Restoration method for degrading soil PCP residue through cooperation of earthworms and microbes
A technology of microbial degradation and repair method, which is applied in the repair field of earthworms and microorganisms to degrade soil PCP residues, can solve PCP residues and other problems, and achieve the effects of accelerated decomposition, accelerated elimination and detoxification, and simple and effective repair
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
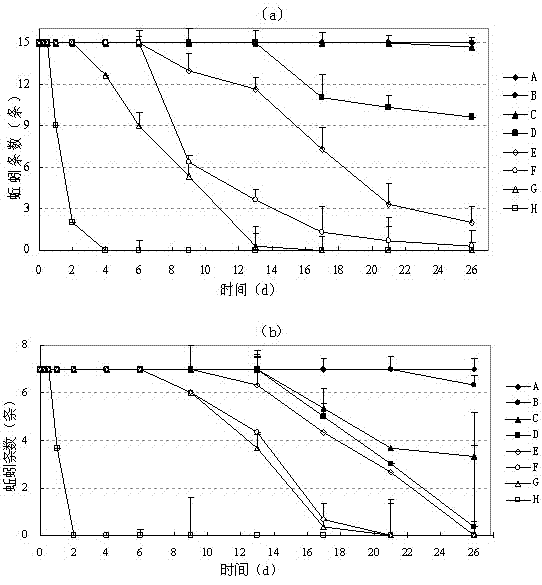
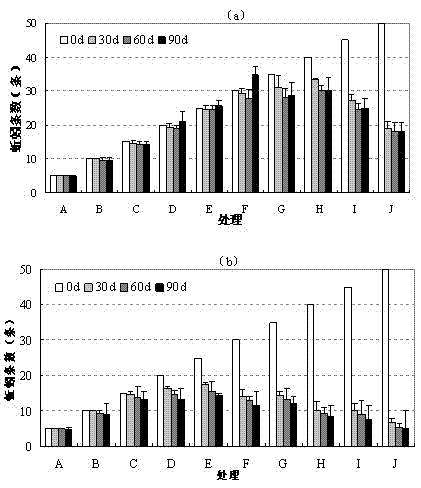
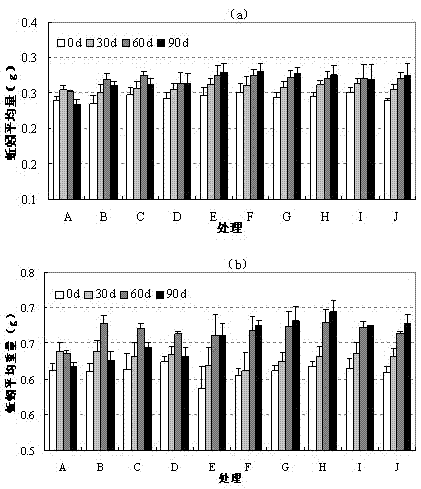
[0032] 1. Tolerance to soil PCP of P.
[0033] Experimental design The number of Eisenia chinensis was 15, and the number of Esperus grandiosa was 7. Experiments were carried out respectively. Different amounts of PCP were added to the soil without PCP, and the PCP concentration was prepared to be 0 mg·kg -1 (A), 20 mg?kg -1 (B), 40 mg?kg -1 (C), 60 mg?kg -1 (D), 80 mg?kg -1 (E), 100 mg?kg -1 (F), 150 mg?kg - 1 (G) and 200 mg·kg -1 (H) Experimental soil, replicated three times for a total of 24 treatments. The weight of the experimental soil was 0.5 kg. The soil moisture in each experiment was always maintained at 60% of the saturated moisture content. Put the experimental soil into the bucket, then put the earthworms in, wrap the mouth of the bucket with tin foil, and pierce several small holes with pins to keep the air circulation in the bucket. Cultivate under shaded conditions. The experimental design measures the biomass of two ecological types of earthworms un...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 Degradation PCP ability identification of microbial strains
[0060] Klebsiella were inoculated into enriched liquid medium for enrichment growth (150 r?min -1 Aerobic shaker culture, 30°C) for 24 h, and each strain setting was repeated three times. Take 10mL of the strain culture solution at 6000 r?min -1 Ultracentrifuge for 10 min, remove the supernatant, rinse with sterilized deionized water, and then centrifuge again, repeat this three times; finally resuspend the cleaned cells with sterilized deionized water. The concentration of the bacterial suspension was measured by the absorbance value at λ = 600 nm. Finally, take 10 mL of bacterial liquid and add it to 90 mL of inorganic salt culture solution, and add PCP at a concentration of 100 mg?L -1 , PCP concentrations in different treatments were measured at 0, 24, 48, 96, and 144 h; the PCP-containing inorganic salt culture solution without adding bacterial solution was used as the control.
[0061] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com