Method for preparing carbon/zinc oxide super-hydrophobic ceramic by sintering plant leaves
A technology of plant leaves and zinc oxide, which is applied in the field of preparing carbon/zinc oxide superhydrophobic ceramics, can solve the problems such as difficulty in obtaining ceramic superhydrophobic materials, and achieve the effect of excellent superhydrophobic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
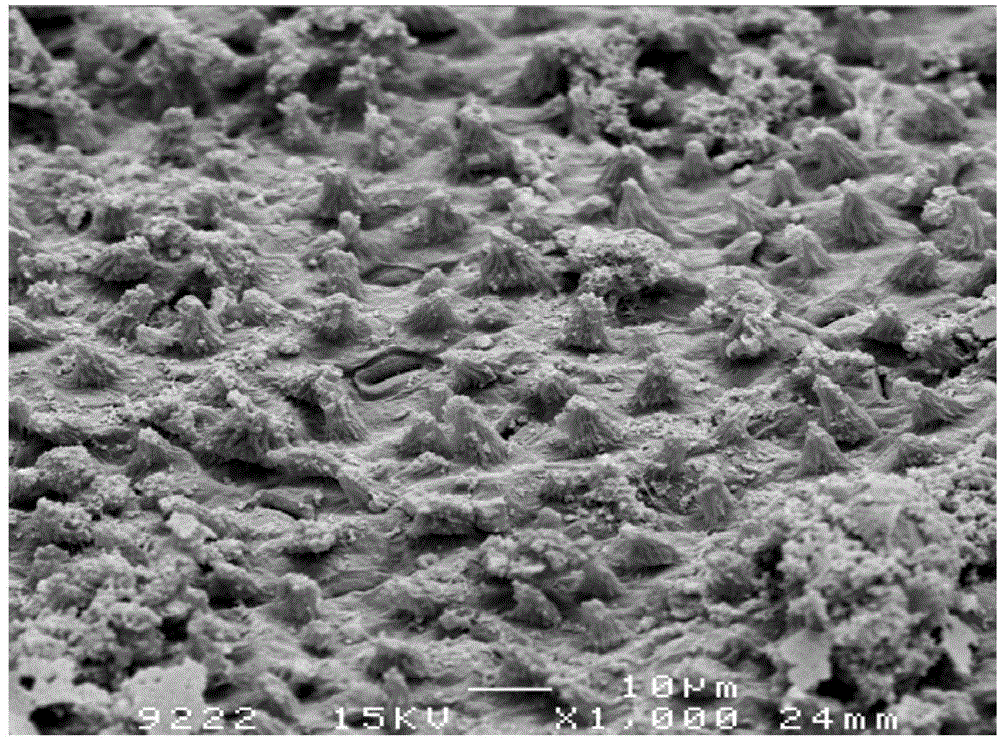
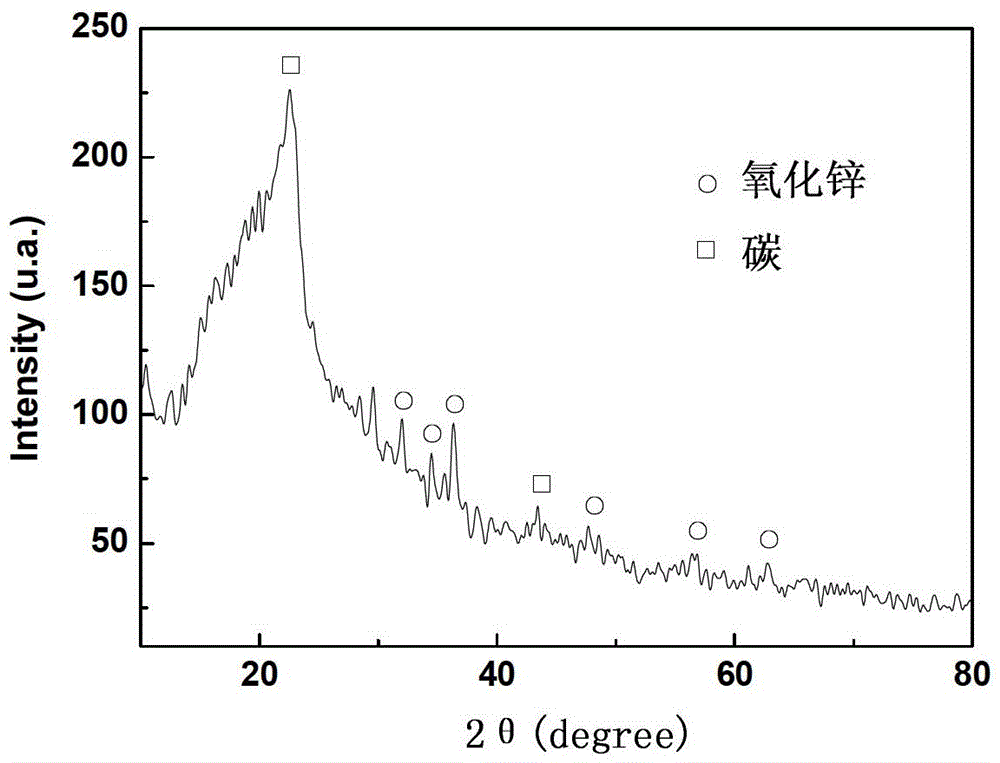
[0034] The lotus leaves were baked and dried in an oven at 100 °C for 48 hours, then heated to 200 °C at a rate of 2 °C / min in an argon atmosphere furnace, and then heated to 800 °C at a rate of 1 °C / min. A carbon ceramic with a lotus leaf microstructure is obtained; the carbon ceramic is then treated with a concentration of 1% Zn(NO 3 ) 2 Immerse in the solution for 2 minutes; take out the impregnated carbon ceramics and dry them; sinter the dried carbon ceramics in an argon atmosphere furnace at a heating rate of 3 °C / min to 150 °C to obtain a carbon with a lotus leaf microstructure. / Zinc oxide ceramics; figure 1 Shown is the X-ray diffraction pattern of the prepared ceramic, from the diffraction peaks it can be seen that the material contains carbon and zinc oxide. figure 2Shown is the scanning electron microscope photo of the microstructure of the prepared carbon / zinc oxide ceramic. It can be seen that the microstructure of the micro-nano protrusions on the surface of...
Embodiment 2
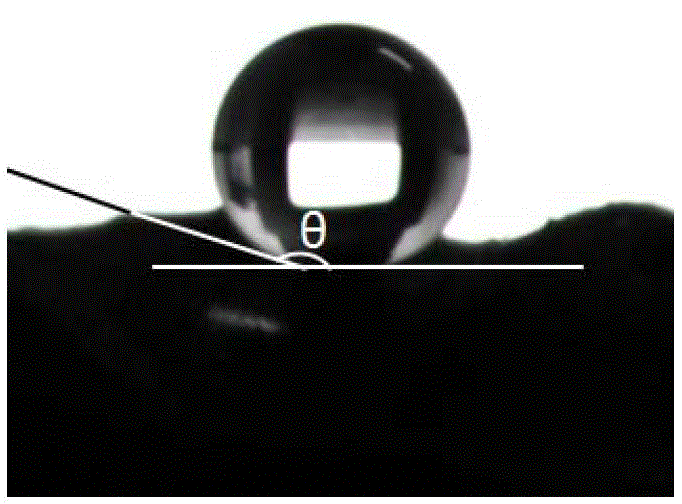
