Patents
Literature
59 results about "Sinter Plant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sinter plants agglomerate iron ore fines (dust) with other fine materials at high temperature, to create a product that can be used in a blast furnace. The final product, a sinter, is a small, irregular nodule of iron mixed with small amounts of other minerals. The process, called sintering, causes the constituent materials to fuse to make a single porous mass with little change in the chemical properties of the ingredients. The purpose of sinter are to be used converting iron into steel.
Cold bonded pellet and method of producing the same
The invention provides a cold-bonded pellet used on the raw material of steelmaking or ironmaking and a preparation method thereof. The component and the mass ratio of the cold-bonded pellet are as follows: 8 to 60 percent of precipitator dust and dust sludge, 20 to 85 percent of iron sheet, concentrate powder and iron-bearing auxiliary material, 0.4 to 15 percent of binder. In the preparation method, the moisture in raw material is utilized to directly mix the raw material with other components in a mixer, then the mixture is pressed and formed via a briquetting press after uniform mixing, and the pellet after forming is maintained at room temperature and dried naturally. The cold-bonded pellet of the invention has the advantages of the simple forming process, the low fabrication cost, the rapid hardening of pellet and taking the short time, the high compressive strength, achieving not only the waste recycling and reducing the environmental pollution, but also the high granulation rate, the low damage rate, the wide applicability and the stable quality. The invention is especially suitable for wide application in sintering plant, ironmaking plant and steelmaking plant.
Owner:尚国洪
Sintering energy-saving technique and system capable of removing multiple pollutants
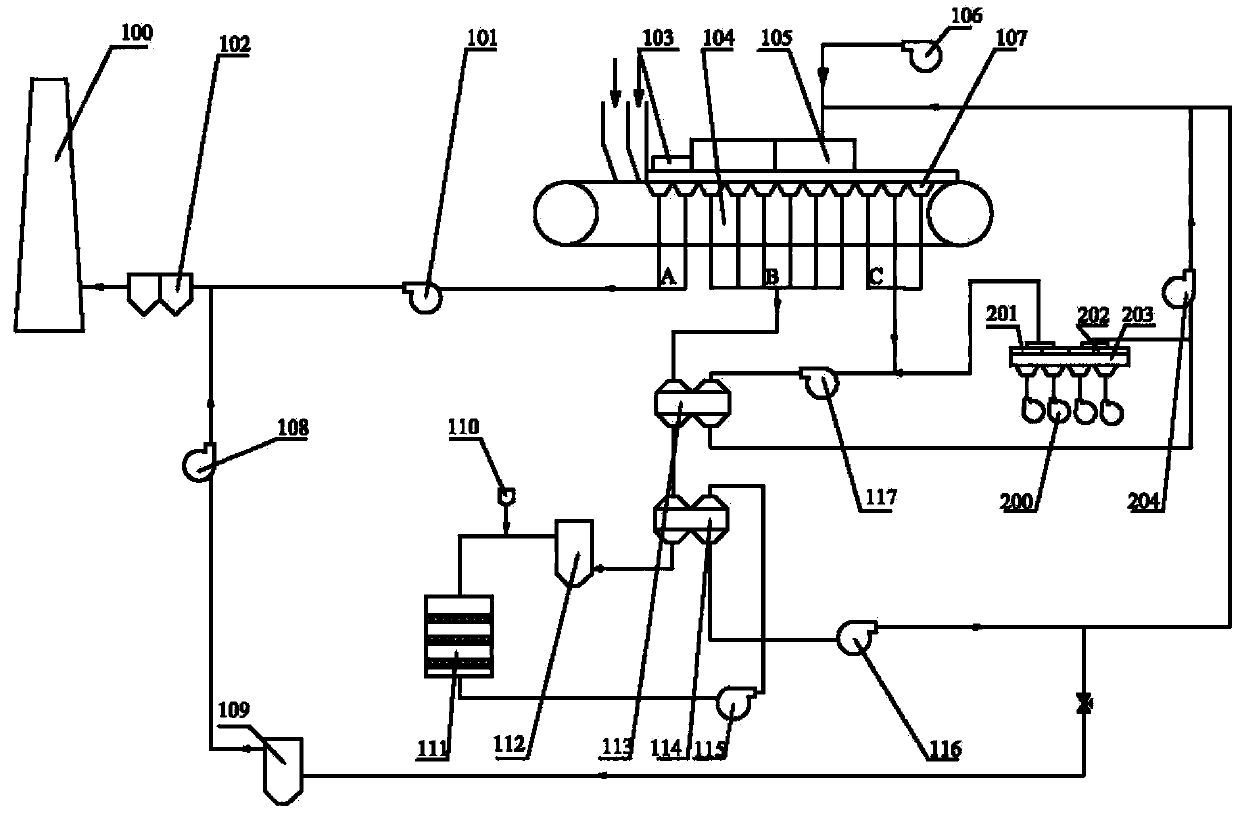
InactiveCN104195326ACompact structureOptimize layoutDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementSinter PlantMulti pollutant
The invention discloses a sintering energy-saving technique capable of removing multiple pollutants. Flue gas discharged by a sintering wind box on the lower part of a sintering machine is sequentially divided into section A flue gas positioned at the head of the sintering machine, section B flue gas positioned in the middle of the sintering machine, and section C flue gas positioned at the tail of the sintering machine; the section A flue gas is discharged after being subjected to dust removal treatment; and the section C flue gas is used for preheating the section B flue gas, the preheated section B flue gas is denitrified and divided into two parts, one part is discharged after being subjected to desulfurization treatment, and the other part is sent into the sintering machine together with the section C flue gas to perform circulating sintering. The invention also discloses a sintering energy-saving system capable of removing multiple pollutants. The technique and system can treat dust, oxynitrides, sulfur dioxide, fluorides, heavy metals and many other pollutants in the sintering flue gas, can utilize the excess heat of the flue gas of the main flue of the sintering machine and the flue gas discharged by the cooling machine, and can lower the energy consumption of the sintering plant, thereby implementing energy saving and emission reduction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
