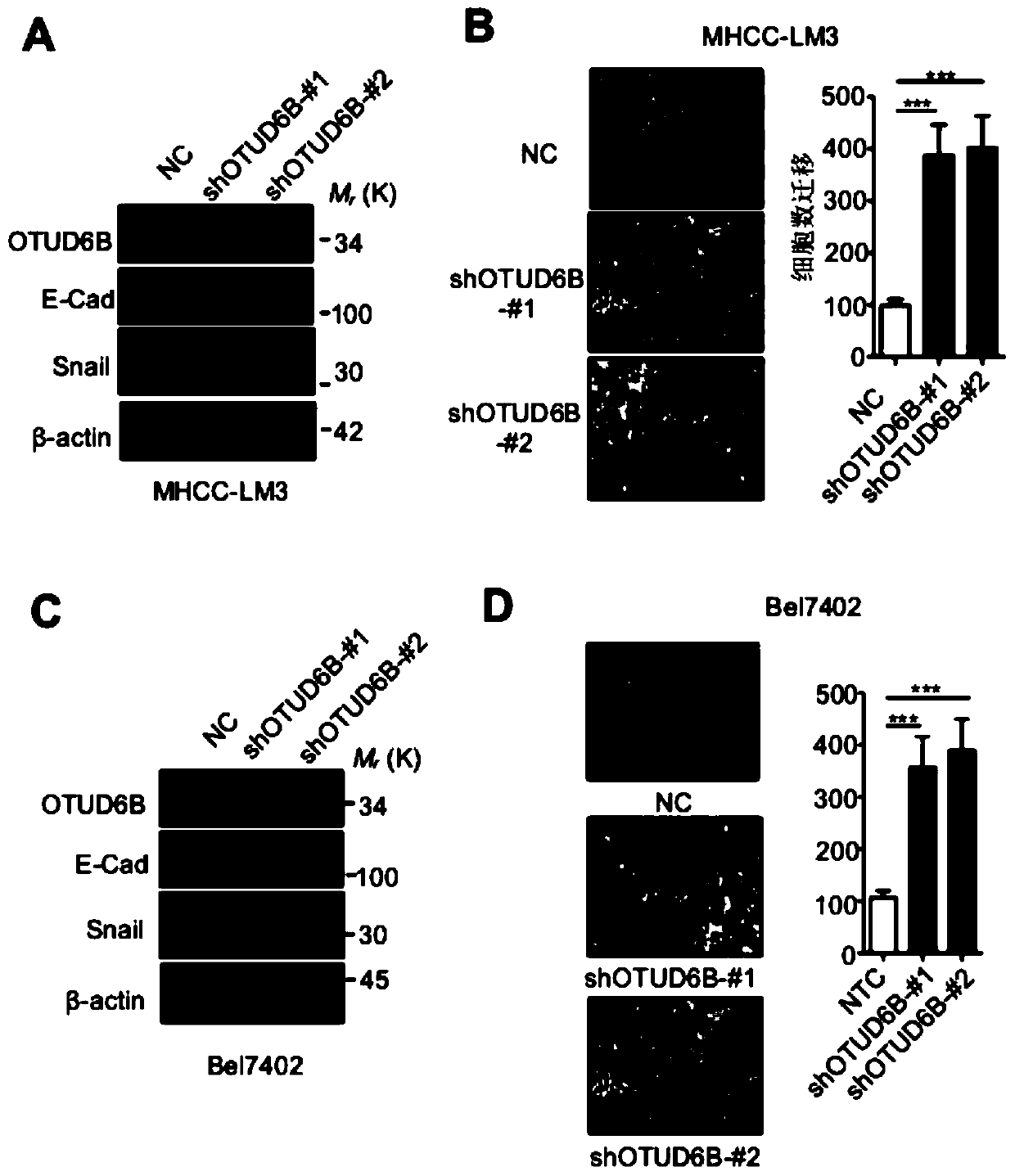
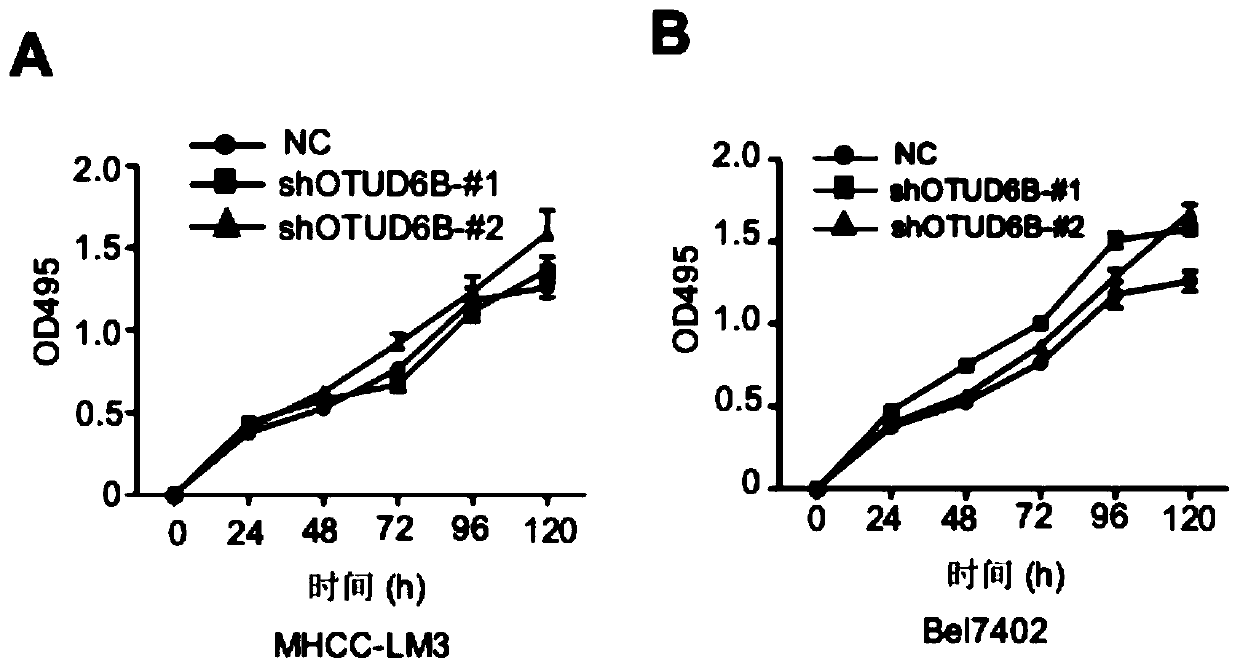
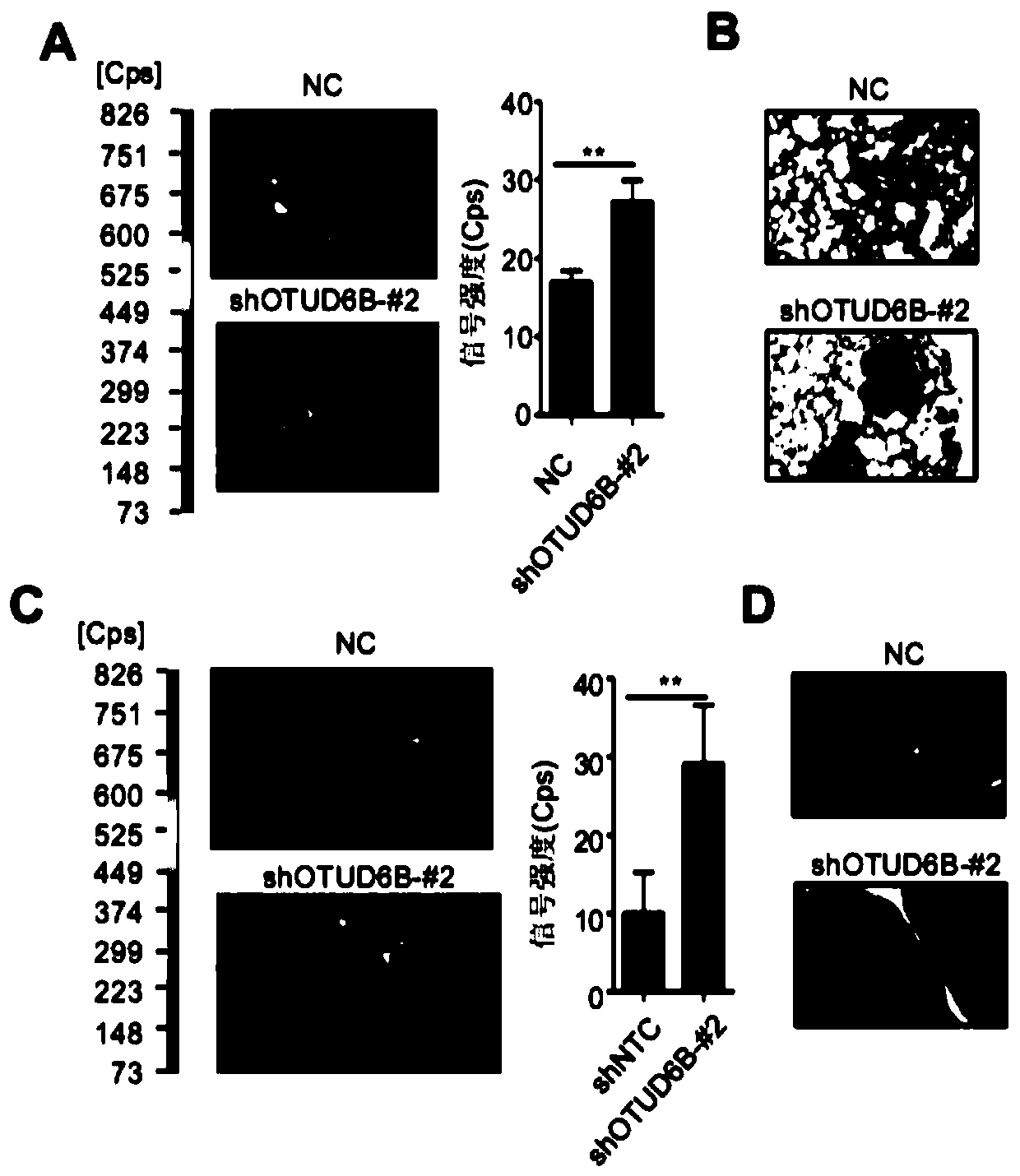
The invention discloses a novel hypoxia signal regulation molecule and application thereof. The hypoxia signal regulation molecule is deubiquitination enzyme OTUD6B protein. Experiments prove that thedeubiquitination enzyme OTUD6B can inhibit liver cancer cell metastasis, and the expression level of the deubiquitinase OTUD6B has significant correlation with liver cancer cell metastasis and recurrence: the lower the expression quantity of the deubiquitinase OTUD6B is, the shorter the total lifetime of liver cancer patients is, and the higher the tumor recurrence rate is; the deubiquitination enzyme OTUD6B can be used for inhibiting generation of blood vessels; the deubiquitination enzyme OTUD6B can be used for lowering the protein levels of HIF-1 alpha and HIF-2 alpha and inhibiting the expression of a plurality of HIF target genes; the deubiquitination enzyme OTUD6B can increase the protein stability of VHL, and the migration ability of the VHL depends on the VHL protein. Therefore, the deubiquitinase OTUD6B is an anoxia signal regulation molecule and can be used for preventing and / or treating hepatocellular carcinoma and other anoxia-related diseases. The invention has importantapplication value.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
