Method for detecting acetic bacteria and lactic acid bacteria in vinegar culture by using fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
A fluorescence quantitative, lactic acid bacteria technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as large flavor differences, poor process controllability, and product quality batch differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment one: the preparation of standard sample
[0039] 1. Design and synthesize specific primers for Acetobacter and Lactobacillus.
[0040] The primer sequences are:
[0041] Acetobacter specific primer sequence (5′→3′):
[0042] Ace-F: CGCAAGGGACCTCTAACACA
[0043] Ace-R: ACCTGATGGCAACTAAAGATAGGG
[0044] Lactic acid bacteria specific primer sequence (5'→3'):
[0045] Lac-F: AGAACACCAGTGGCGAAGG
[0046] Lac-R: CAGGCGGAGTGCTTAATGC
[0047] 2. Extraction of pure bacterial DNA.
[0048] isolated and purified Gluconacetobacter (Gluco nacetobacter sp. ) and Lactobacillus pentose ( Lactobacillus pentosus ) for shake flask culture, and DNA extraction was performed on the two culture fluids by using bacterial extraction kits.
[0049] 3. Cloning of target fragments.
[0050] The DNA of Acetobacter pasteurii and Lactobacillus helveticus were used as templates, and Ace-F / AceR and Lac-F / Lac-R were used as primers for PCR amplification. The amplified products...
Embodiment 2
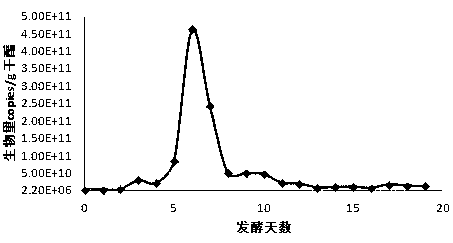
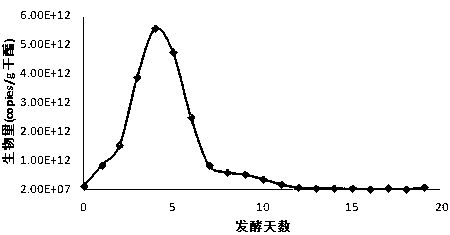
[0060] Example 2: Quantitative analysis of the genus Acetobacter and Lactobacillus in the microbial community of vinegar fermented grains.
[0061] 1. Collection of samples of vinegar fermented grains.
[0062] Taking the fermentation of Zhenjiang fragrant vinegar as the research object, the samples of vinegar unstrained spirits at different time points during the vinegar fermentation process were collected. If the DNA could not be extracted in time after the samples were collected, they should be frozen immediately.
[0063] 2. Extraction method of microbial total DNA in vinegar fermented grains.
[0064] Weigh 2 g of vinegar unstrained spirits, add liquid nitrogen into a mortar and grind thoroughly, and transfer to a 50 mL centrifuge tube. Add 6 mL of DNA extraction buffer to the centrifuge tube, then add 100 μL of lysozyme (50 mg / mL), and shake at 225 rpm at 37°C for 30 min. Add 1.5 mL of 10% SDS to the centrifuge tube, bathe in water at 65°C for 2 h, invert gently every ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com