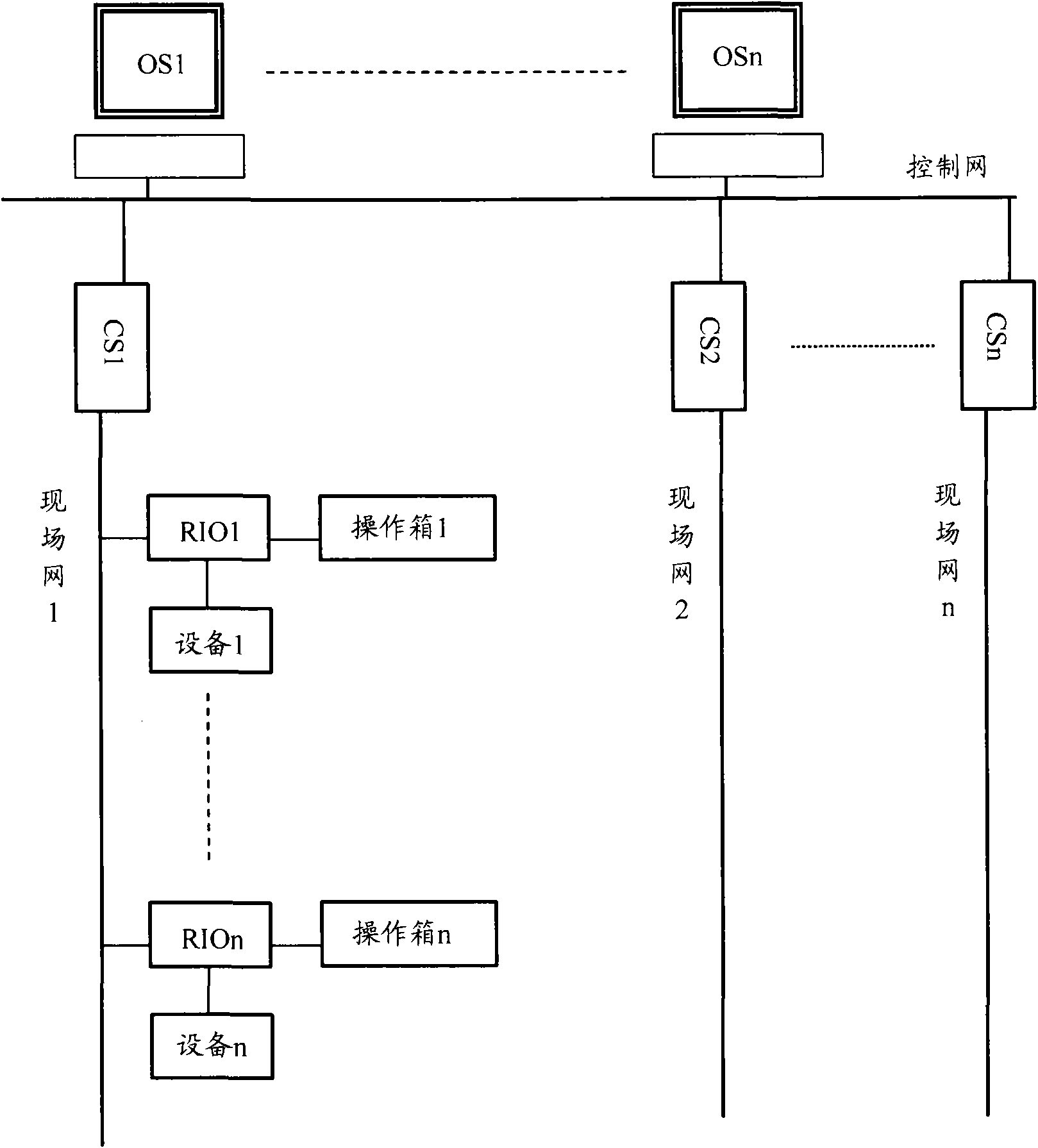
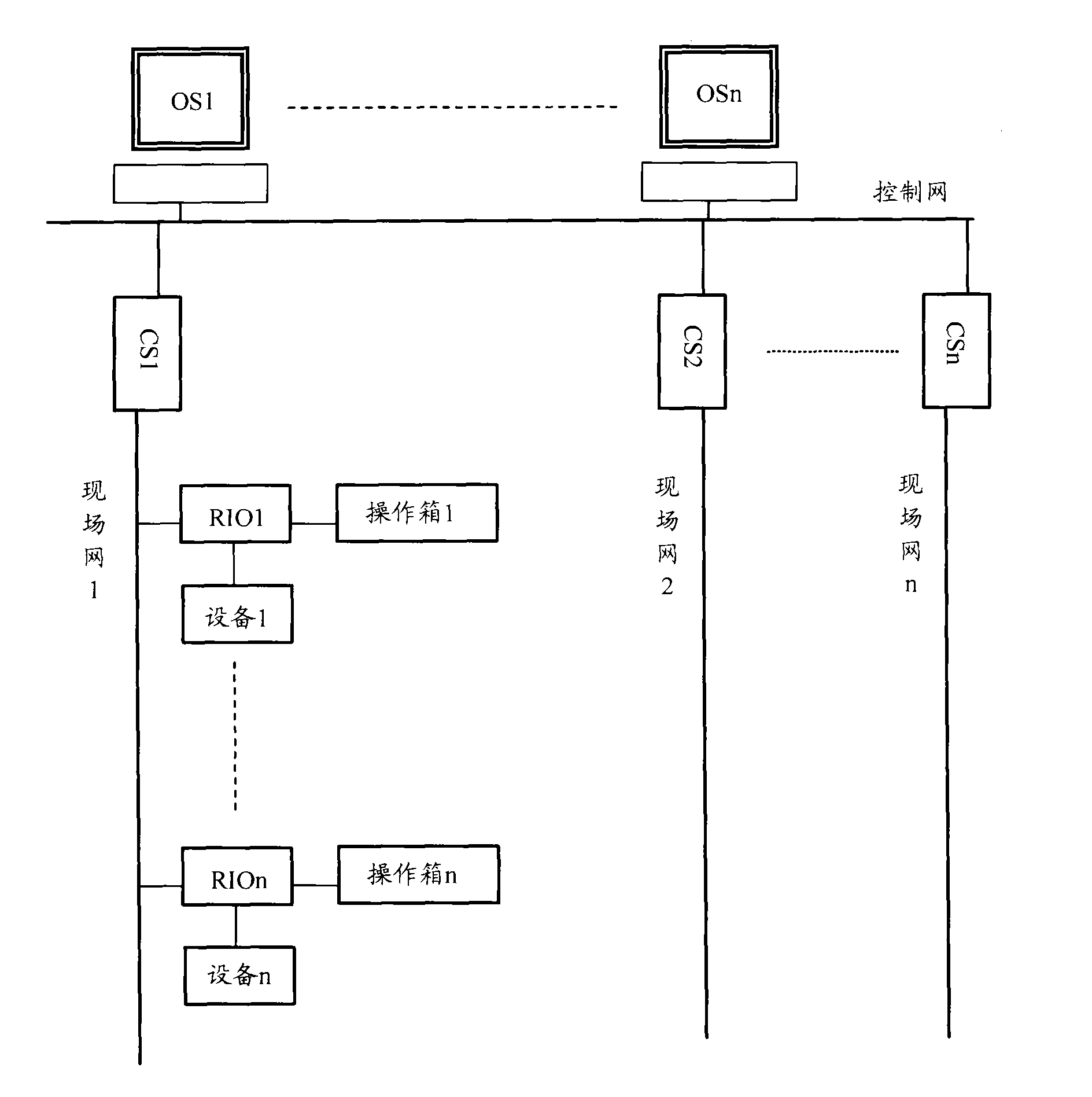
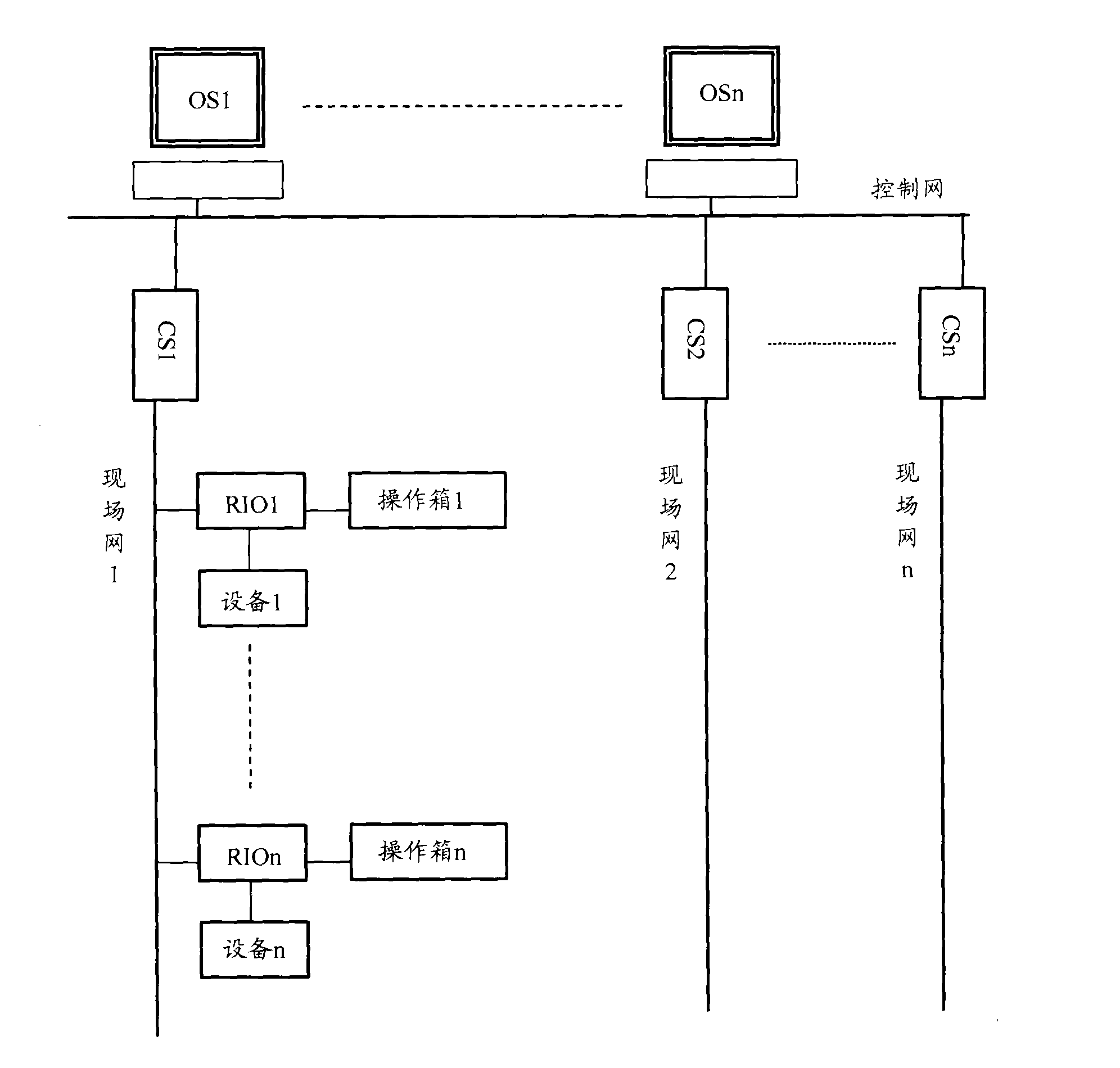
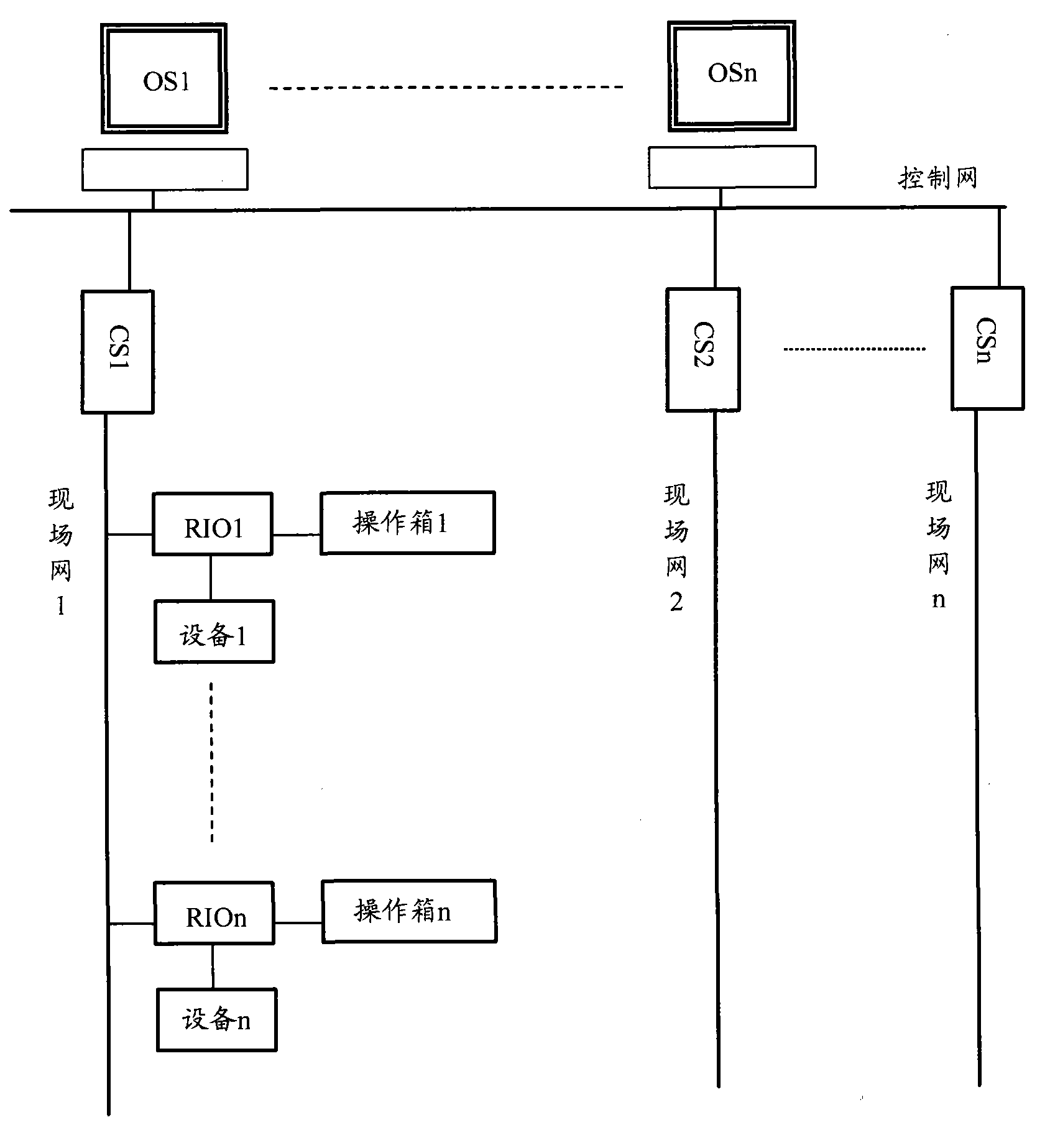
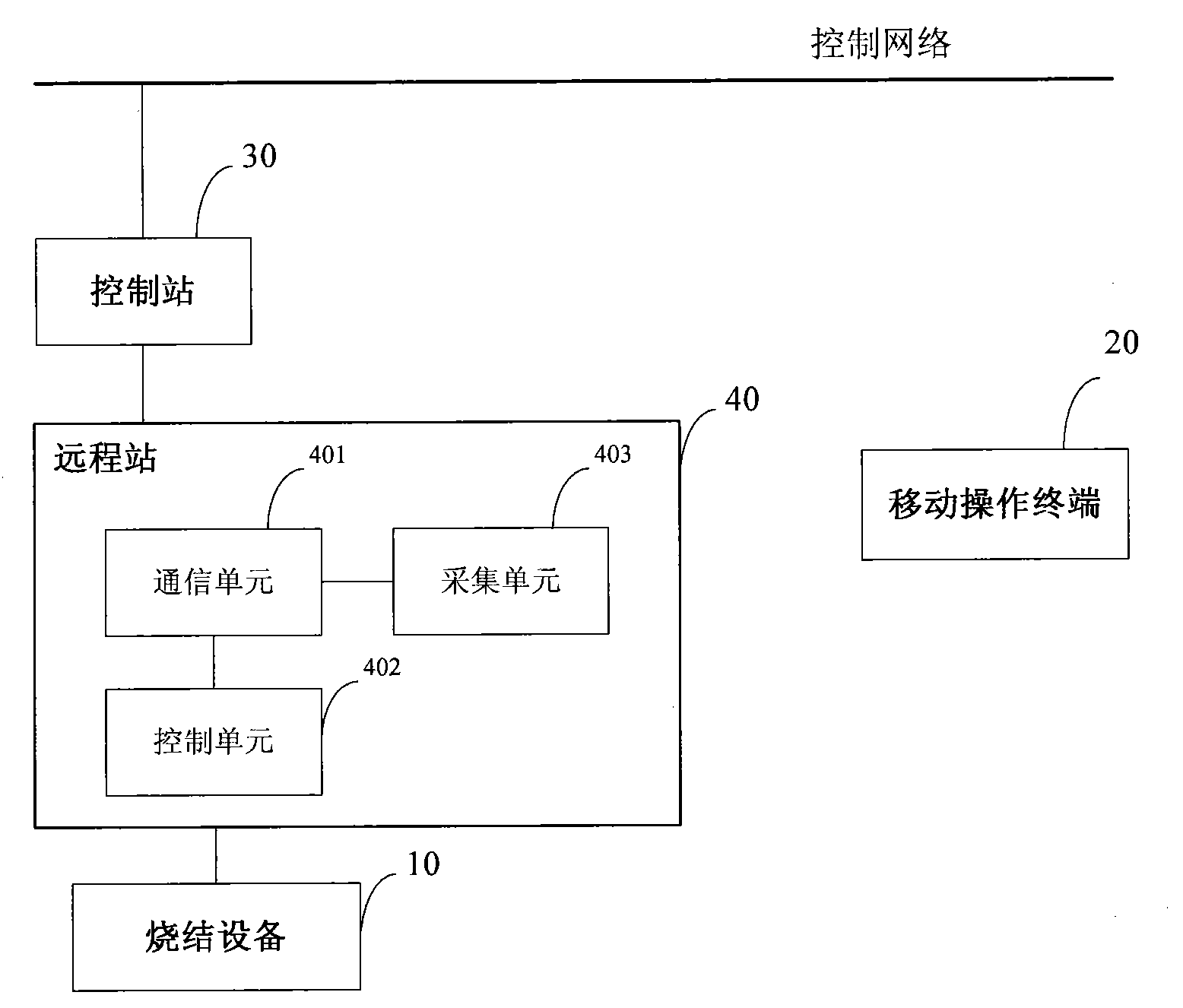
Sintering plant control system
ActiveCN102063097AAvoid misuseLow failure rateTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlSinter PlantControl system
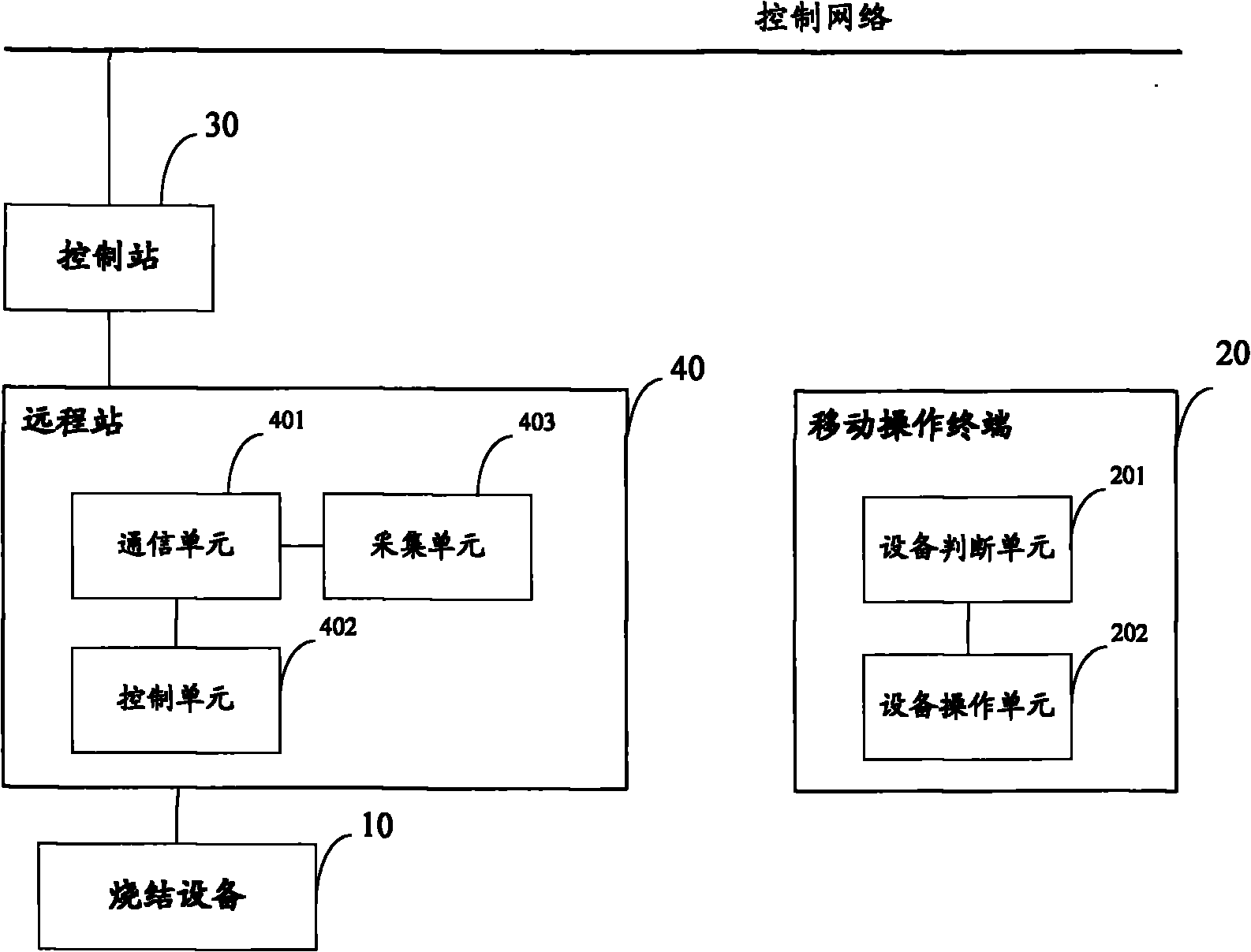
The invention discloses a sintering plant control system which comprises equipment, a control network, a mobile operation terminal, a control station and a remote station, wherein the mobile operation terminal acquires detailed information of the equipment, displays the detailed information of the equipment to the operating personnel, and receives the judgment result on whether the equipment is to be operated, which is returned by the operating personnel; if the equipment is to be operated, the mobile operation terminal generates an operation request signal according to an equipment operation instruction received from the operating personnel, converts the operation request signal into a radio signal, and transmits the radio signal to the remote station; and the remote station receives and transmits a radio signal with a specific frequency, receives a radio signal for operating the equipment, which is transmitted by the mobile operation terminal, converts the radio signal into the operation request signal, retransmits the operation request signal to the control station, and receives the equipment operation instruction returned by the control station so as to operate the equipment. The system provided by the invention can help the operating personnel to operate the field equipment more accurately.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
Low-temperature high-activity flue gas denitrification catalyst and preparation thereof
ActiveCN104941630ALow denitrification catalytic efficiencyHigh denitrification catalytic efficiency of flue gas at low temperature (90-120°C)Dispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRare-earth elementSinter Plant
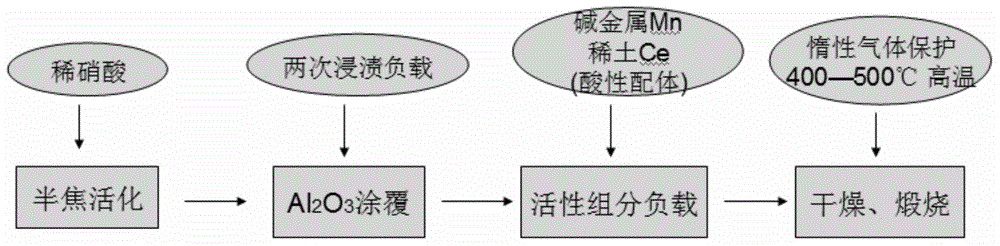
The invention relates to a low-temperature high-activity flue gas denitrification catalyst and preparation thereof. According to the catalyst, a carbon-base material serves as a carrier and carries one or more metal active components of active Al2O3, Mn, Cu and Fe and one or two of rare earth active components of Ce and La. The content of the carbon-base carrier ranges from 35% to 65%, the carrying content of the Al2O3 ranges from 2% to 5% by the content of the aluminum element, the content of the metal active components ranges from 13% to 26% by the content of the metal elements, and the carrying content of the rare earth active components ranges from 20% to 39% by the content of the rare earth elements. According to the catalyst, the carbon-base material is activated through dilute nitric acid and then is coated with aluminum oxide sol, the metal active components and the rare earth active components are carried, then drying and sintering are carried out in the inert atmosphere, and the catalyst is obtained. The catalyst high in flue gas denitrification catalytic efficiently at the low temperature (90-120 DEG C) and not likely to cause poisoning and failures is obtained. The catalyst is low in production cost, simple in production technology and especially suitable for thermal power plants, steel plants, sintering plants and other enterprises with heavy fuel gas emission.