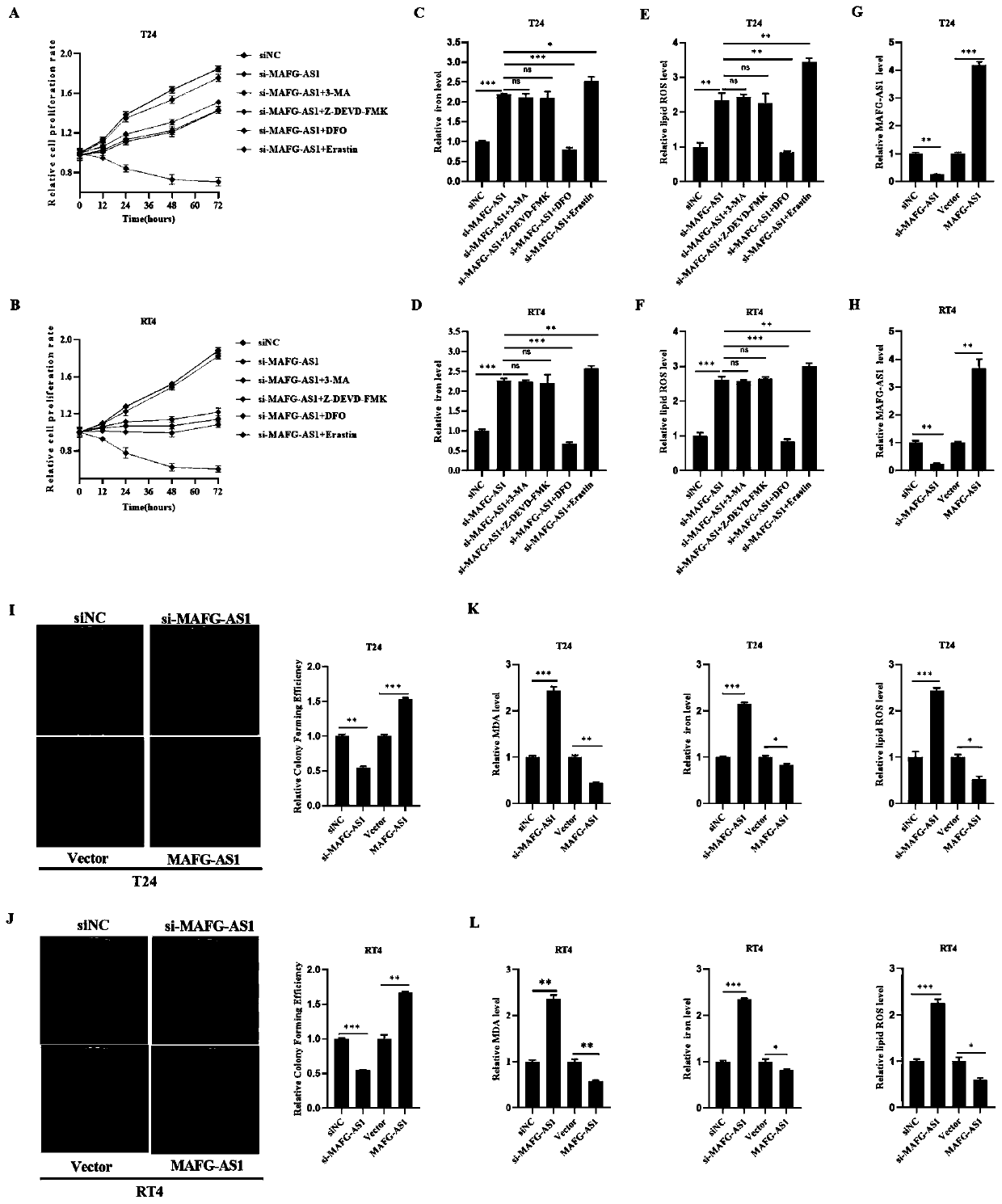
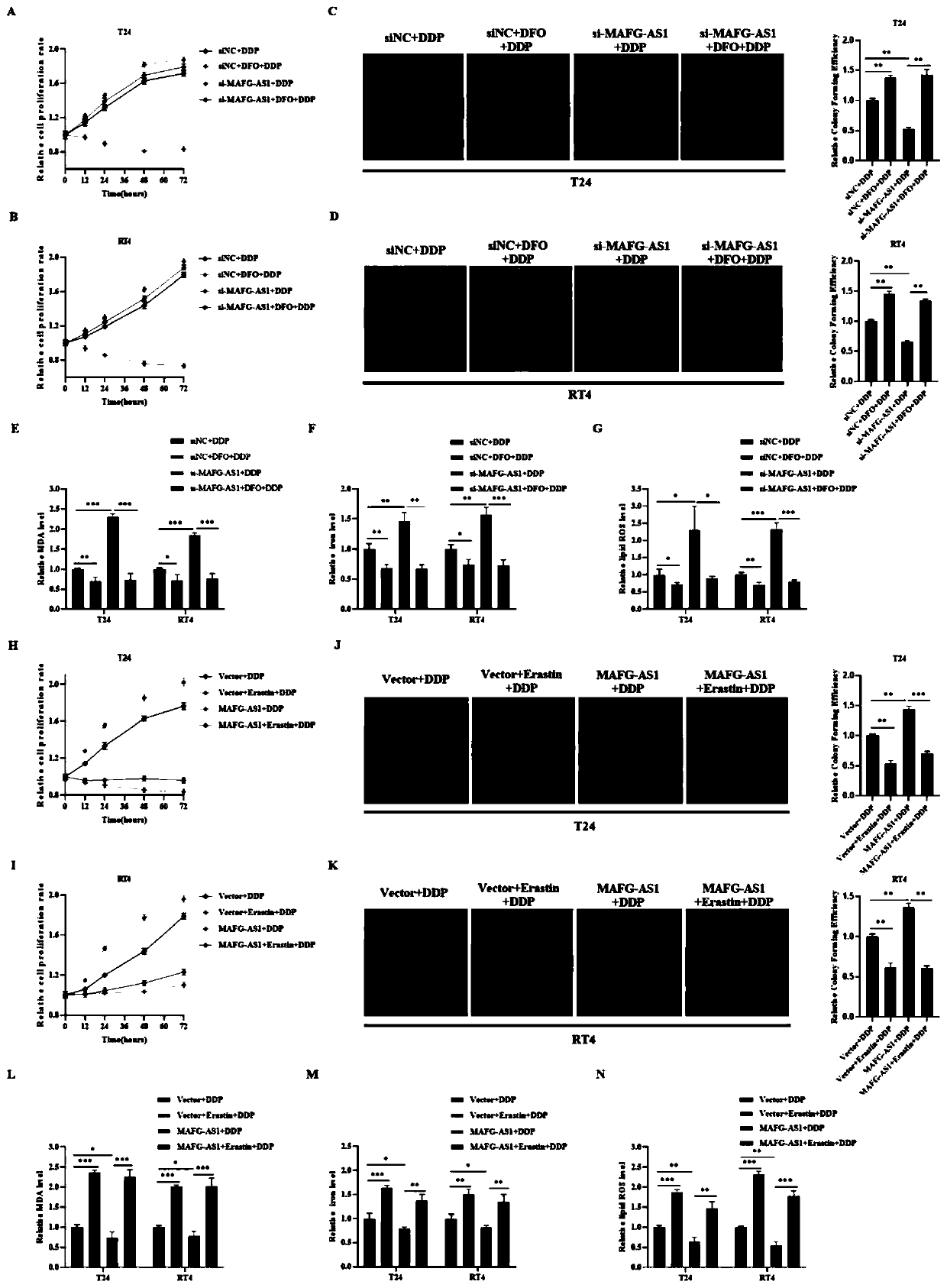
Application of MAFG-AS1/PCBP2/FPN1 regulation axis as target site detection reagent in preparation of medicine for treating bladder cancer
ActiveCN110806486AEasy to transportFacilitate transport outCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBladder cancer patientBladder cancer cell
The invention discloses an application of an MAFG-AS1 / PCBP2 / FPN1 regulation axis as a target site detection reagent in preparation of a medicine for treating the bladder cancer. The research proves that MAFG-AS1 with the increased expression is combined with PCBP2 in a bladder cancer cell and then a deubiquitination enzyme UCHL5 is recruited to stabilize the expression of the PCBP2, iron ions aretransferred to FPN1 on a cell membrane under the transportation effect of the PCBP2 to promote transferring of iron out of the cell so as to cause iron death resistance. Therefore, the existence of the MAFG-AS1 / PCBP2 / FPN1 regulation axis in the bladder cancer is proved for the first time and the regulation axis is a valuable potential therapeutic drug in the field of bladder cancer treatment. Andthus the PCBP2 can be used as a target site in the preparation of a medicament for treating the bladder cancer and is also a molecular marker for clinically predicting a bladder cancer patient.
