Method for removing lithium ion battery nickel-rich material surface lithium residues by liquid phase precipitation method
A lithium-ion battery, liquid-phase precipitation technology, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low ion diffusion coefficient, hinder lithium ion transmission, affect material rate performance, etc., achieve simple preparation process, improve comprehensive Electrochemical properties, physical properties and the effect of excellent electrochemical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
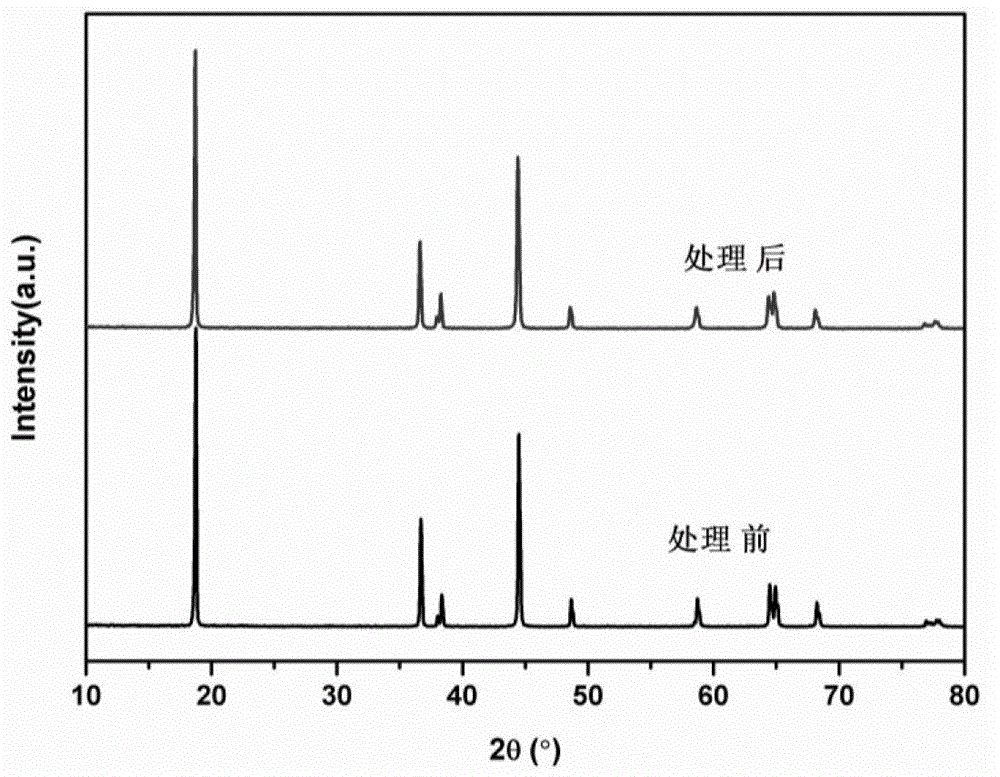
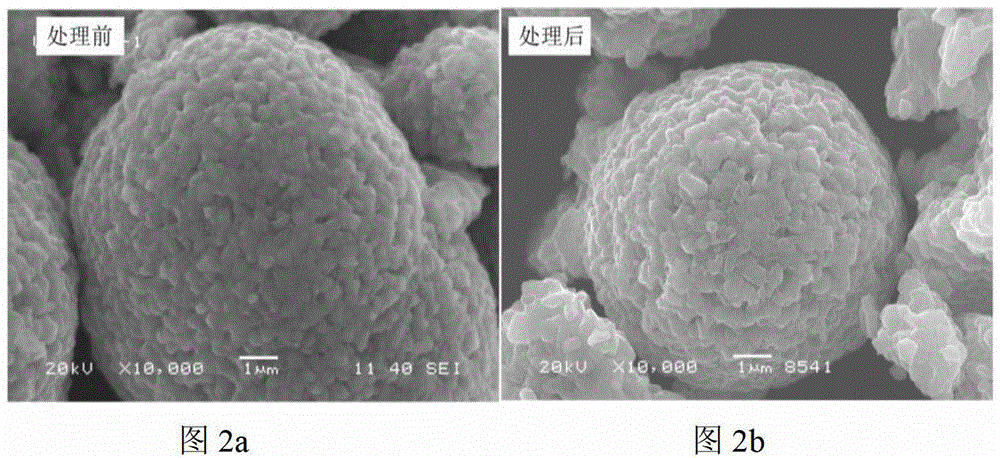
[0052] A certain amount of LiNi 0.8 co 0.2 o 2 The material was dispersed in an aqueous solution, filtered, and titrated with hydrochloric acid to roughly estimate the lithium residue content on the surface of the material. Will completely precipitate 100g LiNi 0.8 co 0.2 o 2 Required for lithium residues on the material surface (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 Dissolve in 25g deionized water, add 100g LiNi to it 0.8 co 0.2 o 2 Material. After evaporating water at 120°C, heat treatment at 800°C for 2 hours, and cooling naturally to obtain a surface coated with dense Li 3 PO 4 layer material. For its physical and chemical properties, see figure 1 , Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. XRD shows that the structure of the material does not change after the precipitation of lithium residues on the surface, and because the Li 3 PO 4 The amount is so small that Li cannot be detected 3 PO 4 Peak, SEM images show that the material morphology does not change significantly before and afte...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A certain amount of LiNi 0.8 co 0.1 mn 0.1 o 2 The material was dispersed in an aqueous solution, filtered, and sulfuric acid titration was used to roughly estimate the lithium residue content on the material surface. According to the theory, 100g LiNi is completely precipitated 0.8 co 0.1 mn 0.1 o 2 H required for lithium residues on the material surface 3 PO 4 60%, 80%, and 150% of the volume were added to 25g deionized water, and 100g LiNi was added to it respectively. 0.8 co 0.1 mn 0.1 o 2 Material. After evaporating water at 120°C, heat treatment at 500°C for 2 hours, and cooling naturally to obtain a surface coated with dense Li 3 PO 4 layer material. Take the above-mentioned materials and untreated materials respectively, beat them with a liquid-solid ratio of 10:1, let them stand for 30 minutes, and test the pH of the materials. The results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from the pH that after adding phosphoric acid, the lithium residue on ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] A certain amount of LiNi 0.85 co 0.1 Al 0.05 o 2 The material was dispersed in an aqueous solution, filtered, and titrated with hydrochloric acid to roughly estimate the lithium residue content on the surface of the material. to (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 and NH 4 h 2 PO 4 The mixture is phosphate, and theoretically 100g LiNi is completely precipitated 0.85 co 0.1 Al 0.05 o 2 Add 60%, 80% and 150% of the required amount of lithium residue on the surface of the material to 25g of deionized water, and add 100g of LiNi to it 0.85 co 0.1 Al 0.05 o 2 Material. After evaporating water at 100°C, heat treatment at 800°C for 10 hours, and cooling naturally to obtain a surface coated with dense Li 3 PO 4 layer material. Take smears of the above materials and untreated materials and assemble the battery, charge it at 0.1C to 4.3V and put it in an environment of 90°C for 7 days, then disassemble the battery, and perform XRD characterization on the pole piece (Figure 7), whi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com