Owner:北京大学包头创新研究院
In-situ synthetic method for WC-Co hard alloy
The present invention belongs to the field of reaction sintering technology. The in-situ synthesis process of hard WC-Co alloy includes the following steps: ball milling the mixture of WO3 in 78-80 wt%, Co3O4 in 5-8 wt% and carbon black in 13-15 wt% with absolute ethanol as protecting medium; stoving and 120 mesh sieving; setting the mixture powder inside mold and sintering in discharging plasma sintering plant; vacuum pumping to 3-4 Pa, applying pressure of 10-15 MPa, raising temperature in 100-120 deg.c / min to 1000-1100 deg.c, maintaining the temperature, raising vacuum degree while increasing the pressure to 30-50 MPa, restoring vacuum degree to 3-4 Pa, raising the temperature in 70-80 deg.c / min to 1200-1300 deg.c, and maintaining for 2-3 before lowering temperature. The process is simple, low in power consumption and low in cost and has hard alloy product with the same structure and component as that obtained in traditional method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Sinter grading charging method
InactiveCN102321798AControl particle size segregationImprove breathabilitySinter PlantMaterial distribution
The invention discloses a sinter grading charging method, which comprises the following steps: dividing incoming materials from sintering plants into at least two grades of sintering materials by a grading sieve according to the particle size D; allowing the graded sintering materials to enter respectively into corresponding ore grooves, delivering the graded sintering materials into a blast furnace through the ore grooves, wherein the particle size of primary sintering materials is larger than the particle size of secondary sintering materials; radially distributing the primary sintering materials and the secondary sintering materials entering the blast furnace in the hearth; allowing the secondary sintering materials to be distributed at the radial periphery of the primary sintering materials. The invention effectively controls the particle size segregation during the charging process, improves the permeability of the material layer, reasonably controls the distribution of coal gas, allows the adjustment of furnace top material distribution to be more flexible, facilitates the realization of large batch, alleviates the contradiction of sinter supply shortage and large particle size fluctuation, greatly increases the utilization rate of coal gas, increases the yield, reduces the coke rate and fuel consumption, and creates favorable conditions for the stable operation of blast furnaces.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Blast furnace material loading process for realizing 3-grade or 4-grade charging of sinter ore
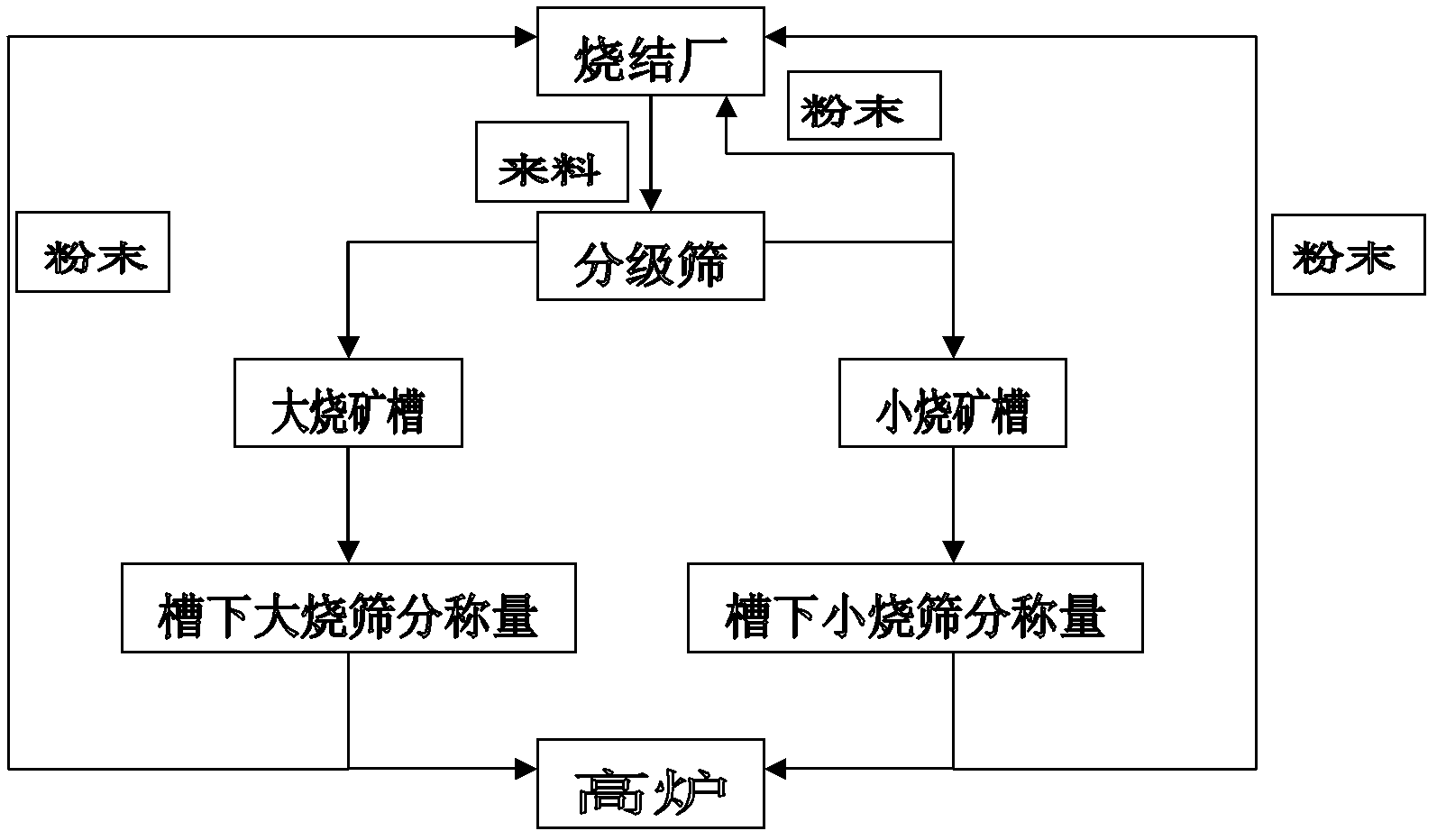
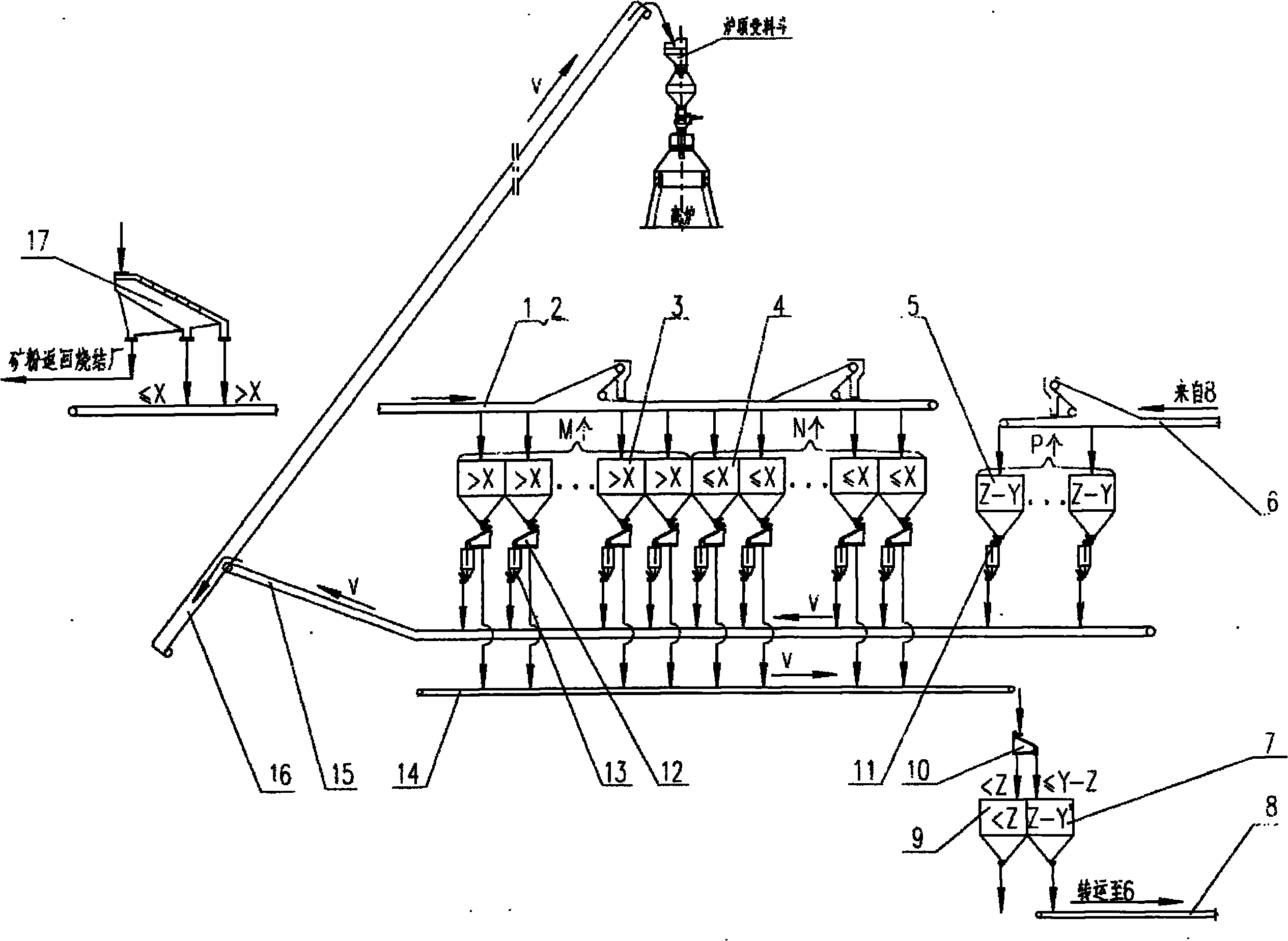
The invention discloses a blast furnace material loading process for realizing 3-grade or 4-grade charging of a sinter ore, belonging to the technical field of blast-furnace iron making. The sinter ore is divided into two stages in grading by a segmentation grading manner. The first stage is the supplied material pregrading in an ore-sintering plant; and the second stage is refining grading in a blast furnace groove, thus realizing the 3-grade or 4-grade charging of the sinter ore. The process comprises the following steps: setting the charging grades as follows: I grade, II grade, III grade or IV grade, wherein, a grain size boundary between the I grade and the II grade is X, X is more than or equal to 15 and is less than or equal to 30; a grain size boundary between the II grade and the III grade is Y, wherein, Y is more than or equal to 5 and is less than or equal to 15; a III-grade minimum boundary grain size is Z, wherein, Z is more than or equal to 0 and is less than or equal to 5 or I-grade and a II-grade grain size boundary is X, wherein, X is more than or equal to 15 and is less than or equal to 30; a grain size boundary between the II grade and the III grade is Y, wherein, Y is more than or equal to 5 and is less than or equal to 15; a grain size boundary between the III grade and IV grade is W, wherein, W is more than or equal to 0 and is less than or equal to 8; and the IV-grade minimum boundary grain size is Z, wherein, Z is more than or equal to 0 and is less than or equal to 5; performing the first stage of pregrading the supplied material in the ore-sintering plant; and performing the second stage of refining grading in the blast furnace groove.
Owner:BEIJING SHOUGANG INT ENG TECH
Preparation method of high heat-resisting cover glue for conveying materials
ActiveCN101921435AExtended service lifeMeet the harsh environment with high temperatureCross-linkPolymer science
The invention relates to a preparation method of high heat-resisting cover glue for conveying materials, comprising the following processing steps of: (1) mixing: mixing thylene propylene rubber A with thylene propylene rubber B in an internal mixer; then adding zinc oxide, magnesium oxide, antiager RD and antiager MB, then adding carbon black and paraffin oil for mixing, and discharging the glue; (2) placing the glue obtained from the glue discharging process at the room temperature for 10-12h and then performing two-section mixing, in the first-section mixing, charging the glue into the internal mixer to obtain mixed glue, and in the section-section mixing, adding zinc oxide, a vulcanizing agent and a cross-linking agent and then mixing for 80-90s at a temperature of 90-100 DEG C; and discharging the glue; and (3) extruding pieces: extruding the glues discharged from the two-section mixing process into pieces on an extruder to obtain the high heat-resisting cover glue. The invention prolongs the service life of a conveyer belt and can be adaptive to the serious environment of high temperature in sintering plants of steel mills together with the adhesive force and burn-resisting capability of steel mesh glue.
Owner:WUXI BOTON CONVEYOR SOLUTION CO LTD
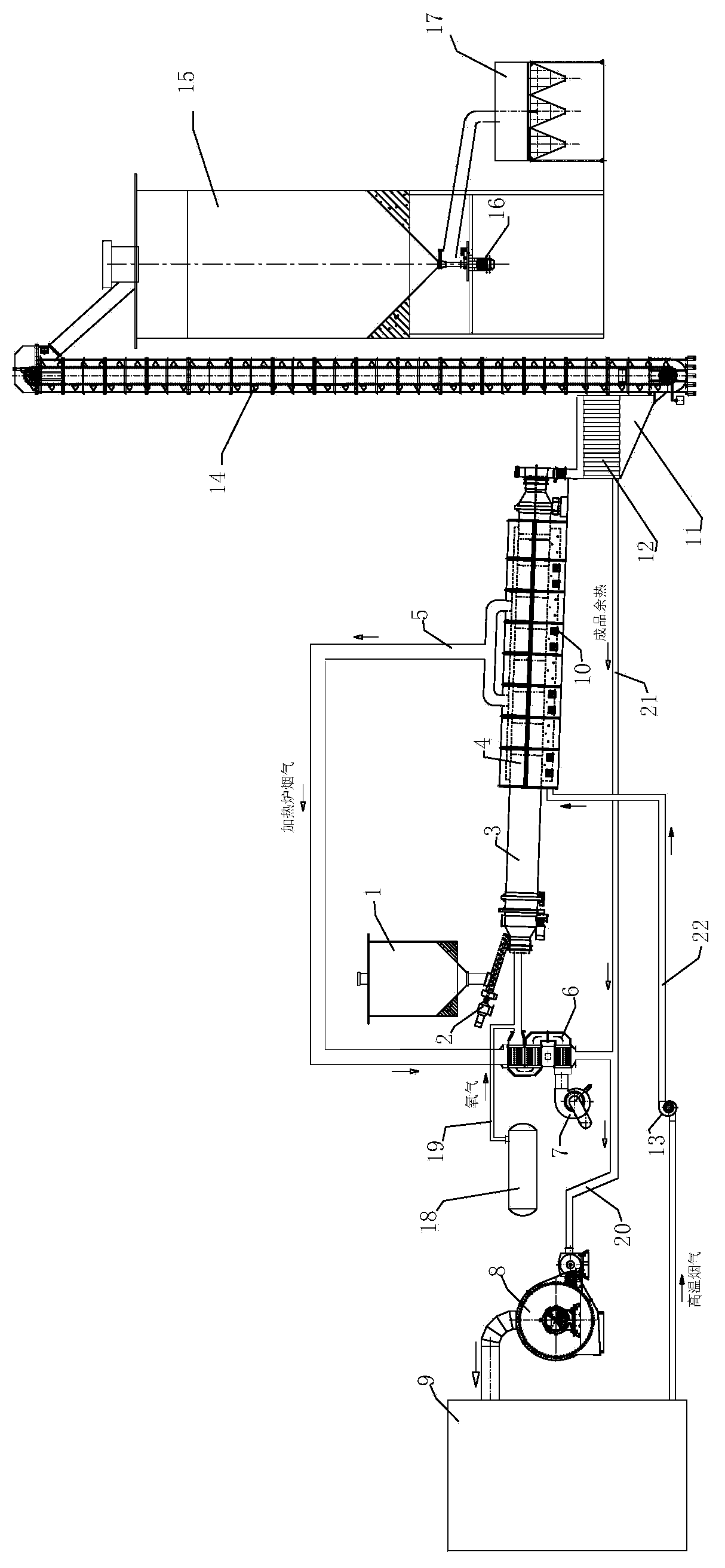
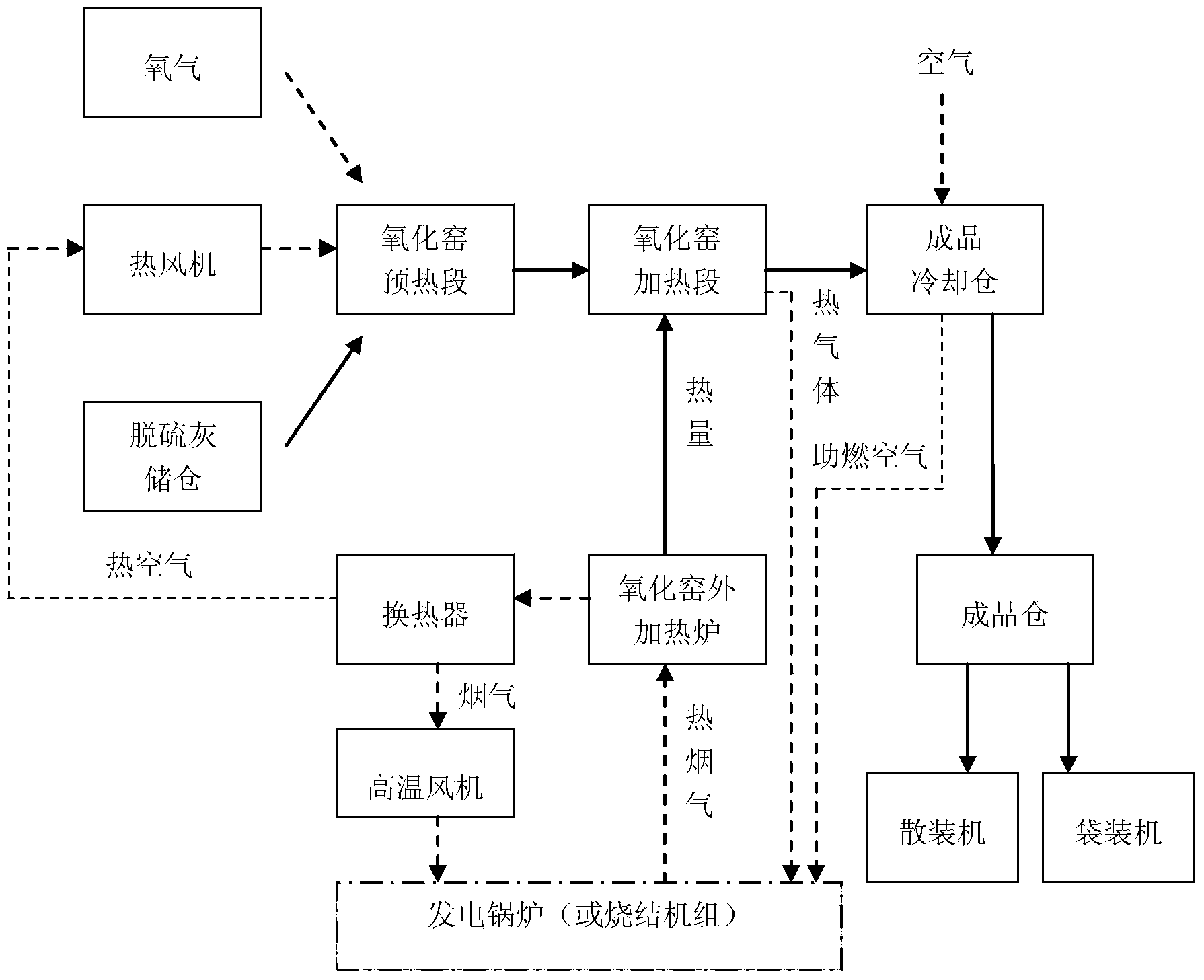
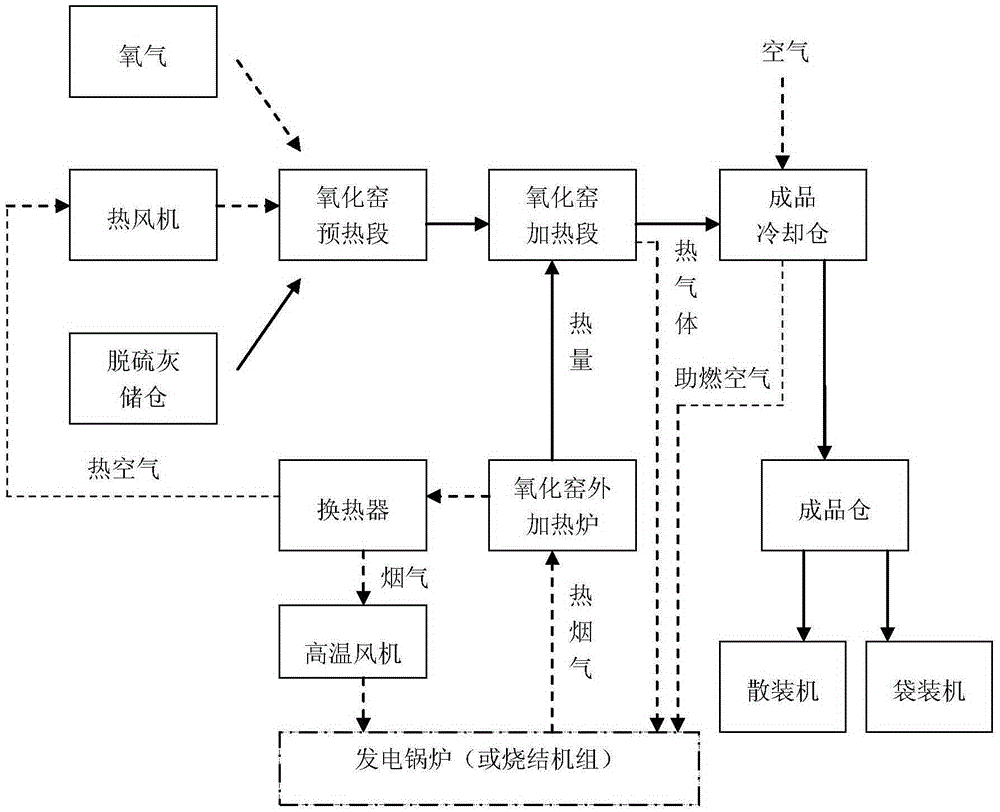
Process for on-line heating and oxidation of desulfurized fly ash by virtue of flue gas from power generating boiler or sintering machine
ActiveCN104229855AAvoid wastingLess investmentCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesEnergy inputProcess systemsSinter Plant
The invention relates to a process for on-line heating and oxidation of desulfurized fly ash by virtue of flue gas from a power generating boiler or a sintering machine. The high-temperature flue gas from the power generating boiler or the sintering machine is adopted as a heat source for a heating furnace of the process system and meanwhile the waste heat of the flue gas from the heating furnace is recovered so as to preheat the desulfurized fly ash inside a two-section type rotary oxidation kiln and the heat-exchanged flue gas of the heating furnace and the waste heat of the finished product cooling bin are sent back to the combustion air system of the power generating boiler or the sintering machine together to be used as combustion air. Compared with the prior art, the process has the beneficial effects that: (1) the existing resources are fully utilized and the waste caused by the repeated construction is avoided; (2) by virtue of the process, the on-line heating oxidation and modification treatment of desulfurized fly ash generated in the power generating plant or a sintering plant are facilitated by virtue of the technological reconstruction, the investment is low, the energy consumption is low, the operating cost is low and the process is suitable for industrial and scale production; (3) oxidized desulfurized fly ash can be directly applied in industries, such as building materials, construction and decoration which is beneficial to the energy conservation and emission reduction and the protection of the land and environment and (4) economic benefits are considerable after the process is applied.