Owner:THE THIRD XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
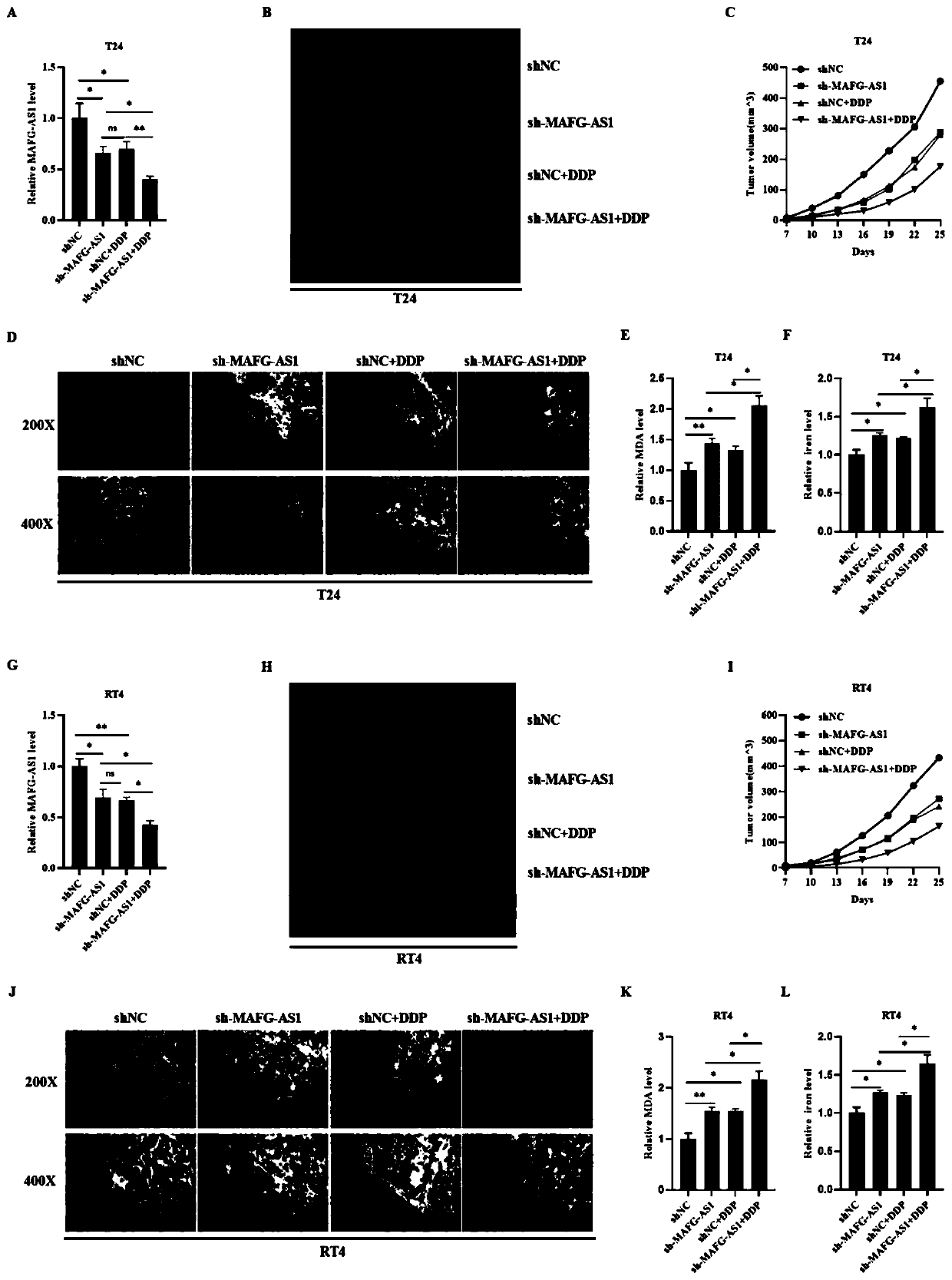
Application of deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 in preparation of medicine for preventing or treating pancreatic cancer
The invention discloses an application of deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 in preparation of a medicine for preventing or treating pancreatic cancer. Research finds that USP28 expression in pancreatic cancer tumor tissue is higher than that in normal pancreatic tissue, and USP28 high expression is remarkably related to malignant phenotype and lifetime shortening of pancreatic cancer patients; overexpression of the USP28 can accelerate growth of pancreatic cancer cells, and down-regulation of the USP28 can inhibit in-vitro and in-vivo growth of the pancreatic cancer cells; USP28 promotes the growth of pancreatic cancer cells by accelerating the cell cycle process and inhibiting cell apoptosis. In the aspect of mechanism, USP28 is subjected to ubiquitination and stabilizes a transcription factor FOXM1, which is a key medium for Wnt / beta-catenin signal transduction, USP28-mediated FOXM1 stabilizes and significantly promotes beta-catenin nucleation so as to further cause activation of a Wnt / beta-catenin pathway, and recovery of FOXM1 expression can alleviate the antitumor effect caused by down regulation of USP28. The deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 promotes the development of the pancreatic cancer by enhancing FOXM1 mediated Wnt / beta-catenin signal channel activation, and a powerful means is provided for potential targeted treatment and prevention of pancreatic cancer patients in the future.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL TO NANCHANG UNIV
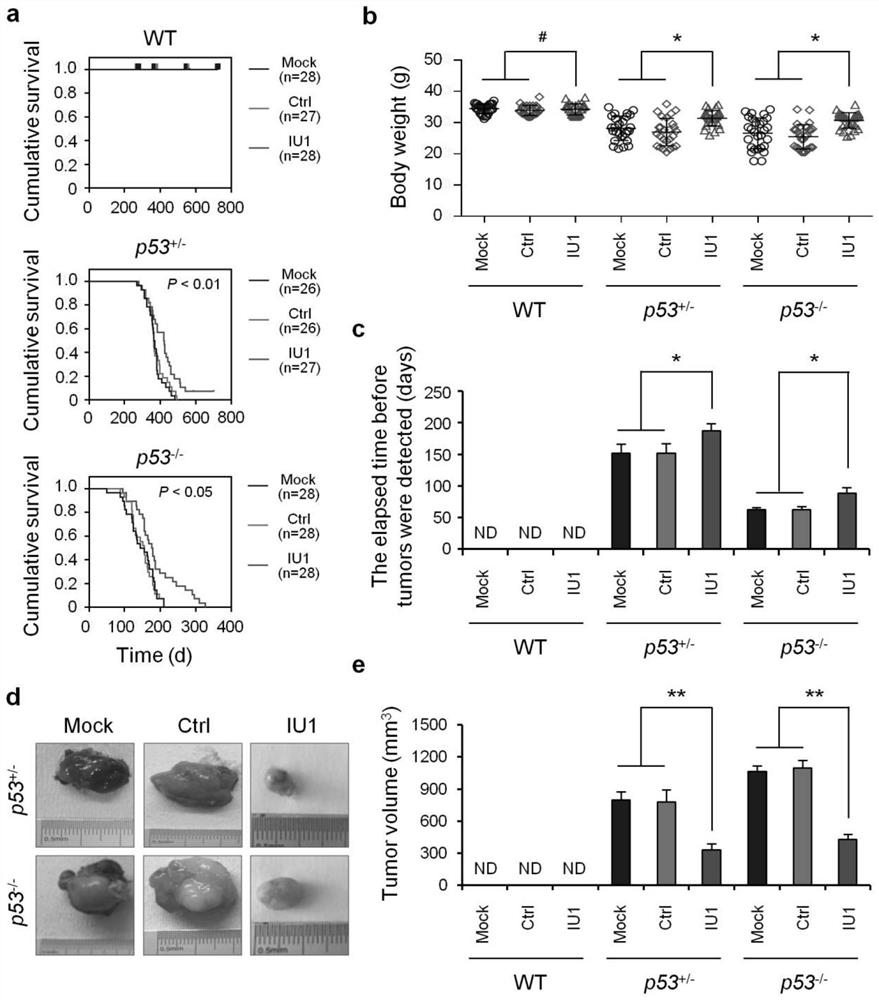
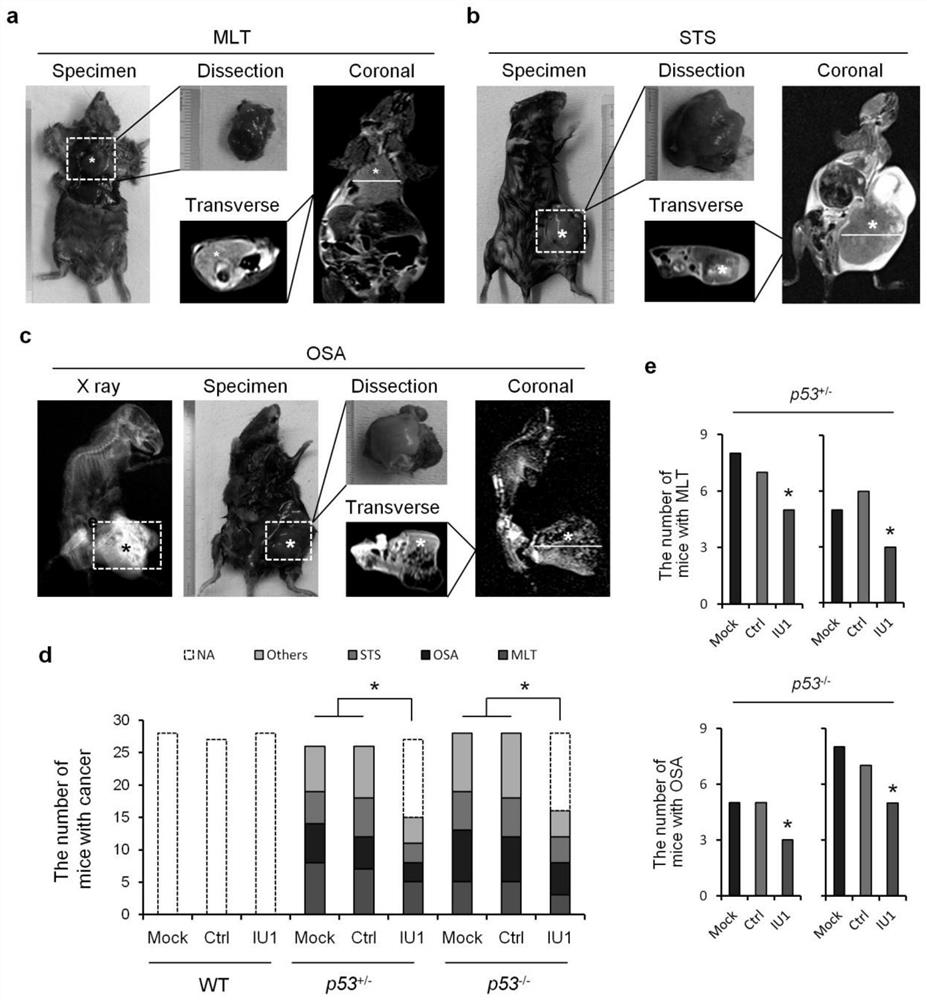
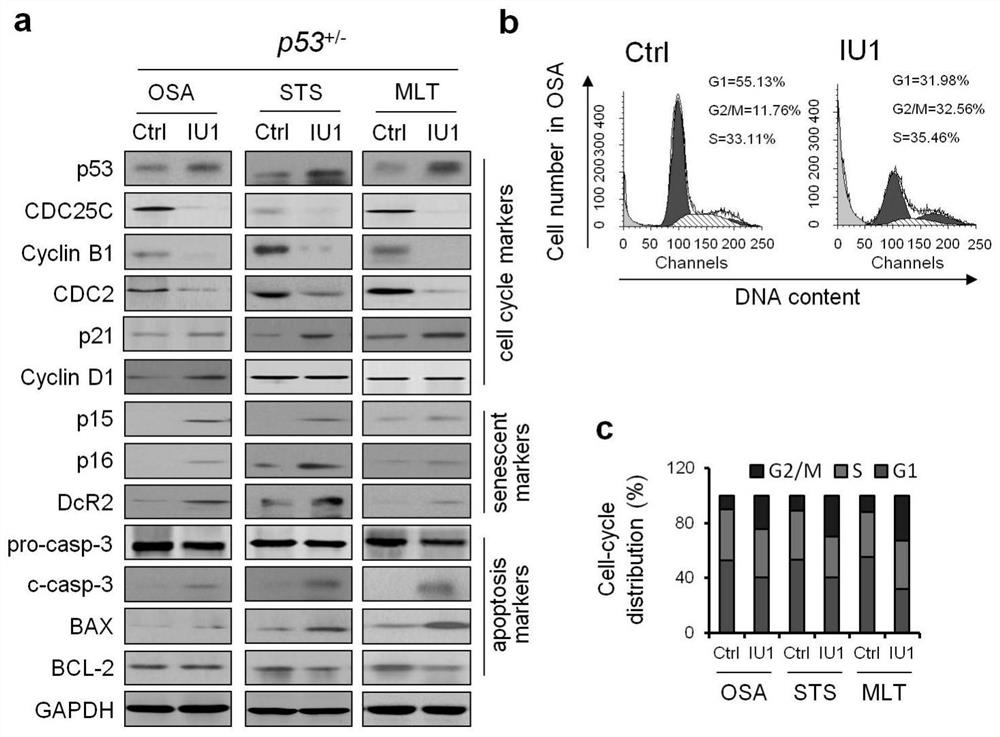
Application of iu1 in the preparation of drugs for the treatment of p53-deficient tumors
ActiveCN110664802BDoes not affect normal tissueOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor regressionOncology
The invention provides the application of IU1 in the preparation of a drug for treating p53-deficient tumors, and belongs to the technical field of tumor drugs. The application of IU1 having the structure shown in formula I in the preparation of a medicament for treating p53-deficient tumors. Specific inhibition of the deubiquitinase USP14 with the small-molecule inhibitor IU1 resulted in persistent tumor regression of lymphomas and sarcomas in p53-deficient mice without affecting normal tissues, and treatment response was associated with increased COPS5 ubiquitination. IU1-specific inhibition of USP14 resulted in durable tumor regression through a mechanism of COPS5 deubiquitination and p53-dependent and independent regulation of USP14.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
