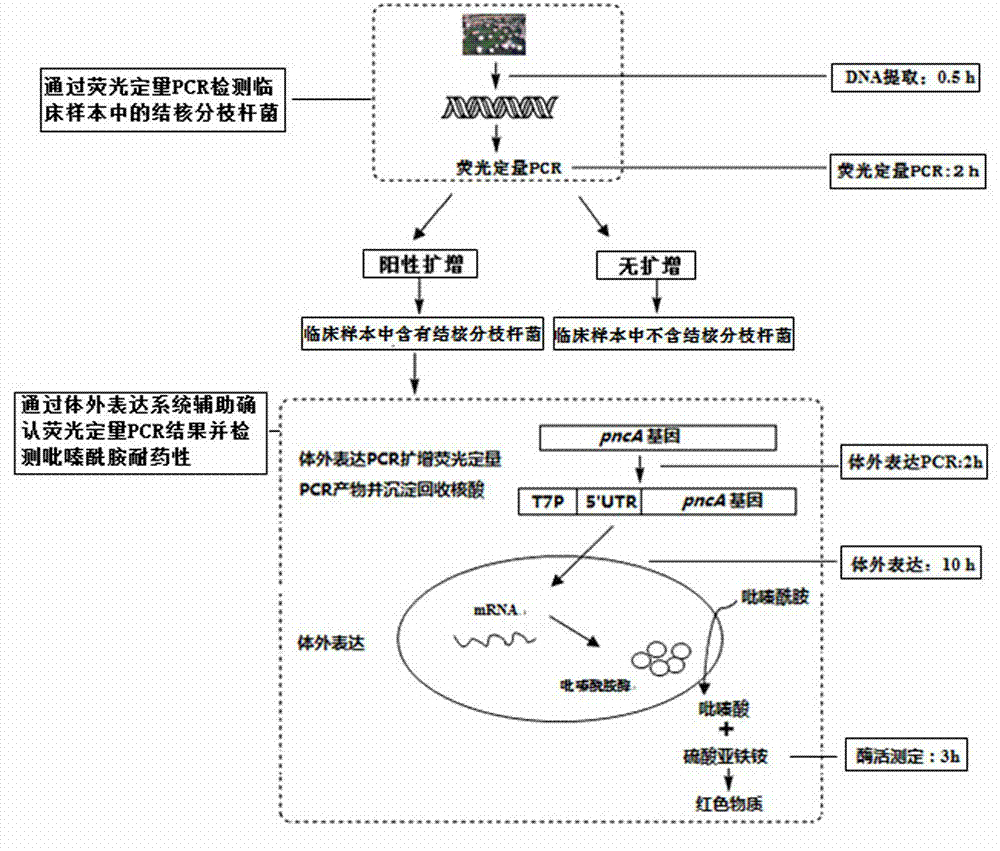
Joint detection method for drug resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis and pyrazinamide in clinical sample
A technology of mycobacterium tuberculosis and pyrazinamide, which is applied in the biological field to achieve the effects of improving sensitivity, short detection time, and shortening time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
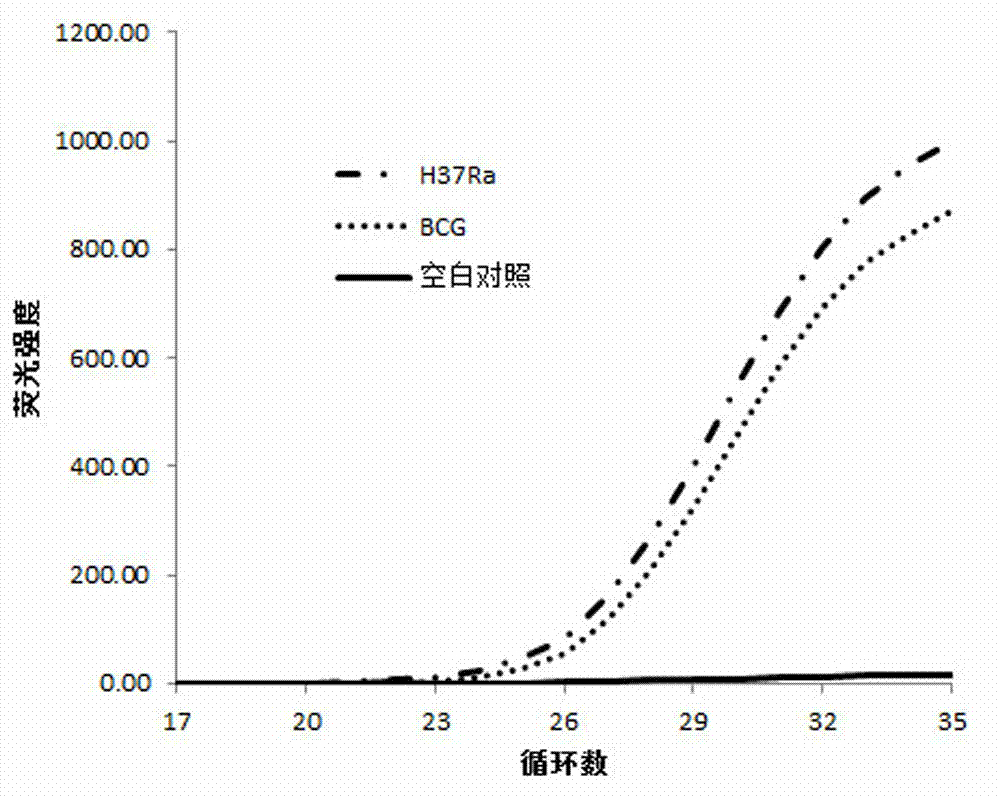
[0046] Mycobacterium tuberculosis standard strain M. tuberculosis H37Ra (American Culture Collection Number: ATCC 25177) was used as a pyrazinamide-resistant control, and the standard pyrazinamide-resistant strain BCG (American Culture Collection Number: ATCC 19274) was used as a pyrazinamide-resistant control. The measurement results of these two cultured tuberculosis strains are used to establish a fluorescent quantitative PCR standard curve for judging whether the actual sample contains Mycobacterium tuberculosis and to test whether the method can distinguish standard pyrazinamide drug-resistant strains from sensitive strains.
[0047] Specific steps are as follows:
[0048] 1. Lysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and DNA extraction:
[0049] (1) From the cultured standard strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis M. tuberculosis On the L-J medium of H37Ra and BCG, scrape a ring of bacteria with an inoculation loop, dissolve in 2 mL NaOH solution, mix well, and incubate at ...
Embodiment 2
[0078] In this embodiment, 3 clinical sputum (No. 218, 271, and No. 8333) collected from Wuhan Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Center as test samples are used as test samples to test whether this method can be used for the classification of tuberculosis in clinical sputum. The detection of mycobacteria and the detection of pyrazinamide resistance were initially verified. Specific steps are as follows:
[0079] 1. Cracking and extracting the DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum;
[0080] (1) Add 2 mL of NaOH solution to a certain amount of sputum (1-5 mL), mix well, and incubate at 37°C for 20 minutes.
[0081] (2) Centrifuge for 10 min, remove the supernatant and retain the precipitate. Wash with PBS, repeat the wash 2 times, remove the supernatant and save the precipitate for detection.
[0082] (3) DNA extraction: Add DNA extraction solution and purified water to the above-mentioned processed specimens. Boiling water bath for 10 min, and then directly use the ...
Embodiment 3
[0103] In the step of pyrazinamide resistance detection, it is necessary to add in vitro expression elements, such as T7 promoter, expression enhancer, etc., to the fluorescent quantitative PCR product. The present embodiment uses pyrazinamide sensitive strain Mycobacterium tuberculosis standard strain M. tuberculosis H37Ra (American Culture Collection Number: ATCC 25177) was used as a pyrazinamide-resistant control, and the standard pyrazinamide-resistant strain BCG (American Culture Collection Number: ATCC 19274) was used as a pyrazinamide-resistant control. The strains were used for in vitro expression PCR with and without primers of an expression enhancer 5' UTR. Then it was added to the wheat germ cell-free expression system to study whether the expression enhancer in the primer would affect the determination of pyrazinamide resistance.
[0104] Specific steps are as follows:
[0105] 1. adopt the same method as in Example 1 to lyse Mycobacterium tuberculosis standard...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com