Owner:LIAONING ENERGY ENVIRONMENT ENG TECH
Method for preparing carbon/zinc oxide super-hydrophobic ceramic by sintering plant leaves
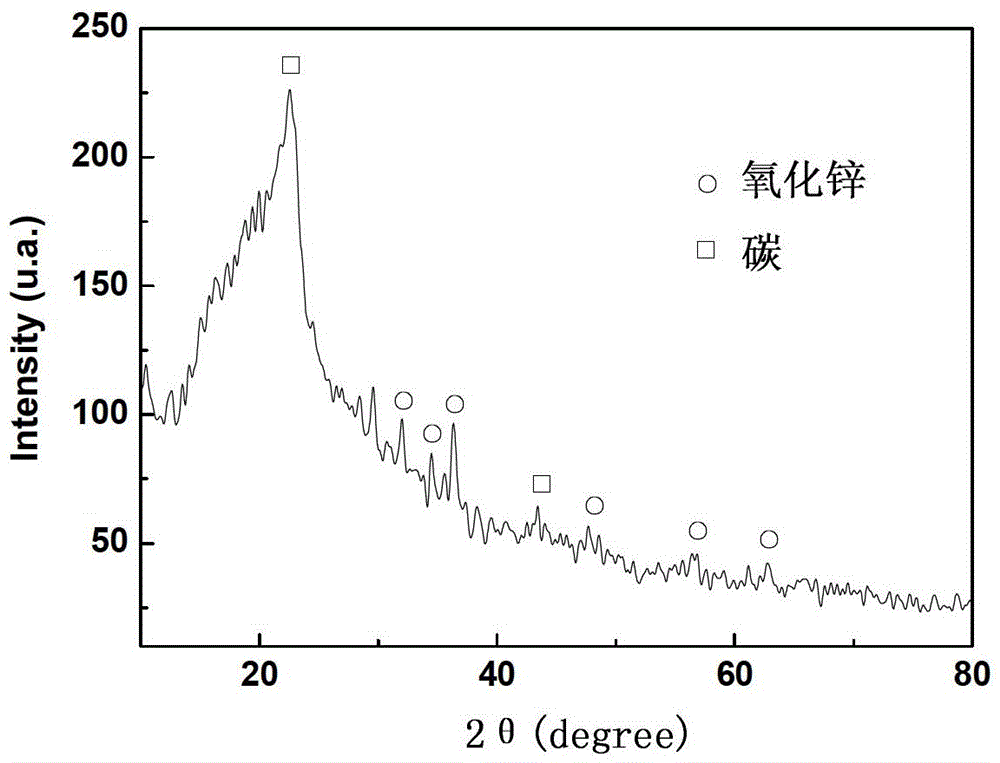
InactiveCN102976763AAchievement of superhydrophobicityExcellent superhydrophobic propertiesOxide ceramicSinter Plant
The invention relates to a method for preparing carbon / zinc oxide super-hydrophobic ceramic by sintering super-hydrophobic plant leaves, which is characterized in that super-hydrophobic plant leaves are used as preparation templates are sintered under the protection of a non-oxidizing atmosphere to obtain carbon ceramic having a leaf structure; the carbon ceramic is impregnated with a zinc nitrate solution and is sintered under the protection of a non-oxidizing atmosphere to obtain carbon / zinc oxide ceramic having a leaf structure; and the surface of the carbon / zinc oxide ceramic is modified with fluorosilane low-surface-energy substances, thus obtaining the carbon / zinc oxide super-hydrophobic ceramic having a leaf structure. According to the invention, the prepared carbon / zinc oxide super-hydrophobic ceramic well keeps the plant leaf microscopic structure, highly imitates the nature and has excellent super-hydrophobic property.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
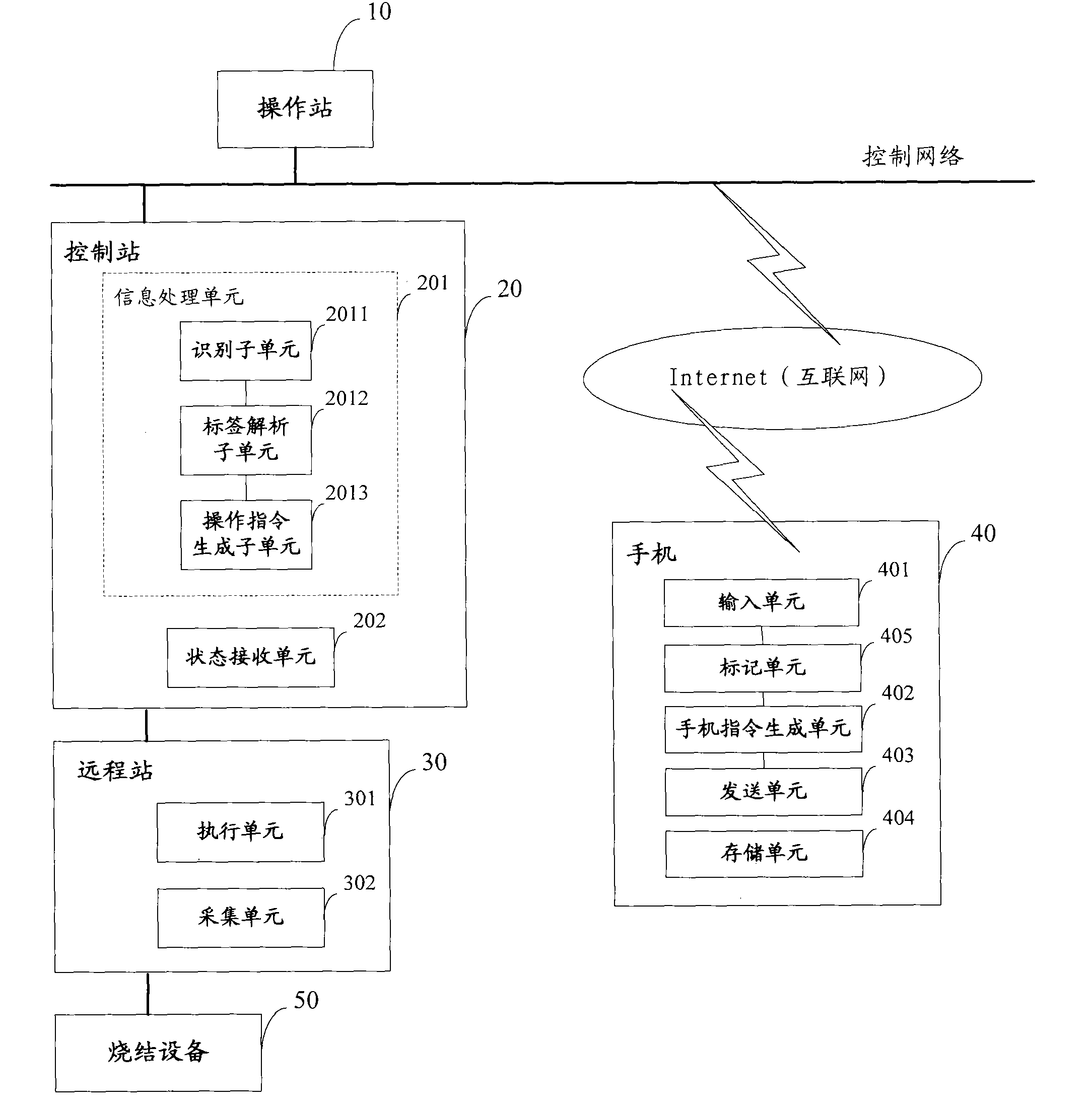
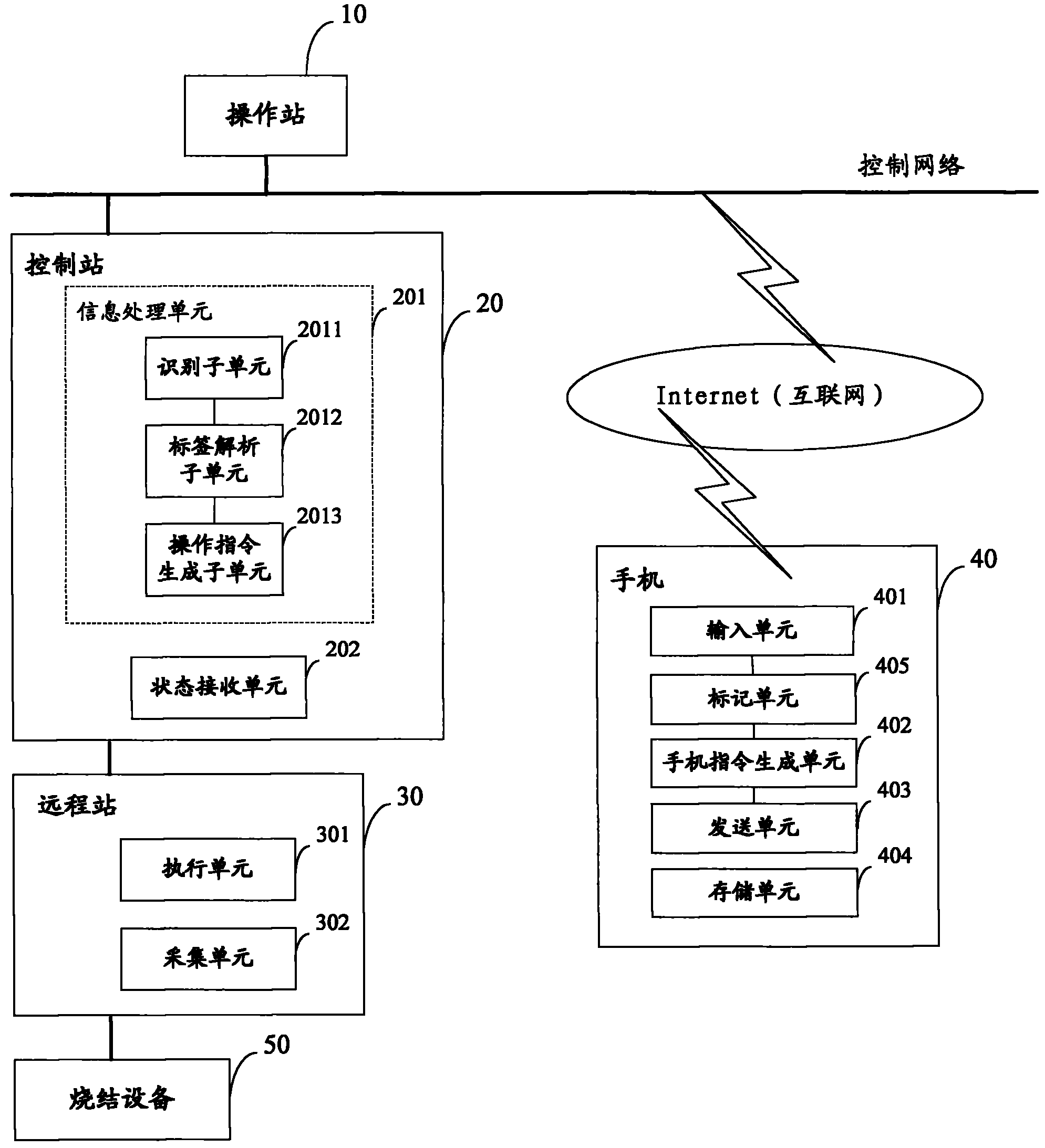
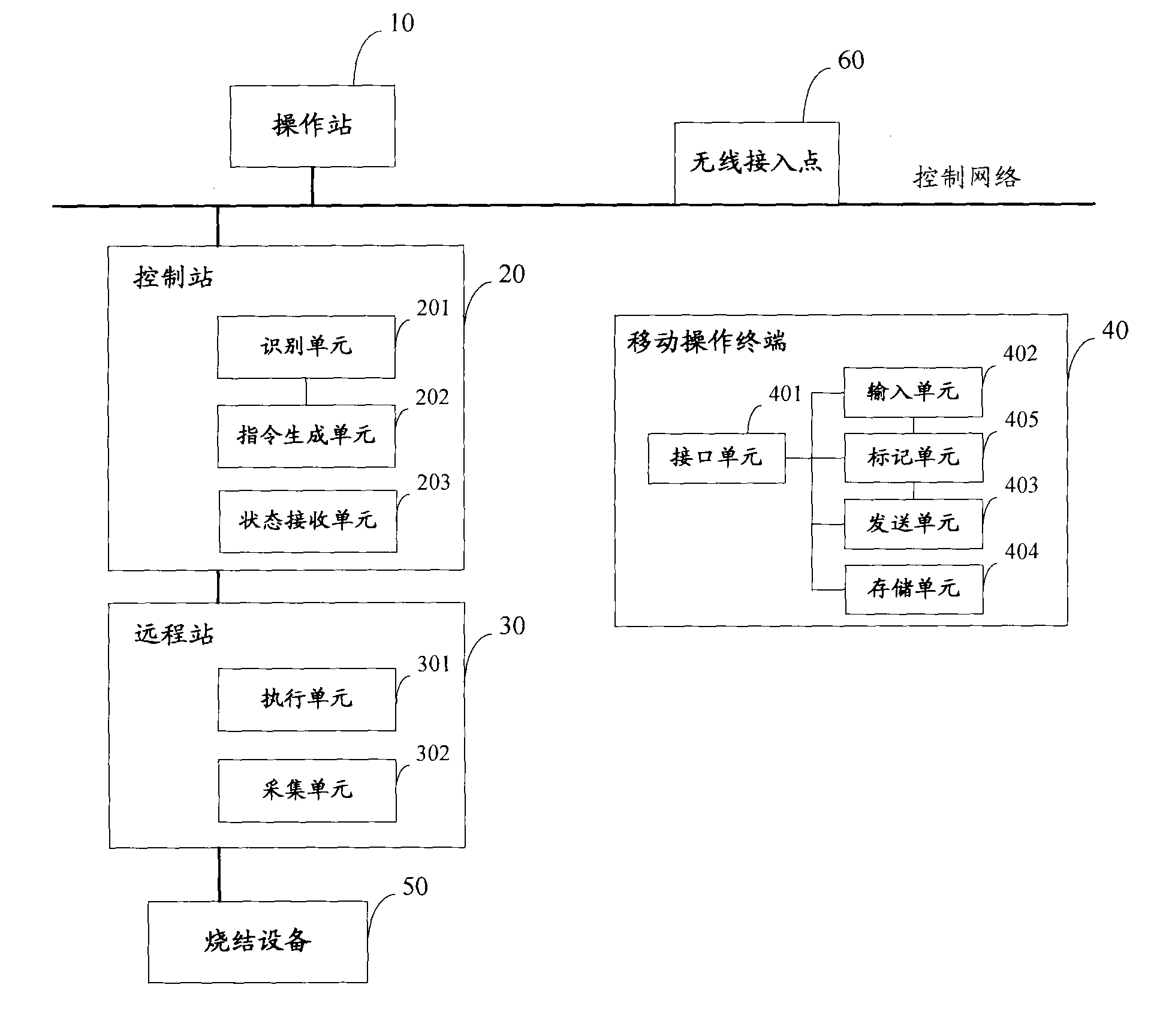
Sintering plant control system
InactiveCN102033521ASave resourcesLess investmentTransmissionTotal factory controlInformation processingSinter Plant
The invention discloses a sintering plant control system. The system comprises sintering equipment, a control network, a mobile phone which accesses an internetwork, a control station connected with the control network, and a remote station accessing the sintering equipment to the control network, wherein the control network accesses the internetwork; the control station comprises an information processing unit, and a state receiving unit for receiving the state information of the sintering equipment; the information processing unit identifies a mobile phone instruction for operating the sintering equipment as a request signal to generate an operation instruction and transmit the operation instruction to the remote station; the remote station comprises an execution unit and an acquisition unit; the execution unit receives the operation instruction transmitted by the control station to operate the sintering equipment; and the acquisition unit is used for acquiring the state information of the sintering equipment to send the state information to the control unit and / or the mobile phone. By using the system, the field arrangement can be simplified, operation intensity can be reduced, the fault time can be shortened, and the production efficiency can be improved.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
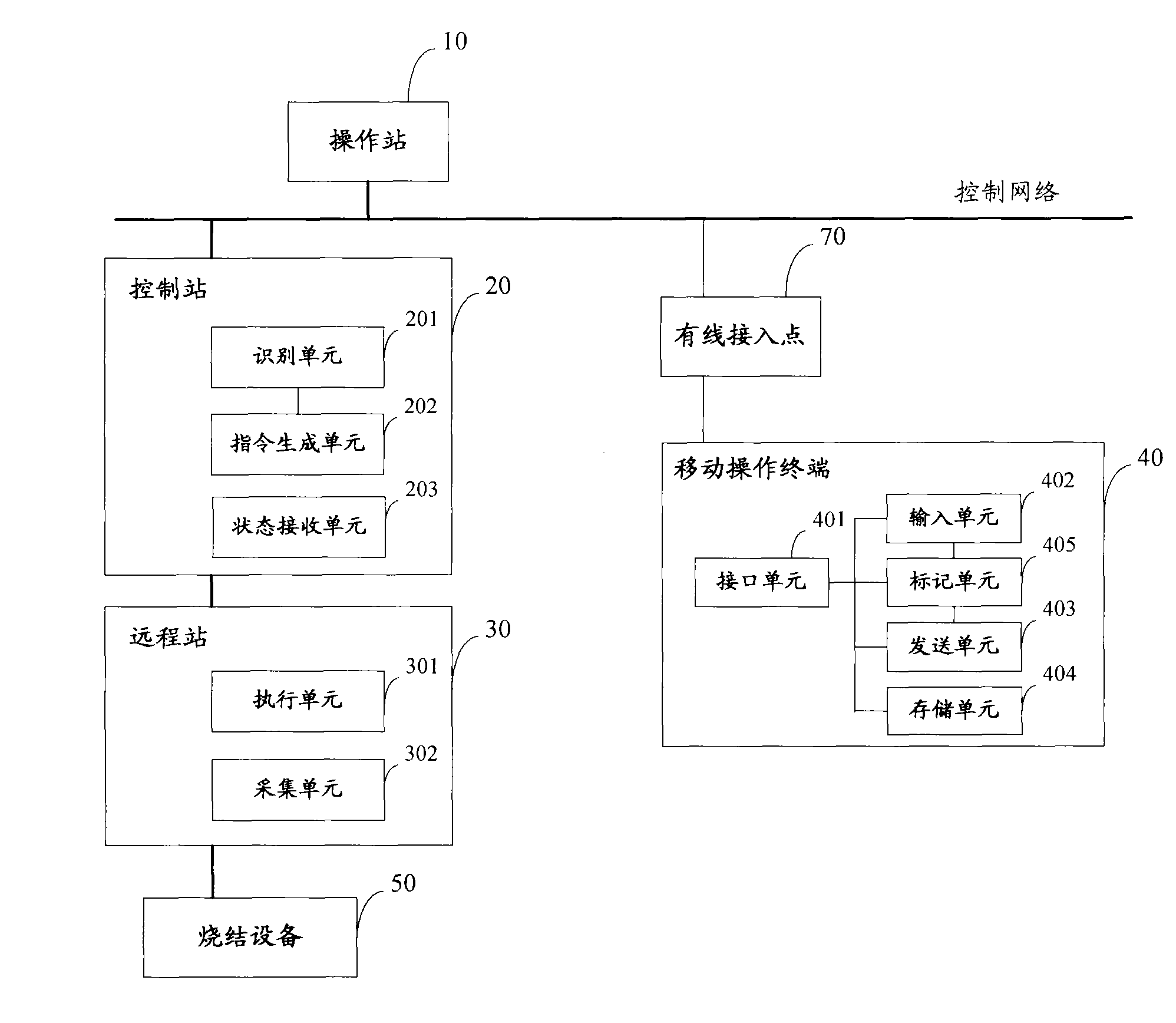
Control system of sintering plant
InactiveCN102033520AReduce downtimeIncrease productivityTransmissionTotal factory controlControl systemSinter Plant
The invention discloses a control system of a sintering plant, comprising a sintering device, a control network, a mobile operating terminal, a control station, a remote station and at least one access point, wherein the control station is connected with the control network, the remote station is used for accessing the sintering device into the control network, the at least one access point is arranged on the control network, the mobile operating terminal is accessed into the control network by one of the access points, the control station comprises a command generating unit and a state receiving unit, wherein the state receiving unit is used for receiving the state information of the sintering device, the command generating unit is used for generating corresponding operating commands of received operation request signal to be issued to the remote station, the remote station comprises an executing unit and a collecting unit, wherein the executing unit is used for receiving the operating commands issued by the control station to operate the sintering device, and the collecting device is used for collecting the state information of the sintering device to be transmitted to the control station and / or the mobile operating terminal. The control system of the sintering plant is capable of simplifying field arrangement, reducing operation strength, shortening fault time and increasing production efficiency.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