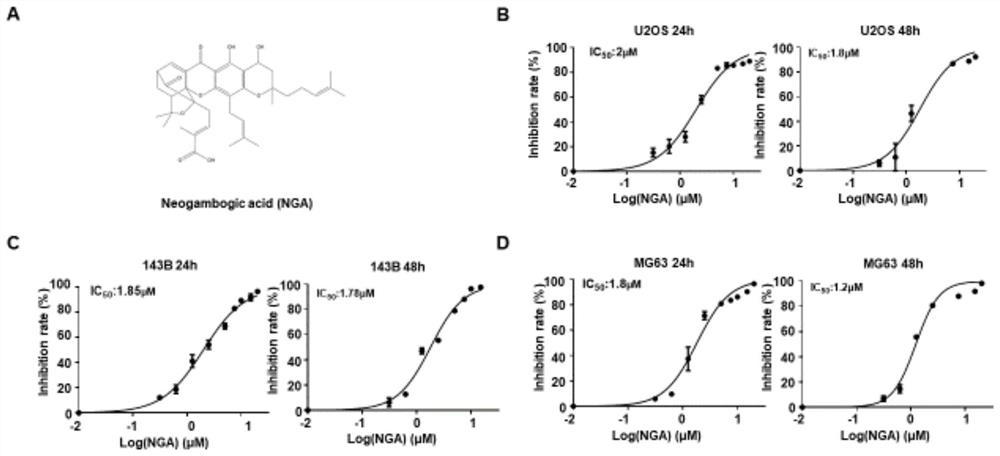
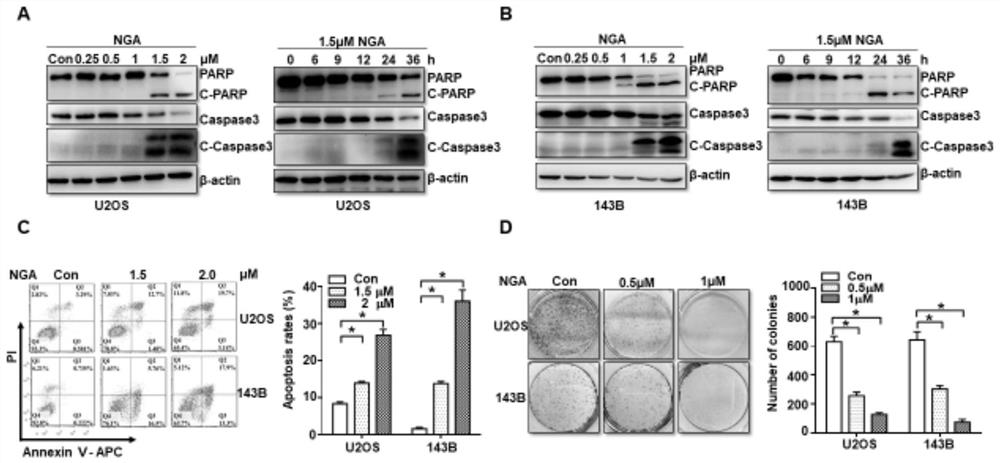
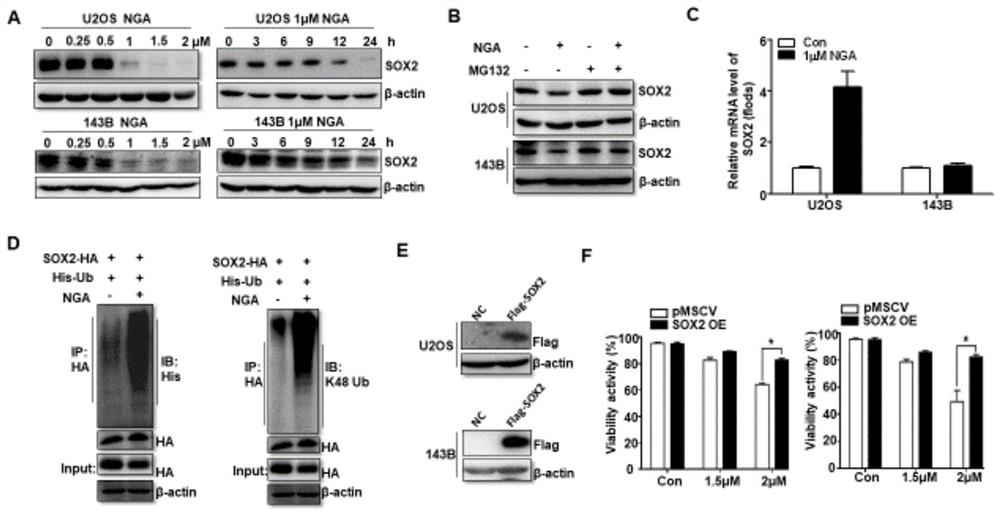
Application of USP9x inhibitor in preparation of medicine for treating osteosarcoma
ActiveCN112206323AAvoid degradationPromote degradationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSOX2Chemotherapeutic drugs
The invention discloses an application of a USP9x inhibitor in preparation of a medicine for treating osteosarcoma. By discovering that the degradation of a proliferation-promoting factor SOX2 can beeffectively promoted by reducing the expression of USP9x or inhibiting the activity of the USP9x in the osteosarcoma, a new target is provided for clinically developing new chemotherapeutic medicinesfor the osteosarcoma; and meanwhile, the research also discovers that NGA can effectively inhibit the deubiquitination enzyme activity of the USP9x, thereby indirectly promoting the ubiquitination degradation of the SOX2, inhibiting the generation and development of tumors, and providing a new molecular structure for clinically discovering new medicines.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
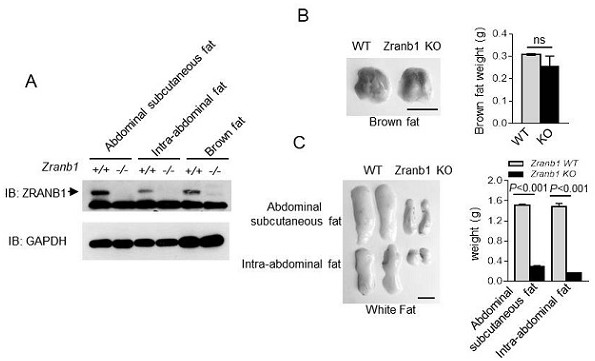
Function and application of deubiquitinating enzyme ZRANB1 for regulating lipid metabolism
ActiveCN114470214AReduce accumulationPromote combustionMetabolism disorderGenetic engineeringDiseaseWhite Adipocytes
The invention discloses a function of a deubiquitination enzyme ZRANB1 for regulating lipid metabolism and application of the deubiquitination enzyme ZRANB1. The invention further discloses application of inhibiting ZRANB1 gene expression in preparing a product with at least one function of treating and / or preventing obesity, promoting white fat cell combustion, promoting slimming and losing weight and inhibiting accumulation / accumulation of subcutaneous and / or intra-abdominal white fat. Experiments prove that ZRANB1, as a newly discovered important fat metabolism regulation molecule, can significantly reduce the content of white fat of an organism after the protein level is reduced. The discovery of the ZRANB1 function provides an important scientific basis and application value for prevention of obesity diseases and treatment of slimming.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