[0036] Put the zong leaves in an oven at 120 ℃ and dry them for 24 hours, then place them in a nitrogen atmosphere furnace and heat them up to 600 ℃ at a rate of 2 ℃ / min to prepare carbon ceramics with the microstructure of zong leaves; Carbon ceramics with a concentration of 3% Zn(NO 3 ) 2 Immerse in the solution for 5 minutes; take out the impregnated carbon ceramics and dry them; put the dried carbon ceramics in a nitrogen atmosphere furnace and sinter to 400 °C at a heating rate of 3 °C / min to obtain carbon with the microscopic structure of zong leaves. / zinc oxide ceramics; carbon / zinc oxide ceramics are soaked in 15% fluorosilane isopropanol solution by volume ratio for 10 days and then taken out to dry to obtain carbon / zinc oxide superhydrophobic ceramics with the microscopic structure of Zongye. Figure 4 Shown is the contact angle of the prepared carbon / zinc oxide superhydrophobic ceramics with water, θ 接触角 =162°, reaching superhydrophobicity.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The rice leaves were baked and dried in an oven at 70 °C for 72 hours, then placed in an argon atmosphere furnace and heated to 500 °C at a heating rate of 1 °C / min to obtain carbon ceramics with the microstructure of rice leaves; The carbon ceramics in the concentration of 5% Zn(NO 3 ) 2 Immerse in the solution for 3 minutes; take out the impregnated carbon ceramics and dry them; put the dried plant leaves in an argon atmosphere furnace and sinter them to 650°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min to obtain carbon ceramics with the microscopic structure of rice leaves. / zinc oxide ceramics; carbon / zinc oxide ceramics are soaked in a fluorosilane isopropanol solution with a volume ratio concentration of 10% for 7 days and then taken out to dry to obtain carbon / zinc oxide superhydrophobic ceramics with the microscopic structure of rice leaves. Figure 5 Shown is the contact angle of the prepared carbon / zinc oxide superhydrophobic ceramics with water, θ 接触角 =160°, reaching sup...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com