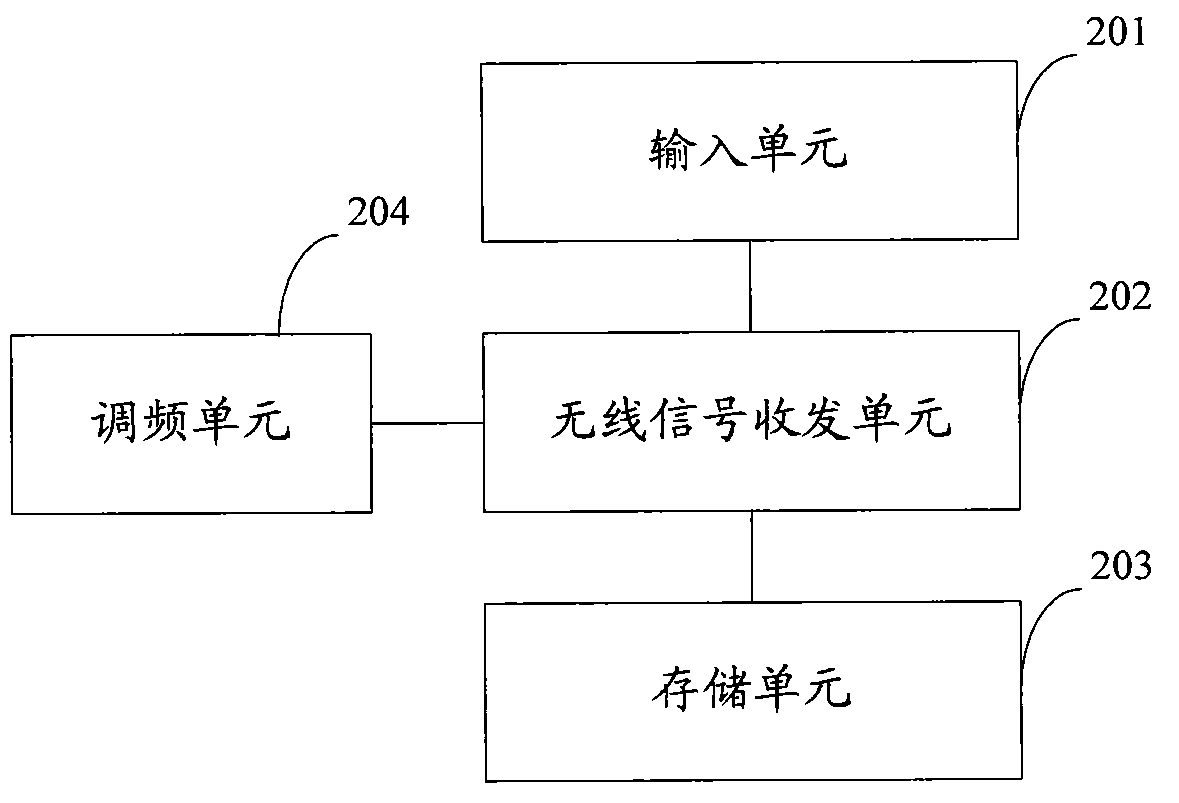
Control system of sinter plant
ActiveCN102033522ASave resourcesSimplify site layoutFurnace typesTotal factory controlCommunication unitSinter Plant
The invention discloses a control system of a sinter plant, comprising a sinter apparatus, a control network, a mobile operation terminal, a control station which is connected with the control network and used for receiving state information of the sinter apparatus and generating an operation instruction for the sinter apparatus, and a remote station which is used for connecting the sinter apparatus into the control network. The remote station comprises a communication unit which is capable of receiving and transmitting a wireless signal of a specific frequency, a control unit and a collection unit; the control unit receives a wireless operation signal, which is sent from the mobile operation terminal and used for operating the sinter apparatus, through the communication unit, converts the wireless operation signal into an operation request signal, transfers the operation request signal to the control station, and receives the operation instruction returned by the control station to operate the sinter apparatus; and the collection unit is used for collecting the state information of the sinter apparatus to transmit the state information to the control station and / or to the mobile operation terminal through the communication unit. The system can simplify the site arrangement, reduce the operation intensity, reduce the fault time and improve the production efficiency.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
Sintering plant operating simulation system
ActiveCN102234719AShorten production timeThere is no security riskTotal factory controlElectronic systemsSinter Plant
The invention discloses a sintering plant operating simulation system, which comprises a power supply subsystem and a computer control subsystem, wherein the power supply subsystem provides power for a main circuit and a control circuit of sintering equipment in a normal production state, and cuts off the main circuit of the sintering equipment and separately provides power for the control circuit of the sintering equipment in an operating simulation state, and the operation of the sintering equipment is simulated through do-nothing operation of the control circuit of the sintering equipment;and the computer control subsystem is used for remotely operating control circuits of various pieces of sintering equipment and controlling the system to be in the normal production state or the operating simulation state. The sintering plant operating simulation system can improve the safety and efficiency of sintering production.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
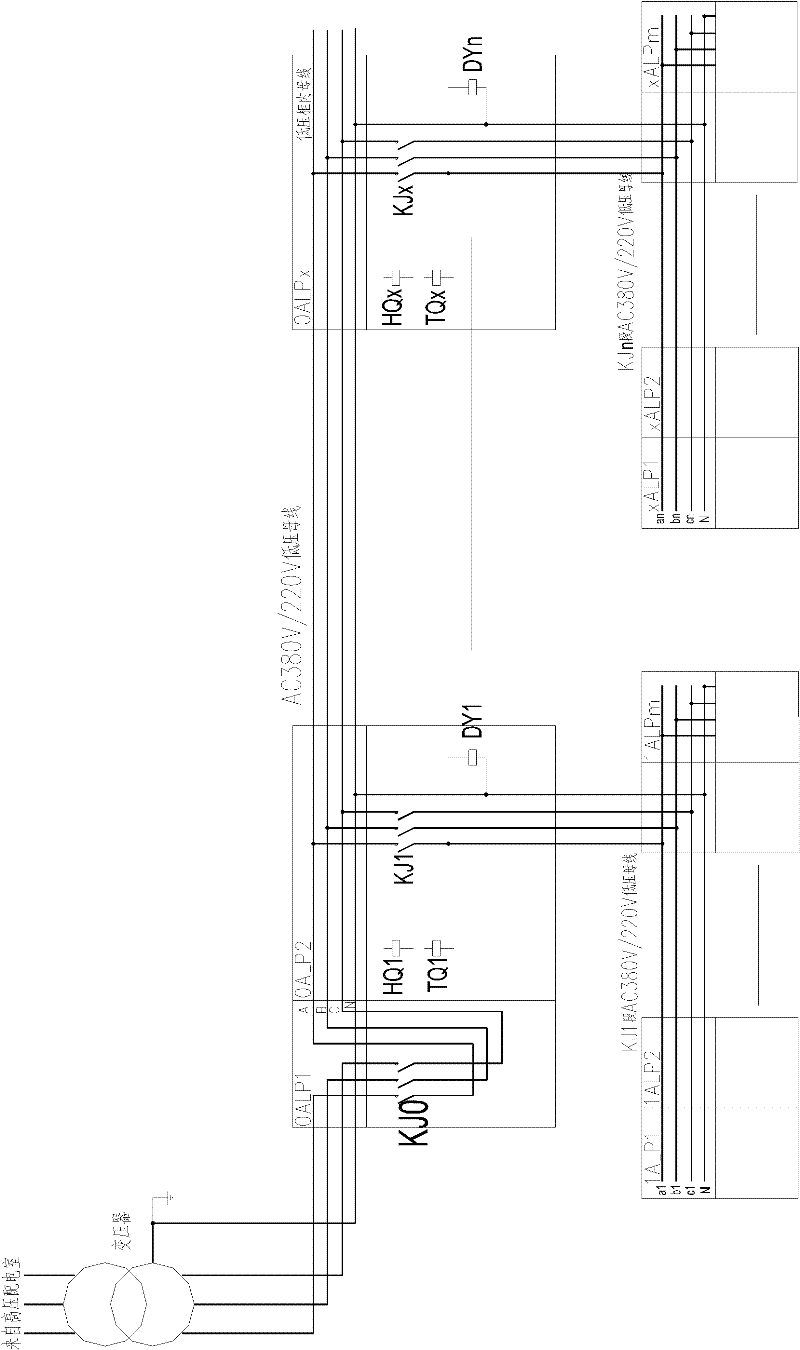
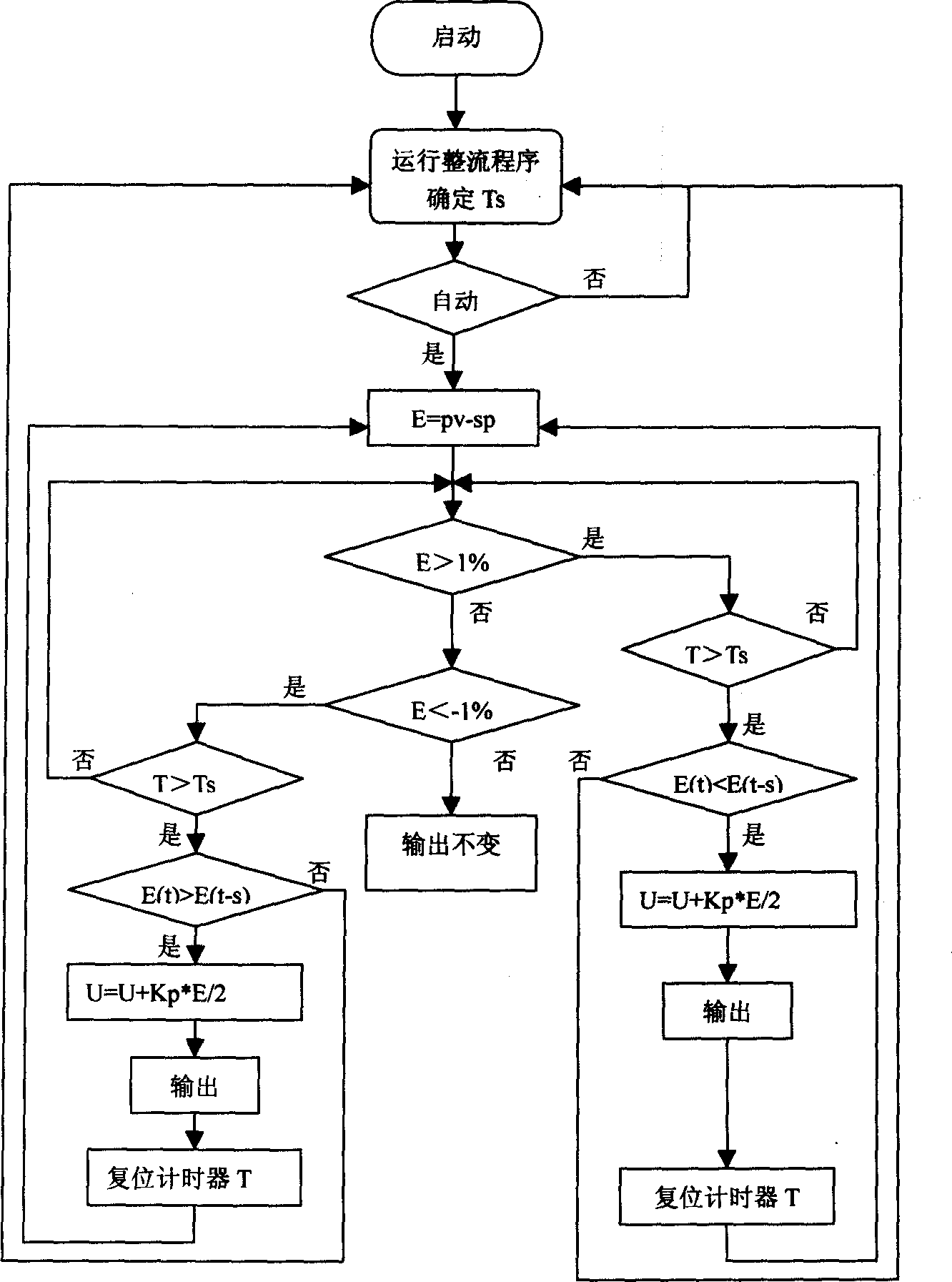
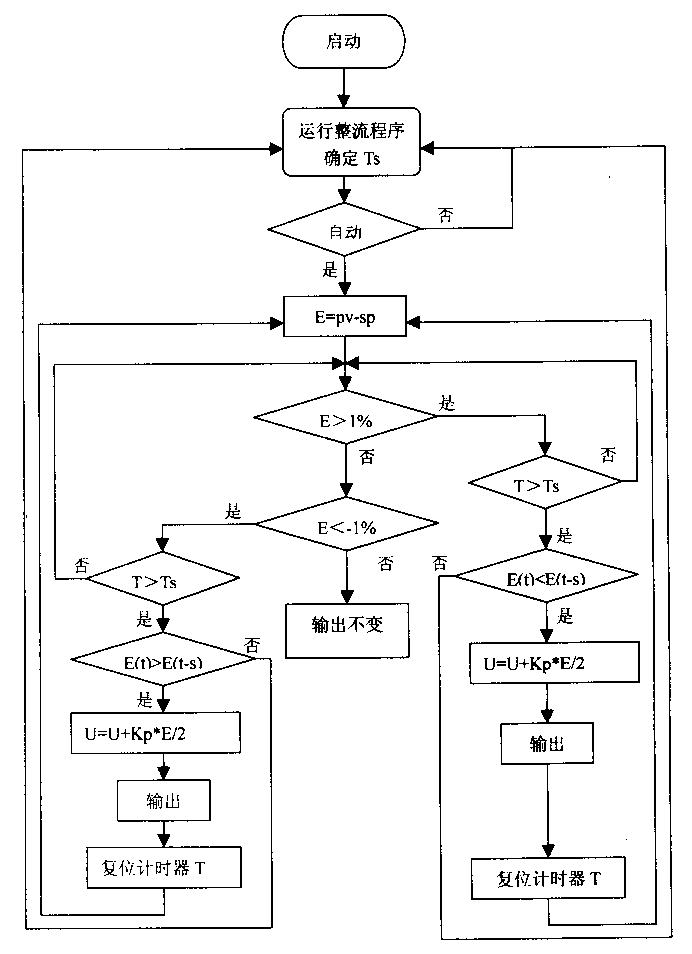
Automatic sintered material controlling method
InactiveCN1357805AGuaranteed stabilityAuto Quick AdjustAdaptive controlAutomatic controlAutomatic train control
The automatic control sintered material compounding method for sintering plant and cement mill features the automatic determination of parameter variation period or stabilizing time period, automatic process value sychronization to calculating control output period after starting the system; and the maintenance of the output or automatic controlling output according to that the process values are within or beyond the tolerant range after automatic material throwing. The present invention is superior in that the system has conveygent control effect and even in case that object parameters are changed, the system can be regulated automatically and fast to ensure stability owing to the divergence diagnosing link.