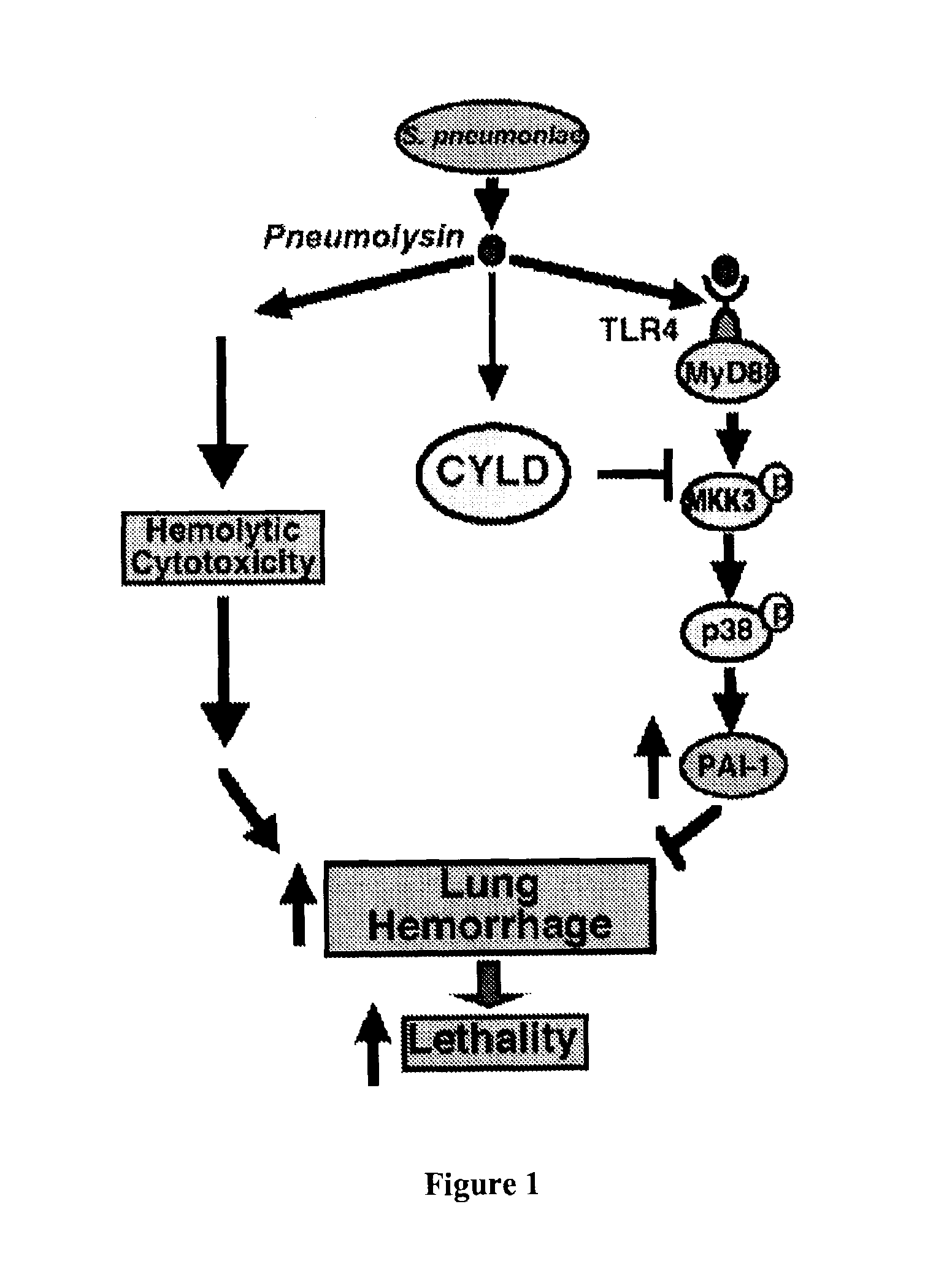
Methods for the treatment or prevention of hemorrhagic conditions
InactiveUS8716237B2Increased mortalityPotentiating mortalityOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesDeubiquitinationSurgery
The present invention relates to a method for treatment or prevention of a hemorrhagic condition in a patient by administering plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (“PAI-1”) and / or an inhibitor of deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD (“CYLD”) to a patient. Pharmaceutical compositions that include one or both of PAI-1 and an inhibitor of CYLD are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
ub‑nanoluc, ub‑ub‑gs‑nanoluc reporter gene system and its construction and application
The present invention discloses an Ub-Nanoluc reporter gene system and an Ub-Ub-GS-Nanoluc reporter gene system, and applications of the Ub-Nanoluc reporter gene system and the Ub-Ub-GS-Nanoluc reporter gene system in deubiquitination enzyme activity detection and deubiquitination enzyme inhibitor throughput-screening, wherein the Ub-Nanoluc reporter gene DNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and the Ub-Ub-GS-Nanoluc reporter gene DNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.4. According to the present invention, the high sensitivity characteristic of luciferase Nanoluc is utilized to provide the method for deubiquitination enzyme activity detection and deubiquitination enzyme inhibitor throughput-screening by using the chemical luminescent reporter gene so as to provide the new action target point and the new ideal for screening and research of new drugs including anticancer drugs, and provide broad application prospects, great enormous benefits, and great social benefits.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
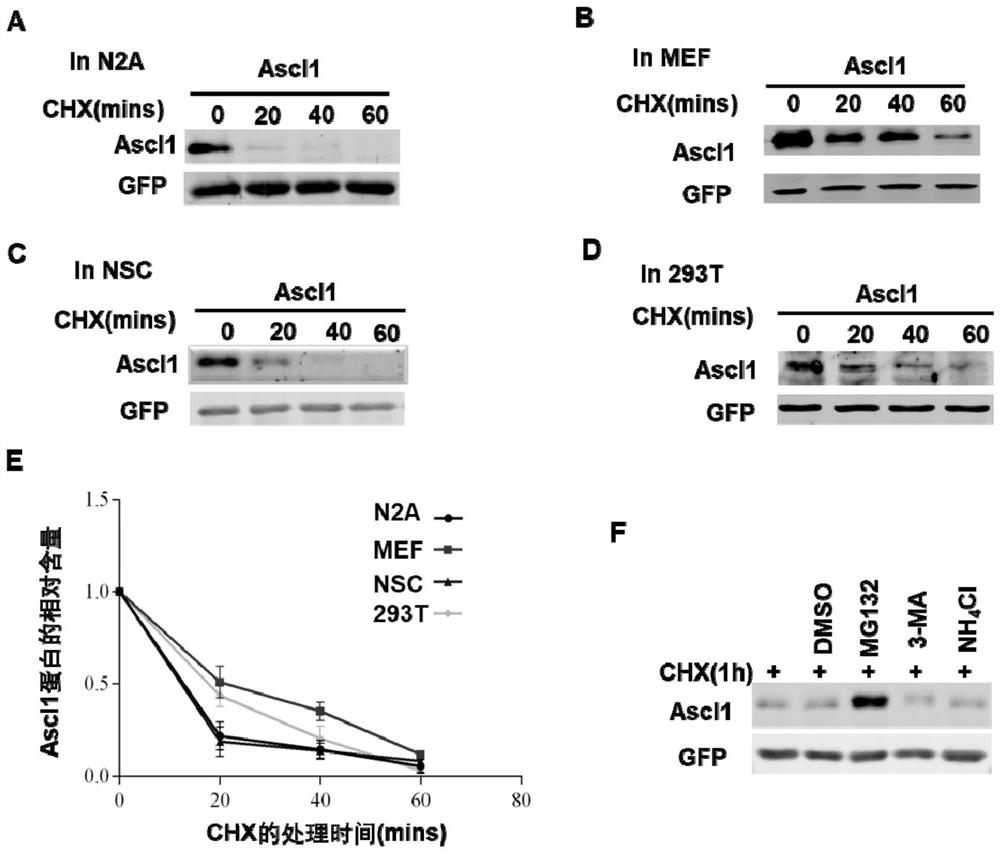
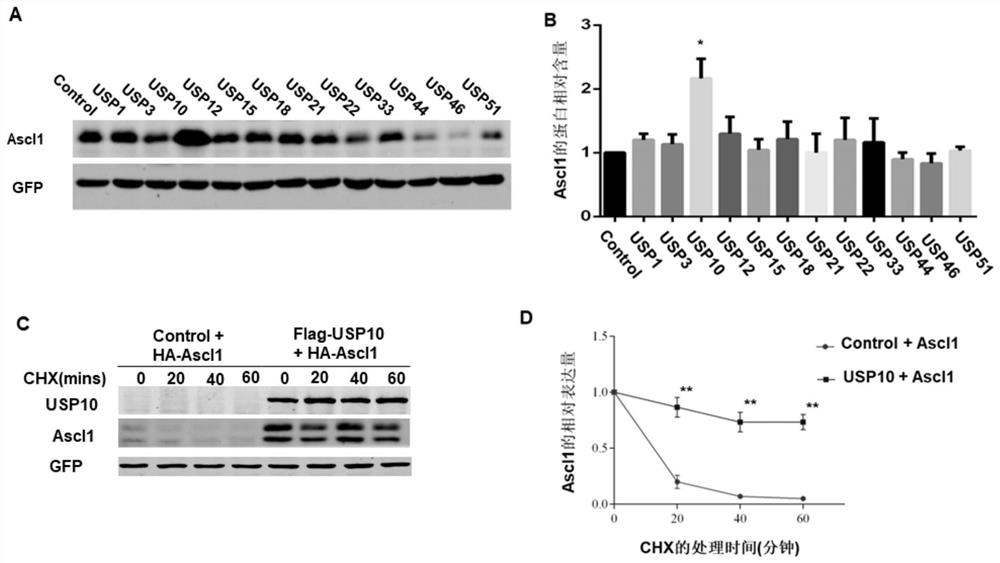
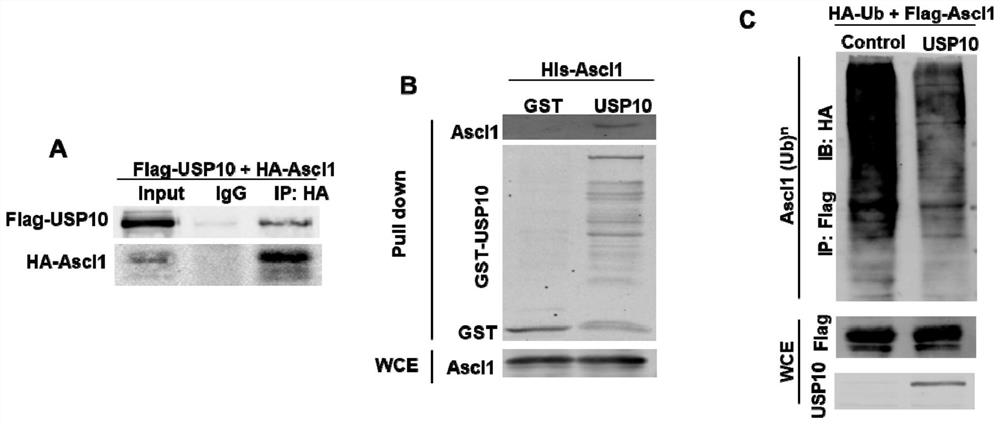
Application and method of USP10 gene and/or Ascl1 gene in inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into neuronal cells
PendingCN114231494AImprove stabilityEfficiently obtainedGenetically modified cellsCulture processTransdifferentiationFibroblastic cell
