Method for detecting content of free tryptophan in tryptophan and serum sample
A detection method, tryptophan technology, applied in the field of detection of free tryptophan content, can solve the problems of biological small molecule probes, irreversible recognition process, unfavorable detection application, etc., to achieve easy large-scale preparation, real-time on-site detection , synthesize simple effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1 (synthesis of probe material)
[0038] Add 4,4',4''-triphenylamine hydrazide (0.76 g, 1.8 mmol) and salicylaldehyde (0.80 g, 6.6 mmol) to the methanol solution, and add 5 drops of glacial acetic acid as a catalyst. Reflux under stirring for 24 hours, filter and dry to obtain 1.06 g of yellow solid, yield: 80.0%. 1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO- d 6 , ppm ): δ 12.10 (s, 3H, H -NH- ), 11.33 (s, 3H, H -OH ), 8.65 (s, 3H, H -CH=N ), 7.97 (d, 6H, J = 7.5Hz, H Ar ), 7.55 (d, 3H, J = 7.2 Hz, H Ar ), 7.31 (s, 3H, H Ar ), 7.24 (m, 6H, H Ar ), 6.93 (m, 6H, H Ar ). 13 C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO- d 6 , ppm ): δ 162.1 ( C -C=O ), 157.5 ( C -OH ), 149.2 (C Ar ), 148.2 ( C -CH=N ), 131.3 ( C Ar ), 129.6 ( C Ar ), 129.5 ( C Ar ), 127.8 ( C Ar ), 123.7 ( C Ar ), 119.3 ( C Ar ), 118.7 ( C Ar ), 116.4 ( C Ar ). Anal. Calc. for C 42 h 33 N 7 o 6 : H 4.55, C 68.94, N 13.40. Found: H 4.68, C 68.51, N 13.12.
Embodiment 2
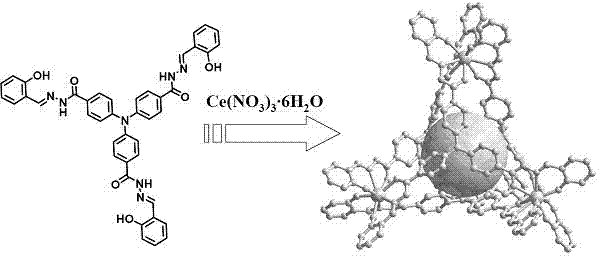
[0039] Example 2 (synthesis of metal-organic tetrahedron as probe material)
[0040] Ce(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O (44.2 mg, 0.15 mmol) and the material of Example 1 (73.0 mg, 0.10 mmol) were dissolved in DMF, stirred for 2 hours, filtered, and diffused with methanol to obtain black crystals, which were filtered and dried with a yield of 65%. 1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO- d 6 , ppm ): δ 13.17 (s, 8H, H -NH- ), 8.61 (s, 12H, H -CH=N ), 8.09 (s, 12H, 5 ), 7.41–7.18 (m, 48H, H Ar ), 6.56 (s, 24H, H Ar ), 5.66 (s, 12H, H Ar ). 13 C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO- d 6 , ppm ): δ 166.8 ( C -C=O ), 157.4 ( C -OH ), 152.5 ( C Ar ), 132.6 ( C -CH=N ), 129.5 ( C Ar ), 129.3 ( C Ar ), 124.0 ( C Ar ), 123.3 ( C Ar ), 122.9 ( C Ar ), 119.4 ( C Ar ), 117.2 ( C Ar ), 116.6 ( C Ar ). Anal. Calc. for Ce 4 (C 42 h 29 N 7 o 6 )4: H 3.37, C 58.13, N 11.30; Found: H 3.85, C 57.35, N 11.26. ESI-MS: m / z: 1155.7824[Ce 4 (HTTS) 3 (H 2 TTS)] 3- ,1734.1365[Ce 4 (HTTS) 2 (H 2...
Embodiment 3
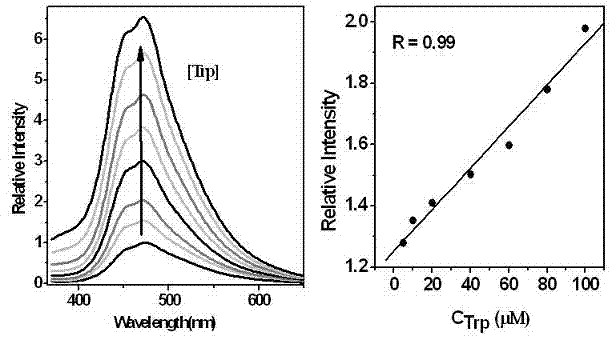
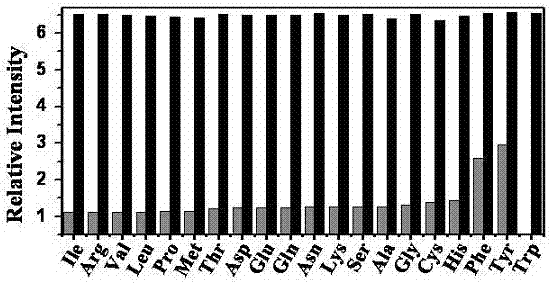
[0041] Embodiment 3 (fluorescence intensity and concentration intensity working curve)
[0042] Weigh the probe material and prepare 15 100 ml DMF / H of M 2 O=9 / 1 standard probe solution, then configure 2.0×10 -2 M tryptophan DMF / H 2 O=1 / 1 solution. Measure 2 ml of the standard probe solution, add the calculated amount of tryptophan solution, and prepare the standard test solution. Excited at 350 nm, the fluorescence emission spectrum was measured, and then the addition of tryptophan was taken as the abscissa, and the relative fluorescence intensity was taken as the ordinate to obtain a standard curve. The test results are as follows figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com