Owner:李伟
Organic acid reinforced steel slag fuel gas desulfurization method
InactiveCN102614772AIncrease profitIncrease pH buffer valueDispersed particle separationOrganic acidSinter Plant
The invention discloses an organic acid reinforced steel slag fuel gas desulfurization method, which is mainly applied to sintering plants, thermal power plants, industrial fire coal boilers and other flue gas desulfurization (FGD) containing sulfur dioxide, and particularly has a good prospect specific to sintering flue gas desulfurization. Due to the adoption of the method, low investment and low running cost of flue gas desulfurization can be realized, and a desulfurization technology is applied more widely. A process adopted by the invention has the advantages of low investment, running and managing costs, realization of steel slag recycling, realization of treatment of waste with waste. The method has superior cost performance and a wide market prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Method and device for recycling oily sludge of iron and steel plant
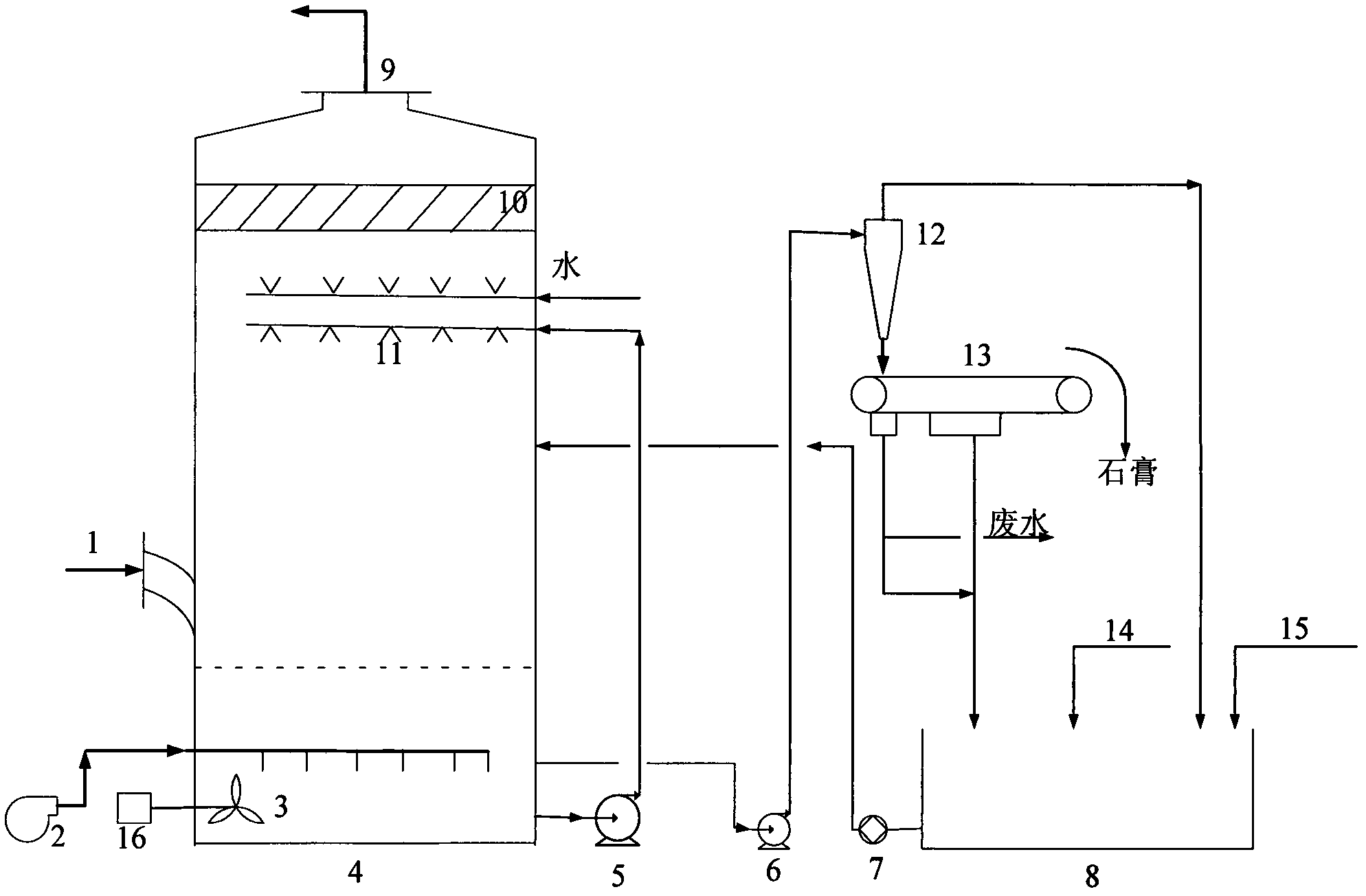
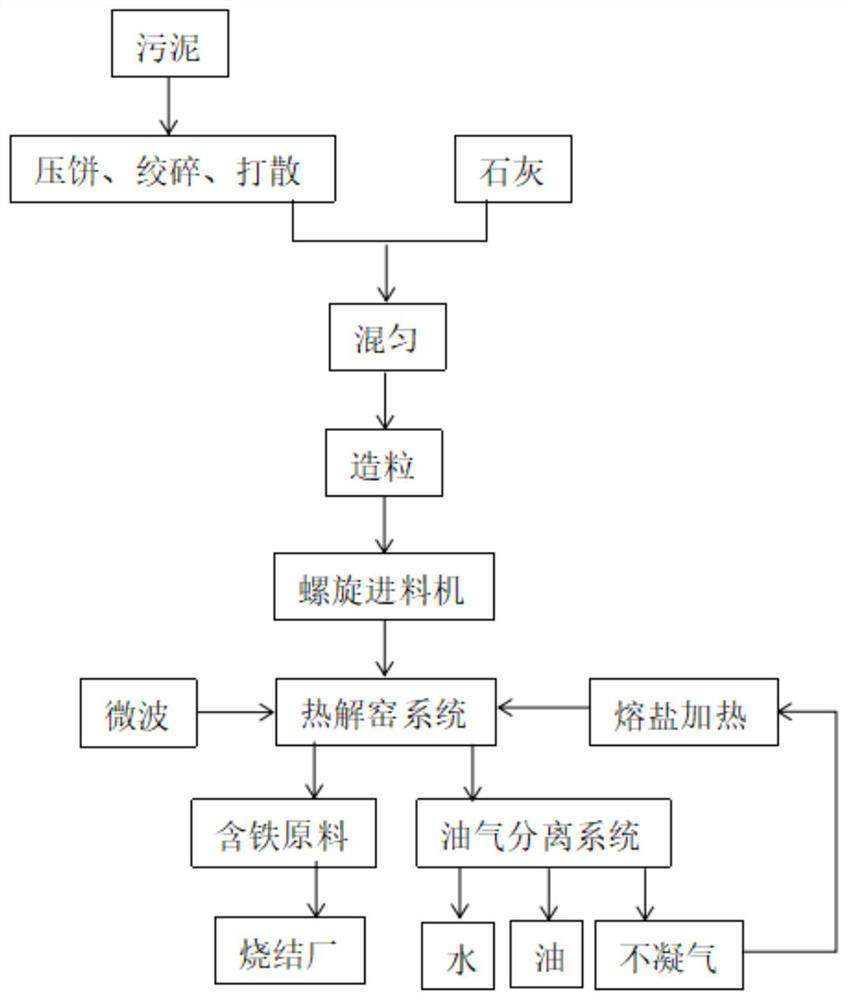
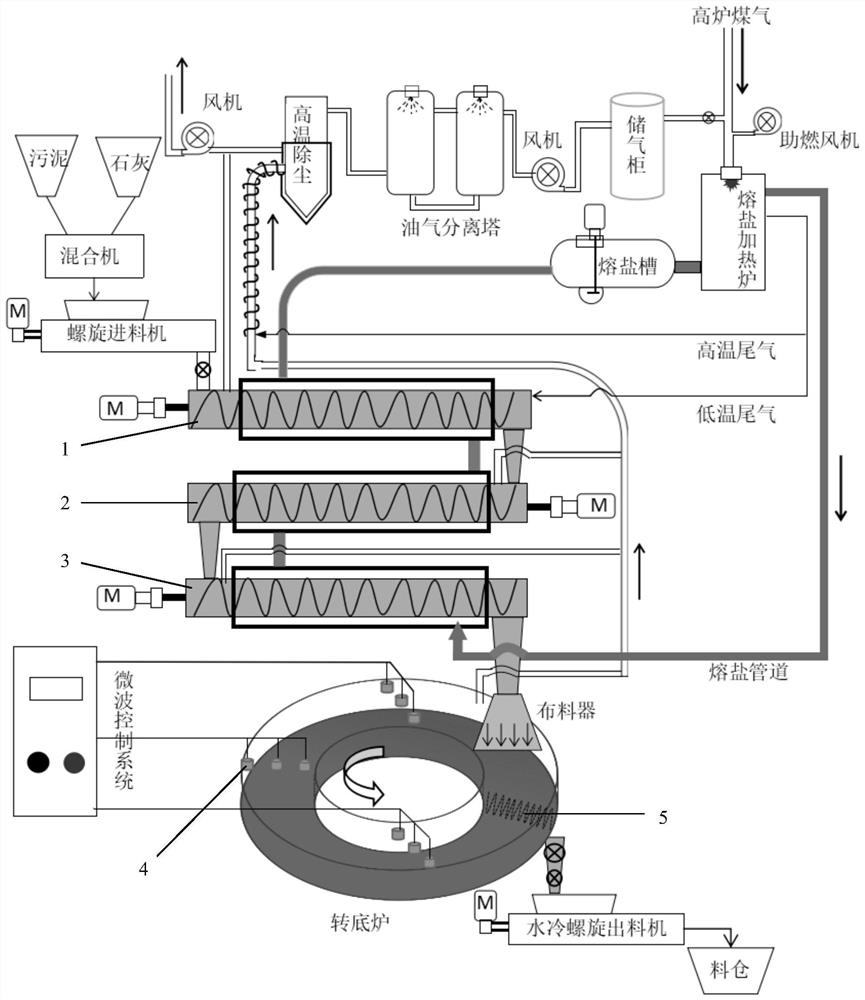
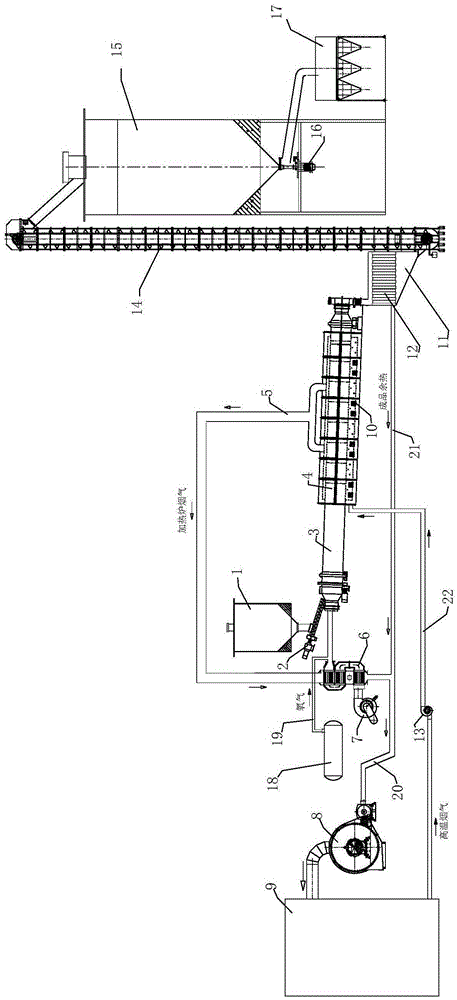
ActiveCN113526821AReduce viscosityPromote absorptionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by pyrolysisOil and greaseSinter Plant
The invention discloses a method and a device for recycling oily sludge of an iron and steel plant, and belongs to the field of sludge treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: loading oily sludge into a stock bin, pressing the oily sludge into cakes, mincing the cakes, scattering, adding lime in proportion, mixing well, and granulating the mixture; carrying out sludge particle heating, preheating dehydration and grease decomposition in a high-temperature fused salt external heating mode; feeding the sludge particles into a rotary hearth furnace, and further deeply pyrolyzing the sludge particles under an anaerobic condition and under the action of a microwave field; after the sludge material in the product stock bin is cooled, conveying the sludge material to a sintering plant; in the sintering plant, recycling the pyrolyzed sludge material as a sintering raw material, adding the pyrolyzed sludge material into a sintering proportioning bin, and blending the pyrolyzed sludge material into uniformly mixed ore according to the proportion required by the production process; and correspondingly reducing the dosage of the flux according to the alkalinity requirement of the sintered ore, and performing uniform mixing and sintering to produce sintered ore. Therefore, the oily sludge of the iron and steel plant is harmlessly treated, the treatment efficiency of the oily sludge and the energy utilization efficiency are improved, and the oily and ferric oxide-containing sludge is recycled.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Repair method for worn central disc of main exhauster in sintering plant
InactiveCN104070269AImprove fusion rateReduce distortionArc welding apparatusSinter PlantWear resistance
The invention relates to a repair method for a worn central disc of a main exhauster in a sintering plant. The repair method comprises steps of preparation before repair, the repair process and detection after repair, and particularly comprises the following steps: cleaning a workpiece; detecting the size of each part of the main exhauster, and determining the damaged part and the abrasion; determining basic parameters of the main exhauster; conducting radial and end surface runout detection on the main exhauster; determining a repair scheme for the main exhauster; determining the repair technique according to a detection result; selecting welding materials, and replacing plates at the seriously worn part and the washing leakage part; partially welding strip-shaped wear layers on a wear-resisting plate, and conducting thermal tailor-melding on the wear-resisting plate; conducting partial thermal treatment on welding parts; polishing the welding parts to be smooth; conducting detection after repair. The repair method is good in wearing resistance, high in rigidity, few in cracks of a repair layer, high in fusion rate of a cladding layer and base metals of the central disc, and low in deformation of the main exhauster.
Owner:河北瑞兆激光再制造技术股份有限公司
On-line heating process of oxidation and desulfurization ash by using flue gas of power generation boiler or sintering machine
ActiveCN104229855BAvoid wastingLess investmentCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesEnergy inputSinter PlantEngineering
The invention relates to a process for online heating of oxidized desulfurization ash by using the flue gas of a power generation boiler or a sintering machine. The high-temperature flue gas of a power generation boiler or a sintering machine is used as the heat source of the heating furnace of the process system, and at the same time, the waste heat of the flue gas of the heating furnace is recovered to heat the air into The desulfurized ash in the two-stage rotary oxidation kiln is preheated, and the flue gas of the heating furnace after heat exchange and the waste heat of the finished product cooling chamber are sent back to the combustion air system of the power plant or sintering plant for use as combustion air. Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects of the present invention are: 1) make full use of existing resources and avoid waste caused by repeated construction; 2) facilitate the on-line oxidation of desulfurization ash produced by power plants or sintering plants through technological transformation Modification treatment, and less investment, low energy consumption, low operating costs, and suitable for industrial and large-scale production. 3) The oxidized desulfurization ash can be directly used in building materials, construction and decoration industries, which is beneficial to energy saving, emission reduction, land protection and environmental protection; 4) The economic benefits are considerable after application.