The invention discloses an application and a method of a USP10 gene and / or an Ascl1 gene in inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into neuronal cells. The invention firstly discloses the application of the USP10 gene and / or the Ascl1 gene in inducing the fibroblast to be transdifferentiated into the neuronal cell or the application in preparing a product for inducing the fibroblast to be transdifferentiated into the neuronal cell. The invention further discloses a method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into neuronal cells. The USP10 capable of improving the stability of the Ascl1 protein and deubiquitinating the Ascl1 is obtained by screening based on the characteristics of the Ascl1. The USP10 gene and the Ascl1 gene are applied to the process of converting fibroblasts into neuronal cells, the GABAergic neuronal cells can be efficiently obtained, the defect that the neuronal cells cannot be efficiently obtained is overcome, and the application has important significance on treatment of nerve-related diseases.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
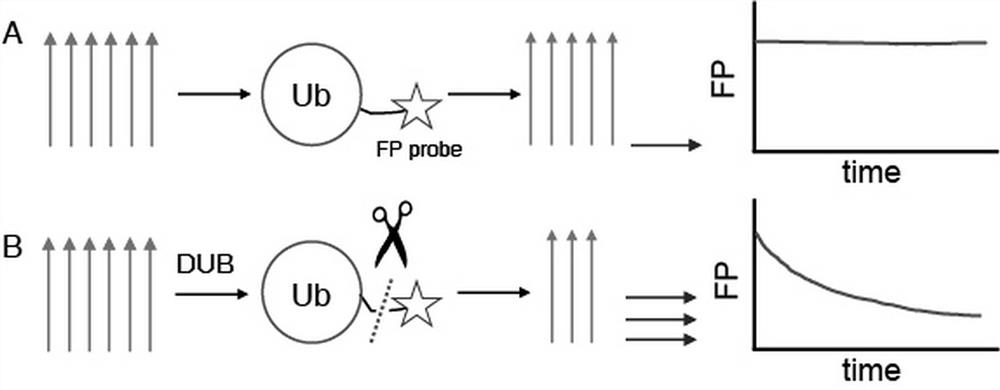
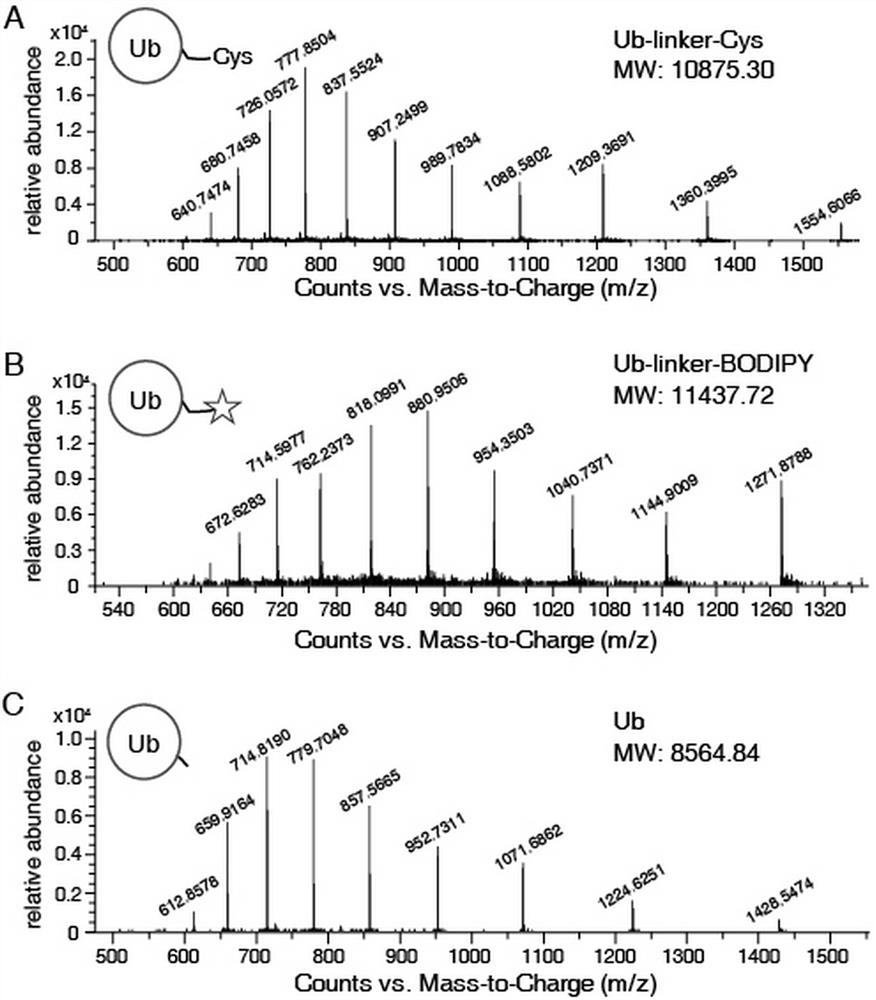
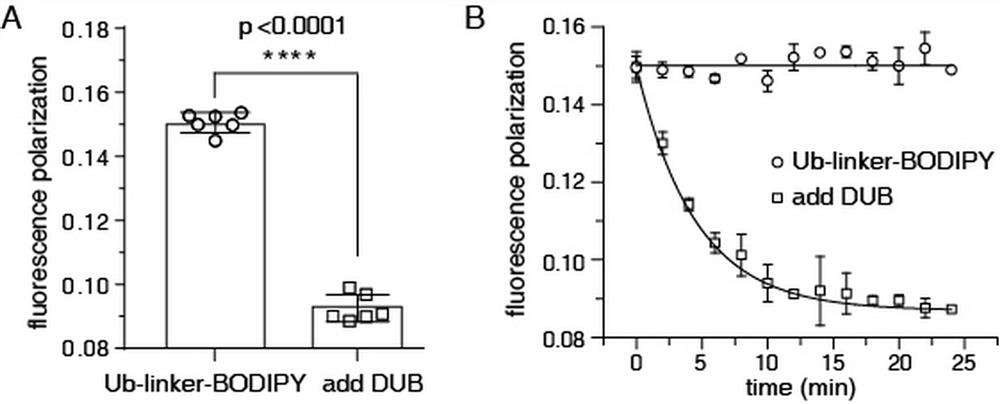
Deubiquitination enzyme activity detection method based on fluorescence polarization
PendingCN113514445ANot easy to interfereReal-time detection of activityFusion with degradation motifMicrobiological testing/measurementDe ubiquitinationDeubiquitination
The invention provides a deubiquitination enzyme activity detection method based on fluorescence polarization. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a deubiquitinating enzyme detection probe: preparing a fusion protein Ub-linker-Cys, connecting a BODIPY probe, and carrying out mass spectrometric detection; 2, detecting the activity of the deubiquitination enzyme: selecting the deubiquitination enzyme and detecting the activity of the deubiquitination enzyme in real time according to the influence of deubiquitination on the FP value of the probe. The detection method is based on detection of fluorescence polarization, the fluorescence polarization detects the proportional relation of the fluorescence intensity in the parallel direction and the fluorescence intensity in the vertical direction, the detection method is not easily interfered by the concentration of the fluorescence probe, the solution temperature, the pH value and other fluorescence signals, when the activity of the deubiquitination enzyme is measured, the steps are simple, the consumed time is short, and the usage amount of the probe and the deubiquitination enzyme is small. In addition, the probe prepared in the method can also be used for screening deubiquitination enzyme inhibitors, and is high in throughput.
