Glass raw material composition, inorganic glass powder, crystalline silicon solar battery aluminum conductive paste and preparation method of the crystalline silicon solar battery aluminum conductive paste
A technology of inorganic glass powder and glass raw material, which is applied to conductive materials dispersed in non-conductive inorganic materials, cable/conductor manufacturing, circuits, etc. Poor performance and other problems, to achieve the effect of increasing the oxidizing atmosphere, preventing high temperature reduction, and high photoelectric conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] (1) Preparation of inorganic glass powder:
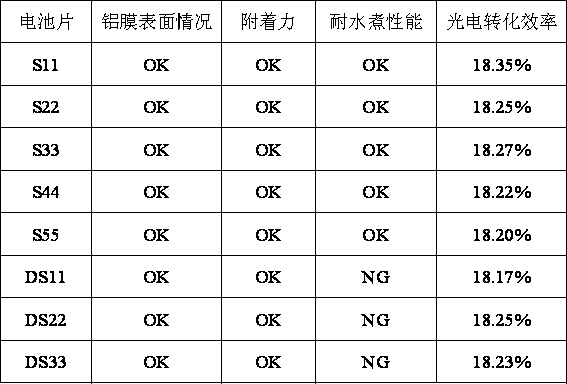
[0044] Weigh 50 parts by weight Bi 2 o 3 , 24 parts by weight B2 o 3 , 15 parts by weight SiO 2 , 2 parts by weight Sb 2 o 3 (median particle size D 50 2.5μm), 3 parts by weight Sb 2 o 5 (median particle size D 50 2.5 μm), 3.5 parts by weight CaO, 1.5 parts by weight MgO, 1.0 parts by weight Al 2 o 3 , 2 parts by weight Mg(NO 3 ) 2 , use a V-type mixer to mix the oxide powders evenly, transfer them into a corundum crucible, and place them in a silicon carbide rod furnace. Raise the temperature in the silicon carbide rod furnace to 550°C, keep it warm for 0.5h, then raise the temperature to 1250°C, keep it warm for 2h, quench and filter with water to obtain glass beads. Put the glass beads into the ball mill tank, according to the mass ratio of zirconia balls: glass beads: deionized water = 4:1:0.7, the tank speed is 300 rpm, wet milling for 6.5 hours, filtered and dried, and then dry milled for 0.5 h, The mass r...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The same steps as in Example 1 were used to prepare the inorganic glass powder S2 and the aluminum conductive paste S20 for crystalline silicon solar cells of this example, the difference being:
[0051] In step (1), weigh 52 parts by weight of Bi 2 o 3 , 24 parts by weight B 2 o 3 , 15 parts by weight SiO 2 , 1 part by weight Sb 2 o 3 (median particle size D 50 3μm), 2 parts by weight Sb 2 o 5 (median particle size D 50 2.5 μm), 3.5 parts by weight CaO, 1.5 parts by weight MgO, 1.0 parts by weight Al 2 o 3 , 0.5 parts by weight Mg(NO 3 ) 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0053] The same steps as in Example 1 were used to prepare the inorganic glass powder S3 and the aluminum conductive paste S30 for crystalline silicon solar cells of this example, the difference being:
[0054] In step (1), weigh 50 parts by weight of Bi 2 o 3 , 24 parts by weight B 2 o 3 , 15 parts by weight SiO 2 , 3 parts by weight Sb 2 o 3 (median particle size D 50 2μm), 5 parts by weight Sb 2 o 5 (median particle size D 50 2μm), 3.5 parts by weight CaO, 1.5 parts by weight MgO, 1.0 parts by weight Al 2 o 3 , 4.5 parts by weight Ca(NO 3 ) 2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com