Owner:LIAONING ENERGY ENVIRONMENT ENG TECH
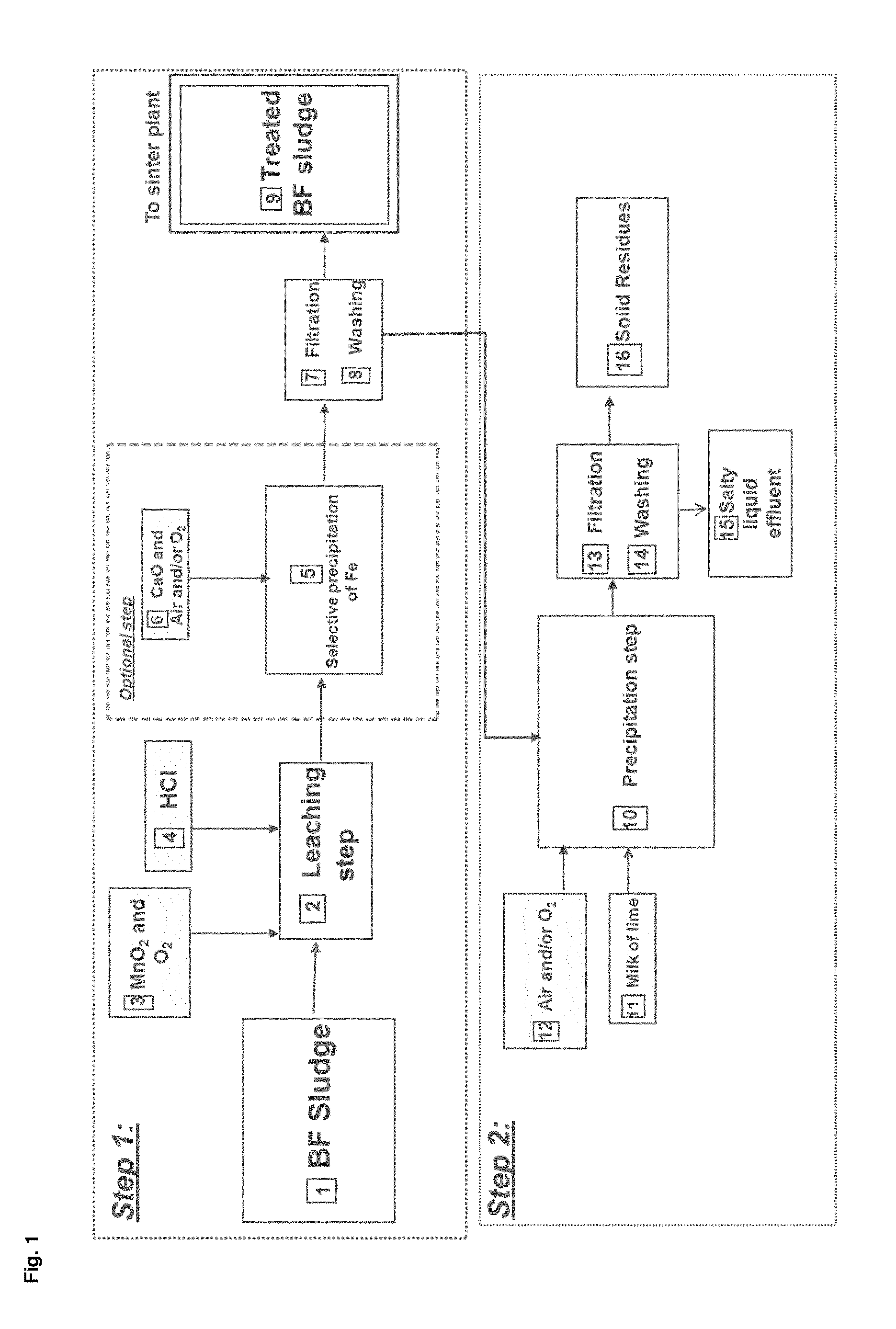
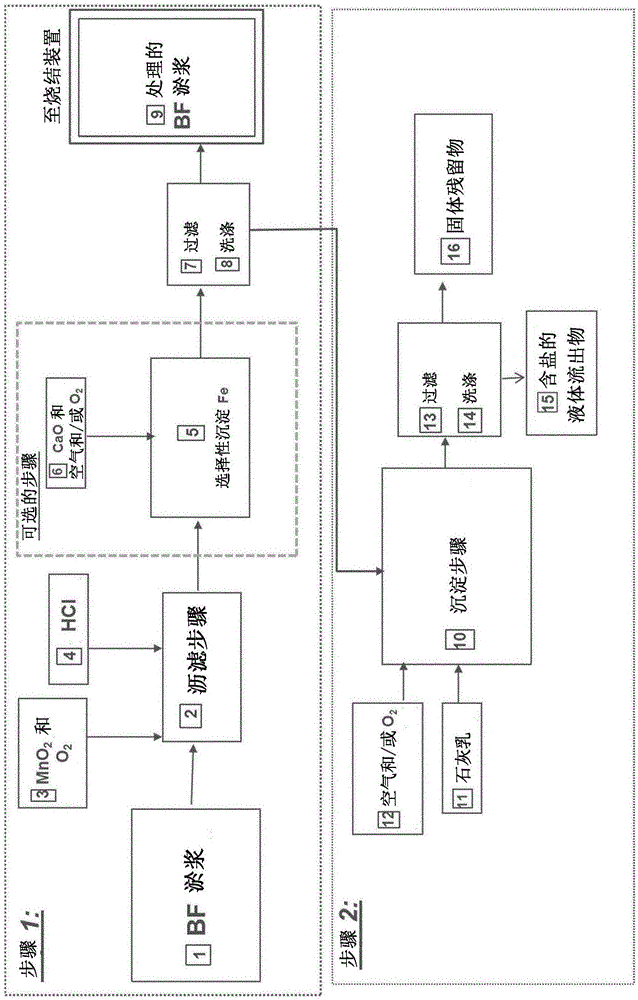
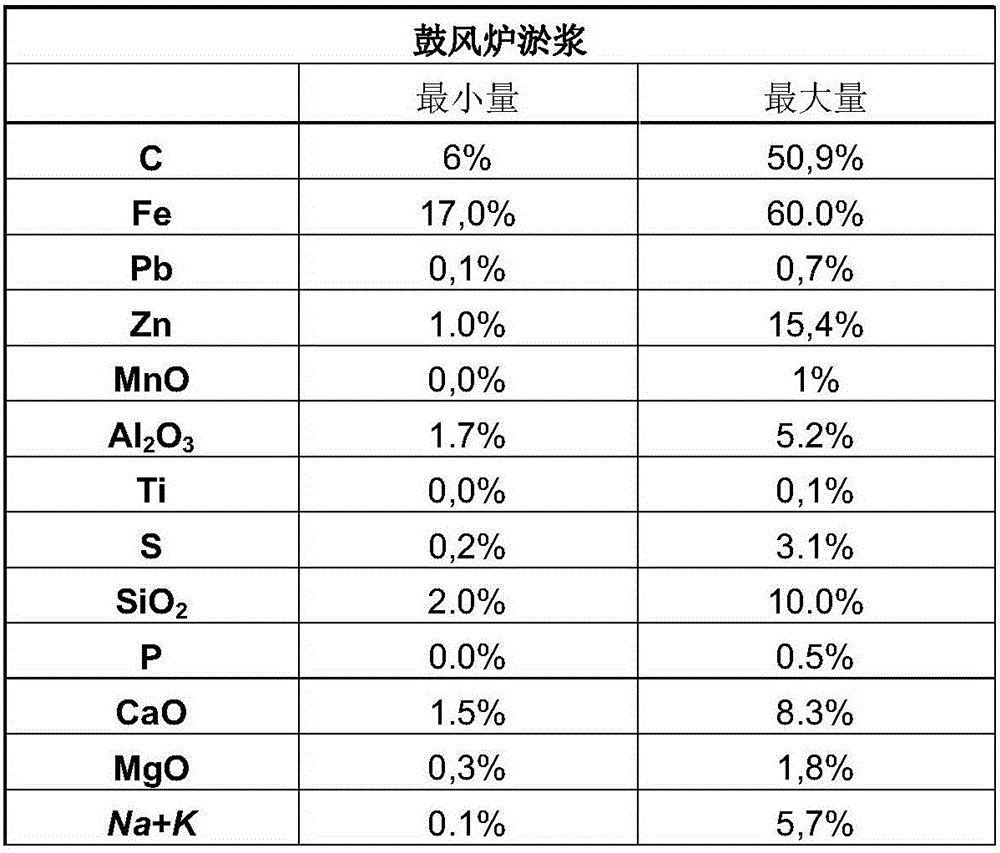
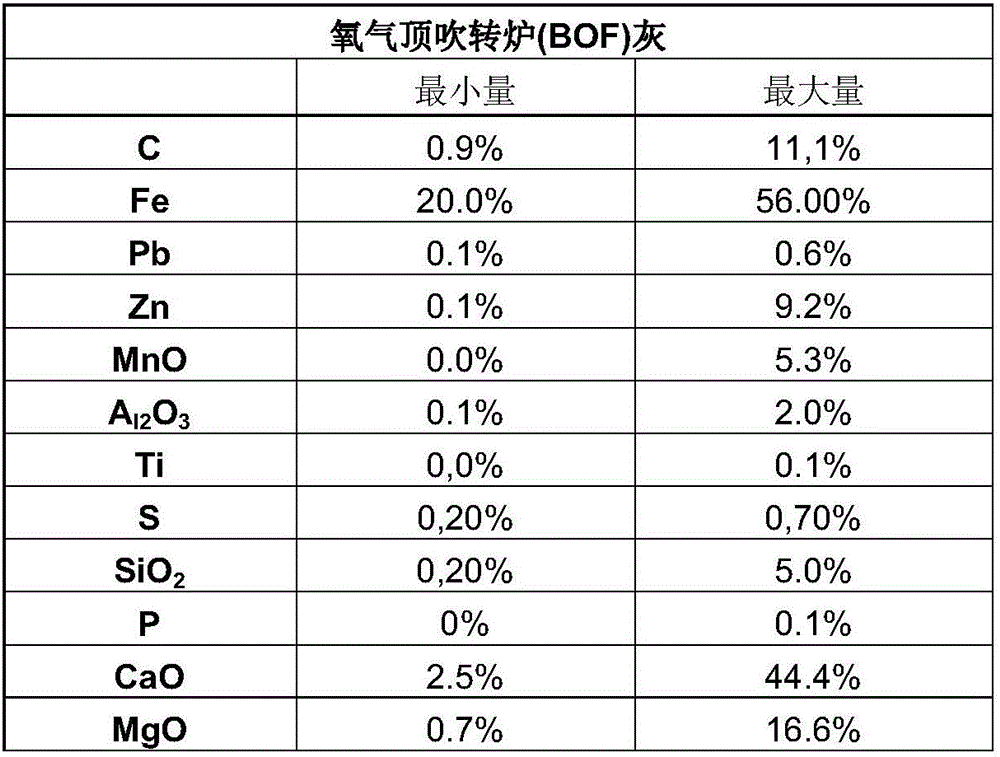
Process for reducing the amounts of zinc (ZN) and lead (PB) in materials containing iron (FE)
InactiveUS20170058378A1Efficient and easy to implement processEasy to implementProcess efficiency improvementAfter treatmentSinter Plant
The present invention relates to a process for reducing the amounts of zinc and lead in starting materials comprising iron which comprises the steps of: —selectively leaching Zn and Pb comprised in the starting materials by mixing the starting materials with hydrochloric acid and an oxidizing agent comprising at least 5 wt-% of manganese dioxide in one or several reactor(s) at a temperature superior or equal to 35° C. and at a p H comprised between 0.5 and 3.5, —filtrating the mixture obtained in order to separate the solid and the filtrate, —washing the solid with water, the resulting solid comprising mainly Fe, a reduced amount of Zn and Pb compared to the original starting materials, —recovering the filtrate of step b) and the washing water of step c) which comprise chloride, solubilized Zn and Pb in one or several reactor(s), —precipitating solubilized Zn, Pb in the recovered filtrate and the washing water by mixing with a neutralizing agent, —filtrating and washing the solid residues obtained in step e) in order to remove the chloride from the solid residues which comprise at least Pb and Zn. The present invention also refers to the use of the materials obtained after treatment in a in a sinter plant and blast furnace or in all pyrometallurgical furnace which value iron such as electrical arc furnace (EAF), cupola furnace, oxycup furnace, submerged arc furnace (SAF), a plasma furnace, rotary hearth furnace.
Owner:PAUL WURTH SA
Tail pulley chain device for hot ore chain scraper conveyor
The invention discloses a tail pulley chain device for a hot ore chain scraper conveyor and belongs to devices in the field of metallurgy. The tail pulley chain device is used for turning at a turning position on the tail portion of a hopper and for bearing the hopper, is mainly used for hot ore chain scraper conveyors of sintering plants in steel and iron enterprises and is suitable for the hot ore chain scraper conveyors of other industries. The tail pulley chain device is structurally characterized in that chain wheels of a tail pulley are toothless, hubs and shafts at two ends of the tail pulley are all fixed, and no rib plate is arranged between chain plates on the chain wheels. The chain wheels of the tail pulley are toothless so that in turning of the tail portion, the excircles on the chain wheels of the tail pulley are tangent with the excircle of an idler wheel on a chain, the distance between centers of the chain wheels and the idler wheel is constant, and the chain wheels of the tail pulley isare arranged between the chain and the chain plates to prevent the chain from moving along the axis direction of a tail pulley shaft. The hubs and the shafts at two ends of the tail pulley are all fixed, the chain wheels on the tail pulley are toothless, the chain wheels at two ends of the tail pulley are not synchronous, copper bushes between the hubs and the shafts are reduced, oil cups are correspondingly reduced, and the structure of the tail pulley is easier. No rib plate is arranged between the chain plates on the chain, and manufacturing of the chain plates is easier.
Owner:SHANDONG LAIWU COAL MINING MACHINERY
Making technology of novel steel structure door
The invention provides a making technology of a novel steel structure door. The technology is characterized in that a production line mainly includes a sintering furnace from a sintering plant, a iron making blast furnace from an iron making plant, a steel making furnace from a steel making plant, and casting and steel rolling devices from a casting and steel rolling workshop; and the technology comprises the following steps: screening iron ores and iron sand ores, sintering high quality raw materials in the sintering furnace from the sintering plant until the raw materials are spherical in shape, mixing the obtained spheres with coke, putting the obtained mixture in the iron making blast furnace from the iron making plant, burning to form molten iron, sending the molten iron to the steel making plant, smelting to make steel, sending molten steel from the steel making plant to the casting and steel rolling workshop, carrying out steel forming, and cooling. Compared with the prior art, the technology has the advantages of simple operation, and realization of light weight, high strength, good ductility, good shock resistance, fire resistance and sound insulation of the novel steel structure door.
Owner:天津市耀强钢结构安装有限公司
Process for reducing the amounts of zinc (Zn) and lead (Pb) in materials containing iron (Fe)
InactiveCN106029921AEasy to recycleProcess efficiency improvementElectric arc furnaceAfter treatment
The present invention relates to a process for reducing the amounts of zinc and lead in starting materials comprising iron which comprises the steps of: - selectively leaching Zn and Pb comprised in the starting materials by mixing the starting materials with hydrochloric acid and an oxidizing agent comprising at least 5 wt-% of manganese dioxide in one or several reactor(s) at a temperature superior or equal to 35 DEG C and at a p H comprised between 0,5 and 3,5, - filtrating the mixture obtained in order to separate the solid and the filtrate, - washing the solid with water, the resulting solid comprising mainly Fe, a reduced amount of Zn and Pb compared to the original starting materials, - recovering the filtrate of step b) and the washing water of step c) which comprise chloride, solubilized Zn and Pb in one or several reactor(s), - precipitating solubilized Zn, Pb in the recovered filtrate and the washing water by mixing with a neutralizing agent, - filtrating and washing the solid residues obtained in step e) in order to remove the chloride from the solid residues which comprise at least Pb and Zn. The present invention also refers to the use of the materials obtained after treatment in a in a sinter plant and blast furnace or in all pyrometallurgical furnace which value iron such as electrical arc furnace (EAF), cupola furnace, oxycup furnace, submerged arc furnace (SAF), a plasma furnace, rotary hearth furnace.
Owner:PAUL WURTH SA
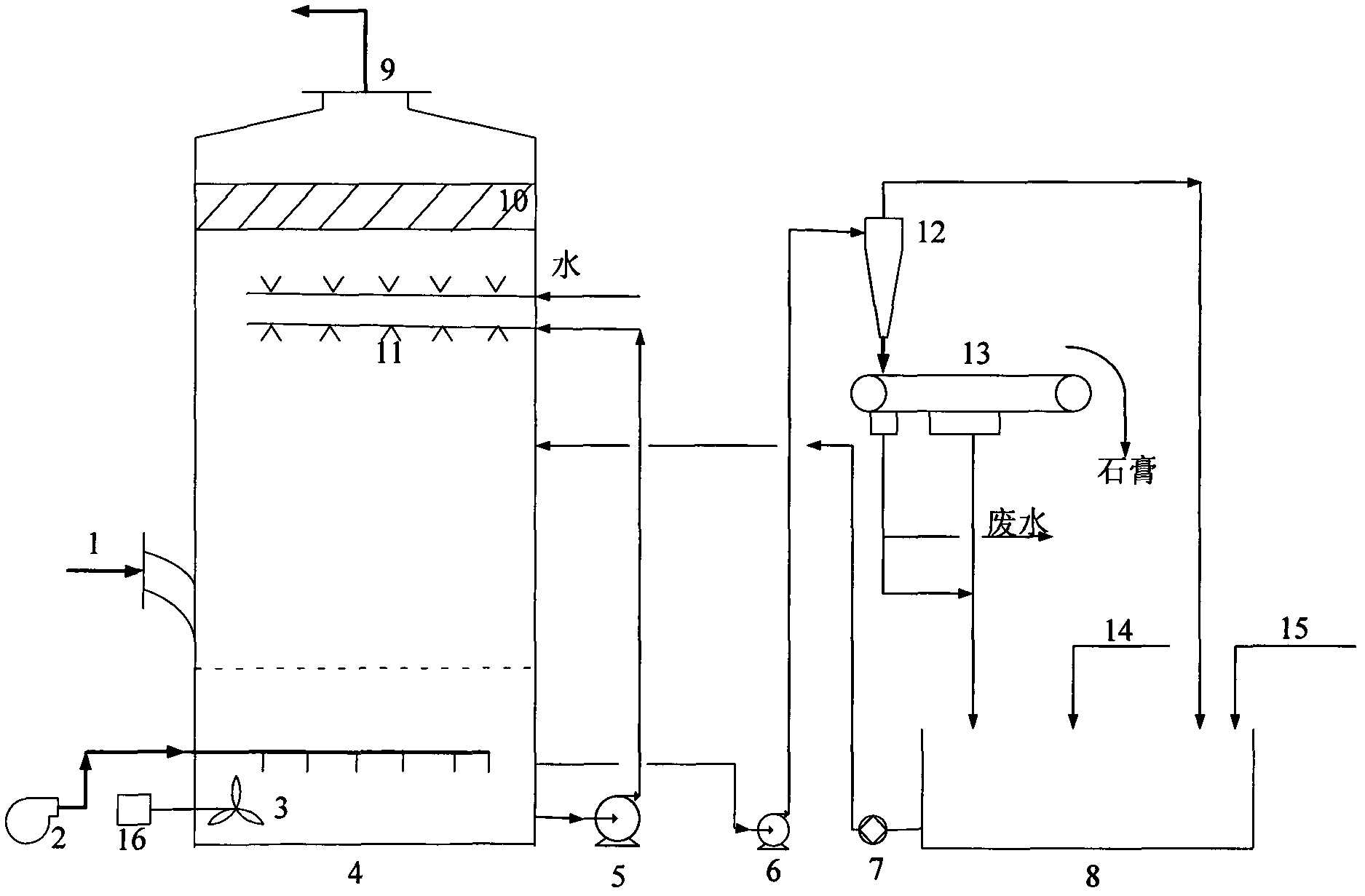
Iron-containing mud and sintered return mine reuse method
The present invention relates to a method for reutilization of iron-containing dust mud and agglomerate return mine, and is characterized by that it uses the agglomerate return mine as nucleus of pellet formation, and mixes it with iron-containnig dust mud and iron-containing waste material powder and stirs them, and utilizes water content being in iron-containing dust mud to make the exterior of agglomerate return mine by roll-covered with iron-containing dust mud and waste material powder to form a mixture material which possesses proper grain size and uniform component and can be reused by sinter plant. Said mixture material can be used as a sintering raw material, does not produce adhesion lumping phonomenon, and its sintering property is good.