Owner:荆州市第一人民医院
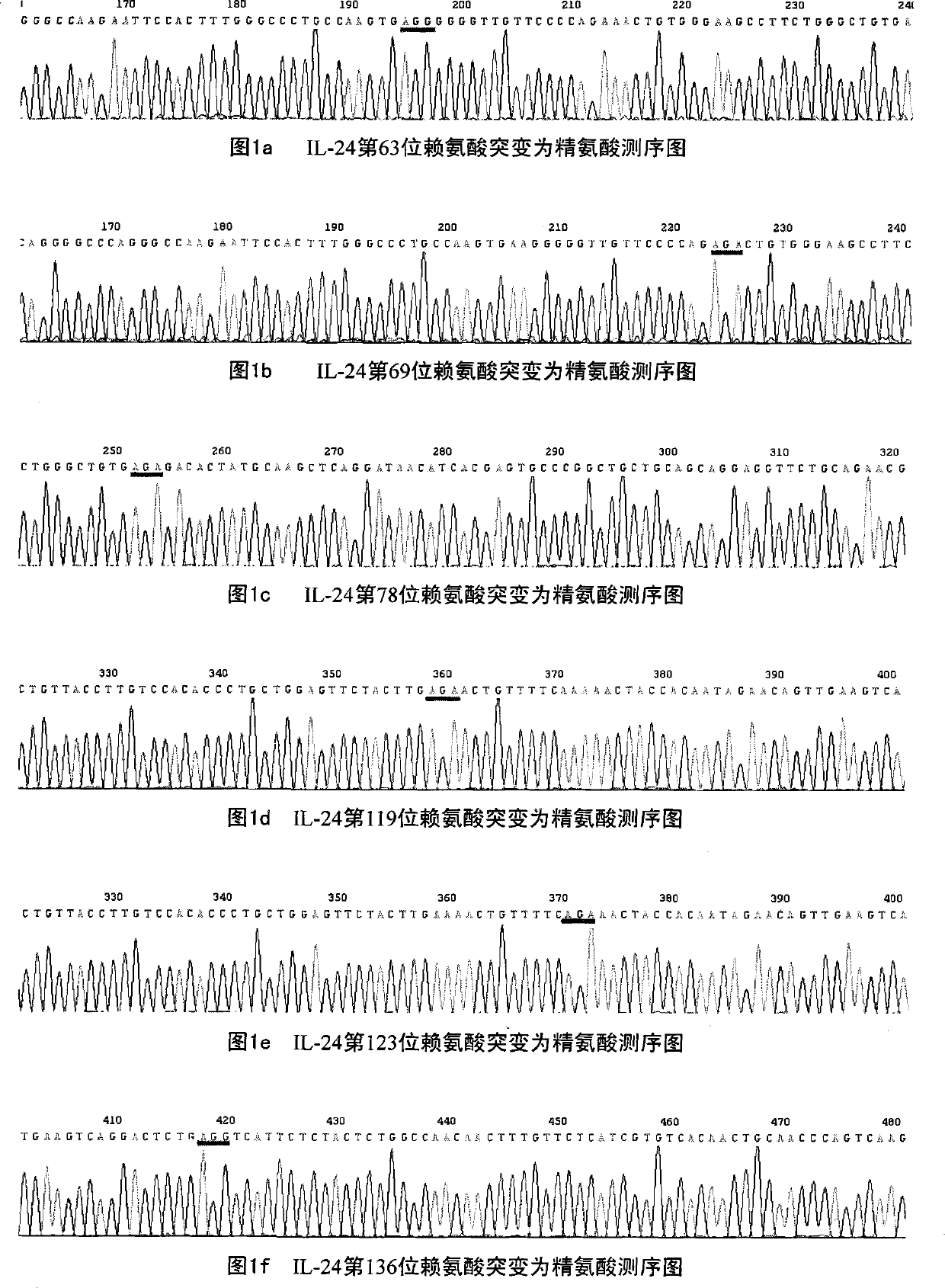
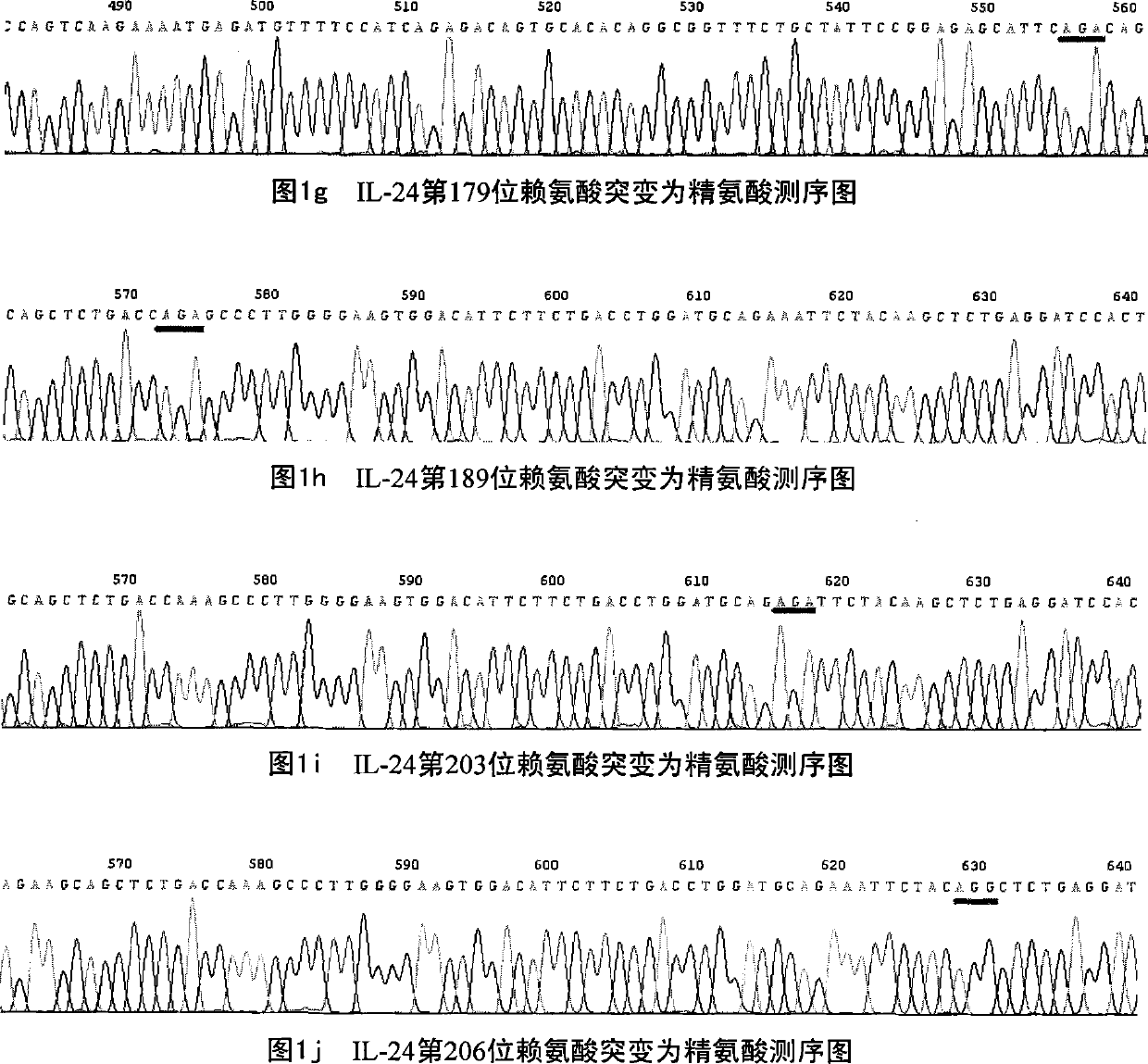
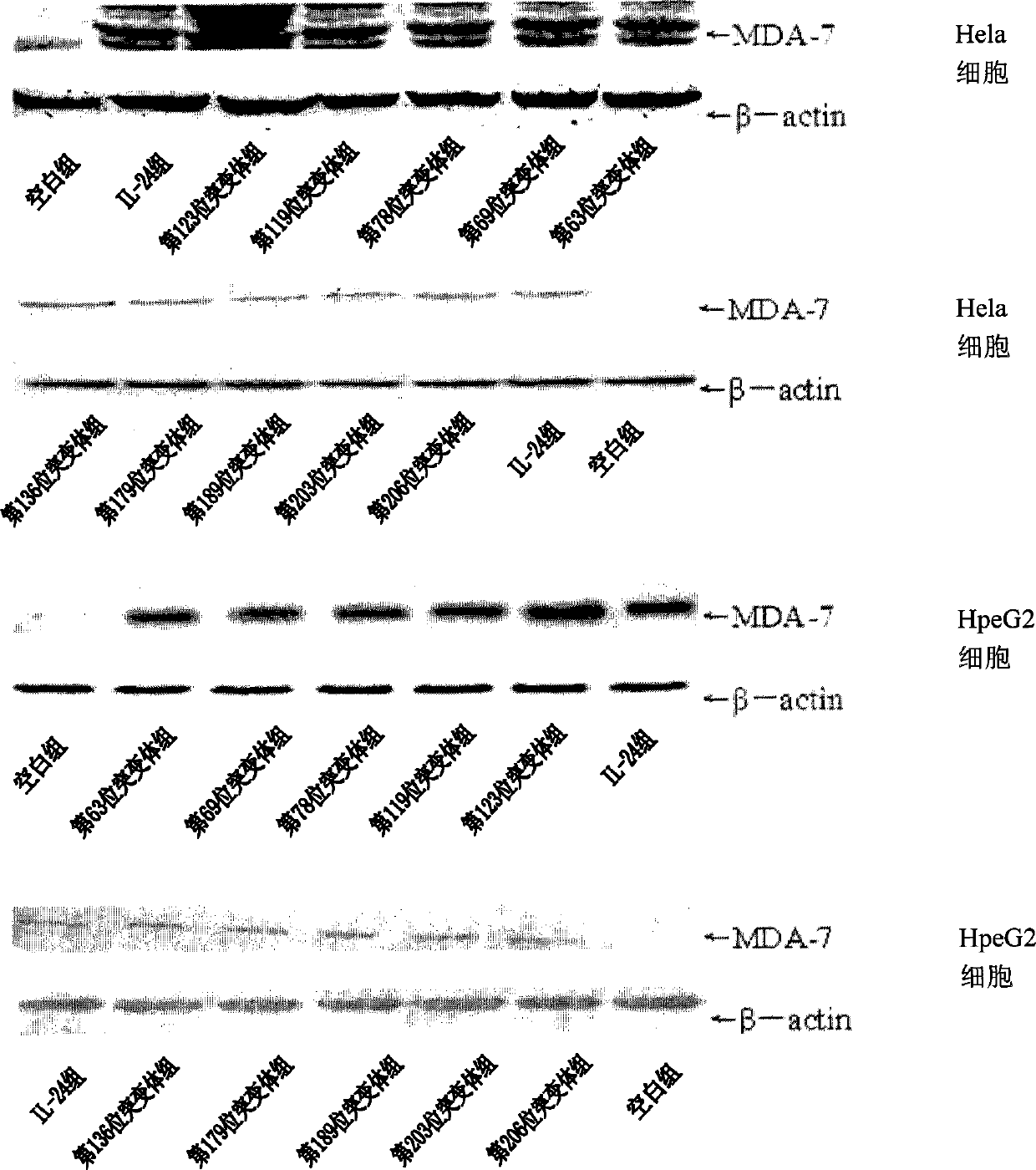
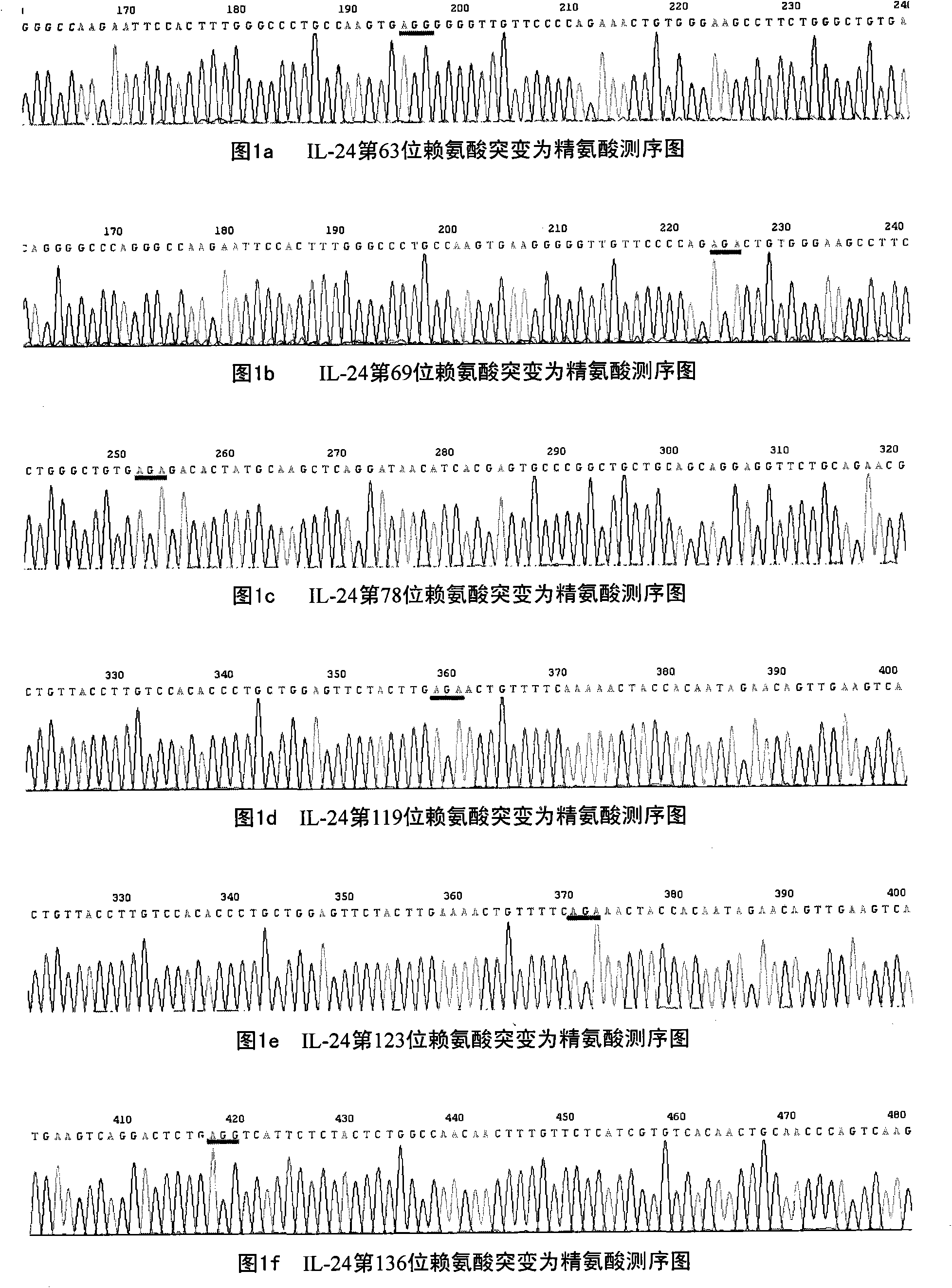
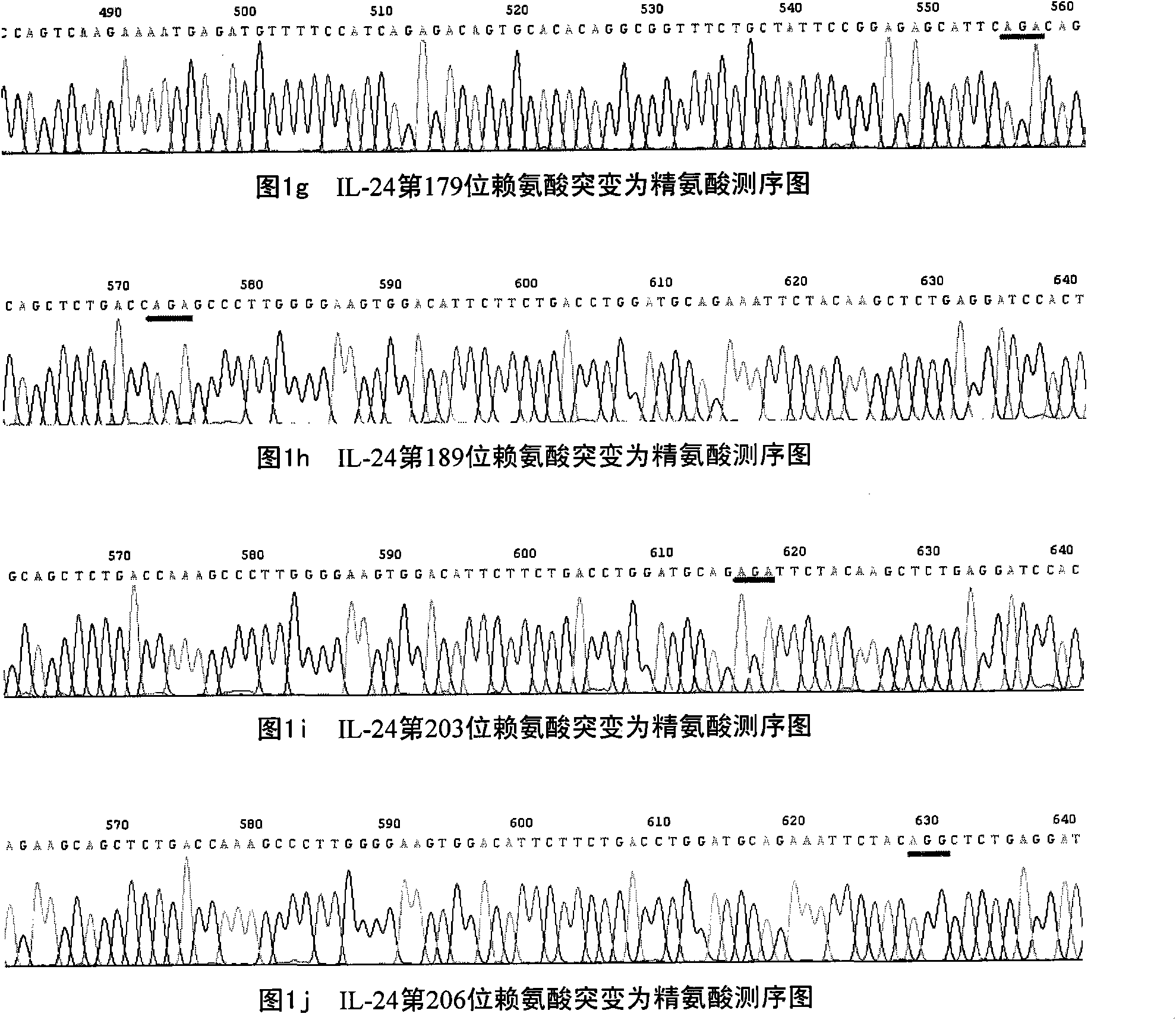
Deubiquitination mutant of mda-7/IL-24
The invention relates to a lysine site mutant of conjugated ubiquitin of mda-7 / IL-24 and application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. In the invention, lysine codons of 63rd, 69th, 78th, 119th, 123rd, 136th, 179th, 189th, 203rd and 206th potential conjugated ubiquitin sites of the mda-7 / IL-24 are mutated into arginine codons by utilizing a site-directed mutation PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology and cloned to pcDNA3.1(+) plasmids; after the mutant plasmids are transfected with cervical carcinoma Hela cells and hepatoma carcinoma HepG2 cells, the expressions of mda-7 / IL-24 protein and ubiquitination mda-7 / IL-24 protein are respectively detected. A result shows that the quantity of the mda-7 / IL-24 protein expressed by a 123rd lysine mutant of the mda-7 / IL-24 is remarkably increased, and the quantity of the ubiquitination mda-7 / IL-24 protein is remarkably decreased. The invention proves that the 123rd lysine of the mda-7 / IL-24 is an ubiquitination site, and mda-7 / IL-24 mutants generated by the mutant plasmids are difficult to be degraded by the in-vivo ubiquitin, thereby enhancing the expression and the action of the mda-7 / IL-24 in tumour cells.
Owner:郑骏年
Application of holomycin in inhibiting nlrp3 inflammasome activation
ActiveCN108815158BInhibit bindingInhibition formationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsASC proteinDisease
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Use of usp33 as a drug target in the preparation of drugs
ActiveCN111748531BPromote autophagyGreat application potentialCompound screeningNervous disorderMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides the use of USP33 as a drug target in the preparation of medicines, belonging to the field of protein engineering. The present invention utilizes co-immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry techniques to discover the deubiquitinating enzyme USP33 that interacts with Parkin, and further discovers that USP33 is located in the mitochondrial outer membrane and can deubiquitinate and modify the E3 ligase Parkin. Knockdown of USP33 will promote the translocation of Parkin to mitochondria, thereby enhancing mitophagy to remove damaged mitochondria, confirming that USP33 regulates mitophagy by affecting the deubiquitination of Parkin, and knocking down USP33 can inhibit the expression of neurons under MPTP treatment. Apoptosis, USP33 can be used as a drug target to prepare drugs, and has good application potential and value.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/60405968-723f-4fe9-a2a8-eeff73c11931/HDA0002851170260000011.png)
![Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/60405968-723f-4fe9-a2a8-eeff73c11931/HDA0002851170260000021.png)
![Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/60405968-723f-4fe9-a2a8-eeff73c11931/HDA0002851170260000031.png)