Owner:湘潭钢铁集团有限公司
Inorganic binder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110698093ALow costThe impact of secondary pollutionCement productionSolid componentSinter Plant
The invention provides an inorganic binder and a preparation method thereof, wherein the inorganic binder comprises the following solid components by weight: 30-90 parts of desulfurization ash, 5-10 parts of limestone, 5-10 parts of dolomite and 0.5-4 parts of a dispersing agent, the inorganic binder further comprises water, and a weight ratio of the solid components to the water is 1:(3-5). According to the invention, most of the used raw materials are from iron and steel sintering plant wastes and are matched with other easily available and low-cost agents, so that the inorganic binder is low in cost, and the purpose of treating of waste with waste is achieved; the pollutant emission in the use process of the binder is almost zero so as not to cause secondary pollution influence on the production of related enterprises and so as to effectively reduce the pollutant emission of enterprises; and the binder can be independently used, can directly enters the production system of a granulation enterprise without matching with other admixtures, and is high in reaction speed and high in efficiency.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Technology for treating rolled steel oiliness oil sludge through steel slag adsorption
ActiveCN105060665AValue maximizationLow costSludge treatmentWaste water treatment from metallurgical processSinter PlantSlag
The invention discloses a technology for treating rolled steel oiliness oil sludge through steel slag adsorption. Rolled steel oil sludge is poured into a slag pool containing steel slag, and the mass proportion of the poured rolled steel oil sludge and the steel slag is 1:60; the steel slag and the oil sludge are fully stirred through an excavator, and after even stirring is conducted, the steel slag is excavated and enters a steel slag magnetic separation line to conduct iron selecting work; fine powder containing iron after iron selecting is conducted is used for a pelletizing plant or a sintering plant, and tailings obtained after iron selecting are used for road and bridge construction. According to the technology, a steel slag treating device of an iron and steel enterprise is used, the technology can be implemented without any investment, cost is low, and the risk of environment pollution is avoided.
Owner:XINJIANG BAYI IRON & STEEL
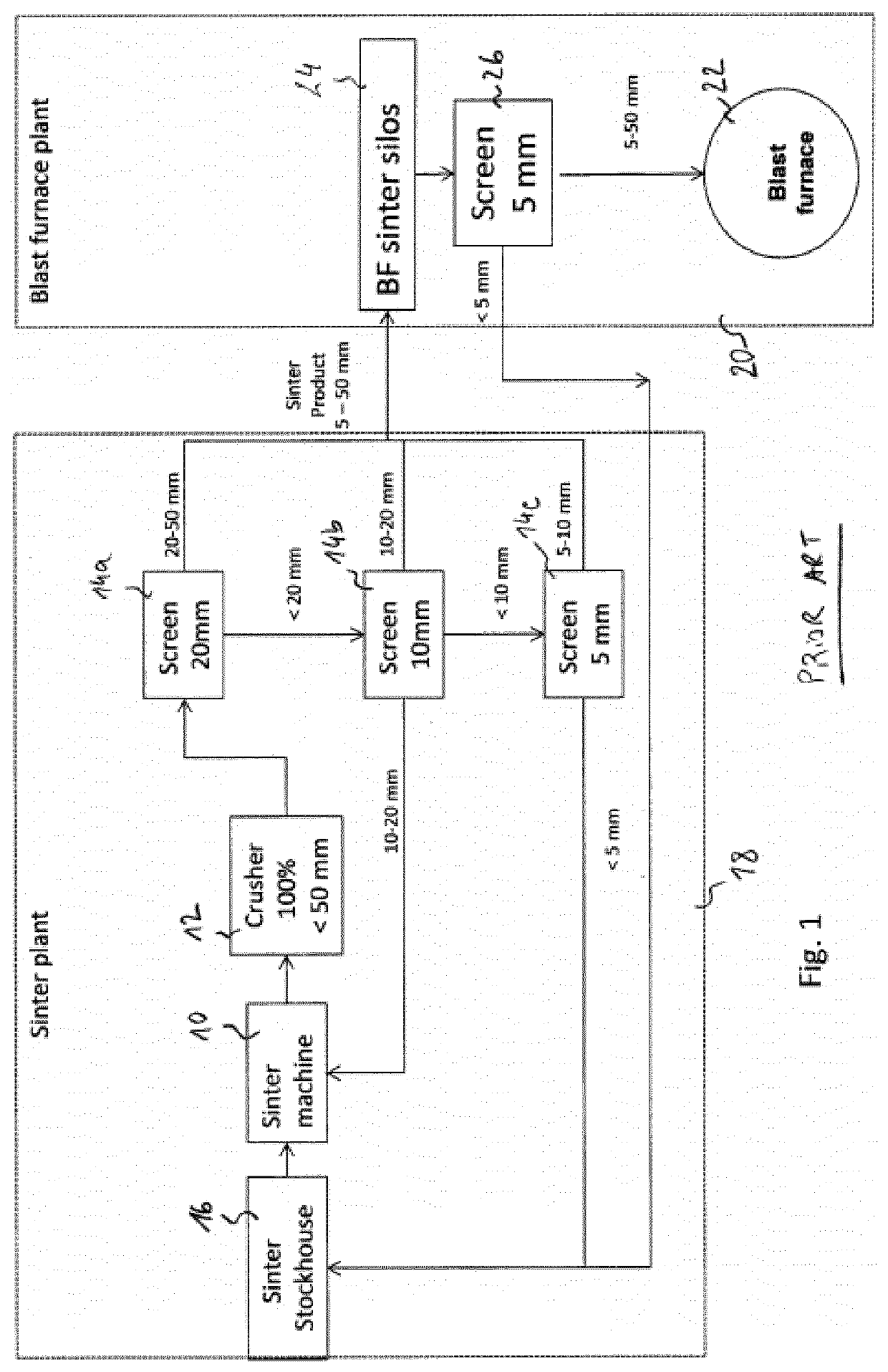
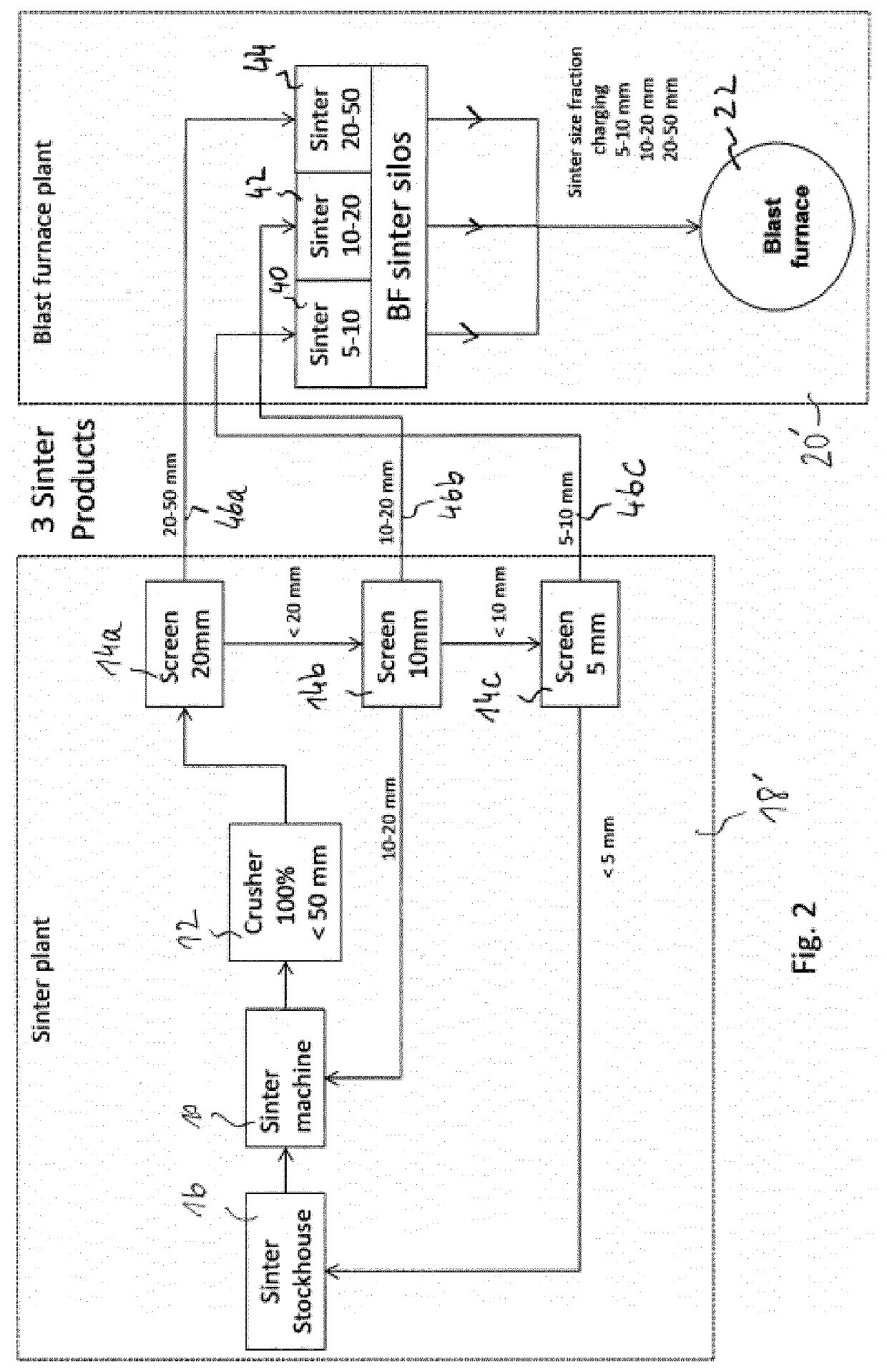
Method of operating a sinter plant
ActiveUS20200102627A1Simple methodLower overall pressure dropBlast furnace detailsSinter PlantIndustrial engineering
The invention concerns a method of operating a sinter plant, where a sinter mix is fired in a sintering machine, the method includingcrushing fired sinter to below an upper particle size limit;screening the crushed sinter to remove fines and separate at least two sinter size fractions, typically smaller, intermediate and upper size fractions;storing each of the at least two sinter size fractions in a respective, separate storage bin, wherethe screened sinter fractions are not mixed again at the sinter plant but are forwarded to the blast furnace plant, where they are stored in respective, separate storage bins, and the screened sinter fractions can be intermediately stored in separate bins at the sinter plant, before being forwarded to the blast furnace.
Owner:PAUL WURTH SA
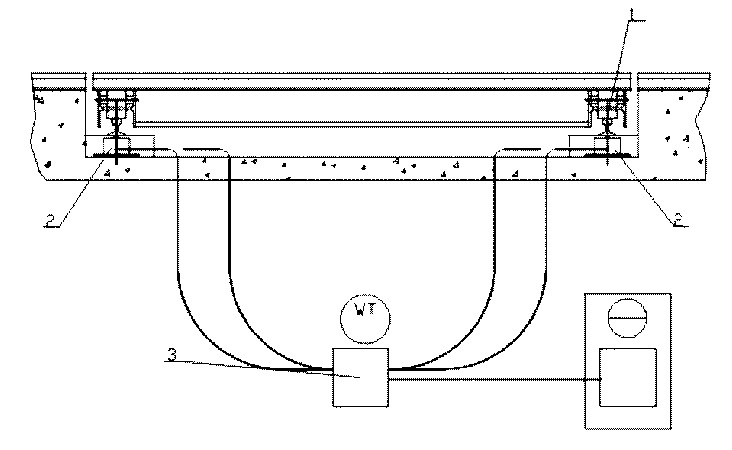
Installation method of indoor horizontal large flue in large sintering plant
Owner:CHINA 22MCC GROUP CORP
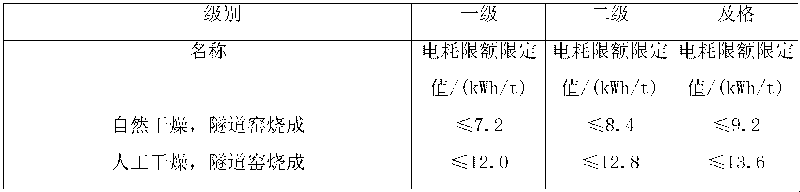
Method for indicating power consumption for yield in per unit in tunnel kiln brick sintering plant and knockout section metering device
InactiveCN101697076AIntuitive monitoringEffective monitoringElectrical measurementsProgramme total factory controlTunnel kilnBrick
The invention discloses a method for indicating power consumption for yield in per unit in a tunnel kiln brick sintering plant and a knockout section metering device. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: arranging metering equipment at a knockout section of a tunnel kiln according to the production process flow of a brick sintering plant to meter the yield of products to obtain a cumulative yield A; arranging plating detecting equipment at power-producing and lighting source feeders in the whole plant and calculating the sum of power used by the whole plant to obtain the total power consumption B; arranging a monitoring computer for computing the cumulative yield A and the total power consumption B to obtain the power consumption for the yield in per unit and carrying out online indication, wherein the indication is instantaneous instruction and accumulative indication of one day, three days, fifteen days, one month or one year. The invention can be used for monitoring the production energy consumption of a brick sintering tunnel kiln directly and effectively and accord with the industrial policies of the state. In addition, low reformation cost is needed.
Owner:贵州省建筑材料科学研究设计院有限责任公司
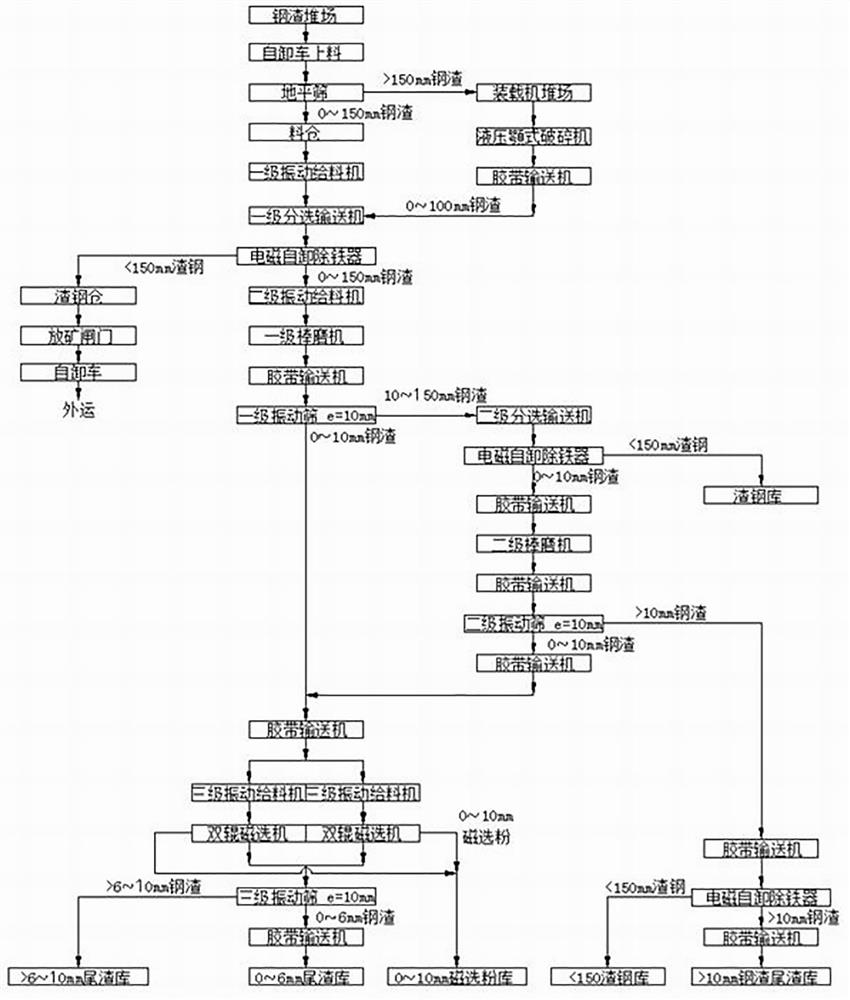
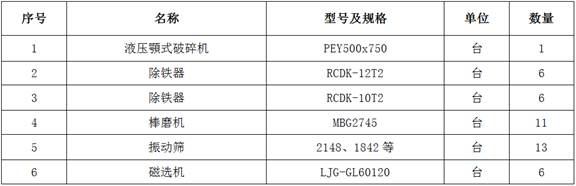
Steel slag processing technology
InactiveCN113996626AEfficient resource recyclingEconomic resource recyclingSolid waste managementSolid waste disposalSinter PlantSlag
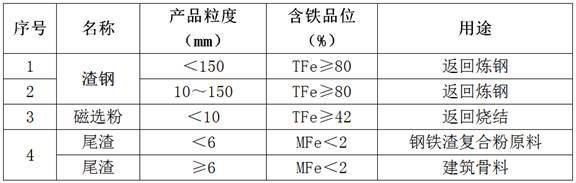
The invention discloses a steel slag processing technology. The steel slag processing technology is mainly used for receiving and processing solid steel slag in all converter hot braising workshops and electric furnace hot braising workshops. The steel slag is subjected to coarse crushing through a crusher and smashing processing through a rod mill, then screening and magnetic separation processing are carried out, and the steel slag is classified into various products with different purposes such as slag steel, magnetic separation powder and tailings. The slag steel is fed into a steel plant to produce steel products with high added value, the magnetic separation powder is fed into a sintering plant to serve as sintering raw materials, and the steel slag tailings are fed into a slag steel powder production line to be deeply processed and used for equivalently replacing cement in various concrete and cement products (the mixing amount is 20%-30%). By means of the processing technology, the metallurgical solid waste can be efficiently and economically recycled in an environment-friendly mode.
Owner:SHAGANG GROUP +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com